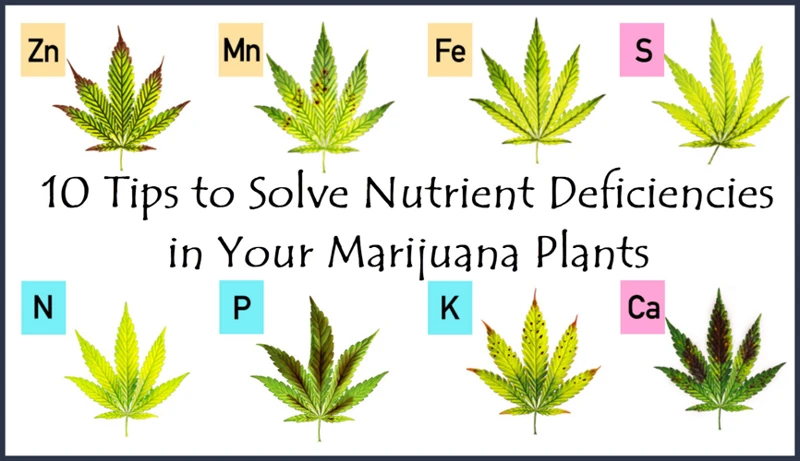
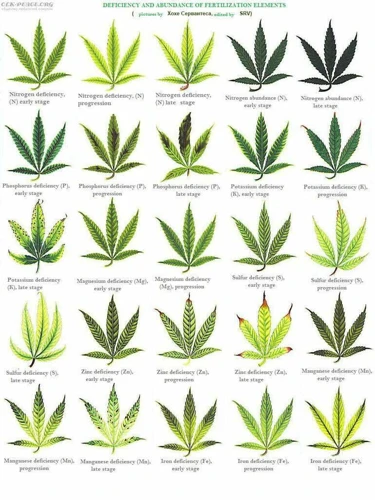
Fixing Common Nutrient Deficiencies in Cannabis Plants
As a cannabis grower, it can be perplexing to determine why your plants are not growing properly or producing the expected yield. One possible reason for stunted growth and unproductive plants could be nutrient deficiencies. Nutrients are essential for plant growth, and cannabis plants require specific nutrients in specific amounts to thrive. This article will explore the role of nutrients in cannabis plant growth and identify common nutrient deficiencies that can impair plant growth. We will also discuss how to fix nutrient deficiencies using fertilizers and methods to prevent them in the first place.
The Role of Nutrients in Cannabis Plant Growth
Contents
The growth and development of cannabis plants greatly depend on the nutrients they receive. Nutrients are essential for various plant processes, such as photosynthesis, respiration, and the creation of structural components. Without the right balance of nutrients, cannabis plants may experience stunted growth, low yields, and a higher susceptibility to diseases and pests. In this section, we will explore the primary, secondary, and micronutrients needed for cannabis plant growth and understand their individual roles. Understanding the importance of nutrients in cannabis plants is crucial for identifying and preventing nutrient deficiencies. So, let’s dive into the intricacies of nutrient absorption and its impact on plant growth!
The Primary Nutrients Needed for Cannabis Plant Growth
To understand the primary nutrients required for cannabis plant growth, it’s essential to know their roles and how they contribute to healthy plant development. The primary nutrients, also known as macronutrients, play a crucial role in the formation of plant tissues and help keep the plant nourished. The three primary nutrients required for cannabis plant growth are Nitrogen (N), Phosphorus (P), and Potassium (K).
The following table highlights the roles of primary nutrients in cannabis plant growth:
| Primary Nutrients | Role in Cannabis Plant Growth |
|---|---|
| Nitrogen (N) | Nitrogen is required for the development of chlorophyll, the essential pigment that helps plants with photosynthesis. Nitrogen also aids in the formation of amino acids, proteins, and nucleic acids, which are vital for cell development. |
| Phosphorus (P) | Phosphorus contributes to healthy cell growth, helps with root development, and aids plants in the conversion of solar energy into food through photosynthesis. It also assists in the natural synthesis of important biochemical compounds that regulate plant growth and stress tolerance. |
| Potassium (K) | Potassium is vital for the creation of robust cell walls and strengthens plants from the inside. It also assists plants in the regulation of water movement and plays a vital role in metabolic activities such as photosynthesis and respiration. |
Cannabis plants require optimal levels of primary and secondary nutrients to develop properly. Nutrient deficiencies can lead to plant stress, stunt growth, and adversely impact final yield, potency, and overall quality. It’s important to identify the common nutrient deficiencies and adequately fertilize with the right nutrient mix to achieve healthy cannabis plant growth.
The Secondary Nutrients Needed for Cannabis Plant Growth
Some secondary nutrients are also required for proper growth and development of cannabis plants. These nutrients are not necessary in as large quantities as primary nutrients, but their deficiency can still hinder growth and lead to undesirable outcomes. Here are some of the secondary nutrients needed for cannabis plant growth:
- Calcium (Ca): Calcium is essential in the production of new plant tissue and cell walls. It also helps regulate nutrient uptake and enzymatic activities. Calcium deficiency can cause stunted growth, leaf curling and yellowing, and eventual death of the plant.
- Magnesium (Mg): Magnesium plays an important role in the formation of chlorophyll, which is needed for photosynthesis. It also aids in the conversion of light energy into sugar, making it vital for plant growth. Magnesium deficiency can cause yellowing of leaves, loss of chlorophyll, and reduced yield.
- Sulfur (S): Sulfur is involved in the production of amino acids, which are building blocks of protein. It also supports root growth and helps fight off pests and diseases. Sulfur deficiency can lead to stunted growth and yellowing of leaves.
While these secondary nutrients may not be required in large quantities, their deficiency can still be damaging to the growth of cannabis plants. It is important to ensure that proper amounts of these nutrients are available to the plants through fertilization or soil amendments.
The Micronutrients Needed for Cannabis Plant Growth
Micronutrients are essential for the healthy growth and development of cannabis plants. Despite being required in smaller quantities as compared to primary and secondary nutrients, micronutrients play a vital role in many metabolic processes that are necessary for plant growth.
Here is a list of micronutrients needed for cannabis plant growth and their functions:
| Micronutrient | Function |
|---|---|
| Iron (Fe) | Helps in the production of chlorophyll and aids in energy transfer within the plant. |
| Manganese (Mn) | Assists in the production of oxygen during photosynthesis and enzyme activation. |
| Zinc (Zn) | Catalyzes enzymes necessary for cell division and aids in the production of growth hormones. |
| Copper (Cu) | Assists in photosynthesis, activates enzymes responsible for metabolism, and facilitates nutrient uptake. |
| Boron (B) | Aids in calcium and cell wall formation, and influences reproductive development and cell division. |
| Molybdenum (Mo) | Helps in the conversion of nitrogen into a form that can be used for protein synthesis and aids in enzyme activation. |
| Chlorine (Cl) | Facilitates proper water balance within the plant and aids in photosynthesis. |
| Nickel (Ni) | Assists in nitrogen metabolism and activates enzymes required for metabolism and respiration. |
It is important to note that even though these micronutrients are required in smaller quantities, a deficiency of even one can significantly impact the overall health and growth of cannabis plants. It is crucial to maintain a balanced nutrient profile in the soil and provide fertilizers that contain all necessary micronutrients.
Common Nutrient Deficiencies in Cannabis Plants
As cannabis plants grow, they require a variety of nutrients to develop properly. However, sometimes these nutrients can become deficient, leading to stunted growth, yellowing leaves, and other issues. Identifying and fixing these nutrient deficiencies can be a perplexing task for any cannabis grower. It’s important to understand which nutrients are vital for cannabis plant growth and how to recognize when they are lacking. Only then can you take the necessary steps to bring your cannabis plants back to their healthy and productive state. Let’s dive into some of the most common nutrient deficiencies in cannabis plants and how to address them.
Nitrogen Deficiency
Nitrogen is an essential nutrient for cannabis plants. It is responsible for the plant’s leaf growth and overall green color. A deficiency in nitrogen can cause the leaves of the plant to turn yellow (chlorosis) and eventually die off. If the deficiency is severe and not addressed, it can lead to stunted growth and reduced yield.
To determine if your cannabis plant is deficient in nitrogen, look for the following symptoms:
| Symptom | Description |
| Pale leaves | The leaves will appear pale, almost yellow, rather than the normal rich green color. |
| Slow growth | The plant will grow more slowly than normal. |
| Yellowing of lower leaves | The lower leaves of the plant will begin to yellow and die off. |
| Small leaves | The leaves will be smaller than normal. |
If your cannabis plant is deficient in nitrogen, there are a few ways to address the problem. The first step is to ensure that you are providing your plant with enough nitrogen through your fertilizer regimen. Nitrogen can be found in most standard fertilizers, but you may need to ensure that you are using a fertilizer with a higher nitrogen content if you are experiencing a severe deficiency.
Additionally, you may need to adjust the overall pH level of the soil to ensure that the plant is able to effectively absorb the nitrogen. Nitrogen is most readily available to the plant when the pH level of the soil is between 6.0 and 7.0.
Finally, you may need to adjust the amount of water that you are giving your cannabis plant. Over-watering can inhibit the plant’s ability to effectively absorb nutrients, including nitrogen. Be sure to monitor the soil moisture level and adjust accordingly.
A nitrogen deficiency can be a serious issue for your cannabis plants. However, with the proper care and attention, it is a deficiency that can be addressed and resolved.
Phosphorus Deficiency
Phosphorus is one of the essential macronutrients needed for the proper development of cannabis plants. It plays a vital role in several processes, including photosynthesis, respiration, and energy transfer. Without sufficient phosphorus, cannabis plants can suffer from stunted growth and reduced yields.
Symptoms of Phosphorus Deficiency
The symptoms of phosphorus deficiency are most noticeable in the leaves of cannabis plants. They can appear dark green or bluish-purple in color, and the leaves may become small and curl. The plant may also exhibit slow and stunted growth. In severe cases, the leaves may start turning yellow, and the plant may eventually die.
To properly diagnose a phosphorus deficiency, it’s essential to look for the following symptoms:
| Symptom | Description |
|---|---|
| Dark green or bluish-purple leaves | The leaves of the plant may turn dark green or bluish-purple in color. |
| Curling leaves | The leaves may become small and curl. |
| Slow and stunted growth | The plant may exhibit slow and stunted growth. |
| Yellowing leaves | In severe cases, the leaves may start turning yellow, and the plant may eventually die. |
Causes of Phosphorus Deficiency
Phosphorus deficiency can be caused by several factors, including:
- Low soil temperatures
- High pH levels in the soil
- Overwatering or poor drainage
- Insufficient use of phosphorus-rich fertilizers
- Damage to roots from pests or over-fertilization
How to Fix Phosphorus Deficiency
The best way to fix phosphorus deficiency is to ensure that your cannabis plants receive adequate amounts of phosphorus-rich fertilizers. You can use fertilizers that contain high levels of phosphorus like bone meal, rock phosphate, or superphosphate.
When applying phosphorus-rich fertilizers, be careful not to over-fertilize your plants. Over-fertilization can lead to phosphorus toxicity, which can be just as harmful to your plants as phosphorus deficiency.
You can also adjust the pH level of your soil to solve phosphorus deficiency. The ideal pH range for cannabis plants is around 6.0 to 7.0. pH levels that are too high or too low can prevent your plants from absorbing phosphorus and other essential nutrients.
Preventing Phosphorus Deficiency
Preventing phosphorus deficiency begins with proper soil preparation. Before planting your cannabis plants, make sure to enrich the soil with organic matter that contains a significant amount of phosphorus.
It’s also essential to maintain proper pH levels in your soil. Regularly testing the pH level of your soil can help you adjust it to the ideal range for cannabis plants.
Lastly, make sure to inspect your plants regularly for signs of pest infestation or disease. Pests like spider mites and root aphids can damage the roots of your cannabis plants, reducing their ability to absorb phosphorus and other essential nutrients. By catching pest infestations early and taking prompt action, you can prevent phosphorus deficiency and ensure that your cannabis plants remain healthy and productive.
Potassium Deficiency
Potassium is a vital nutrient for the growth and development of cannabis plants. It plays a major role in maintaining the plant’s water balance, as well as its enzyme and protein production. A potassium deficiency can lead to stunted growth, weak stems, lower yields, and increased susceptibility to disease and pests.
Symptoms of potassium deficiency typically start to appear on the bottom leaves of the plant and progress upwards. Leaves may develop small, yellow spots that eventually merge together, turning the entire leaf yellow. The edges of the leaves may also start to curl or burn, and the plant may become more susceptible to wilting and heat stress.
To combat potassium deficiency, it is important to use a fertilizer that is high in potassium. Some of the best fertilizers for this purpose include potassium sulfate, potassium nitrate, and potassium chloride. These fertilizers can be added to the soil or water in appropriate amounts, depending on the stage of growth and severity of the deficiency.
When adding fertilizer to soil or water, it is important to use the appropriate application method to ensure that the plant receives the correct amount of fertilizer. Excessive potassium can be just as damaging as a deficiency, so it is important to measure carefully and follow instructions on the packaging.
In addition to adding fertilizers, it is important to prevent potassium deficiency by maintaining proper soil pH levels and avoiding over-watering. Roots may become less efficient at absorbing potassium when soil pH levels are too low or too high, so it is important to keep the pH within the optimal range of 6.0 to 7.0. Additionally, over-watering can cause nutrients, including potassium, to leach out of the soil before the plant can absorb them.
Regularly inspecting and monitoring cannabis plants for signs of nutrient deficiencies, including potassium, can help prevent problems before they arise. With proper care and attention, cannabis plants can thrive and produce a successful harvest.
Calcium Deficiency
Calcium deficiency is a common issue in cannabis plants that can result in stunted growth, brown spots on leaves, and even tip burn. Calcium is an essential secondary nutrient that helps keep the cell walls of the plant strong and healthy. Without sufficient calcium, the cell walls can break down, which can lead to a variety of problems.
Here is a table that outlines the symptoms of calcium deficiency in cannabis plants:
| Symptom | Description |
|---|---|
| Stunted growth | Plants may appear smaller than healthy plants of the same age |
| Brown spots on leaves | Irregular brown spots may appear on the leaves, often beginning at the tips and edges |
| Tip burn | The tips of the leaves may turn brown and dry out, giving the appearance of being burnt |
| Leaf curling | The leaves may curl inward or outward, and may become brittle |
| Poor fruit development | Calcium deficiency can also affect the development and ripening of fruits, leading to poor quality or even premature rotting |
If you suspect your cannabis plants are suffering from a calcium deficiency, it is essential to address the issue promptly. One way to do this is by using a calcium-rich fertilizer, such as gypsum or dolomite lime. These can be added to the soil or nutrient solution to help provide the plant with the calcium it needs.
Another option is to use a foliar spray containing calcium. These sprays can be applied directly to the leaves and absorbed by the plant, providing a quick boost of calcium.
It’s also crucial to ensure that the pH of the soil or nutrient solution is within the appropriate range for calcium absorption. A pH range of 6.0 to 7.0 is considered optimal for calcium uptake.
Finally, preventative measures can help prevent calcium deficiency from occurring in the first place. This includes maintaining proper soil preparation, managing nutrient levels, and regularly inspecting plants for signs of stress or imbalance. By staying on top of plant health and addressing potential issues promptly, you can help ensure a healthy and fruitful harvest.
Magnesium Deficiency
Magnesium deficiency is a common problem in cannabis plants. Magnesium is an essential nutrient needed for the plant’s growth and development. When a cannabis plant lacks magnesium, it can show several symptoms that can harm its growth and health.
Signs of magnesium deficiency include yellowing leaves, particularly at the bottom of the plant, and leaves that have green veins but are turning yellow between the veins. This yellowing can then turn into necrosis, where the affected leaves die and fall off.
To fix magnesium deficiency, it’s important to first diagnose the issue. This can be done by checking the pH level of the soil, as low pH levels can prevent the plant from absorbing magnesium. If the pH level is fine, then it’s likely a magnesium deficiency.
The best way to fix magnesium deficiency is by using a fertilizer that is high in magnesium. A balanced fertilizer that contains all the essential nutrients, including magnesium, is a good option. Another option is to use Epsom salts, which contain magnesium sulfate. Using Epsom salts can be an effective method for fixing magnesium deficiency.
When applying fertilizers or Epsom salts, it’s important to follow the package instructions carefully. Overfeeding can result in fertilizer burn, which can cause further damage to the plant.
Some of the best fertilizers for magnesium deficiency include:
- Cal-Mag
- Dyna-Gro Mag-Pro
- Botanicare Cal-Mag Plus
- Jacks Professional Cal-Mag
It’s important not just to treat the symptoms of magnesium deficiency but also to prevent it from happening in the first place. Maintaining proper soil pH levels between 6.0-7.0, ensuring adequate drainage and moisture levels, and balancing nutrient levels can help prevent magnesium deficiency. Regularly inspecting plants and catching issues early can also help prevent more severe deficiencies.
Magnesium deficiency can harm the growth and health of cannabis plants. The best way to fix it is by using a fertilizer that is high in magnesium, such as Epsom salts or a balanced fertilizer containing all necessary nutrients, including magnesium. By preventing and treating magnesium deficiency, growers can ensure that their cannabis plants grow healthy and strong.
Sulfur Deficiency
Sulfur is an essential micronutrient that is required for various plant functions. It is involved in the production of chlorophyll, amino acids, and enzymes. Sulfur deficiency in cannabis plants can cause several issues, including stunted growth, yellowing of leaves, and reduced potency.
Symptoms of Sulfur Deficiency
One of the main symptoms of sulfur deficiency is the yellowing of leaves. However, unlike other nutrient deficiencies, the yellowing begins at the base of the plant and moves upwards. The new growth may appear pale or yellowish, and the leaves may become smaller and distorted. In severe cases, the leaves may curl, and the plant may become stunted.
Causes of Sulfur Deficiency
There are several reasons why cannabis plants may suffer from sulfur deficiency. One of the most common causes is acidic soil. When the soil is too acidic, sulfur becomes less available to the plant. Other causes of sulfur deficiency include poor soil quality, lack of organic matter, and overuse of fertilizers that do not contain sulfur.
How to Fix Sulfur Deficiency with Fertilizers
Sulfur deficiency can be corrected with the use of fertilizers that contain sulfur. While many fertilizers contain sulfur, it is essential to choose the right one for your plants. A soil test can help determine the best fertilizer for your cannabis plants.
Here is an example of a table outlining some suitable fertilizers for fixing sulfur deficiency:
| Fertilizer | Sulfur Content |
|---|---|
| Epsom Salt | 51% |
| Sulfur Powder | 90% |
| Fish Emulsion | 2-3% |
| Blood Meal | 1% |
Application Method
When applying fertilizers to correct sulfur deficiency, it is essential to follow the instructions on the fertilizer label. Over-fertilizing can cause more harm than good. It is also important to avoid direct contact of the fertilizer with the cannabis plant’s foliage to prevent leaf burn.
Preventing Sulfur Deficiency
Preventing sulfur deficiency in cannabis plants involves maintaining the proper pH level of the soil. The ideal pH range for cannabis is between 6.0 and 7.0. If soil pH is below this range, sulfur may become unavailable to the plant. It is also essential to maintain proper soil quality and use organic matter to improve soil fertility.
Sulfur deficiency in cannabis plants can lead to various issues, including stunted growth and reduced potency. However, the problem is easily fixable with the right fertilizers and application methods. Preventing sulfur deficiency involves maintaining the proper soil pH and quality.
Iron Deficiency
Iron deficiency is one of the most common nutrient deficiencies in cannabis plants. It is important for the formation of chlorophyll, which is responsible for the plant’s green color and ability to photosynthesize. Without sufficient iron, leaves can turn yellow or white, with the vein network remaining green. This condition is known as chlorosis.
Symptoms of Iron Deficiency:
- Yellowing of new leaf growth
- Green veins on yellow leaves (interveinal chlorosis)
- Slow growth and stunted development
- Small flower buds
Iron deficiency is often caused by high pH levels in the soil, which make iron less available to the plant. Iron may also be lacking if the soil is too wet or if the plant is over-fertilized with phosphorus or zinc, which can interfere with iron uptake.
How to Fix Iron Deficiency with Fertilizers:
- Choose a fertilizer that contains chelated iron or iron sulfate
- Apply the fertilizer according to package instructions
- Water the plants with a solution of 1 tablespoon of iron sulfate per gallon of water
- Avoid over-fertilizing with phosphorus or zinc, which can worsen the deficiency
It is important to note that overuse of iron fertilizers can lead to toxic buildup in the soil, so it is important to follow application instructions carefully.
Preventing Iron Deficiency:
- Maintain proper soil pH levels between 6.0 and 6.5
- Do not over-water the plants
- Avoid over-fertilizing with phosphorus or zinc
- Regularly inspect the plants for signs of deficiency
By regularly monitoring your cannabis plants for iron deficiency and taking preventative measures, you can ensure that your plants are healthy and continue to grow to their full potential.
Manganese Deficiency
Manganese is an essential micronutrient needed for the normal growth and development of cannabis plants. It is essential for the process of photosynthesis and helps plants produce chlorophyll. Manganese deficiency can cause a number of problems in cannabis plants and can result in stunted growth, yellowing leaves and small buds.
There are a few signs that your cannabis plant may be suffering from manganese deficiency. Firstly, the tips of the leaves may turn brown or appear dead. Secondly, the leaves may start to curl or develop a mottled appearance. Finally, the new growth on your cannabis plants may become distorted or stunted.
If your cannabis plant is suffering from manganese deficiency, there are a few things you can do to fix the problem. Firstly, you can add a manganese-rich fertilizer to the soil. This will help to increase the availability of manganese in the soil and will help your plant to absorb the nutrient more effectively. Some good sources of manganese for cannabis plants include kelp meal, fish bone meal and dolomite lime.
Another option is to use a foliar spray that contains manganese. This can be applied directly to the leaves of your cannabis plant and will help to quickly correct the nutrient deficiency. However, it is important to note that foliar sprays should only be used as a temporary fix and should not be relied on as a long-term solution.
In order to prevent manganese deficiency from occurring in the first place, it is important to maintain a balanced pH level in your soil. Manganese is most readily available to cannabis plants when the soil pH is between 5.5 and 6.5. If the pH level is too high or too low, manganese absorption can be inhibited.
Regularly inspecting your plants for signs of nutrient deficiencies is also important. This will help you to catch any problems early on and take corrective action before any damage can occur. By taking the time to monitor the health of your cannabis plants and providing them with the nutrients they need, you can ensure that they grow strong and healthy and produce high-quality buds.
Zinc Deficiency
Zinc is a vital micronutrient required for the healthy growth of cannabis plants. Zinc deficiency in cannabis plants can result in stunted growth, leaf discoloration, and reduced yields. Some of the common symptoms of zinc deficiency in cannabis plants include:
- Pale and yellowing leaves: Zinc deficiency can cause the leaves of the cannabis plant to turn pale or yellow, particularly around the edges.
- Deformed leaves: Zinc deficiency can also cause the leaves of the cannabis plant to become deformed, with crinkled or curled edges.
- Slow growth: Zinc deficiency can stunt the growth of cannabis plants, resulting in slow growth and reduced yields.
If you notice these symptoms in your cannabis plants, it is essential to take action as soon as possible to avoid further damage. Fortunately, zinc deficiency can be easily corrected using fertilizers.
To fix a zinc deficiency in cannabis plants, you can choose from a range of fertilizers containing zinc. One of the most commonly used fertilizers for zinc deficiency is zinc chelate. Zinc chelate is a liquid fertilizer that can be added to the soil to help correct zinc deficiency quickly.
Additionally, there are fertilizers that contain a variety of micronutrients that can help prevent zinc deficiency in cannabis plants. Look for fertilizers with a high concentration of zinc and other micronutrients to ensure that your cannabis plants are getting all the nutrients they need for healthy growth.
It is also essential to maintain proper soil pH levels to prevent zinc deficiency in cannabis plants. Zinc uptake by the roots is impacted by soil pH levels, with a pH of 6.0-7.0 being optimal for zinc uptake.
Zinc is a critical micronutrient required for the healthy growth of cannabis plants, and a deficiency can cause stunted growth, leaf discoloration, and reduced yields. Choosing the right fertilizer and maintaining proper soil pH levels are essential to fix and prevent zinc deficiencies in cannabis plants.
Copper Deficiency
Copper is one of the micronutrients needed for cannabis plant growth and is necessary for the production of chlorophyll. A copper deficiency can cause stunted growth and yellowing of leaves, particularly around the edges. The leaves may also become twisted and brittle.
To fix copper deficiency, it’s important to choose a fertilizer that contains copper. Options include:
| Fertilizer | Copper Content |
|---|---|
| Hydroponic Solutions Copper Supplement | 2% |
| General Hydroponics FloraMicro | 0.05% |
| Fox Farm Grow Big Hydroponic Liquid Plant Food | 0.0005% |
It’s also important to apply the fertilizer correctly. Copper is only needed in small amounts, so be cautious not to over-fertilize. Start with a small dose and gradually increase if necessary.
To prevent copper deficiency, make sure to maintain proper pH levels in the soil. Copper is less available to plants in acidic soil, so a pH level of around 6.5 is ideal for cannabis plants. Additionally, make sure to inspect your plants regularly for signs of deficiencies and adjust your nutrient plan accordingly.
Copper deficiency can be a frustrating problem for cannabis growers, but with the right fertilizer and nutrient management techniques, it can be successfully managed.
Boron Deficiency
Boron is a micronutrient essential for the growth and development of cannabis plants. Boron deficiency can be identified by the yellowing and death of the growing tips of the plant, a slowing of growth, and brown spots on leaves. In severe cases, boron deficiency can cause stunted growth and distorted leaves.
There are several factors that can cause boron deficiency in cannabis plants. One of the main factors is low boron levels in the soil. Additionally, high levels of calcium, magnesium, or potassium can interfere with the plant’s ability to take up boron. Soil pH levels that are either too acidic or too alkaline can also contribute to boron deficiency.
To address boron deficiency in cannabis plants, it’s important to first test the soil for boron levels. If the soil is deficient in boron, then adding boron-containing fertilizers will help. Good sources of boron include boric acid, borax, and calcium borate.
When using boron-containing fertilizers, it’s essential to follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully. Applying too much boron can be toxic to cannabis plants and cause further damage. In general, applying 1-3 pounds of boron-containing fertilizer per acre is sufficient to correct boron deficiency.
It’s also important to monitor the levels of other nutrients in the soil, as high levels of calcium, magnesium, or potassium can interfere with the plant’s ability to take up boron. Additionally, maintaining a balanced pH level of between 6.0 and 7.0 is essential for optimal boron uptake.
Preventing boron deficiency in cannabis plants involves proper soil preparation and maintenance. This includes testing the soil for nutrient levels and pH, and amending the soil as needed. Regularly inspecting plants for signs of nutrient deficiency is also important, as catching and addressing issues early can prevent further damage.
Molybdenum Deficiency
Molybdenum is a micronutrient that is extremely important for the growth and development of cannabis plants. When a cannabis plant lacks molybdenum, it can lead to a variety of health issues and slow growth. Some common symptoms of molybdenum deficiency in cannabis plants include:
- Yellowing of leaves: One of the most visible signs of molybdenum deficiency is yellowing of the leaves. This yellowing starts at the base of the plant and works its way up over time.
- Leaf curling: Molybdenum deficiency can also cause the leaves to curl downwards or upwards, especially at the tips.
- Poor growth: The plant may also exhibit poor growth, with stunted development and smaller leaves.
- Reduced flowering: Molybdenum plays a key role in the blooming and flowering phases of the cannabis plant. A deficiency can result in a reduced number of flowers or a delay in the flowering cycle.
Molybdenum deficiencies are not very common, especially in cannabis grown in soil. However, hydroponically grown cannabis plants are at a higher risk of developing molybdenum deficiencies than those grown in soil.
To fix a molybdenum deficiency, it is important to identify and address the underlying cause. In some cases, adjusting the pH levels of the soil or water can help. For hydroponic growers, adding a molybdenum supplement to the nutrient solution can be an effective treatment. Some fertilizers also contain molybdenum as part of their nutrient mix, such as those specifically formulated for hydroponic cannabis cultivation.
Regularly inspecting your plants and addressing any nutrient deficiencies promptly is crucial for ensuring their healthy growth and optimal yields.
How to Fix Nutrient Deficiencies with Fertilizers
Once you have identified a nutrient deficiency in your cannabis plants, it’s important to take action to remedy the issue. Using fertilizers is an effective way to correct nutrient deficiencies and help your plants thrive. However, it’s important to choose the right fertilizer for your specific needs and apply it correctly to avoid causing further damage to your plants. In this section, we will discuss how to fix nutrient deficiencies with fertilizers, including choosing the right fertilizer, application methods, and the best fertilizers for different nutrient deficiencies.
Choosing the Right Fertilizer for Your Cannabis Plants
When choosing the right fertilizer for your cannabis plants, there are a few things to consider. First, determine whether you want to use organic or synthetic fertilizers. Organic fertilizers are derived from natural sources such as compost, blood meal, or bone meal, while synthetic fertilizers are chemically formulated. Both types have their own benefits and drawbacks, so it’s important to choose based on your specific needs.
Table: Comparison of Organic and Synthetic Fertilizers
| Factors | Organic Fertilizers | Synthetic Fertilizers |
| ————————–| ——————– | ———————– |
| Nutrient Release | Slow | Fast |
| Nutrient Variety | Limited | Wide range |
| Soil Health | Improves | Decreases |
| Environmental Impact | Low | High |
| Cost | Moderate | Low |
Another factor to consider is the nutrient ratios in the fertilizer. Cannabis plants have different nutrient needs throughout their growth cycle, so it’s important to choose a fertilizer that provides the right balance of nutrients at each stage. Look for a fertilizer with a high N-P-K (nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium) ratio during the vegetative stage, and a lower ratio during the flowering stage.
Table: Nutrient Ratios for Cannabis Growth Stages
| Growth Stage | Nitrogen (N) | Phosphorus (P) | Potassium (K) |
| ——————-| ———— | —————| ————–|
| Vegetative | High | Medium | High |
| Pre-flowering | Medium | High | High |
| Flowering | Low | High | High |
Lastly, consider the form of the fertilizer. Fertilizers come in liquid, powder, and granular forms, each with their own application methods and benefits. Liquid fertilizers are fast-acting and easy to apply, while powder and granular fertilizers release nutrients slowly over time.
Choosing the right fertilizer for your cannabis plants requires careful consideration of the type, nutrient ratios, and form of the fertilizer. By taking these factors into account, you can ensure your plants receive the nutrients they need for healthy growth and high yields.
Fertilizer Application Methods
When it comes to applying fertilizers to your cannabis plants, there are a few different methods you can use. The method you choose will depend on the type of fertilizer you are using and the specific needs of your plants. Here are some common fertilizer application methods:
- Top Dressing: This method involves sprinkling dry fertilizer on top of the soil around the base of the plant. Make sure to spread the fertilizer evenly and avoid getting it on the leaves, as this can burn them.
- Foliar Feeding: This method involves spraying a liquid fertilizer directly onto the leaves of the plant. This can be a good option if your plants are experiencing a nutrient deficiency, as it allows them to quickly absorb the nutrients they need.
- Hydroponic Feeding: If you are growing your cannabis plants in a hydroponic system, you will need to add your fertilizer directly to the water. Make sure to follow the manufacturer’s instructions for proper dosing.
- Drenching: This method involves pouring a diluted liquid fertilizer directly onto the soil around the base of the plant. This allows the roots to absorb the nutrients they need.
- Injection: This method is typically used in commercial growing operations and involves injecting a fertilizer solution directly into the irrigation water.
No matter which method you choose, it’s important to follow the manufacturer’s instructions for proper dosing. Over-fertilizing can be just as harmful as under-fertilizing, so make sure to take it slow and monitor your plants closely for any signs of stress.
Best Fertilizers for Nutrient Deficiencies
When your cannabis plants show signs of nutrient deficiencies, it’s important to address the issue quickly to prevent further damage. One effective solution is applying fertilizers that are specifically formulated to address the nutrient deficiencies.
Here are the best fertilizers for nutrient deficiencies in cannabis plants:
| Nutrient Deficiency | Best Fertilizers |
|---|---|
| Nitrogen Deficiency | Organic Blood Meal, Fish Emulsion, or Synthetic Urea |
| Phosphorus Deficiency | Bat Guano, Organic Rock Phosphate, or Synthetic Superphosphate |
| Potassium Deficiency | Organic Potash, Greensand, or Synthetic Potassium Sulfate |
| Calcium Deficiency | Organic Gypsum, Lime, or Synthetic Calcium Nitrate |
| Magnesium Deficiency | Organic Epsom Salt or Synthetic Magnesium Sulfate |
| Sulfur Deficiency | Elemental Sulfur, Organic Sulfate of Potash, or Synthetic Ammonium Sulfate |
| Iron Deficiency | Chelated Iron or Iron Sulfate (Ferrous Sulfate) |
| Manganese Deficiency | Manganese Sulfate or Chelated Manganese |
| Zinc Deficiency | Zinc Sulfate or Chelated Zinc |
| Copper Deficiency | Copper Sulfate or Chelated Copper |
| Boron Deficiency | Boron Frit or Solubor |
| Molybdenum Deficiency | Ammonium Molybdate or Sodium Molybdate |
Each nutrient deficiency requires a specific fertilizer to correct the issue. It is essential to correctly identify the nutrient deficiency affecting your plants before applying any fertilizer. A soil test can help determine the specific nutrient deficiencies that need to be addressed.
It’s important to use the right type of fertilizer for your cannabis plants. There are organic and synthetic fertilizers available in the market. Organic fertilizers are made from natural ingredients such as plant and animal materials, while synthetic fertilizers are made from chemical compounds designed to mimic the natural nutrients needed for plant growth. Choose the fertilizer that suits your preference and budget.
Use the appropriate fertilizers to fix the nutrient deficiencies in your cannabis plants. Refer to the table above to choose the right fertilizer for your specific needs. Remember to follow the instructions and apply the fertilizer correctly to avoid over-fertilizing, which could cause more harm than good.
Preventing Nutrient Deficiencies in Cannabis Plants
One of the most important aspects of growing healthy cannabis plants is preventing nutrient deficiencies. It can be frustrating to watch your plants struggle due to lack of essential nutrients, especially if you have put a lot of effort and resources into your grow. However, there are several steps you can take to ensure your plants have the nutrients they need to thrive. In this section, we will explore some of the best practices for preventing nutrient deficiencies in cannabis plants, from proper soil preparation and pH level maintenance to regular plant inspections. By following these guidelines, you can help your plants stay healthy and vibrant throughout their lifecycle.
Proper Soil Preparation and pH Level Maintenance
Proper soil preparation and pH level maintenance are essential for preventing nutrient deficiencies in cannabis plants. Soil preparation involves ensuring that the soil is fertile, well-draining, and rich in organic matter. One way to achieve this is by incorporating compost, manure, and other organic materials into the soil. These materials provide the necessary nutrients and also improve the soil structure and water-holding capacity.
Another important aspect of soil preparation is testing the pH level of the soil. Cannabis plants grow best in slightly acidic soil with a pH range between 6.0 and 6.5. If the soil is too acidic or alkaline, the plants will struggle to absorb the nutrients they need, even if they are present in the soil. A soil pH test kit can be used to determine the pH level of the soil, and adjustments can be made accordingly.
Adjusting the pH level can be done by adding lime to acidic soil or sulfur to alkaline soil. It’s important to note that the process of adjusting pH can take time, and it’s essential to monitor the pH level regularly to ensure that it remains within the optimal range.
In addition to proper soil preparation and pH level maintenance, it’s also important to use high-quality fertilizers that are specifically formulated for cannabis plants. These fertilizers are designed to provide the essential nutrients that cannabis plants need to grow and thrive.
Proper soil preparation and pH level maintenance are crucial for preventing nutrient deficiencies in cannabis plants. Testing the pH level, adjusting it as needed, and using high-quality fertilizers are all vital steps in ensuring that your plants receive the nutrients they need to grow strong and healthy. By following these guidelines, you can help your cannabis plants reach their full potential and produce high-quality buds with excellent potency and flavor.
Managing Nutrient Levels
Managing nutrient levels in cannabis plants is a crucial aspect of ensuring healthy and robust plant growth. There are several ways to ensure that your plants are receiving the appropriate nutrients they need to thrive. Here are some tips for managing nutrient levels in your cannabis plants:
1. Conduct Regular Soil Tests: The first step in managing nutrient levels is to test the soil. This will give you an indication of the nutrient content and pH levels. A soil test will tell you the soil’s pH level, which is important for nutrient uptake. Nutrient deficiencies can be caused by the unbalanced pH level of the soil. By conducting regular soil tests, you can identify any nutrient deficiencies and make the necessary adjustments through fertilization.
2. Use Nutrient-Dense Soil: Choosing the right soil for your plants is essential. There are different types of soil available on the market, and each type contains different levels of nutrients. It is best to choose organic soil that is high in nutrients, such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. This will ensure that your plants receive the necessary nutrients during the growth cycle.
3. Adjust Fertilizer Use: Over-fertilization is a common problem faced by growers. Too much fertilizer can cause nutrient burn or toxicity, which can harm plant growth. Conversely, under-fertilization can lead to nutrient deficiencies, which can stunt plant growth. By adjusting fertilizer use and considering the nutrient requirements of your plants, you can avoid both these problems.
4. Monitor Plant Growth: As cannabis plants grow, they will show signs of nutrient deficiencies, such as yellowing leaves or stunted growth. Regularly monitor your plants for any physical symptoms that may indicate a nutrient deficiency. This will help you identify the problem early on and make the appropriate adjustments.
5. Maintain Proper pH Levels: Maintaining the correct pH level is essential for nutrient uptake. An unbalanced pH level can result in nutrient deficiencies, as certain nutrients require specific pH levels to be absorbed by the roots. It is crucial to maintain a consistent pH level throughout the growth cycle.
By following these tips, you can manage nutrient levels in your cannabis plants efficiently. An appropriate balance of nutrients is essential for robust plant growth and healthy yields. With regular testing, proper soil choice, and monitoring, you can ensure that your plants receive the right amount of nutrients they need to thrive.
Regularly Inspecting Your Plants
Inspecting your plants regularly is vital to ensure they are getting the right amount and balance of nutrients. It is important to inspect your plants with a keen eye and attention to detail to catch early signs of nutrient deficiencies. Here are some key steps you can take:
- Look for visual cues: Check for any discoloration, stunted growth or other anomalies in your plants’ leaves, stalks, or buds.
- Check pH levels: Nutrient deficiencies can be caused by improper pH levels in the soil. Use a pH meter to regularly test the soil to make sure it is within the optimal range for nutrient uptake.
- Test nutrient levels: Soil testing kits can help you monitor nutrient levels in your soil. This information can help you make informed decisions about what fertilizers to add and how much to add.
- Observe the weather and growing conditions: Weather and environmental factors such as humidity and temperature can affect nutrient uptake in your plants. Keep track of these factors and adapt accordingly.
Regularly inspecting your plants and addressing any nutrient deficiencies as soon as possible can help prevent more serious problems down the road. It’s important to remember that each plant is unique and may require different nutrient levels, so it’s essential to stay vigilant and monitor your plants regularly.
Conclusion
In conclusion, it is important for cannabis growers to pay close attention to the nutrient needs of their plants. Nutrient deficiencies can have a significant impact on plant growth, yield, and overall health.
Choosing the right fertilizer is crucial for ensuring that your plants are receiving the proper nutrients. It is important to not only consider the specific nutrients needed, but also the ratios in which they should be applied. Using a fertilizer with too much of one nutrient can lead to imbalances and potentially other issues.
Application methods also play a role in ensuring that the nutrients are being properly absorbed by the plants. Fertilizer should be applied evenly and at the appropriate times throughout the plant’s life cycle.
When addressing nutrient deficiencies, it is important to use the best fertilizers for the specific deficiency being experienced. There are many fertilizers available, and choosing the right one can make a significant difference in plant health and growth.
However, it is also important to prevent nutrient deficiencies from occurring in the first place. Proper soil preparation and pH level maintenance, managing nutrient levels, and regularly inspecting plants can all help to ensure that plants are receiving the proper nutrients they need to thrive.
In summary, nutrient deficiencies are a common issue for cannabis growers, but with proper attention and care, they can be avoided or quickly remedied. By choosing the right fertilizers, applying them properly, and preventing deficiencies, growers can help to ensure a successful harvest and healthy plants.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the primary nutrients needed for cannabis plant growth?
The primary nutrients needed for cannabis plant growth are nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium.
What are the secondary nutrients needed for cannabis plant growth?
The secondary nutrients needed for cannabis plant growth are calcium, magnesium, and sulfur.
What are the micronutrients needed for cannabis plant growth?
The micronutrients needed for cannabis plant growth are iron, manganese, zinc, copper, boron, and molybdenum.
What is a nitrogen deficiency in cannabis plants?
A nitrogen deficiency in cannabis plants occurs when there is not enough nitrogen for the plant to grow properly. Symptoms include yellowing of leaves and stunted growth.
What is a phosphorus deficiency in cannabis plants?
A phosphorus deficiency in cannabis plants occurs when there is not enough phosphorus for the plant to grow properly. Symptoms include darkening of leaves and slow growth.
What is a potassium deficiency in cannabis plants?
A potassium deficiency in cannabis plants occurs when there is not enough potassium for the plant to grow properly. Symptoms include brown spots on the edges of leaves and weak stems.
What is the best way to prevent nutrient deficiencies in cannabis plants?
The best way to prevent nutrient deficiencies in cannabis plants is by properly preparing your soil and maintaining the pH level, managing nutrient levels, and regularly inspecting your plants.
What is the best fertilizer for cannabis plants?
The best fertilizer for cannabis plants will vary depending on the specific needs of your plants. It is important to choose a fertilizer that is balanced and contains the necessary nutrients.
What are some signs of a nutrient deficiency in cannabis plants?
Some signs of a nutrient deficiency in cannabis plants include yellowing or browning of leaves, stunted growth, and weak stems.
Can nutrient deficiencies in cannabis plants be fixed with fertilizers?
Yes, nutrient deficiencies in cannabis plants can be fixed with fertilizers. It is important to choose the right fertilizer and apply it properly.