The Environmental Impact of Organic vs Synthetic Nutrients in Cannabis Cultivation
The world of cannabis cultivation is constantly evolving, and one of the most crucial decisions that growers must make is the choice between organic and synthetic nutrients. While both options have their advantages and disadvantages, the environmental impact of cannabis cultivation cannot be ignored. It is important to weigh the benefits and drawbacks of each type of nutrient in terms of their impact on water and soil quality, effects on wildlife, and overall carbon footprint. By examining the environmental impact of organic and synthetic nutrients, growers can make informed decisions about their practices and contribute to a more sustainable future for the cannabis industry.
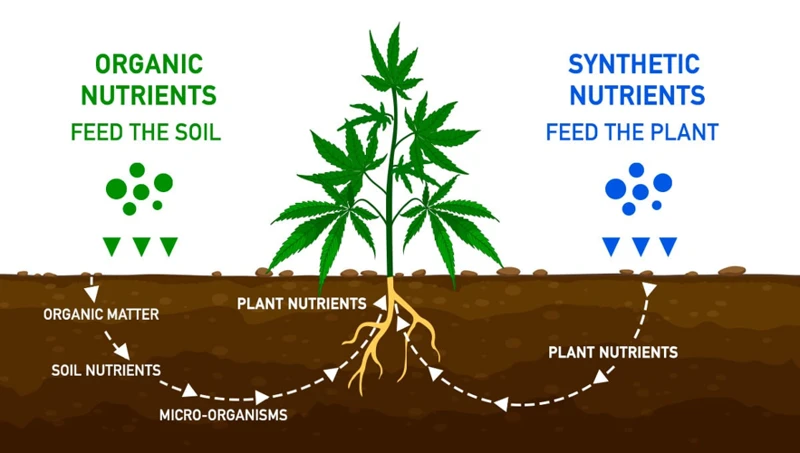
Organic Nutrients
Contents
When it comes to marijuana cultivation, the nutrients used can have a significant impact on the quality and potency of the final product. There are two main types of nutrients that growers can use in their operations: organic and synthetic. While both types of nutrients can help plants grow and thrive, there are distinct differences between the two. In this section, we will explore organic nutrients in greater detail, including their definition and the advantages and disadvantages of using them in cannabis cultivation.
Definition of Organic Nutrients
Organic nutrients for cannabis cultivation are derived from natural sources such as plant matter, animal waste, and other organic materials. These nutrients are composed of living organisms or contain carbon and other essential minerals. Some examples of organic nutrients include compost, bone meal, blood meal, fish emulsion, and humic acid.
Compost – Compost is a well-known organic fertilizer that is made up of decaying plant and animal matter. It is rich in nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium which are essential for healthy plant growth.
Bone meal – Bone meal is made up of finely ground animal bones that are high in phosphorus and calcium. It is commonly used to promote strong root growth and to prevent calcium and phosphorus deficiencies.
Blood meal – Blood meal is made from dried animal blood and is high in nitrogen, making it an excellent source of plant food for cannabis. However, it should be used sparingly as too much can burn the roots.
Fish emulsion – Fish emulsion is a liquid organic fertilizer made from fermented fish. It is a rich source of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, and also contains trace minerals that are essential for healthy plant growth.
Humic acid – Humic acid is a natural compound that is found in soil and is made up of decayed plant matter. It is known to improve soil structure and water retention, making it easier for plants to absorb nutrients.
Organic nutrients are often a preferred choice for many cannabis cultivators because they offer a more sustainable and natural approach to fertilizing, but they can also come with some disadvantages.
Advantages of Organic Nutrients
Organic nutrients are those that are derived from natural sources, such as animal or plant matter, and are typically gentler on the plant and the environment. Some of the advantages of organic nutrients include:
- Slow Release: Organic nutrients tend to be released slowly over time, providing a consistent source of nutrition for the plant. This slow release can also help to prevent nutrient burn – a condition in which the plant receives too much of a particular nutrient and is unable to absorb it all.
- Improved Nutrient Absorption: Organic nutrients are typically easier for the plant to absorb and utilize, as they are already in a form that is similar to what the plant would encounter in nature. This can help to ensure that the plant is able to take in all of the necessary nutrients it needs for healthy growth.
- Less Likely to Cause pH Imbalances: Because organic nutrients are derived from natural sources, they tend to have a pH that is closer to neutral than synthetic nutrients. This can help to prevent fluctuations in soil pH, which can negatively impact plant growth.
- Better for Soil Health: Organic nutrients can help to improve soil structure and fertility over time, as they are broken down by microorganisms in the soil. This can lead to healthier plants and a more sustainable growing environment in the long run.
- Reduced Risk of Chemical Buildup: Organic nutrients are less likely to build up in the soil over time, reducing the risk of chemical buildup that can occur with synthetic nutrients. This can help to prevent toxic conditions in the soil that can harm plants and wildlife.
The use of organic nutrients can help to promote a more sustainable and environmentally-friendly approach to cannabis cultivation, while also providing numerous benefits to the plants themselves.
Disadvantages of Organic Nutrients
Organic nutrients, while lauded for their natural origin and benefits, do have some disadvantages. Here are a few:
- Slow Release: Organic nutrients tend to break down and release their nutrients slowly over time, which means that the benefits may not be immediately apparent, and may take longer to reach optimal nutrient levels.
- Inconsistent Quality: Since organic nutrients are derived from natural sources, their composition can vary between batches, making it harder to predict and control nutrient levels.
- Expensive: Organic nutrients tend to be more expensive than synthetic nutrients, which can make it challenging for growers on a tight budget.
- Risk of Contamination: Since organic nutrients are derived from natural sources, there is a higher risk of contamination from bacteria, fungi or other pathogens than with synthetic nutrients, which can be manufactured under sterile conditions.
- Not Concentrated: Organic nutrients typically have a lower concentration of nutrients per volume than synthetic nutrients, which may require more frequent applications to achieve the desired nutrient levels.
Despite these disadvantages, many growers still prefer organic nutrients due to their sustainability and minimal environmental impact.
Synthetic Nutrients
When it comes to cultivating cannabis, synthetic nutrients have become increasingly popular due to their convenience and ability to produce high yields. These nutrients are created in a laboratory using a combination of chemicals to mimic the nutrients found in organic matter. While synthetic nutrients offer a range of benefits, they also come with their fair share of drawbacks that growers should consider before incorporating them into their cultivation practices. Let’s take a closer look at the definition, advantages, and disadvantages of using synthetic nutrients in cannabis cultivation.
Definition of Synthetic Nutrients
Synthetic nutrients are man-made chemical compounds created in a laboratory, often used in cannabis cultivation due to their predictable nutrient composition. These types of fertilizers are usually water-soluble and contain a blend of essential plant nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. In addition to these primary nutrients, synthetic fertilizers can be formulated with secondary nutrients such as calcium, magnesium, and sulfur, as well as micronutrients like iron, copper, and zinc.
Advantages of Synthetic Nutrients
Synthetic nutrients are highly efficient and can provide a precise balance of nutrients that are easily absorbed by the cannabis plant. They are also more affordable than organic nutrients due to the manufacturing process, which can result in lower production costs. Additionally, synthetic nutrients can be tailored to meet the specific needs of different strains of cannabis, allowing for maximum growth and yield.
Disadvantages of Synthetic Nutrients
One of the major disadvantages of synthetic nutrients is their potential to harm the environment. When these chemical compounds are overused or not properly regulated, they can contribute to the degradation of soil quality and water pollution. Synthetic nutrients are also known for their high salt content, which can lead to toxic buildups in the soil if not flushed out properly. Lastly, continued use of synthetic fertilizers can result in a depletion of soil nutrients and can make it more difficult to transition to organic methods later on.
To summarize, synthetic nutrients are man-made chemical compounds used in cannabis cultivation for their predictable nutrient composition. They offer precise and customizable nutrient options for optimal growth and yield, but can have negative impacts on soil and water quality if not used properly.
Advantages of Synthetic Nutrients
When it comes to the advantages of synthetic nutrients, there are various benefits that make them a popular choice for cannabis cultivation. Below is a table summarizing some of the key advantages:
| Advantages of Synthetic Nutrients |
|---|
| 1. Consistent Nutrient Levels: Synthetic nutrients are formulated to provide precise levels of key plant nutrients. This ensures consistent and predictable growth for cannabis plants, which can be essential to achieving desired yields. |
| 2. Longer Shelf Life: Unlike organic nutrients, synthetic nutrients can be stored for longer periods without losing potency. This means less waste and less frequent trips to the store. |
| 3. Fast-Acting: Synthetic nutrients are designed to be quick-acting and readily available to the plants. This means that they can have an immediate impact on growth and development, especially during critical stages. |
| 4. Controlled pH Levels: Synthetic nutrients are formulated to work within specific pH ranges. This allows growers to have more control over the pH levels of their nutrient solution, which can be important for cannabis plants as they are sensitive to pH fluctuations. |
| 5. Lower Risk of Contamination: Synthetic nutrients are typically free from contaminants, such as bacteria or fungi, which can be harmful to cannabis plants. This means less risk of crop failure due to disease. |
Synthetic nutrients offer a range of benefits for cannabis cultivation, including consistent nutrient levels, longer shelf life, fast-acting properties, controlled pH levels, and a lower risk of contamination. However, it is important to understand the potential downsides as well and weigh the pros and cons before choosing between organic and synthetic nutrients.
Disadvantages of Synthetic Nutrients
When it comes to synthetic nutrients, there are a number of potential disadvantages that should be taken into consideration:
- Potential for chemical buildup: One of the biggest issues with synthetic nutrients is that they can leave behind harmful chemical residues in the soil. Over time, these chemicals can build up and affect plant health and soil quality.
- Environmental impact: The production of synthetic nutrients typically involves a significant amount of energy, resources, and chemicals. This can have negative effects on the environment, including contributing to climate change and polluting water and air quality.
- Overuse can harm soil microbiome: Synthetic nutrients are often designed to provide plants with high doses of specific nutrients. However, this can disrupt the delicate balance of the soil microbiome, which can have long-term negative effects on soil health.
- Increased risk of nutrient burn: Synthetic nutrients can easily be over-applied, which can result in nutrient burn. This occurs when plants are given too much of a particular nutrient and can lead to yellowing leaves and stunted growth.
- High cost: Synthetic nutrients can be more expensive than organic alternatives, which can make them less accessible for small-scale growers.
While synthetic nutrients do offer a number of advantages in terms of precision and efficiency, their potential drawbacks should not be overlooked. It’s important for growers of all scales to carefully consider their options and select the nutrients that best fit their needs and priorities.
Environmental Impact Comparison
As the demand for cannabis cultivation continues to grow, so does the concern for its environmental impact. One major factor in this impact is the type of nutrients used during cultivation. Both organic and synthetic nutrients have their own unique advantages and disadvantages, but it’s important to consider their impact on the environment as well. In this section, we’ll compare the environmental impact of organic and synthetic nutrients in cannabis cultivation, focusing on water and soil quality, impact on wildlife, and carbon footprint.
Water Quality
Water quality is a crucial consideration in cannabis cultivation, and choosing the right nutrient source is one way to minimize negative impacts on water quality. When it comes to organic and synthetic nutrients, both can have an impact on water quality, but the degree and type of impact may differ.
Organic Nutrients:
- Organic nutrients can leach into water sources, leading to an increase in organic matter and nutrient levels. This can contribute to harmful algal blooms and reduced oxygen levels, which can negatively impact aquatic life.
- However, organic nutrients are generally less water-soluble than synthetic nutrients. This means they are more likely to remain in the soil, especially in soils with high cation exchange capacities.
- Organic cultivation techniques, such as composting and cover cropping, can help to improve soil structure and water infiltration rates. This can reduce runoff and erosion, which can improve water quality.
Synthetic Nutrients:
- Synthetic nutrients are highly water-soluble and can quickly enter water sources through runoff and leaching. This can lead to an increase in nutrient levels, which can cause algal blooms and other water quality issues.
- The use of synthetic nutrients can also contribute to nitrogen pollution. When synthetic nitrogen fertilizers are applied in excess, the excess nitrogen can leach into water sources, leading to hypoxia (low oxygen levels) and other negative impacts.
To minimize negative impacts on water quality, it is important to properly manage nutrient application rates, regardless of whether organic or synthetic nutrients are used. This can include regular soil testing to determine nutrient needs, as well as the use of erosion controls and other best management practices. Additionally, using organic cultivation techniques and minimizing the use of synthetic fertilizers can help to reduce negative impacts on water quality.
Soil Quality
Soil is one of the most important components of cannabis cultivation, as it provides the necessary nutrients for plant growth. Soil quality can be affected by the use of both organic and synthetic nutrients, but the extent of the impact varies.
Organic Nutrients
Organic nutrients are derived from natural sources, including compost, animal manure, and bone meal. These nutrients improve soil quality by promoting the growth of beneficial microorganisms and improving soil structure. Organic nutrients also release slowly over time, providing a consistent source of nutrition for plants.
However, the use of organic nutrients can also lead to soil erosion and nutrient leaching. This can occur when organic matter breaks down too quickly, causing the soil to become too loose and allowing nutrients to be washed away by rain or irrigation. It is important to use organic nutrients in moderation and take steps to prevent erosion, such as maintaining ground cover or using erosion control measures.
Synthetic Nutrients
Synthetic nutrients are created through chemical processes, and are often used in cannabis cultivation due to their convenience and consistency. These nutrients are designed to provide plants with specific amounts of essential nutrients, making it easier for growers to tailor their nutrient program to the needs of their plants.
However, the use of synthetic nutrients can lead to a decline in soil quality over time. Synthetic fertilizers can leach nutrients from the soil, leading to soil degradation and decreased soil fertility. Additionally, the overuse of synthetic nutrients can lead to soil acidification, making it more difficult for plants to access nutrients.
Soil Quality Comparison
To compare the impact of organic and synthetic nutrients on soil quality, we can look at a few key factors:
| Organic Nutrients | Synthetic Nutrients | |
|---|---|---|
| Nutrient Retention | Organic nutrients release slowly over time, providing a consistent source of nutrition for plants. This can help to improve soil quality by promoting the growth of beneficial microorganisms and improving soil structure. | Synthetic nutrients can leach nutrients from the soil, leading to soil degradation and decreased soil fertility over time. Additionally, the overuse of synthetic nutrients can lead to soil acidification, making it more difficult for plants to access nutrients. |
| Erosion Risk | Organic matter can break down quickly, causing soil to become too loose and leading to nutrient leaching. However, erosion can be prevented by maintaining ground cover or using erosion control measures. | Synthetic nutrients can contribute to nutrient pollution in waterways, which can harm aquatic ecosystems and lead to increased algae growth. However, synthetic fertilizers can also help to prevent erosion by promoting plant growth and stabilizing soil. |
| Overall Impact | The use of organic nutrients can help to improve soil quality by promoting the growth of beneficial microorganisms and improving soil structure. However, the risk of erosion and nutrient leaching must be managed carefully to prevent soil degradation. | The use of synthetic nutrients can provide a quick and convenient source of nutrition for plants, but can also lead to soil degradation and nutrient pollution over time. Soil acidification can also be a concern with the overuse of synthetic fertilizers. |
While both organic and synthetic nutrients have their advantages and disadvantages, it is important to consider their impact on soil quality when choosing a nutrient program for cannabis cultivation. By managing the risks of erosion and nutrient leaching, growers can help to ensure soil health and plant vitality for years to come.
Impact on Wildlife
The impact of organic and synthetic nutrients on wildlife in cannabis cultivation is a significant concern. Here are some ways in which each type of nutrient affects animals in the surrounding ecosystem:
Organic Nutrients:
- Organic nutrients are derived from natural sources and are generally considered safe for wildlife.
- However, the use of organic fertilizers can lead to the growth of harmful invasive plant species that disrupt the natural balance of the ecosystem. This can have a destructive impact on wildlife habitats.
- Additionally, organic fertilizers can increase the nitrogen content in soil, which can lead to algal blooms in nearby bodies of water. These blooms can deplete oxygen levels in the water, leading to fish kills and other negative impacts on aquatic life.
Synthetic Nutrients:
- Synthetic nutrients are often made from petroleum-based products and chemicals, which can have toxic effects on wildlife.
- The use of synthetic fertilizers can lead to the contamination of nearby bodies of water with chemicals that are harmful to aquatic life. This can also affect animals that drink from those bodies of water.
- The chemicals in synthetic fertilizers can remain in the soil for long periods of time, creating a toxic environment for plant and animal life.
Conclusion: Both organic and synthetic nutrients have potential negative impacts on wildlife in cannabis cultivation. It’s important for growers to be mindful of the potential environmental impacts of their nutrient choices and to take steps to minimize harm to wildlife habitats. This might include using organic fertilizers that are certified safe for use in environmentally sensitive areas, or implementing measures to prevent runoff and contamination of nearby bodies of water.
Carbon Footprint
When it comes to the environmental impact of cannabis cultivation, the carbon footprint is a crucial factor to consider. The carbon footprint refers to the amount of greenhouse gas emissions that are generated during the production and use of a product. In the case of cannabis cultivation, the use of synthetic fertilizers and pesticides can significantly contribute to the carbon footprint. On the other hand, organic cultivation methods are generally considered to have a lower carbon footprint since they rely on natural processes and ingredients.
To compare the carbon footprint of organic and synthetic nutrients in cannabis cultivation, let’s take a look at some key factors:
| Factors | Synthetic Nutrients | Organic Nutrients |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Requires significant energy and generates greenhouse gas emissions during the manufacturing process. | Uses natural ingredients and processes, resulting in lower greenhouse gas emissions during production. However, transportation of organic materials may generate emissions. |
| Application | May require energy-intensive equipment for application and generate emissions during use. | May require more labor-intensive application methods but generally does not generate significant emissions during use. |
| Disposal | May generate emissions during disposal of unused or expired synthetic fertilizers and pesticides. | Organic materials can be composted or recycled, resulting in minimal emissions during disposal. |
It is clear that the use of synthetic nutrients in cannabis cultivation can generate more significant greenhouse gas emissions than organic methods. However, it is worth noting that the transportation of organic materials can also contribute to emissions. It is essential to consider not only the type of nutrient but also the entire cultivation process’s environmental impact.
Conclusion
After considering the advantages and disadvantages of both organic and synthetic nutrients, as well as their respective impact on the environment, it is clear that there is no one-size-fits-all approach to cannabis cultivation.
Organic nutrients have numerous benefits, in that they are generally considered safer for human consumption and tend to promote healthier and more diverse soil microbiology, helping plants to develop stronger roots and resist disease. However, they may be less effective in delivering the precise nutrients that cannabis plants require and may result in lower yields.
Synthetic nutrients, on the other hand, can provide more precise and reliable nutrient profiles, leading to potentially higher yields. However, they can be more environmentally damaging and can lead to a buildup of salts in the soil that can harm plant health over time.
In terms of environmental impact, it is clear that organic nutrients have several significant advantages over synthetic counterparts. For one, they typically do not contain harmful chemicals or artificial additives, which can be harmful to aquatic life and other wildlife. Additionally, organic cultivation methods can help to support healthy soil and water systems, which can have a ripple effect on the wider ecosystem.
In conclusion, while both organic and synthetic nutrients have their advantages and drawbacks, the best approach to cannabis cultivation will depend on a number of factors, including the desired yield, the specific nutrient requirements of the strains being grown, and the specific environmental conditions of the grow site. By weighing these factors carefully and employing sustainable cultivation practices, it is possible to strike a balance between plant health, yields, and environmental responsibility in cannabis cultivation.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are some common examples of organic nutrients used in cannabis cultivation?
Common organic nutrients used in cannabis cultivation include blood meal, bone meal, guano, kelp meal, fish emulsion, and compost.
Can organic nutrients be harmful to the environment?
While organic nutrients are generally considered safer for the environment than synthetic nutrients, they can still harm the environment if overused or misused.
What are some common examples of synthetic nutrients used in cannabis cultivation?
Common synthetic nutrients used in cannabis cultivation include ammonium nitrate, potassium sulfate, and phosphoric acid.
Do synthetic nutrients have any advantages over organic nutrients?
Synthetic nutrients may have advantages over organic nutrients in terms of consistency and control over nutrient levels.
How do organic and synthetic nutrients impact water quality?
If not used properly, both organic and synthetic nutrients can leach into water sources and lead to pollution and harm to aquatic life.
What is the impact of nutrient runoff on soil quality?
Nutrient runoff can lead to soil compaction, nutrient loss, and reduced soil fertility, regardless of whether organic or synthetic nutrients are used.
Do organic nutrients have a lower carbon footprint than synthetic nutrients?
While organic nutrients are often considered more environmentally friendly, the carbon footprint of the production and transportation of organic nutrients can still be significant.
Can synthetic nutrients be used in organic cannabis cultivation?
No, synthetic nutrients cannot be used in organic cannabis cultivation, as one of the key principles of organic cultivation is the use of only natural and minimally processed inputs.
How do organic and synthetic nutrient use affect wildlife?
Excessive use of both organic and synthetic nutrients can have negative impacts on wildlife, such as harmful algal blooms and habitat destruction. However, organic methods are often considered more wildlife-friendly overall.
What is the best way to minimize the environmental impact of cannabis cultivation?
The most effective approach to minimizing the environmental impact of cannabis cultivation is to use sustainable, low-impact agricultural practices, whether using organic or synthetic nutrient inputs.