Optimizing Soil Nutrients for Maximum Cannabis Growth
Introduction
Contents
It’s no secret that cannabis is a finicky plant that requires particular attention to detail in order to thrive. One of the key factors that significantly impact the growth and health of cannabis plants is the soil in which they are grown. Proper soil nutrients are crucial for achieving a bountiful cannabis harvest. This article will guide you through the importance of soil nutrient management, exploring the key soil nutrients for cannabis growth, assessing soil nutrient levels, and maximizing cannabis growth with optimal soil nutrient management. With the right soil nutrient management practices in place, you can grow healthy cannabis plants with exceptional yields.
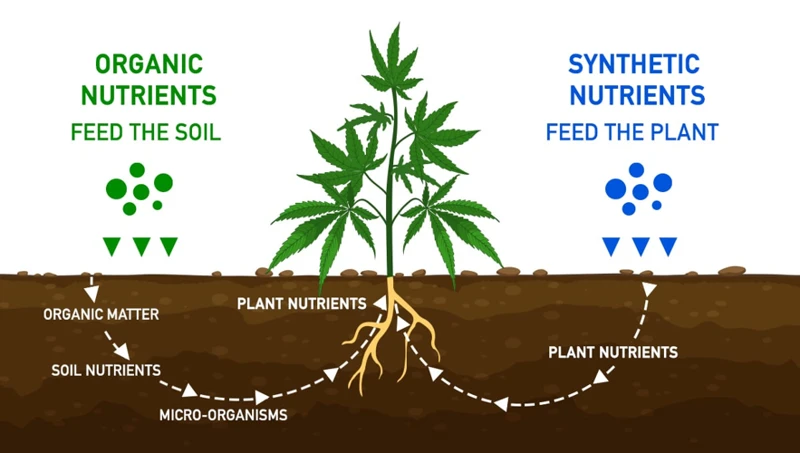
What are Soil Nutrients?
Soil nutrients refer to the essential chemical elements found in soil that are necessary for plant growth and development. These nutrients are obtained from the breakdown of organic matter, weathering of rocks, and other natural processes. There are a variety of different soil nutrients that can affect plant growth, with some being more important than others. Here are the key soil nutrients that every cannabis grower should be aware of:
- Nitrogen: Nitrogen is an essential component of amino acids and proteins, which are necessary for plant growth. It is also involved in photosynthesis, the process by which plants use sunlight to produce energy.
- Phosphorus: Phosphorus is critical for root development and helps plants grow and store energy. It is also a key component of DNA and RNA.
- Potassium: Potassium is essential for the functioning of plant cells and helps regulate water balance. It also aids in photosynthesis and helps plants resist disease and pests.
- Calcium: Calcium is necessary for cell wall development and helps plants absorb other nutrients. It also aids in root growth and helps regulate soil pH.
- Magnesium: Magnesium is a component of chlorophyll, which is necessary for photosynthesis. It also helps plants produce energy and aids in nutrient uptake.
- Sulfur: Sulfur is necessary for the synthesis of some amino acids and proteins. It also plays a role in root development and helps plants resist disease.
These soil nutrients are essential for cannabis growth and need to be present in the right amounts and ratios for optimal plant development. Understanding how to assess and amend soil nutrient levels is critical for producing a healthy and productive cannabis crop.
Why are Soil Nutrients Important for Cannabis Growth?
Cannabis plants are highly dependent on soil nutrients for their growth and development. This is because soil nutrients provide the essential elements that cannabis plants require to carry out their metabolic processes.
Below are some reasons why soil nutrients are important for cannabis growth:
- Supports Plant Structure and Growth: Soil nutrients are essential for the formation of plant tissues, including the leaves, stems, flowers, and buds. Without a sufficient supply of soil nutrients, cannabis plants can experience stunted growth, or even die off.
- Enhances Photosynthesis: Soil nutrients such as nitrogen and magnesium are critical for chlorophyll production, a key organic molecule that enables cannabis plants to photosynthesize and produce food. A lack of these essential nutrients can limit photosynthesis, leading to decreased yields.
- Boosts Yield and Quality: By providing the right balance of soil nutrients, cannabis growers can increase their plant’s yield and improve the potency and quality of their buds. Nutrient-rich soil can also contribute to higher levels of terpenes and cannabinoids, which are responsible for the plant’s aroma and effects.
- Improves Resistance to Disease and Pests: Soil nutrients can help reinforce the plant’s natural defenses and immunity against pests and diseases. For example, compounds found in healthy soil, such as humic acid, can stimulate the growth of beneficial microorganisms, which can improve soil health and protect the plants from pathogenic attacks.
- Promotes Overall Plant Health: Proper soil nutrient management can promote healthy plant growth, robust root development, and increase the plant’s ability to tolerate environmental stressors such as extreme temperatures, drought, or excessive rain.
Soil nutrients play a crucial role in optimizing the growth and yielding potential of cannabis plants. It is essential for cannabis growers to understand the importance of soil nutrients for their plants and how to maintain a healthy soil nutrient balance throughout the plant’s life cycle.
Key Soil Nutrients for Cannabis Growth
One of the most crucial factors that determine the successful growth of cannabis plants is the presence of essential soil nutrients. Without an adequate supply of nutrients, the plants will not be able to reach their full potential, and their growth and productivity will be compromised. Understanding the key soil nutrients required for cannabis growth is of utmost importance for any cannabis cultivator. In this section, we will discuss the most crucial soil nutrients in detail, including nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, magnesium, and sulfur.
Nitrogen
Nitrogen is one of the most important soil nutrients for cannabis growth. It is essential for chlorophyll production, which allows plants to carry out photosynthesis and produce energy. Nitrogen plays a key role in the formation of amino acids, the building blocks of proteins. Without adequate nitrogen, cannabis plants will be stunted and weak.
Sources of Nitrogen:
– Organic matter: Organic amendments such as compost, manure, and worm castings are rich sources of nitrogen.
– Chemical fertilizers: Fertilizers containing nitrogen are typically labeled with an “N” number, indicating the percentage of nitrogen by weight.
– Atmospheric nitrogen fixation: Some plants, like legumes, are able to fix atmospheric nitrogen into a usable form in the soil.
Nitrogen deficiencies:
When cannabis plants are lacking in nitrogen, they will exhibit yellowing leaves (chlorosis) starting from the bottom of the plant and moving up. The plant will also have stunted growth and reduced yields.
Nitrogen toxicity:
Too much nitrogen can be harmful to cannabis plants as well. Symptoms of nitrogen toxicity include dark green leaves, slowed growth, and leaf curling.
Nitrogen management:
Proper nitrogen management involves ensuring that cannabis plants have adequate access to nitrogen without overloading the soil. Organic amendments should be used to boost soil nitrogen levels, and fertilizers should be used sparingly and according to package instructions. Regular soil testing can also help growers monitor their soil nitrogen levels and make adjustments as needed.
Phosphorus
Phosphorus is another essential soil nutrient for cannabis growth. It is an essential component of many vital organic compounds, including DNA and ATP, which are important molecules for plant growth and development.
Functions of Phosphorus in Cannabis Growth
Phosphorus plays several critical roles in the growth and development of cannabis plants:
- It is essential for the formation of strong root systems
- It is necessary for the transfer of energy within the plant
- It is important for the development of healthy flowers and buds
- It facilitates the uptake of other nutrients, such as nitrogen and potassium
Symptoms of Phosphorus Deficiency
When cannabis plants don’t receive enough phosphorus, they develop several symptoms that indicate a deficiency. These symptoms include:
- Dark green leaves
- Purpling of stems, branches, and petioles
- Poor flower and bud development
- Reduced growth rate
Sources of Phosphorus
Phosphorus is present in most soils, but it may not be available to plants because of complex chemical interactions with other soil components. The primary sources of phosphorus for cannabis plants are:
| Source | Description |
| Bone Meal | A slow-release organic fertilizer that provides a source of phosphorus over several weeks |
| Rock Phosphate | A natural mineral mined from ancient deposits that slowly releases phosphorus into the soil over time |
| Phosphate Fertilizers | Manufactured fertilizers that contain a high concentration of phosphorus and other essential nutrients |
Applying Phosphorus to Cannabis Plants
Applying phosphorus to cannabis plants is essential for maximizing growth and flower development. However, it is important to use the correct amount and application method to avoid damaging the plant.
Phosphorus is best applied during the vegetative and early flowering stages of cannabis growth. Avoid applying phosphorus during the later stages of flowering, as it can negatively affect the taste and quality of the buds.
When using a fertilizer containing phosphorus, always follow the manufacturer’s instructions for proper application rates and methods. Over-fertilization can lead to nutrient burn and damage the plant.
Phosphorus is an essential soil nutrient for healthy cannabis growth. By understanding its function and symptoms of deficiency, cannabis growers can optimize the nutrient content of their soil, apply proper adjustments, and maximize growth potential.
Potassium
Potassium is an essential nutrient for cannabis growth, playing a vital role in various physiological processes. Potassium is involved in the formation of stems and roots, aids in the transport of water and nutrients throughout the plant, and helps with the regulation of stomata, which are tiny pores on leaves responsible for gas exchange.
Here are some important facts you should know about the role of potassium in cannabis growth:
- Potassium helps with drought resistance: Potassium is involved in controlling the water balance in cells. When potassium is present in adequate levels, a cannabis plant can better withstand periods of drought. This is because potassium helps regulate water loss from leaf cells, ensuring that the plant has enough water to continue photosynthesis and maintain proper growth.
- Potassium improves the quality of the buds: Potassium plays a critical role in the development and growth of flower buds. Adequate potassium levels promote the formation of dense, resinous buds with a stronger aroma and flavor profile. Potassium also helps improve bud density, which is crucial for a successful harvest.
- Potassium helps with disease resistance: Potassium is involved in strengthening cell walls, making cannabis plants less vulnerable to disease and pest infestations. By increasing the rigidity of cell walls, potassium can also help prevent the spread of pathogens within the plant.
- Potassium aids nutrient uptake: Potassium is involved in the transportation of nutrients from the roots to the rest of the plant. When potassium is present in adequate levels, it helps ensure that cannabis plants can efficiently take up and use other essential nutrients like nitrogen and phosphorus.
- Potassium levels should be balanced: While potassium is essential for cannabis growth, excessive levels can also be harmful. Overly high levels of potassium can interfere with the uptake of other nutrients, leading to deficiencies. It is crucial to maintain the proper balance of potassium with other essential nutrients for optimal plant growth.
Adequate potassium levels are essential for healthy cannabis plants. By playing key roles in water regulation, bud development, disease resistance, nutrient uptake, and overall plant growth, potassium represents a vital component of any successful cannabis nutrient management plan.
Calcium
Calcium is another essential nutrient for cannabis growth. It is a structural component of cell walls and is crucial for overall plant development. Calcium aids in the transportation of other nutrients throughout the plant.
Below is a table outlining the importance of calcium for cannabis growth:
| Function | Effect of Deficiency | Symptoms of Deficiency |
|---|---|---|
| Aids in cell development and structure | Weakened plant structure, resulting in stunted growth | Tip burn, curled leaves |
| Facilitates nutrient transport | Reduced nutrient uptake, resulting in stunted growth | Purple stems, yellow leaves, reduced growth |
Calcium deficiency can be particularly problematic in hydroponic systems, where there is no soil to naturally provide this nutrient. It is important to monitor calcium levels in hydroponic systems and supplement as needed with calcium-rich fertilizers or additives.
To optimize calcium levels in soil, gardeners can amend with materials such as gypsum, lime, or bone meal. It is important to avoid over-amending with these materials, as excessive calcium levels can interfere with the uptake of other nutrients.
Ensuring proper calcium levels in soil is crucial for healthy cannabis growth and development.
Magnesium
Magnesium is another critical nutrient for cannabis growth. It plays a vital role in the photosynthesis process as it is a central component of chlorophyll molecules. Without enough magnesium, cannabis plants will exhibit signs of chlorosis, a condition where plants have yellowing leaves due to insufficient chlorophyll production.
Although magnesium is not technically a macronutrient, it is required by cannabis plants in relatively large amounts compared to other secondary nutrients. Some of the key functions that magnesium performs in cannabis plants include:
- Activating enzymes needed for plant growth and development
- Regulating nutrient uptake
- Holding the plant’s cell walls together
- Facilitating the conversion of light into energy
Cannabis plants that experience magnesium deficiency often have stunted growth, with leaves being small and thin. If the deficiency persists, the leaves will eventually curl down and die. It is essential to monitor magnesium levels in the soil to ensure that cannabis plants grow optimally.
One of the most effective ways of providing magnesium to cannabis plants is by using Epsom salt (magnesium sulfate). It is a readily available and affordable source of magnesium that can be easily added to the soil as a fertilizer. Additionally, it is advisable to include compost and other organic material in the soil. These organic materials are high in magnesium and can provide a sustainable source of the nutrient to plants.
However, it is crucial to note that over-fertilizing with magnesium can have adverse effects on cannabis plants. Too much magnesium can lead to a buildup of salts in the soil, which can harm the roots and cause other nutrient deficiencies. It is crucial to maintain a balance of soil nutrients and pH levels.
Magnesium is vital for the growth and development of cannabis plants. Understanding its functions and how to maintain optimal levels is critical to ensuring that cannabis plants thrive. Providing magnesium through Epsom salt and organic matter, while avoiding over-fertilization, can go a long way in maximizing cannabis yields.
Sulfur
Sulfur is an essential nutrient for cannabis growth, as it aids in the production of chlorophyll and the development of proteins. Without sufficient sulfur, cannabis plants may experience stunted growth and yellowing of the leaves.
| Sulfur | Function in cannabis growth | Symptoms of deficiency |
|---|---|---|
| Helps in the production of chlorophyll | Chlorophyll is essential for photosynthesis, which is the process by which plants convert light into energy. | Yellowing of the leaves |
| Aids in the development of proteins | Proteins are necessary for plant growth and development, and sulfur helps to create them. | Stunted growth |
To ensure that your cannabis plants are receiving enough sulfur, it is important to include it in your overall nutrient management plan. Sulfur can be added to soil through the use of fertilizers or organic matter amendments such as compost or manure. It is also important to monitor soil sulfur levels regularly through soil testing methods to ensure that they remain within the appropriate range.
If you notice symptoms of sulfur deficiency in your cannabis plants, it is important to address the issue promptly. This may involve amending the soil with additional sulfur, adjusting your fertilizer regimen, or adjusting other aspects of your nutrient management plan. By taking a proactive approach to sulfur and other soil nutrient management, you can help ensure that your cannabis plants grow healthy and strong.
Assessing Soil Nutrient Levels
Determining the nutrient levels in the soil is a critical step in ensuring successful cannabis growth. Assessing soil nutrient levels helps growers understand which nutrients may be lacking in the soil and which ones may be in excess, which in turn helps them determine the appropriate actions to take to achieve optimal nutrient levels. However, evaluating soil nutrients can be a complicated process, and many growers may have difficulty interpreting soil test results. As such, it is essential to understand the various soil testing methods available and how to interpret the results accurately.
Soil Testing Methods
To assess the nutrient levels in soil, various testing methods can be used. Proper soil testing is critical to ensuring optimal nutrient levels for cannabis growth. Below are some common soil testing methods.
| Testing Method | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Home Test Kits | -Inexpensive -Easy to use |
-May not provide accurate results -Limited number of nutrients tested |
| Laboratory Soil Testing | -Provides comprehensive analysis of soil nutrients -Accurate results |
-More expensive than home kits -Takes longer to receive results |
| Electrical Conductivity Testing | -Quick and provides a general indication of nutrient levels | -Not as accurate as laboratory testing -Does not test specific nutrients |
| Visual Soil Assessment | -Provides a quick evaluation of soil quality and potential nutrient deficiencies | -Subjective -Limited scope of nutrient analysis |
Home test kits are affordable and easy to use, but may not provide accurate results and may only test for a limited number of nutrients. For more comprehensive analysis, laboratory soil testing is recommended, although it can be more expensive and take longer to receive results. Electrical conductivity testing provides a quick indication of nutrient levels but doesn’t test for specific nutrients. Visual soil assessment can be useful for quickly evaluating soil quality and potential nutrient deficiencies, but it is subjective and has only a limited scope of nutrient analysis.
Interpreting Soil Test Results
After conducting a soil test, it is important to interpret the results in order to determine which soil nutrients are lacking or present in excess. Here are some key points to consider when interpreting soil test results:
- Consider the ideal nutrient levels: Soil test results include a chart or graph that compares the actual nutrient levels to the ideal range for optimal plant growth. It is important to compare your results to these ranges to determine which nutrients may need to be increased or decreased.
- Prioritize macronutrient deficiencies: Macronutrients, such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, are essential for plant growth and development. If your soil test indicates a deficiency in any of these macronutrients, it is important to address those first before addressing any micronutrient deficiencies.
- Take into account soil type and pH: The nutrient availability in soil depends on factors such as soil type and pH. Acidic soils may have lower levels of certain nutrients, while alkaline soils may have excessive levels of others. It is important to take these factors into consideration when interpreting soil test results.
- Consider the plant’s growth stage: The nutrient needs of a cannabis plant will vary depending on its growth stage. For example, plants in the vegetative stage require more nitrogen, while those in the flowering stage require more phosphorus and potassium. It is important to interpret soil test results in the context of the plant’s growth stage.
- Adjust nutrient levels slowly: When amending soil to correct nutrient deficiencies or excesses, it is important to make adjustments slowly over time. Rapid changes in nutrient levels can shock plants and lead to nutrient burn or deficiencies.
Interpreting soil test results requires careful consideration of several factors, including nutrient levels, soil type and pH, and the plant’s growth stage. By taking these factors into account and making adjustments slowly over time, it is possible to optimize soil nutrient content for optimal cannabis growth.
Optimizing Soil Nutrient Content
Now that we understand the key soil nutrients necessary for cannabis growth, it’s important to focus on optimizing the nutrient content in the soil. Proper soil nutrient levels are crucial for plant health and maximizing yields. In this section, we will discuss various methods to amend soil with organic matter, use fertilizers to boost nutrient levels, and most importantly, how to avoid soil contamination. By following these practices, we can ensure that our cannabis plants receive the necessary nutrients to thrive.
Amending Soil with Organic Matter
One way to optimize soil nutrient content for healthy cannabis growth is by amending the soil with organic matter such as compost or manure. Organic matter helps to improve soil structure and increase nutrient content.
Types of Organic Matter
There are several types of organic matter that can be used to amend soil for cannabis growth, including:
| Type of Organic Matter | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Compost | Decomposed plant matter, food waste, and other organic materials | Improves soil structure, increases nutrient content, supports microbial life |
| Manure | Animal waste, often mixed with bedding | Rich in nutrients such as nitrogen and phosphorus, improves soil structure |
| Cover crops | Plants grown specifically for soil improvement, such as clover or alfalfa | Increases organic matter, adds nitrogen to the soil, prevents erosion |
Application of Organic Matter
When amending soil with organic matter, it is important to do so in a way that does not harm the cannabis plants. Here are some tips for applying organic matter:
- Avoid applying too much organic matter, which can result in nutrient imbalances or root rot.
- Apply organic matter to the topsoil, and mix it in gently with a garden fork or tiller.
- Wait several weeks before planting cannabis, to allow the organic matter to decompose and settle into the soil.
By amending soil with organic matter, cannabis growers can improve soil fertility, structure, and overall health, leading to better cannabis growth and yields.
Using Fertilizers to Boost Soil Nutrient Levels
One of the most common methods for boosting soil nutrient levels is by using fertilizers. Fertilizers are essential for providing plants with the necessary macro and micronutrients to grow and thrive. However, it’s crucial to use fertilizers correctly to avoid over-fertilization or under-fertilization, which can harm plant growth and negatively impact the environment.
Types of Fertilizers: There are various types of fertilizers available in the market for both organic and conventional growers. Commonly used fertilizers include:
- Organic fertilizers: Manure, compost, bone meal, fish emulsion, and blood meal;
- Synthetic fertilizers: Nitrogen (N), phosphorous (P), and potassium (K) fertilizers, which are often referred to as NPK fertilizers.
Choosing the Right Fertilizer: The right fertilizer depends on various factors such as soil type, plant nutrient needs, and the crop growth stage. It’s crucial to select the right fertilizer and understand the nutrient requirements of the cannabis plant to avoid over-fertilization or under-fertilization.
Applying Fertilizers: When applying fertilizers to the soil, follow the application rate and timing instructions on the fertilizer label. Over-fertilization can cause nutrient toxicity, inhibit growth, and stress the plant. Under-fertilization, on the other hand, can result in nutrient deficiencies, which can also negatively impact the plant’s growth and yield.
Calculating Fertility: Knowing the soil’s residual nutrient levels, including macronutrients and micronutrients, helps determine the amount of fertilizer needed. Soil testing can provide accurate results to determine the right amount and type of fertilizer.
Avoiding Contamination: Using fertilizers can lead to contamination through runoff, leaching, and volatilization, which can negatively impact the plant and surrounding environment. It’s crucial to use fertilizers correctly and carefully to avoid contamination.
Using fertilizers can be an effective way to boost soil nutrient levels, but it’s crucial to use them correctly and avoid harmful effects on the plant and environment. Combining fertilizer usage with organic matter amendments can also provide additional micronutrients to the soil and enhance the overall soil fertility.
Avoiding Soil Contamination
Contamination of soil can be a big problem for cannabis growers. Pesticides, heavy metals, and other harmful substances can be present in soil, which can negatively affect plant growth and even harm human health if consumed. It is important to take steps to avoid soil contamination. Here are some ways to do so:
- Use organic cultivation methods: Organic cultivation methods, such as using compost and other natural fertilizers, can help reduce the risk of soil contamination. Avoid using synthetic pesticides and chemical fertilizers that can leave harmful residues in the soil.
- Choose a clean growing location: Avoid planting in areas that have a history of contamination, such as former industrial sites or areas near heavily-trafficked roads. Consider conducting soil tests before planting to ensure the soil is suitable for growing cannabis.
- Test soil and water sources: Regularly test soil and water sources for potential toxins or contaminants that could affect plant growth or human health. If contaminants are found, work to remediate the issue before planting.
- Properly dispose of waste: Make sure any waste generated during cultivation, such as plant material or soil, is properly disposed of to avoid contaminating the surrounding environment.
- Practice good hygiene: Practice good hygiene when working with plants to avoid spreading contaminants from one plant or location to another. This includes washing tools and wearing gloves and protective clothing when necessary.
By taking these steps and being vigilant about potential sources of contamination, growers can better protect their cannabis plants and ensure a safe and healthy end product.
Maximizing Cannabis Growth with Proper Soil Nutrient Management
Once the soil nutrient levels have been assessed and optimized for cannabis growth, it’s important to maintain these levels to maximize plant growth and yield. This can be achieved through proper soil nutrient management, which involves monitoring and adjusting the nutrient levels as needed. With the right management practices in place, growers can ensure that their cannabis plants are receiving the nutrients they need to thrive and produce high-quality yields. Let’s explore the key factors that contribute to effective soil nutrient management for cannabis cultivation.
Monitoring Soil Nutrient Levels
To ensure optimal cannabis growth, it’s important to monitor soil nutrient levels on a regular basis. This involves using soil testing methods to assess the levels of key nutrients, including nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, magnesium, and sulfur. Keeping track of these levels can help identify any imbalances or deficiencies that may be hindering growth.
One way to monitor soil nutrient levels is through the use of a soil testing kit. These kits typically come with a set of instructions, which will guide users through the process of gathering soil samples and testing nutrient levels. Alternatively, soil samples can be sent to a professional testing lab for analysis.
Once the results are obtained, it’s important to interpret them correctly in order to determine the best course of action. This involves looking at the levels of each nutrient and assessing whether they fall within the optimal range for cannabis growth. If nutrient levels are too low, it may be necessary to amend the soil or use fertilizers to boost levels. Conversely, if the nutrient levels are too high, it may be necessary to reduce the amount of fertilizer being used.
Documenting soil nutrient levels is also an important part of monitoring. Keeping a log or spreadsheet of soil test results can help growers keep track of changes over time and make adjustments accordingly. This information can also be helpful in identifying patterns or trends that may be affecting growth.
Monitoring soil nutrient levels is an essential part of cannabis cultivation. By keeping tabs on key nutrients and making adjustments as needed, growers can ensure optimal growth and maximize yield.
Adjusting Soil Nutrient Levels as Needed
After assessing soil nutrient levels and finding imbalances, adjustments must be made to ensure proper nutrient availability for cannabis growth. This is done through targeted fertilization and amendments to soil.
Adjusting Nitrogen Levels:
If nitrogen levels are low, fertilizers with a higher nitrogen content can be added. Organic matter such as compost or manure can also be incorporated into the soil to increase nitrogen availability. On the other hand, if nitrogen levels are excessive, reducing the amount of nitrogen-rich fertilizers and increasing soil testing frequency can help prevent further negative impacts.
Adjusting Phosphorus Levels:
Low phosphorus levels can be addressed by using fertilizers with a higher phosphorus content, while high levels can be mitigated by reducing the amount of phosphate-based fertilizers used.
Adjusting Potassium Levels:
Potassium levels can be adjusted by using fertilizers with a higher potassium content or incorporating potassium-rich organic matter such as wood ash or banana peels into the soil. If potassium levels are excessive, reducing the amount of potassium-rich fertilizers can help prevent toxicity.
Adjusting Calcium and Magnesium Levels:
These nutrients can be adjusted by adding lime or gypsum to the soil, respectively. Care should be taken to not over-amend the soil, as excessive levels can lead to imbalances with other nutrients.
Adjusting Sulfur Levels:
Sulfur levels can be raised by using fertilizers that contain sulfur, such as gypsum, or by adding elemental sulfur to the soil.
It is important to note that changes to soil nutrient levels should be made gradually and regularly monitored to ensure proper growth and prevent potential negative impacts on the cannabis plants. Keeping a record of soil testing results and fertilization schedules can aid in making informed adjustments to soil nutrient levels.
Best Practices for Soil Nutrient Management
As a cannabis grower, ensuring that your soil is rich in essential nutrients is vital for healthy plant growth and maximum yield. However, not all soil is created equal, and some may require additional management practices for optimal nutrient content. In this section, we will discuss some of the best practices for soil nutrient management that can help you maximize the potential of your cannabis plants while minimizing the risk of contamination and nutrient deficiency. By following these recommendations, you can establish a solid foundation for your plants to thrive and produce high-quality buds.
Following Recommended Guidelines
When it comes to soil nutrient management for cannabis growth, it is crucial to follow recommended guidelines. These guidelines have been developed based on research and expert knowledge of the ideal nutrient levels for cannabis growth. Here are some key recommendations to keep in mind:
- Use reputable sources: Make sure the information you are using to guide your nutrient management practices comes from reputable sources such as academic research, government agriculture departments, and experienced cannabis cultivators.
- Don’t over-fertilize: It can be tempting to add more fertilizer than necessary in hopes of achieving faster growth or larger yields. However, over-fertilization can lead to nutrient imbalances, toxic build-up, and plant damage. Use fertilizers according to their recommended application rates and frequency.
- Prioritize balanced nutrient ratios: Cannabis plants require a balance of nutrients in order to grow properly. Don’t focus solely on adding more of one nutrient without considering its ratio to other nutrients. For example, excess nitrogen can lead to poor bud development if phosphorus and potassium levels are not also high enough.
- Consider the growing environment: The nutrient requirements of cannabis can vary depending on factors such as the growing medium, temperature, humidity, and lighting conditions. When following recommended guidelines, take into account the specific conditions of your growing environment.
- Be aware of changing needs: As cannabis plants go through different growth stages, their nutrient needs may change. Consult recommended guidelines regularly and adjust nutrient levels as needed throughout the growing process.
By following recommended guidelines for soil nutrient management in cannabis cultivation, you can ensure that your plants receive the right balance of nutrients for healthy growth and maximum yields.
Documenting Soil Nutrient Levels
One important aspect of soil nutrient management for cannabis growth is documenting the nutrient levels of your soil. This allows growers to track changes in soil nutrient levels over time and make informed decisions about how to adjust their nutrient management practices.
To document soil nutrient levels, growers should regularly test their soil using a reliable soil testing method. This can be done using soil test kits or by sending samples to a laboratory for analysis. The results of these tests should be recorded and compared over time to determine if the nutrient levels in the soil are stable, increasing, or decreasing.
In addition to documenting nutrient levels through soil testing, growers should also track any amendments made to the soil, such as adding organic matter or applying fertilizers. This information can be recorded in a soil nutrient management log, which provides an ongoing record of the nutrient levels and treatments applied to the soil.
By documenting soil nutrient levels and amendments, growers can identify trends in nutrient levels over time and make strategic decisions about how to optimize the nutrient content of their soil for optimal cannabis growth. This information can also be shared with other growers or experts for further analysis and guidance on soil nutrient management practices.
Conclusion
In conclusion, it is crucial to prioritize soil nutrient management to achieve optimal cannabis growth. Soil nutrients play a vital role in the plant’s physiological processes, and their absence or deficiency can lead to poor growth and low yield. Therefore, maintaining adequate levels of key soil nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, magnesium, and sulfur is essential for healthy cannabis growth.
Assessing soil nutrient levels regularly through soil testing methods is essential to identify any nutrient deficiencies or excesses. Interpreting soil test results accurately helps to optimize soil nutrient content, which can be achieved through amending the soil with organic matter and using fertilizers.
It is crucial to avoid soil contamination to prevent harmful substances from being absorbed by the plants. Monitoring soil nutrient levels throughout the growth cycle and making adjustments as needed is essential to maximize cannabis growth potential.
Following recommended guidelines for soil nutrient management and documenting soil nutrient levels are best practices to ensure consistent and successful cannabis growth. By prioritizing soil nutrient management, growers can increase yields, improve plant health, and produce higher quality cannabis products.
Overall, proper soil nutrient management can make a significant difference in cannabis growth and yield. By understanding the importance of soil nutrients and implementing best practices, growers can optimize their soil nutrient content, resulting in successful cannabis cultivation.
Frequently Asked Questions
What role do soil nutrients play in cannabis growth?
Soil nutrients are essential for cannabis growth as they provide the necessary elements required for plant growth, development, and reproduction.
What are the primary soil nutrients for cannabis growth?
The primary soil nutrients for cannabis growth are nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, magnesium, and sulfur.
How can I determine the nutrient levels in my soil?
Soil testing is the best way to determine the nutrient levels in your soil. There are several soil testing methods available, including laboratory analysis and soil test kits.
What should I do if my soil nutrient levels are too low?
If your soil nutrient levels are too low, you can amend your soil with organic matter or use fertilizers to boost nutrient levels. It’s important to avoid over-fertilization, as this can harm your plants.
What can I do to avoid soil contamination?
You can avoid soil contamination by using organic fertilizers, avoiding the use of synthetic pesticides and herbicides, and practicing proper waste disposal.
What is the recommended pH range for cannabis growth?
The recommended pH range for cannabis growth is between 6.0 and 7.0. A pH outside of this range can make it difficult for plants to absorb nutrients from the soil.
Why is nitrogen important for cannabis growth?
Nitrogen is important for cannabis growth as it is a key component of chlorophyll, which is responsible for photosynthesis. It also plays a vital role in the development of foliage and stems.
What can I do if my soil pH is too low?
If your soil pH is too low, you can raise it by adding lime or wood ash to your soil. It’s important to make small adjustments at a time and retest your soil to avoid over-correcting.
Why is calcium important for cannabis growth?
Calcium is important for cannabis growth as it plays a role in cell wall development, root growth, and nutrient uptake. It also helps to regulate pH levels in the soil.
How often should I monitor my soil nutrient levels?
It’s recommended to monitor your soil nutrient levels at least once a year. However, if you notice any issues with plant growth or appearance, it may be necessary to test more frequently.