Water pH Level and Nutrient Uptake in Cannabis Plants
For cannabis growers, achieving a healthy and bountiful harvest is the ultimate goal. However, ensuring that plants receive the proper nutrients and conditions can be a complex task. One crucial aspect of plant health is maintaining the correct water pH level. This factor directly impacts nutrient uptake, which affects the overall growth and yield of the plant. In this comprehensive guide, we will take a look at the importance of water pH level and nutrient uptake, how to measure and adjust water pH level, and managing nutrient uptake for optimal plant health. Whether you are a novice or experienced grower, this guide will provide valuable insights into achieving thriving cannabis plants.
Understanding Water pH Level and Nutrient Uptake
Contents
As a cannabis grower, understanding the relationship between water pH level and nutrient uptake is crucial for achieving healthy and thriving plants. Water pH level affects the availability of nutrients in the soil, which can have a direct impact on the growth and development of your plants. It is important to grasp the science behind this relationship to effectively manage your plant’s nutrient uptake, and ultimately yield a successful crop. Let’s explore the significance of water pH level and how it affects nutrient uptake in cannabis plants.
The Importance of Water pH Level
The water pH level is a vital factor to consider when growing cannabis plants. To ensure that your plants grow healthy and strong, the pH level of the water used should be maintained within a specific range. Here are some important reasons why pH level is crucial for cannabis plant growth:
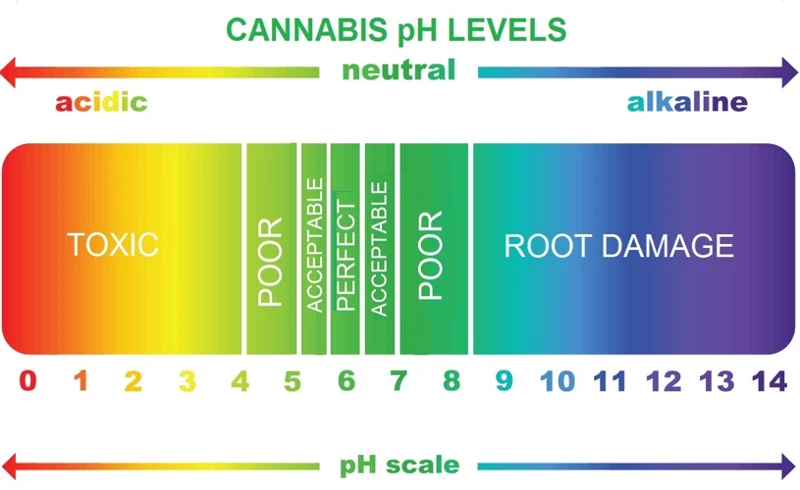
- Availability of Nutrients: The water pH level affects the availability of nutrients for cannabis plants. The ideal pH level for most nutrient uptake is between 5.5 and 6.5. If the pH level of the water is too high or too low, the nutrients in the soil become unavailable to the plant’s roots. This results in nutrient deficiencies that may impair the growth and yield of your plants.
- Enzyme Activity: Enzymes play an essential role in the growth and development of cannabis plants. They catalyze reactions that break down nutrients for plant use. Enzymes activity is affected by the pH level of the water. If the pH level is too low or too high, enzymatic activity slows down, which causes stunted growth and reduced yields.
- Nutrient Imbalances: High or low pH levels can cause nutrient imbalances that can ultimately harm cannabis plants. When pH is too high or too low, the plant may absorb some nutrients too quickly, while others remain trapped in the soil. These imbalances can lead to nutrient toxicities or deficiencies, both of which can negatively impact growth and yield.
- Plant Stress: Cannabis plants can become stressed when their environment is disrupted. Poor pH levels can stress plants, which can lead to wilting, slow growth, and other signs of distress. To minimize stress, it is essential to maintain the pH level within the optimal range.
Maintaining the proper water pH level is a crucial part of growing healthy, robust cannabis plants. By ensuring the pH level remains within an optimal range, you’ll maximize nutrient absorption, minimize nutrient imbalances, enhance enzymatic activity, and minimize plant stress.
How Nutrient Uptake is Affected by pH Level
The pH level of water is a crucial factor that affects the nutrient uptake in cannabis plants. When the water pH level is either too high or too low, the plant’s ability to absorb nutrients is greatly reduced. This happens due to the solubility of certain nutrient ions being negatively influenced by pH levels that are outside of optimal ranges.
Optimal pH Ranges for Nutrient Uptake
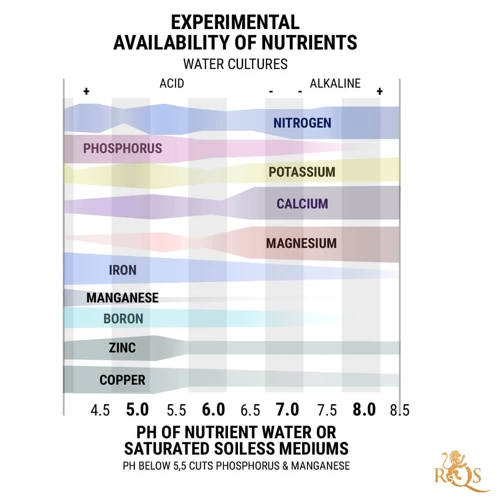
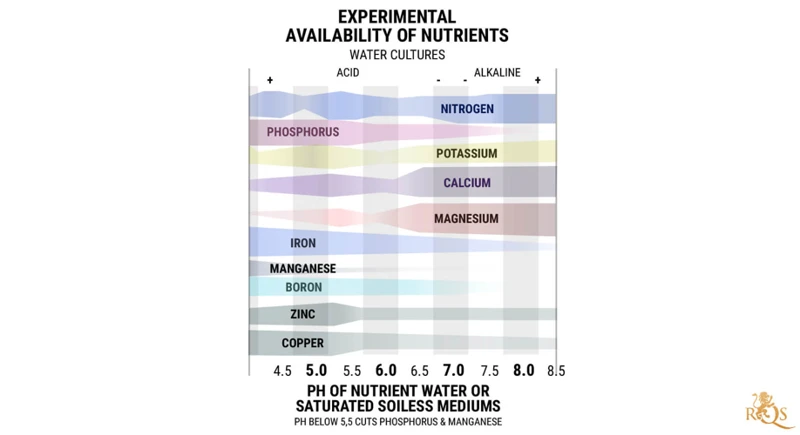
Different nutrients have different optimal pH ranges for uptake by cannabis plants. The ideal pH range for most nutrients is between 6.0 and 7.0, which is slightly acidic to neutral. However, some nutrients have more specific requirements as shown in the following table:
| Nutrient | Optimal pH Range |
|---|---|
| Nitrogen (N) | 6.0-7.0 |
| Phosphorus (P) | 6.0-7.0 |
| Potassium (K) | 5.5-6.5 |
| Calcium (Ca) | 6.2-7.2 |
| Magnesium (Mg) | 6.0-7.0 |
| Sulfur (S) | 5.5-6.5 |
| Boron (B) | 5.0-6.0 |
| Copper (Cu) | 5.0-6.0 |
| Iron (Fe) | 5.0-6.5 |
| Manganese (Mn) | 5.5-6.5 |
| Zinc (Zn) | 6.0-7.0 |
Effects of Low pH
When the pH level of water is too low (below 6.0), the solubility of nutrient ions like calcium and magnesium decreases. These nutrients become less available to the plant, leading to deficiencies. Additionally, manganese, iron, and zinc can become more available at lower pH levels, leading to toxicities.
Effects of High pH
When the pH level of water is too high (above 7.0), the solubility of nutrient ions like phosphorus, iron, and manganese decreases. These nutrients become less available to the plant, leading to deficiencies. Additionally, calcium and magnesium can become more available at higher pH levels, leading to toxicities.
Maintaining the optimal pH range for nutrient uptake in cannabis plants is crucial for their overall health and growth. By understanding the specific pH requirements for each nutrient and monitoring the pH levels of water, growers can ensure that their plants are receiving the nutrients they need for maximum growth and yield.
Measuring Water pH Level
Determining the pH level of the water you use to grow cannabis is crucial to ensure optimal plant growth and yield. Without measuring the pH level, it’s impossible to know if your plants are receiving the proper nutrients they need to thrive. But, the process of measuring pH level can seem daunting at first. Fear not! With the right tools and step-by-step process, you can easily and accurately measure the pH level of your water. Let’s dive into it.
The Tools You’ll Need
When measuring the pH level of your water for your cannabis plants, you’ll need a few tools to ensure accuracy. Here are the key items you’ll need:
| Piece of Equipment | Function |
|---|---|
| pH Meter | A device used to measure the pH level of the water. It’s important to use a digital pH meter for accurate readings as opposed to test strips, which may provide less accuracy. |
| Calibration Solution | A solution used to calibrate the pH meter before use. This ensures accurate readings. |
| Clean Water | Clean tap or distilled water will be used to wash the pH meter probe in between measurements to ensure accurate readings. |
| pH-Down Solution | Used to lower the pH level of the water if it is too high. |
| pH-Up Solution | Used to raise the pH level of the water if it is too low. |
Having these tools on hand will make the process of measuring the water pH level much easier and accurate. It’s important to calibrate the pH meter before using it and to use clean water to wash the probe between measurements to prevent contamination. Using pH adjusters as needed will help to maintain optimal pH levels for your cannabis plants to ensure healthy nutrient uptake.
Step-by-Step Process of Measuring Water pH Level
Measuring the pH level of your water may seem daunting at first, but it’s actually a simple process that you can do at home. Here are the step-by-step instructions for measuring water pH level:
- Gather your materials: Before you start, you will need a pH testing kit that includes pH testing solution, pH test strips, or a pH meter (if you are using a pH meter, make sure it has been calibrated recently).
- Take a water sample: Fill a clean glass or plastic container with water from your reservoir or tap.
- Prepare the testing solution: If you are using pH testing solution, add a few drops to the water sample. If you are using pH test strips, dip one strip into the water sample, making sure it’s fully submerged. If you are using a pH meter, dip the electrode into the water sample.
- Wait for the result: Wait for the color to change (if you’re using pH test strips) or for the meter to stabilize (if you’re using a pH meter). If you’re using pH testing solution, compare the color of your water sample to the color chart included in the kit.
- Take a pH reading: Once you have the color or value reading, record the pH level (e.g. 6.5).
- Repeat the measurement: For accuracy, take two or three measurements and average them out. If the measurements are drastically different, check your testing equipment or the water sample for any contaminants that may have affected the pH level.
Remember to always clean your testing equipment before and after use to prevent contamination, which could affect the accuracy of your results.
Adjusting Water pH Level
Maintaining the proper pH level of your water is crucial for cultivating healthy cannabis plants. However, sometimes the pH level may not be in the optimal range for nutrient uptake. Fortunately, there are various methods to adjust the pH level of water, but with the abundance of options, choosing the right method can be overwhelming. In this section, we’ll explore different ways to adjust water pH levels, determine the amount of adjusting agents to use, and examine natural pH adjusters. Understanding these methods will help you tackle pH imbalance and ensure your cannabis plants get the most out of their nutrient supply.
Methods for Adjusting pH Level
When it comes to adjusting water pH level for your cannabis plants, there are several methods that you can choose from. Here are some of the most popular ones:
- Chemical pH adjusters: This is the most common method for adjusting pH levels. Chemical pH adjusters come in two forms – pH-Up and pH-Down – and are specifically formulated to raise or lower the pH level of your water. These products can be found at most hydroponic stores and garden centers. However, it’s important to use these products with caution, as they can be quite potent and can easily cause damage to your plants if not used properly.
- Natural pH adjusters: If you prefer a more natural approach, there are several natural substances that can be used to adjust your water pH level. Some popular options include vinegar, citric acid, and lemon juice for lowering the pH, and baking soda or limestone for raising the pH. Keep in mind that these products are not as precise as chemical pH adjusters, so it may take some trial and error to find the right amount to use.
- Reverse osmosis: Reverse osmosis is a water filtration process that removes impurities and minerals from the water. This results in water that has a neutral pH level, which can be ideal for growing cannabis. However, reverse osmosis systems can be quite expensive, and may not be necessary unless you have extremely hard water or a high level of mineral content in your water supply.
- DIY pH adjusters: If you’re feeling creative, you can also make your own pH adjusters using household items. For example, you can use eggshells to raise the pH level of your water, or collect rainwater to naturally lower the pH level.
No matter which method you choose, it’s important to regularly monitor the pH level of your water and make adjustments as necessary. Remember, maintaining the correct pH level is crucial for ensuring that your cannabis plants are able to absorb the nutrients they need for healthy growth and development.
How to Calculate the Amount of Adjusting Agents to Use
Before adjusting the pH level of your water, it’s essential to calculate the amount of adjusting agents to use to avoid under or over-adjustment. Here are the steps to follow:
- Test the pH level of your water: Use a reliable pH meter or pH test strips to determine the current pH level of your water.
- Determine your target pH level: Check the optimal pH level for your cannabis plants in the nutrient solution you are using. Most cannabis strains prefer a pH level between 5.5 and 6.5.
- Calculate the difference: Subtract the target pH level from the current pH level to determine the amount of adjustment required.
- Calculate the volume of your water: Measure the amount of water you need to adjust. This step is essential as the amount of adjusting agent you need for a gallon of water will be different from that of 5 gallons of water.
- Refer to the label of your adjusting agent: Check the label of your chosen pH adjuster to find out the concentration level and recommended dosage. Different products have varying concentrations.
- Calculate the amount of adjusting agent to use: Use a pH calculator to determine the amount of your chosen adjusting agent to use based on the volume of water and the amount needed to achieve your target pH level.
Following these steps will help you determine the amount of adjusting agent to use accurately. Remember, it’s essential to avoid over or under-adjusting your water pH level as it can have a significant impact on plant growth and yield.
Using pH-Down and pH-Up Solutions
When it comes to adjusting the pH level of water for your cannabis plants, pH-Down and pH-Up solutions are popular options. pH-Down solutions contain highly concentrated acids, such as nitric or phosphoric acid, that lower the pH level of water. pH-Up solutions usually contain potassium hydroxide or sodium hydroxide, which raise the pH level of water.
It’s essential to be careful when using pH-Down and pH-Up solutions. It’s recommended to wear gloves and eye protection while handling these chemicals. It’s crucial to follow the instructions on the label and never exceed the recommended amount.
The amount of pH-Down or pH-Up solution you’ll need to add depends on the volume of water and the desired pH level. You can use a pH meter to measure the pH level and calculate how much of the solution to add.
Here’s a table to help you calculate the amount of pH-Down or pH-Up solution to add based on the volume of water and the desired pH level:
| Volume of Water | Desired pH Level | pH-Down Solution to Add | pH-Up Solution to Add |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 gallon | 5.5 | 1 mL | NA |
| 1 gallon | 6.0 | 0.5 mL | 1 mL |
| 1 gallon | 6.5 | NA | 2 mL |
| 5 gallons | 5.5 | 5 mL | NA |
| 5 gallons | 6.0 | 2.5 mL | 5 mL |
| 5 gallons | 6.5 | NA | 10 mL |
Note that these amounts are just estimates and may vary depending on the brand of solution you’re using. After adding the solution, stir the water well and measure the pH level again to ensure it’s at the desired level.
Remember to always handle pH-Down and pH-Up solutions with care and keep them out of reach of children and pets.
Using Natural pH Adjusters
One way to adjust the pH level of water without using synthetic pH adjusters is by using natural substances like lemon juice, vinegar, or baking soda. Here are some natural pH adjusters that you can use in your cannabis grow:
- Lemon juice: Lemon juice is a perfect natural acidifier that can lower the pH of water. Simply squeeze one lemon per gallon of water and mix well. Keep testing the pH level until it reaches the desired range.
- Vinegar: Like lemon juice, vinegar is also acidic and can be used to adjust the pH of water. Mix one tablespoon of vinegar per gallon of water and test the pH level regularly until you reach your desired range.
- Baking soda: Baking soda is an excellent alkaline pH adjuster that can be used to raise the pH level of water. Dissolve a quarter teaspoon of baking soda in a gallon of water and stir it well. Keep testing the pH level until it reaches the desired range.
- Citric acid: Citric acid, which can be easily found in stores, is a good natural acidifier that can be used to lower the pH of water. Dissolve a quarter teaspoon of citric acid in a gallon of water and mix it well. Keep testing the pH level until it reaches the desired range.
- Seashells: Crushed seashells can be used to increase the pH level of water, as they contain calcium carbonate. You can add some crushed seashells to the water, stir it well, and test the pH level regularly until it reaches the desired range.
It’s important to note that using natural pH adjusters may not be as precise as synthetic pH adjusters, and they can be less effective in adjusting the pH level of tap water with high alkalinity. However, they are a good alternative for those who prefer natural methods and want to avoid using chemicals in their cannabis grow.
Managing Nutrient Uptake
As a cannabis grower, managing the nutrient uptake of your plants is a crucial aspect of ensuring a successful harvest. It can be perplexing to determine the optimal nutrients needed, the proper amounts, and how to troubleshoot any issues that may arise. However, with the right approach and understanding, you can provide your cannabis plants with the necessary nutrients they need to thrive. In this section of the article, we will explore the relationship between nutrient uptake and water pH levels, the essential nutrients required for healthy cannabis growth, and how to troubleshoot any nutrient deficiencies or toxicities that may occur. Let’s dive in.
The Relationship Between Nutrient Uptake and pH Level
Maintaining the correct pH level is essential for proper nutrient uptake in cannabis plants. The pH level of the soil or growing medium affects the solubility of nutrients in the water, which in turn affects how well the plant can absorb them. The table below summarizes the relationship between pH level and nutrient uptake.
| pH Level | Effect on Nutrient Uptake |
|---|---|
| Below 5.0 | Nutrient availability is reduced and can cause nutrient deficiencies |
| 5.0 to 6.0 | Optimal range for nutrient uptake |
| 6.1 to 7.0 | Nutrients start to become less available, and some deficiencies may begin to appear |
| Above 7.0 | Nutrient availability is drastically reduced and can cause toxicity to plants |
As shown in the table, a pH level outside of the optimal range of 5.0 to 6.0 can lead to various problems with nutrient uptake. If the pH level is too low, nutrients become less available, and deficiencies can occur. Conversely, if the pH level is too high, nutrients become less available, and toxicities can occur. It is essential to maintain the optimal pH level to ensure that the plant can absorb the necessary nutrients properly.
Different nutrients have different pH requirements for proper absorption by the plant. For instance, in soil, iron and manganese are better absorbed by the plant in acidic conditions, while phosphorus and potassium absorb better in neutral to slightly alkaline soil. It’s crucial to monitor the pH level and nutrient uptake of the growing medium consistently.
What Nutrients Cannabis Plants Need
Cannabis plants, like any other plants, require a range of essential nutrients in order to grow healthy and strong. These nutrients can be broken down into two categories: macronutrients and micronutrients.
Macronutrients are nutrients that the plant needs in large quantities. These include:
- Nitrogen (N): Nitrogen is an essential component of chlorophyll, the molecule that allows plants to carry out photosynthesis. Without enough nitrogen, cannabis plants will have stunted growth and yellowing leaves.
- Phosphorus (P): Phosphorus is important for root development and flower production. Cannabis plants that don’t receive enough phosphorus will have stunted growth and weak flowers.
- Potassium (K): Potassium helps plants regulate water uptake and uses, and is important for overall plant health. Plants deficient in potassium will have wilted leaves and slow growth.
- Calcium (Ca): Calcium is necessary for strong cell walls and overall plant structure. Calcium deficiency can result in stunted growth and weak stems.
- Magnesium (Mg): Magnesium is required for chlorophyll production and plays a crucial role in photosynthesis. Cannabis plants deficient in magnesium will have yellowing leaves.
- Sulfur (S): Sulfur is involved in the production of proteins and enzymes. Cannabis plants deficient in sulfur may have slow growth and yellowing leaves.
Micronutrients are nutrients that the plant needs in smaller quantities. These include:
- Iron (Fe): Iron is essential for chlorophyll production and photosynthesis. Cannabis plants deficient in iron will have yellowing leaves.
- Manganese (Mn): Manganese is involved in enzyme function and helps with chlorophyll production. Deficiencies can result in stunted growth and yellowing leaves.
- Boron (B): Boron is important for cell wall development and flower production. Cannabis plants deficient in boron may have poor flower development.
- Copper (Cu): Copper is involved in enzyme function and is important for plant metabolism. Deficiencies can result in stunted growth and yellowing leaves.
- Zinc (Zn): Zinc is involved in enzyme function and regulates plant hormones. Deficiencies can result in stunted growth and yellowing leaves.
- Molybdenum (Mo): Molybdenum is important for nitrogen fixation and protein synthesis. Plants deficient in molybdenum may have yellowing leaves and stunted growth.
It’s crucial to ensure that your cannabis plants are receiving the correct amount of all these nutrients in order to grow healthy and produce high-quality flowers. Monitoring and adjusting the pH level of your water can also help ensure that nutrient uptake is optimized.
How Much Nutrients Your Plants Need
When it comes to growing cannabis plants, it’s important to understand the right balance of nutrients to provide for optimal growth. While there are many different nutrients that cannabis plants need, the three main ones are nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K). There are different ratios of these nutrients that are ideal for different stages of growth.
Seedling Stage: During the first few weeks of life, seedlings don’t require much in the way of nutrients. In fact, too much can be harmful to their delicate roots. Stick to a simple NPK fertilizer with ratios of 2-1-2 or 3-1-2.
Veg Stage: Once your plants start to grow a bit more, they’ll require more nutrients to keep up with their development. At this stage, a fertilizer with higher levels of nitrogen (N) is appropriate. Look for a 3-1-2 or 4-1-3 ratio.
Flowering Stage: When your plants start to transition into the flowering stage, they require nutrients that are higher in phosphorus (P) and potassium (K) to support flower growth. A ratio of 1-3-2 is ideal for this stage.
It’s important to note that there is no one-size-fits-all approach to providing your plants with nutrients. The type and amount of fertilizer you’ll need will depend on a number of factors, including the strain of cannabis you’re growing, the size of your plants, and the type of growing environment you’re using.
Before adding any nutrients to your plants, it’s important to test the pH level of your water to ensure that it’s within the proper range for nutrient uptake. Adjusting the pH level can make all the difference in terms of how well your plants are able to absorb nutrients.
Troubleshooting Nutrient Deficiencies and Toxicities
Nutrient deficiencies and toxicities can be a common issue for cannabis growers, but they can be prevented and treated with proper attention to the plant’s needs. Here are some tips for troubleshooting nutrient issues:
- Identify the symptoms: The first step is to identify the symptoms. This can be anything from yellowing leaves or stunted growth to burnt tips or spots on the leaves. Once you have identified the symptoms, you can start to diagnose the issue.
- Check the pH level: The pH level of the soil or water can have a significant impact on nutrient uptake. Make sure to check the pH level and adjust it if necessary. If the pH level is too high, try adding a pH-down solution. If it’s too low, use a pH-up solution.
- Check the nutrient levels: Make sure you are giving your plants the right amount of nutrients. Too much or too little of any nutrient can cause issues. Use a digital nutrient meter or testing kit to accurately measure the nutrient levels in the soil or water.
- Avoid over-watering: Over-watering can lead to nutrient deficiencies, as it disrupts the root system and makes it harder for the plant to absorb nutrients. Make sure to water your plants only when they need it.
- Flush the soil: If you suspect a nutrient toxicity, try flushing the soil to remove excess nutrients. Use pH-neutral water and water until it runs through the drainage holes. This will help reset the nutrient levels in the soil.
- Adjust the nutrient mix: If you have identified a nutrient deficiency or toxicity, adjust the nutrient mix accordingly. Use a high-quality nutrient mix designed for cannabis and follow the recommended dosage instructions.
- Consider the growth stage: Different stages of growth require different nutrients. Make sure you are giving your plants the right nutrients at the right time. For example, during the vegetative stage, plants require higher levels of nitrogen, while during the flowering stage, they need more phosphorus and potassium.
- Seek professional advice: If you’ve tried everything and still can’t diagnose the issue, don’t be afraid to seek professional help. There are many resources available, including cannabis forums and local grow shops, where experts can provide guidance and advice.
Remember, preventing nutrient deficiencies and toxicities is much easier than treating them once they’ve occurred. Regularly monitoring your plant’s pH and nutrient levels, and adjusting as necessary, is key to a healthy and productive crop.
Conclusion
In conclusion, ensuring the proper water pH level is crucial for healthy nutrient uptake in cannabis plants. With the understanding of how water pH level affects nutrient absorption, it is important to measure and adjust the water pH level accordingly. Measuring water pH level can be done using various tools, such as pH meters, pH test strips or drops. Once the water pH level is determined, it can be adjusted using various methods, such as using pH-up and pH-down solutions or natural pH adjusters like lemon juice or vinegar.
Managing nutrient uptake in cannabis plants is also crucial for achieving optimal growth and yields. It is important to understand which nutrients cannabis plants need, such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, and how much of each nutrient is required at different stages of growth. Nutrient deficiencies and toxicities can be diagnosed by observing the plant’s leaves and symptoms can be alleviated by adjusting the nutrient solution.
By following the steps outlined in this comprehensive guide, cannabis cultivators can effectively manage water pH levels and nutrient uptake in their plants, resulting in healthy, high-yielding crops. Taking these steps will ultimately lead to a successful and rewarding cannabis cultivation experience.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is water pH level important for cannabis plants?
The pH level of water affects the availability and uptake of nutrients by cannabis plants. If the pH level is too high or too low, the plant may not be able to absorb certain nutrients.
How do I measure the pH level of water?
You can measure the pH level of water using a pH meter or pH test kit.
What is the ideal pH level for cannabis plants?
The ideal pH level for cannabis plants is between 6.0 and 7.0.
What happens if the pH level is too high?
If the pH level is too high, the cannabis plant may not be able to absorb certain nutrients such as iron, manganese, and zinc.
What happens if the pH level is too low?
If the pH level is too low, the cannabis plant may not be able to absorb certain nutrients such as phosphorus, calcium, and magnesium.
What are some methods for adjusting the pH level of water?
Methods for adjusting the pH level of water include using pH-up or pH-down solutions, natural pH adjusters such as lemon juice or vinegar, or adding alkaline or acidic minerals such as dolomite or sulfur.
How do I calculate the amount of adjusting agents to use?
You can calculate the amount of adjusting agents needed by following the instructions on the product label, or by using a pH adjustment calculator.
What nutrients do cannabis plants need?
Cannabis plants need a variety of macro and micronutrients including nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, magnesium, sulfur, iron, manganese, zinc, copper, boron, and molybdenum.
How much nutrients do my cannabis plants need?
The amount of nutrients cannabis plants need can vary depending on the stage of growth and the strain of plant. It’s important to follow a nutrient feeding schedule and to monitor your plants for any signs of nutrient deficiencies or toxicities.
What do I do if my plants are showing signs of nutrient deficiencies or toxicities?
If your plants are showing signs of nutrient deficiencies or toxicities, you may need to adjust the pH level of your water, adjust your nutrient feeding schedule, or switch to a different nutrient formula. It’s important to diagnose the issue early and take action quickly to prevent further damage to your plants.