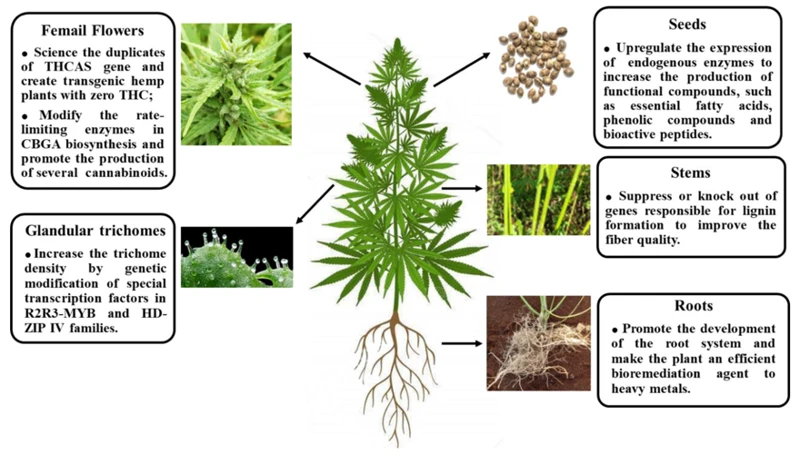
Exploring the Genetics of High-Yielding Cannabis Strains
As the demand for cannabis continues to rise, so does the pursuit for high-yielding strains that can produce bountiful harvests. However, achieving these harvests is not just a matter of luck or chance – it involves a deep understanding of the genetics behind cannabis strains. Many growers are perplexed by the complexity of cannabis genetics and the role they play in determining a plant’s yield potential. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the basics of cannabis genetics, the different types of strains and their yield potential, as well as the importance of cannabinoids, terpenes, and flavonoids. We’ll also dive into choosing the best genetics for high-yield cannabis, improving and troubleshooting low-yielding genetics, and more. So, whether you’re a beginner or a seasoned grower, join us on this journey to uncover the secrets of high-yield cannabis genetics.
Why Genetics Matter for Cannabis Yield
Contents
When growing cannabis, one of the main goals for cultivators is to achieve a high yield. However, simply providing the plant with adequate nutrition and environmental conditions may not be enough to guarantee optimal yield outcomes. This is where genetics play a crucial role in the process. Understanding how genetics influence cannabis yield can help growers select the best strains for their desired outcomes and improve their cultivation techniques. By exploring the basics of cannabis genetics and the role of cannabinoids, terpenes, and flavonoids, growers can gain insight into how these elements come together to influence plant growth and development. Let’s dive into the details of why genetics matter for cannabis yield. And for those who want to skip ahead, check out our list of high-yielding strains to get started on selecting the best genetics for your grow.
Understanding the Basics of Cannabis Genetics
Cannabis genetics refers to the study of the inheritance of the genetic traits that determine the characteristics of a cannabis plant. Genetics play an important role in the yield potential of a cannabis strain, as well as its potency and flavor.
Cannabis is a dioecious plant, meaning that it has male and female plants that are responsible for reproduction. Female cannabis plants produce the psychoactive compounds that are sought after by cannabis enthusiasts, while male plants produce pollen for fertilization.
Cannabis genetics is based on the inheritance of traits through genetic material known as genes. Genes are responsible for a variety of physical and chemical traits in cannabis plants, including stem structure, leaf shape, flower size and shape, and cannabinoid and terpene profiles.
Cannabis genetics are inherited through chromosomes, which are structures found in the nucleus of cannabis cells that carry genes. Cannabis plants have 38 chromosomes, which are divided into 19 pairs. Each pair of chromosomes carries alleles for particular traits.
Alleles are different versions of the same genes that are found on each chromosome. For example, one allele may code for a tall stem structure, while another allele codes for a short stem structure. These alleles can be dominant or recessive. Dominant alleles will always express their traits, while recessive alleles only express their traits when paired with another recessive allele.
In the process of crossbreeding, cannabis breeders attempt to create new strains with specific characteristics by selectively breeding plants with desirable traits. This process can be based on Mendelian genetics or other methods, such as phenotype selection. Phenotype selection involves selecting plants based on their physical characteristics rather than their genetic makeup.
Understanding the basics of cannabis genetics is crucial for growers and breeders looking to develop high-yielding cannabis strains with desirable characteristics. By carefully selecting and breeding plants with desired traits, growers can maximize their yield potential and produce high-quality cannabis products.
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Genetics | The study of the inheritance of genetic traits that determine a cannabis plant’s characteristics. |
| Inheritance | The process by which genetic traits are passed down from parent to offspring. |
| Dioecious plant | A plant with separate male and female individuals that are required for reproduction. |
| Psychoactive compounds | Chemicals found in cannabis that affect the brain and alter consciousness. |
| Genes | Genetic material responsible for physical and chemical traits in cannabis plants. |
| Chromosomes | Structures in the nucleus of cells that carry genes. |
| Alleles | Different versions of a gene that are found on each chromosome. |
| Dominant alleles | Alleles that will always express their traits. |
| Recessive alleles | Alleles that only express their traits when paired with another recessive allele. |
| Crossbreeding | The process of selectively breeding plants with desirable traits to create new strains. |
| Phenotype selection | Selecting plants based on their physical characteristics rather than their genetic makeup. |
| Yield potential | The maximum amount of cannabis that can be produced from a given strain. |
The Three Types of Cannabis Strains and their Yield Potential
When it comes to cannabis genetics and their potential yield, it’s important to understand the different types of cannabis strains that are available. Generally, there are three main types of cannabis strains: Indica, Sativa, and Hybrid. Each of these types has different characteristics and yield potential, so let’s take a closer look at each one.
| Strain Type | Characteristics | Yield Potential |
|---|---|---|
| Indica | Indica strains are known for their relaxing, sedative effects. They typically have a shorter flowering time, making them an ideal choice for indoor growers. Indica plants tend to be shorter and bushier with wider leaves compared to Sativa plants. | Generally, Indica strains have a higher yield potential because they tend to have larger and denser buds. However, their shorter stature may mean that overall yield per plant is lower compared to Sativa strains. |
| Sativa | Sativa strains are known for their uplifting, energizing effects. They typically have a longer flowering time and are better suited for outdoor growing. Sativa plants tend to be taller with thinner leaves compared to Indica plants. | Although Sativa plants may produce smaller buds compared to Indica plants, they can produce a higher overall yield per plant due to their taller stature and potential for larger, longer buds. |
| Hybrid | Hybrid strains are a cross between Indica and Sativa strains, and can have varying characteristics depending on the specific genetics. They can offer a combination of the relaxing effects of Indica with the energizing effects of Sativa, and can be grown both indoors and outdoors. | Hybrid strains can have varying yield potentials depending on the specific hybrid genetics. They can offer the best of both worlds in terms of yield potential, with the potential for both large, dense buds and a taller stature. |
Understanding the characteristics and yield potential of each strain type can help growers make informed decisions when choosing which genetics to grow to maximize their yield potential. However, it’s important to note that there can be significant variation within each strain type based on specific genetics, so it’s important to do further research into individual strains before making a decision.
The Role of Cannabinoids, Terpenes, and Flavonoids in Cannabis Yield
Cannabinoids, terpenes, and flavonoids are organic compounds found in cannabis plants that play important roles in their yield potential. Here is a breakdown of the different roles they play:
- Cannabinoids: Cannabinoids such as THC and CBD are the main chemical compounds in cannabis that are responsible for its effects. They interact with the body’s endocannabinoid system and can affect various functions such as mood, appetite, and pain perception. When it comes to yield, certain cannabinoids have been shown to promote plant growth and photosynthesis, ultimately leading to bigger and healthier plants. THC, in particular, has been shown to increase the growth rate of plants and increase their resistance to pests and diseases.
- Terpenes: Terpenes are aromatic compounds found in many plants and are responsible for their distinct scent and flavor. In cannabis, terpenes can also affect the effects of different strains. For example, myrcene is a terpene found in some indica strains and is believed to contribute to their relaxing effects. When it comes to yield, scientists have found that certain terpenes can also have antibacterial and antifungal properties, which can help protect the plant from diseases that can reduce yield potential.
- Flavonoids: Flavonoids are pigments that give cannabis its distinct color and can also play a role in its yield potential. They have been shown to have antioxidant properties and can therefore protect the plant from oxidative stress, which can harm its growth and ultimately reduce its yield. Flavonoids may also affect the plant’s immune system, which can help it fight off pests and diseases that can harm its yield potential.
Cannabinoids, terpenes, and flavonoids all play important roles in cannabis growth and yield potential by affecting various functions such as photosynthesis, pest and disease resistance, and antioxidant protection. By understanding how these compounds work, cultivators can choose the best strains and growing techniques to maximize their yield potential.
Choosing the Best Genetics for High Yield Cannabis
When it comes to growing high-yielding cannabis, choosing the right genetics is pivotal. With so many strains available from seed banks and breeders, the sheer variety can be overwhelming. How do you know which genetics are best for maximizing your yield potential? In this section, we will explore the key elements to consider when selecting genetics for high yield cannabis, including the characteristics of different cannabis strains, the role of cannabinoids, terpenes, and flavonoids, and how to identify high-yielding strains from reputable sources. We will also examine the differences between indica, sativa, and hybrid strains and how this impacts yield potential. By the end of this section, you will be equipped with the knowledge you need to select the genetics that are best suited to achieve a high yield from your cannabis crop.
Identifying High-Yield Strains from Seed Banks and Breeders
One of the first steps in choosing the best genetics for high yielding cannabis is to identify high-yield strains from seed banks and breeders. Here are some steps to help you do this effectively:
Research reputable seed banks and breeders: Do your research to find seed banks and breeders that are well-known for their high-quality genetics. Look for those with a track record of producing high-yielding strains, as well as those with positive customer reviews.
Look for strains with high yield potential: When choosing strains, make sure to pay attention to their potential yield. Look for strains that are known for producing large, dense buds with high THC content.
Consider the genetics: The genetics of a strain can play a significant role in its potential yield. Look for strains with genetics that have a proven track record of high yields, such as those with strong Indica or Sativa genetics.
Check for stability: It’s important to choose strains that are stable and consistent in their genetics. Look for strains that have been stabilized through several generations of breeding, ensuring that their genetics are consistent across different plants.
Consider the flowering time: The length of a strain’s flowering time can also affect its yield potential. Look for strains with a reasonable flowering time that is suitable for your growing environment.
By following these steps, you can better identify high-yield strains from seed banks and breeders, increasing your chances of a successful harvest with strong, high-yielding genetics.
Reviewing Genetics of Popular High-Yielding Strains
When it comes to choosing the best genetics for high-yield cannabis, it’s essential to understand the genetics of popular high-yielding strains. Below is a table that provides a brief overview of some popular high-yielding cannabis strains and their genetics:
| Strain Name | Genetics |
|---|---|
| Gorilla Glue #4 | Chem Sister x Sour Dubb x Chocolate Diesel |
| Girl Scout Cookies | Durban Poison x OG Kush |
| Blue Dream | Blueberry x Haze |
| Green Crack | Skunk #1 x Afghani |
| Granddaddy Purple | Purple Urkle x Big Bud |
Gorilla Glue #4, for example, is a popular strain with a genetic makeup of Chem Sister x Sour Dubb x Chocolate Diesel. Girl Scout Cookies, another favorite among cannabis enthusiasts, is known for its potent effects and is a blend of Durban Poison and OG Kush genetics. Blue Dream, a hybrid strain, is a combination of Blueberry and Haze genetics, while Green Crack’s genetics are Skunk #1 and Afghani. Finally, Granddaddy Purple is a strain that was created by crossing Purple Urkle and Big Bud genetics.
By understanding the genetics of these popular high-yielding strains, cannabis growers can make informed decisions about which genetics to cultivate for optimal yield. However, keep in mind that genetics alone aren’t the only factor in achieving a high yield. Other variables like environmental factors, nutrient management, and plant training techniques also play a crucial role in maximizing yield potential.
Comparing Indica vs. Sativa vs. Hybrid Genetics for Yield Potential
When it comes to choosing the right genetics for high yield cannabis, knowing the differences between Indica, Sativa, and Hybrid strains is crucial.
Indica Genetics
Indica strains are typically shorter and bushier than Sativa strains, and they have a faster flowering time. They also tend to have a higher yield potential due to their densely packed buds. Indica strains are known for their relaxing effects, making them a popular choice for those seeking relief from anxiety, insomnia, and other medical conditions.
Sativa Genetics
On the other hand, Sativa strains typically grow taller and have longer flowering times. They tend to produce smaller, less dense buds, but they make up for it in yield due to their overall longer plant structure. Sativa strains are known for being uplifting and energetic, making them great for daytime use.
Hybrid Genetics
As their name suggests, hybrid strains are a combination of Indica and Sativa genetics. These strains can be bred specifically for their high yield potential, incorporating the best of both worlds – the denser buds of Indica strains and the longer plant structure of Sativas. Hybrid strains can also offer a variety of effects, depending on the specific genetics involved.
When selecting genetics for high yield cannabis, it’s important to consider which type of strain will work best for your growing conditions, as well as the desired effects you’re looking for in your final product. Some growers may prefer Indica-dominant strains for their higher yields, while others may opt for Sativa-dominant or hybrid strains for their unique effects and growth patterns.
Understanding Phenotypes and how they Affect Yield
Phenotypes are the physical expression of the genetic traits of a cannabis plant. These traits can affect the yield potential of the plant as well as its other properties, such as potency, flavor, and aroma. Understanding phenotypes is crucial for selecting the right cannabis genetics for high-yield crops.
There are various phenotypes that can affect the yield potential of a cannabis plant. One of the most important is the plant’s growth pattern. This includes the height of the plant, the size of the leaves, and the length of the internodes. Plants with a compact growth pattern tend to produce higher yields than those with a more stretchy growth pattern.
Another important phenotype is bud structure. Plants that produce dense, compact buds tend to yield more than those that produce looser, less dense buds. The shape of the buds can also affect yield. Plants that produce long, cylindrical buds tend to yield less than those that produce short, compact buds.
The color of the plant can also be a phenotype that affects yield potential. Plants with darker leaves tend to produce higher yields than those with lighter leaves. This is because darker leaves are able to absorb more light energy, which is necessary for photosynthesis and ultimately, yield.
The branching pattern of a plant is yet another important phenotype that can affect yield potential. Plants with more branches tend to produce higher yields than those with fewer branches. However, it is important to balance the number of branches with the overall size of the plant. Plants that are too bushy can actually yield less than those that are more streamlined.
Phenotypes can also affect the ripening time of the plant. Plants that mature early tend to yield less than those that mature later. However, early-maturing plants can be advantageous in climates with shorter growing seasons.
Understanding the various phenotypes that can affect yield potential is crucial for selecting the right cannabis genetics for high-yield crops. By selecting plants with desirable phenotypes, growers can maximize their yields and produce high-quality cannabis.
| Phenotype | Effect on Yield Potential |
|---|---|
| Plant Growth Pattern | Compact plants tend to yield more than stretchy plants |
| Bud Structure | Dense, compact buds tend to yield more than less dense buds |
| Leaf Color | Plants with darker leaves tend to yield more than those with lighter leaves |
| Branching Pattern | Plants with more branches tend to yield more than those with fewer branches, but too many branches can reduce yield |
| Maturity Time | Plants that mature later tend to yield more than those that mature early, but early-maturing plants can be advantageous in shorter growing seasons |
Improving Your Cannabis Genetics for Yield
As a cannabis grower, it’s essential to continuously strive to improve your yield potential. One of the most effective ways to achieve this is by improving the genetics of your plants. By carefully selecting and breeding high-yielding strains, using techniques such as cloning and cross-breeding, and understanding the principles of backcrossing, you can significantly enhance your cannabis crop’s yield potential. In this section, we’ll explore the various methods and techniques you can use to improve your cannabis genetics for maximum yield.
Using Clones to Maximize the Yield Potential of Your Crop
One way to maximize the yield potential of your crop is by using clones, which are genetic copies of a mother plant that already has desirable traits such as high yield potential.
How do clones work?
Clones are created by taking a cutting from the mother plant and rooting it, so it can grow into a new plant. Because the clone has the same genetics as the mother plant, it will exhibit the same growth patterns, potency, and yield potential.
What are the benefits of using clones?
Using clones ensures that your plants will have the desired traits from the mother plant, so you don’t have to rely on chance or genetics from seed. This can save time and money by eliminating the need to search through many seeds to find a high-yielding plant.
How to make clones?
Making clones involves taking cuttings from a healthy mother plant, rooting them, and transplanting them into a new container. The cuttings are typically taken from the bottom of the plant, where the growth is the freshest and most vigorous. Special rooting hormones, like IBA or NAA, can be used to help the cutting form roots, and cloning gels or powders can help prevent the cutting from drying out too quickly.
How to care for clones?
Clones need to be nurtured carefully in their early stages of growth to ensure they develop strong roots, healthy stems, and vibrant leaves. Adequate watering, light, and nutrients will help the clone grow into a healthy plant with high yield potential.
Are there any downsides to using clones?
One downside to using clones is that they can be more susceptible to disease or pests because they have the same genetics as the mother plant. It’s important to ensure that the mother plant is healthy and disease-free before taking cuttings. Additionally, clones may have a limited lifespan because they share the same genetics as the mother plant and may start to lose vigor over time.
Using clones can be a great way to maximize the yield potential of your cannabis crop by guaranteeing that your plants will have the desired traits of a high-yielding mother plant. With proper care and maintenance, clones can thrive and produce bountiful yields.
Cross-Breeding Techniques to Stitch Together High-Yielding Genetics
When it comes to cross-breeding high-yielding cannabis genetics, there are a few techniques that breeders can use to achieve the desired result. Here are some of those techniques:
- Selective breeding: This is a classic breeding technique that has been used for generations. It involves selecting the best male and female plants and using their seeds to create a hybrid that is hopefully better than the parents. Breeders can choose plants that exhibit desirable traits such as high yield, potency, or disease resistance and create a hybrid that combines those traits.
- Backcrossing: This technique involves breeding a hybrid back to its parent to reinforce desirable traits from the parent. For example, if a hybrid has high yield but the parent has even higher yield, breeders can backcross the hybrid with the parent to create a new hybrid with even higher yield. This technique can also help to stabilize the genetic traits of a hybrid and eliminate undesirable traits.
- Interspecific hybridization: This technique involves crossbreeding two different species of cannabis. This technique can be more difficult because the plants may not be genetically compatible, but it can also result in hybrids that have unique traits not found in either parent. For example, breeders could crossbreed cannabis indica and cannabis sativa to create a new hybrid with high yield and a unique terpene profile.
- Marker-assisted breeding: This technique involves using molecular markers to identify genetic traits in plants. Breeders can analyze the DNA of different plants to identify desirable traits such as high yield or disease resistance. This can help breeders to create hybrids that are more likely to have those desirable traits.
By using these cross-breeding techniques, breeders can create new hybrids that have the best traits of their parent plants. This can help to create high-yielding cannabis genetics that are more resistant to pests and diseases and produce a high-quality product. However, it’s important to remember that breeding cannabis can be a complex process that requires a lot of trial and error. Breeders must be patient and persistent in their efforts to create the perfect cannabis hybrid.
Principles and Benefits of Backcrossing as a Genetic Improvement Technique
Backcrossing is a genetic improvement technique that is aimed at transferring the desirable genes of a particular strain into a new strain. It is particularly useful when trying to maximize the yield of a specific strain by introducing new genetic traits.
In backcrossing, a plant with desirable traits is crossed with a recipient plant to achieve greater yields. The resulting plants are then crossed back with the parent strain multiple times. This process helps to eliminate any undesirable genetic traits that may have been introduced during the initial cross, while retaining the desirable traits of the parent strain.
One of the benefits of backcrossing is that it allows for the retention of the parent strain’s original genetic makeup, while still introducing new genetic traits. This means that growers can create a new strain with desirable traits while retaining the same plant’s potency, taste, and aroma.
Another key advantage of backcrossing is that it’s relatively simple to accomplish. With the right parental strain and recipient plant, growers can use this technique to create a new strain that’s perfectly suited to their particular growing environment.
Backcrossing is an effective genetic improvement technique that can help improve the yield of cannabis strains. It allows growers to create new strains that retain desirable traits while introducing new genetic traits, resulting in a more productive and profitable yield.
The Role of Genetics in Cannabis Pests and Diseases Resistance
Cannabis plants, like any other plant, are susceptible to various pests and diseases that can significantly impact yield. However, the genetics of the plant can play a crucial role in its resistance to pests and diseases.
Various cannabis strains can develop varying degrees of resistance to pests and diseases. This depends on the genetic makeup of the strain and its ability to fend off infections. The table below highlights some common pests and diseases, their impact on plants, and the genetics associated with resistance.
| Pest/Disease | Impact on Plants | Genetics |
|---|---|---|
| Spider mites | Can cause defoliation and yield loss | Genetics play a role in resistance, but environmental controls are also important |
| Thrips | Can spread viruses and cause aesthetic damage, resulting in lower yield | Resistance is largely based on genetics |
| Botrytis (bud rot) | Can cause significant yield loss by infecting buds | Genetics play a role in resistance, but environmental factors like humidity and temperature also affect susceptibility |
| Powdery mildew | Causes white, powdery growth and can lower plant vigor and yield | Genetics play a role in resistance, but environmental controls are also important |
| Fusarium | Can cause wilting and yellowing of leaves as well as yield loss | Resistance is largely based on genetics |
| Verticillium wilt | Causes wilting and yellowing of leaves and can severely impact yield | Resistance is largely based on genetics |
Developing a genetically resistant strain through selective breeding can be challenging and time-consuming. However, by understanding the genetic links to pests and diseases, growers can take steps to mitigate the risks associated with these issues. This can include ensuring the environment is well-controlled and selecting strains that have demonstrated resistance to specific pests and diseases. Additionally, maintaining a clean growing environment and implementing proper hygiene protocols can drastically reduce the risk of pest and disease outbreaks.
Troubleshooting Low Yielding Cannabis Genetics
For any cannabis grower, low yields can be frustrating after putting in so much time and effort to cultivate their plants. Many factors can affect the yield of cannabis genetics, ranging from genetics to environmental factors to pests and diseases. Troubleshooting low-yielding cannabis genetics requires a systematic approach to identify the root causes of the problems and address them effectively. In this section, we will delve into the common causes of low-yielding cannabis genetics, strategies for improving yield through environmental controls and nutrient management, and techniques for maximizing yield through plant training.
Identifying the Common Causes of Low-Yielding Cannabis Genetics
When it comes to low-yielding cannabis genetics, there can be several underlying causes. It’s important for growers to identify and address these issues in order to maximize their yield potential. Here are some common causes:
| Cause | Symptoms |
|---|---|
| Poor Genetics | Small buds, low resin production, weak plants |
| Nutrient Deficiencies | Yellowing leaves, stunted growth, poor bud development |
| Pest Infestations | Bite marks, holes in leaves, damaged buds |
| Disease | Brown spots on leaves, mold on buds, stunted growth |
| Inadequate Lighting | Stretching plants, small buds, slow growth |
| Inconsistent Temperature and Humidity | Stunted growth, decreased yield, mold and mildew growth |
| Overcrowding | Small buds, decreased yield, competition for resources |
By identifying the specific cause(s) of low yield, growers can take appropriate steps to address the issue and improve their crop. This may include adjusting nutrient levels, addressing pest or disease issues, optimizing lighting and environmental controls, or selecting higher quality genetics. It may also involve using plant training techniques or exploring different growing methods to improve overall yield potential.
Improving Genetic Yield through Environmental Controls and Nutrient Management
One of the key factors that can affect the yield potential of your cannabis genetics is the environment in which they are grown. By understanding the optimal conditions for your plants and providing them with proper nutrient management, you can improve their genetic yield.
Environmental Controls:
1. Temperature: The optimal temperature range for cannabis growth is between 65-80°F. High temperatures can cause stress and stunted growth, while low temperatures can slow down photosynthesis and delay flowering.
2. Humidity: Controlling humidity is crucial for preventing mold, mildew, and other fungal diseases. The ideal range is between 50-70% during vegetative growth and 40-50% during flowering.
3. Light: Providing your plants with the proper amount of light is essential for healthy growth and maximizing yield potential. Cannabis plants require a minimum of 12 hours of light per day, but some strains may require up to 18 hours during the vegetative stage.
4. CO2 levels: Increasing the CO2 levels in your grow room can boost the growth rates and productivity of your plants. The ideal range is between 800-1200 ppm.
Nutrient Management:
1. pH levels: Maintaining the correct pH level in the soil or hydroponic system is crucial for nutrient uptake and plant growth. The optimal range is between 6.0-7.0.
2. Nutrient Ratio: Providing the right amount of essential nutrients such as Nitrogen (N), Phosphorus (P) and Potassium (K) is necessary for healthy plant development. Different stages of plant growth require different ratios of these nutrients.
3. Organic vs. Synthetic: Choosing the right type of nutrients for your plants will depend on your personal preference and growing style. Organic nutrients are derived from natural sources and can improve the flavor of your crop, while synthetic nutrients are more precise and can be tailored to specific plant requirements.
4. Watering: Overwatering or underwatering your plants can stunt growth and affect yield potential. Providing the right amount of water is crucial for plant health and avoiding nutrient imbalances.
By implementing these environmental controls and nutrient management techniques, you can optimize the genetic yield potential of your cannabis plants. However, it’s important to note that genetics also play a significant role in determining the final yield, so it’s crucial to choose high-yielding strains and proper breeding techniques to maximize your results.
Using Plant Training Techniques to Maximize Yield from Your Genetics
Plant training techniques provide a way to maximize the yield from your cannabis genetics. By controlling the shape and size of your plants, you can help them receive more light and nutrients, leading to bigger and better buds. Here are some effective plant training techniques that can help boost your yield:
- TOPPING: Topping involves removing the top of the main stem of your plant, which stimulates the growth of new side branches. This allows the plant to distribute its energy among more branches, resulting in more bud sites and higher yield.
- LST (LOW-STRESS TRAINING): LST involves manipulating the branches of your plant to create a more horizontal canopy. This allows more light to penetrate to lower parts of the plant, leading to more even growth and bigger yields.
- SCROG (SCREEN OF GREEN): SCROG involves using a screen or net to keep the plant’s branches flat and spread out. This creates a more uniform canopy and maximizes the amount of light that each bud site receives, leading to bigger buds and higher yield.
- SUPER CROPPING: Super cropping involves gently bending the branches of your plant to create more bud sites and increase their exposure to light. This technique also strengthens the branches, allowing them to support bigger buds without breaking.
By using these plant training techniques, you can help your cannabis plants reach their full potential and achieve maximum yield. It’s important to remember that each strain may respond differently to these techniques, so it’s important to do some research and experimentation to find what works best for your genetics.
Real-life Examples of Genetic Troubleshooting and Improvement
Real-life examples of genetic troubleshooting and improvement can provide valuable insight into the practical application of genetic principles to cannabis cultivation. Here are a few examples of how growers have used genetic troubleshooting and improvement to maximize yield:
- Example 1: A grower noticed that their high-yield strain was producing smaller buds than usual. After ruling out environmental factors, the grower suspected a genetic anomaly. Upon consulting with a cannabis geneticist, it was determined that the plant had developed a mutation that caused reduced bud growth. The grower then used a backcrossing technique to restore the plant’s original genetics and improve the yield.
- Example 2: Another grower experienced low yields despite using high-yield genetics. Upon closer inspection, the grower discovered that the genetics had been exposed to a virus that damaged the plant’s reproductive system. The grower then used a cloning technique to salvage the genetics and remove the virus, ultimately increasing the yield.
- Example 3: A third grower had trouble with their plants developing mold and mildew, which affected the yield. After researching the genetics of mold and mildew-resistant strains, the grower used a cross-breeding technique to introduce those genetics into their high-yield strain. This resulted in a more robust and healthy plant that produced higher yields.
These real-life examples demonstrate how important it is for growers to understand the genetics of their cannabis strains and to use genetic troubleshooting and improvement techniques to maximize yield. By identifying genetic anomalies, using cloning and cross-breeding techniques, and selecting for desirable traits, growers can improve the genetics of their cannabis plants and produce high yields.
Conclusion
As we conclude this in-depth exploration of the genetics behind high-yielding cannabis strains, one cannot help but be amazed at the complexity and potential held within each plant’s DNA. From understanding the basics of cannabis genetics to identifying high-yield strains and improving their yields, we have seen how genetics plays a fundamental role in the success of any cannabis grower. As with any living organism, each cannabis strain has its unique genetic makeup that affects its growth, yield potential, and resistance to pests and diseases. By taking the time to educate ourselves on the intricacies of cannabis genetics and investing in improving them, we can create a sustainable and thriving cannabis industry that benefits everyone involved. Let us continue to push the boundaries of what is possible with cannabis genetics and unlock the full potential of this incredible plant.
Final Thoughts on Understanding Genetics for High-Yield Cannabis Strains
As we wrap up our discussion on the genetics behind high-yielding cannabis strains, it is important to understand that genetics play a crucial role in determining the yield potential of your cannabis crop. While environmental factors like lighting, temperature, and nutrients also contribute significantly to the success of your crop, having the right genetics is the foundation for achieving high yields.
Choosing the right genetics: When choosing genetics for your crop, it is important to consider the strain’s yield potential, cannabinoid content, terpene profile, and your personal preferences. Whether you prefer Indica, Sativa, or hybrid strains, there are several high-yielding genetics to choose from.
Improving the genetics: If you want to further improve the genetics of your cannabis crop, there are several techniques you can employ, such as cloning, cross-breeding, and backcrossing. These techniques can help you stitch together the attributes of different strains to create a hybrid that offers the best of both worlds.
Troubleshooting low-yielding genetics: If your genetics are not producing the desired yield, it is important to troubleshoot the problem by identifying the common causes of low yields – such as pest infestations, nutrient deficiencies, or inadequate lighting. Once you have identified the problem, you can take corrective action to improve your yield.
Understanding the genetics behind high-yielding cannabis strains is essential to achieving success in your cannabis cultivation. By selecting the right genetics, employing improvement techniques, and troubleshooting low yields, you can maximize the potential of your crop and produce high-quality cannabis with impressive yields.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between genotype and phenotype in cannabis genetics?
Genotype refers to the specific genetic makeup of a plant while phenotype refers to the observable physical characteristics of a plant.
What are cannabinoids and how do they affect cannabis yield?
Cannabinoids are chemical compounds found in cannabis that interact with our bodies’ endocannabinoid system. Certain cannabinoids, like THC and CBD, have been shown to potentially increase cannabis yield through their effects on plant growth and development.
What are terpenes and how do they contribute to cannabis yield?
Terpenes are aromatic compounds found in cannabis that contribute to its flavor and aroma. Certain terpenes have also been shown to potentially increase cannabis yield by improving soil quality and repelling pests.
What is the difference between Indica, Sativa, and Hybrid cannabis strains?
Indica strains are typically associated with relaxing effects and a shorter, bushier plant structure. Sativa strains are typically associated with uplifting effects and a taller, more slender plant structure. Hybrid strains are a combination of both Indica and Sativa genetics.
How can I identify high-yielding cannabis strains from seed banks and breeders?
Look for strains with a reputation for high yield, as well as those with genetics known for their growth and development traits that promote larger yields.
What is cloning and how can it help me maximize my cannabis yield?
Cloning involves taking a cutting from a mature cannabis plant and rooting it to grow into a new plant with identical genetics. This allows for more consistent and predictable yields as each plant will have the same growth and development traits.
What is backcrossing and how can it improve my cannabis genetics?
Backcrossing involves breeding a plant with its parent or an individual with the desired trait to create offspring with a higher likelihood of exhibiting the desired trait. This can help strengthen and stabilize genetics for desired traits and potentially increase yield.
What are some common causes of low-yielding cannabis genetics?
Poor environmental conditions, nutrient deficiencies or imbalances, inadequate lighting, and genetic variability can all contribute to low yield in cannabis plants.
What is plant training and how can it help me maximize my cannabis yield?
Plant training involves manipulating the growth of a plant in order to promote more even canopy development and larger bud sites. Techniques like topping, pruning, and LST (low-stress training) can help increase yield by maximizing light exposure and airflow.
Can genetics affect a cannabis plant’s resistance to pests and diseases?
Yes, certain genetics may have natural resistance or tolerance to pests and diseases. By selecting and breeding for these traits, growers can potentially reduce the risk of infestations and improve overall plant health and yield.