Organic vs Synthetic Nutrients for Cannabis: Which Is Better?
When it comes to growing cannabis, one of the most important factors for achieving a successful harvest is providing the plants with the right nutrients. But with so many options available, choosing between organic and synthetic nutrients can be a perplexing task for any grower. Each option has its own benefits and drawbacks, and it’s crucial to understand them in order to make an informed decision. In this article, we’ll take a closer look at both organic and synthetic nutrients, exploring their composition and pros and cons. Finally, we’ll compare the two options in terms of nutrient absorption, plant health and yield, flavor and smell, environmental impact, and cost to determine which is better for cultivating healthier and more potent cannabis plants.
What are Organic Nutrients?
Contents
When it comes to growing cannabis, one of the most popular debates is whether to use organic or synthetic nutrients. While both types of nutrients can provide your plants with the essential elements they need to grow, there are key differences between them. For those unfamiliar with organic nutrients, it may be unclear what they are, what they contain, and how they differ from synthetic nutrients. Let’s dive into the world of organic nutrients and explore their composition, advantages, and disadvantages.
Definition
When it comes to the definition of organic and synthetic nutrients, there are a few key differences to keep in mind. Below is a table that highlights these differences:
| Organic Nutrients | Synthetic Nutrients |
|---|---|
| Derived from naturally occurring sources, such as plant and animal waste. | Manufactured chemically, often derived from petroleum. |
| Contain a variety of micro and macronutrients in balance, creating a complex nutrient profile. | Tend to have a more simplified nutrient profile, typically consisting of only a few key nutrients. |
| Slow-release nutrients that feed the soil and provide long-term benefits. | Fast-release nutrients that provide instant plant uptake, but may lead to nutrient burn if overused. |
| Can promote soil health and microbial activity, benefiting the overall health of the cannabis plant. | May contain certain salts or compounds that can be harmful to the soil and environment if not used carefully. |
It’s important to note that not all organic or synthetic nutrients are created equal. There are a variety of options within each category, and it’s important for growers to do their research and choose high-quality nutrients that align with their growing methods and goals. Nonetheless, the above table illustrates some of the main differences between organic and synthetic nutrients in the context of cannabis cultivation.
Composition
When it comes to the composition of organic and synthetic nutrients, there are some significant differences.
Organic Nutrients
Organic nutrients for cannabis are made up of natural substances that are derived from living organisms or their by-products. These nutrients contain essential elements that are required for plant growth, such as nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K), as well as other micronutrients like calcium, magnesium and sulfur.
Some of the most commonly used organic nutrients for cannabis include:
| Nutrient | Source |
|---|---|
| Blood meal | Dried, powdered animal blood |
| Bone meal | Dried, powdered animal bones |
| Fish emulsion | Emulsified fish residue |
| Compost tea | Steeped compost |
The main advantage of organic nutrients is their complex composition, as they contain a wide range of trace elements and beneficial microorganisms that can improve soil quality and plant health. They also tend to be slow-release, meaning they provide nutrients to the plant over a longer period of time.
However, organic nutrients also have some drawbacks. They can be expensive and may require additional preparation time, such as brewing compost tea or mixing dry powders. They can also have an unpleasant odor, especially fish-based nutrients.
Synthetic Nutrients
Synthetic nutrients, on the other hand, are made from inorganic salts and minerals that are derived through a chemical process. They are also referred to as mineral or artificial nutrients. These nutrients are highly concentrated and can provide plants with a precise balance of essential elements.
Some commonly used synthetic nutrients include:
| Nutrient | Composition |
|---|---|
| Nitrogen | Ammonium nitrate, urea |
| Phosphorus | Monopotassium phosphate, diammonium phosphate |
| Potassium | Potassium nitrate, potassium sulfate |
One advantage of synthetic nutrients is their affordability and availability. They also tend to be more water-soluble than organic nutrients, which can make them easier to administer through hydroponic systems.
However, synthetic nutrients have been criticized for their negative impact on soil quality and the environment. They can lead to a buildup of salt and other chemicals in the soil, which can affect the soil structure and reduce its ability to retain water and nutrients. They also lack the diverse range of trace elements and microorganisms that are found in organic nutrients.
Pros and Cons
When it comes to using organic nutrients, there are a number of pros and cons to consider:
Pros:
- Organic nutrients come from natural sources, making them a more sustainable and eco-friendly option.
- They often contain a wider variety of micronutrients that can improve the overall health of your plants.
- Organic nutrients are often slower to release, which means they can provide a more gradual and sustained source of nutrients over time.
- Using organic nutrients can lead to better flavor and aroma in your cannabis.
- They can be less expensive in the long run, as you can create your own organic fertilizers at home using things like compost and worm castings.
Cons:
- Organic nutrients can be more difficult to measure and regulate, which can lead to inconsistencies in the quality of your plants.
- They can also be more expensive upfront, as purchasing organic fertilizers can be pricier than synthetic alternatives.
- Because the composition of organic fertilizers can vary depending on its source and manufacturing process, it can be difficult to know exactly what your plants are getting.
- Organic nutrients can also introduce unwanted microorganisms and pests into your growing environment if not properly composted or sterilized.
On the other hand, synthetic nutrients also have their pros and cons to consider:
Pros:
- Because synthetic nutrients are formulated in a laboratory, they are often more precise and consistent in their nutrient content.
- They can be easier to measure and adjust, giving you more control over your plants’ growth and development.
- Synthetic fertilizers are often less expensive upfront than organic alternatives.
- They can be used in hydroponic systems where organic nutrients would be impractical to use.
Cons:
- Synthetic nutrients are often derived from non-renewable sources, making them less sustainable and less environmentally friendly.
- They can leach salts into the soil, which can be harmful to your plants if not properly flushed out.
- Using synthetic nutrients can limit the micronutrients that your plants receive, which can lead to deficiencies and poor overall health.
- Cannabis grown using synthetic nutrients may have a less desirable taste and aroma due to the lack of natural micronutrients.
When deciding whether to use organic or synthetic nutrients for your cannabis, it’s important to weigh the pros and cons of each to determine which option is best for you and your growing environment.
What are Synthetic Nutrients?
When it comes to nutrients for cannabis, there is another option besides organic: synthetic nutrients. These are man-made compounds that contain the essential elements required for plant growth. Unlike organic nutrients, synthetic nutrients are chemically formulated, using a combination of mineral salts and other chemical compounds. While they have their benefits, there are also some concerns associated with their use. Let’s take a closer look at what makes synthetic nutrients different from the organic ones.
Definition
Organic nutrients refer to the nutrients that are derived from natural sources such as plant and animal matter. These nutrients contain living organisms such as bacteria, fungi, and other microorganisms that are beneficial for plant growth. The composition of organic nutrients can vary greatly depending on their source, but they are typically made up of organic matter, such as compost or manure, and sometimes minerals as well.
Pros of Organic Nutrients:
- Organic nutrients promote soil health and improve soil structure, which can lead to better water retention and drainage.
- They contain a variety of micronutrients that may not be present in synthetic nutrients.
- Organic nutrients can help to stimulate beneficial microorganisms, such as mycorrhizae, which can help plants better absorb nutrients.
- Organic nutrients are often more sustainable and environmentally friendly than synthetic nutrients, as they are made from renewable resources.
Cons of Organic Nutrients:
- They can be less predictable in terms of nutrient content, as compost and manure can vary greatly in their composition.
- Organic nutrients may be more difficult to dissolve and use in hydroponic systems.
- They can be more expensive than synthetic nutrients due to the costs of production and transport.
Organic nutrients are a viable option for those looking for a more natural and sustainable approach to growing cannabis. However, they may require more effort and expertise to use effectively, and may not always provide the same level of consistency as synthetic nutrients.
Composition
Organic nutrients are derived from natural sources such as manure, compost, and bone meal. They contain complex carbohydrates, proteins, and a variety of micronutrients essential for plant growth. Organic nutrients include:
- Compost: Compost is made by decomposing organic matter such as yard waste and food scraps. It is rich in nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, as well as other micronutrients.
- Blood Meal: Blood meal is a byproduct of the meat industry. It is high in nitrogen and is used as a quick-release fertilizer to support vegetative growth.
- Bone Meal: Bone meal is made from ground-up animal bones and is high in phosphorus. It helps support root development and blooming.
- Fish Emulsion: Fish emulsion is made from fish waste and is a good source of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. It is often used during the vegetative stage to support leafy growth.
- Kelp: Kelp is a type of seaweed that is high in potassium, which helps support fruiting and flowering.
On the other hand, synthetic nutrients are made from chemical sources and are designed to provide a precise combination of macronutrients and micronutrients. The composition of synthetic nutrients includes:
- Nitrogen: Synthetic nitrogen is often derived from ammonia and is easily absorbed by plants. It supports vegetative growth and helps make foliage greener.
- Phosphorus: Synthetic phosphorus is often derived from rock phosphate and is less expensive than organic sources. It helps support root development and blooming.
- Potassium: Synthetic potassium is often derived from potash and is easily absorbed by plants. It helps support fruiting and flowering.
- Micronutrients: Synthetic micronutrients are often added to fertilizers to ensure that plants receive all the necessary nutrients. These micronutrients include calcium, magnesium, copper, and iron, among others.
While synthetic nutrients can provide a precise balance of nutrients, they can also be overly concentrated and lead to nutrient burn if overused. Organic nutrients, on the other hand, release nutrients slowly over time and are less likely to cause nutrient burn or other problems.
Pros and Cons
When it comes to organic and synthetic nutrients, there are several pros and cons to consider for each. Let’s take a closer look at both:
| Organic Nutrients Pros | Organic Nutrients Cons |
|---|---|
| • Can improve soil quality and microbial activity • Releases nutrients slowly over time • May improve plant health and disease resistance over time |
• Can be more expensive • Nutrient content can be difficult to measure accurately • May have a distinct odor that may be unpleasant during application |
| Synthetic Nutrients Pros | Synthetic Nutrients Cons |
| • Nutrient content is consistent and easily measured • Generally less expensive than organic nutrients • Can be customized to specific plant needs |
• Can potentially harm soil quality and microbial activity over time • Often requires more frequent application • Can be harmful to the environment if used excessively |
Organic nutrients have the potential to improve soil health and the overall health of the plant, which can lead to better yields and disease resistance. However, the cost can be higher, and it may be more difficult to measure nutrient content accurately. There can also be a distinct odor during application.
Synthetic nutrients are generally less expensive and can be easily customized to meet specific plant needs. However, they can potentially harm the soil and the environment over time, and often require more frequent application.
Both organic and synthetic nutrients have their pros and cons, and the decision on which to use ultimately depends on individual preferences, budget, and growing goals.
Organic vs Synthetic Nutrients for Cannabis
As cannabis cultivation continues to gain mainstream popularity, growers are faced with a perplexing choice: whether to use organic or synthetic nutrients. While both types of nutrients can provide successful yields, there are distinct differences between them that can impact the overall health and quality of the plant. When considering factors like nutrient absorption, plant health and yield, flavor and smell, environmental impact, and cost, it’s important to carefully weigh the pros and cons of each option before making a decision. Let’s take a closer look at how organic and synthetic nutrients compare when it comes to growing cannabis.
Nutrient Absorption
One of the major differences between organic and synthetic nutrients for cannabis relates to nutrient absorption. Organic nutrients are derived from natural sources and therefore tend to have a slower rate of release than their synthetic counterparts. This means that plants may take longer to absorb organic nutrients and may not receive them in the same concentrations as synthetic nutrients, which can be easily adjusted.
However, because organic nutrients tend to release nutrients slowly over time, they can help prevent overfeeding and reduce the risk of nutrient burn. Synthetic nutrients, on the other hand, can be easily overused and can cause nutrient burn or other issues if not carefully controlled.
Another factor to consider when comparing organic and synthetic nutrients is the pH level of the growing medium. Organic nutrients tend to have a lower pH, which can make it easier for plants to absorb them. Synthetic nutrients may require more adjustments to the pH of the growing medium in order to ensure that plants can properly absorb them.
Ultimately, the rate of nutrient absorption will depend on a variety of factors, including the type and quality of the nutrients being used, the growing medium, and the specific needs of the individual cannabis plant.
Plant Health and Yield
The health and yield of cannabis plants can be greatly affected by the type of nutrients used. Both organic and synthetic nutrients have their advantages and disadvantages when it comes to plant health and yield.
Organic nutrients can have a slower release rate than synthetic nutrients, which means they may take longer to have an effect on plant growth. However, organic nutrients contain a wider range of micronutrients that are essential for plant health. These micronutrients are not found in synthetic nutrients and help to improve plant growth and development.
One of the main advantages of synthetic nutrients is that they can be formulated to provide a specific balance of nutrients for the plant’s needs. This means that plants can receive exactly what they need at each growth stage, which can lead to higher yields. However, synthetic nutrients can also be overused, which can lead to nutrient burn and other forms of nutrient toxicity.
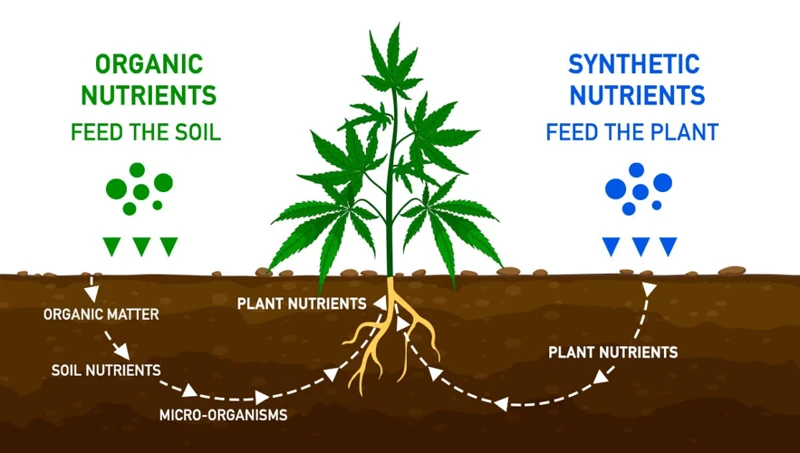
Organic nutrients provide a more balanced and slow-release source of nutrients that promote a healthy and vigorous growth of the cannabis plants. They do not create the high EC levels (Electrical Conductivity) that synthetic nutrients can cause, leading to an increased need for flushing. Organic nutrients feed the soil, as well as the plants, leading to healthier soil over time.
On the other hand, synthetic nutrients can cause excessive salt build-up in the soil, which can lead to poor plant health and reduced yields. They may also cause soil pH to become imbalanced, which can reduce nutrient uptake and cause other plant health issues.
Both organic and synthetic nutrients have pros and cons when it comes to plant health and yield. However, using organic nutrients can lead to a more balanced and sustainable source of nutrients for cannabis plants, promoting soil health and long-term plant health.
Flavor and Smell
When it comes to flavor and smell, organic and synthetic nutrients can have very different effects on cannabis.
Organic Nutrients:
- Many cannabis growers believe that organic nutrients result in a more complex and flavorful taste and aroma
- Organic nutrients contain a range of micronutrients that may not be present in synthetic nutrients, leading to a more diverse terpene profile
- Organic nutrients are often derived from natural sources, such as compost or worm castings, which can add unique flavors and aromas to the final product
- However, if organic nutrients are not used correctly, they can also introduce unwanted flavors and aromas, such as a strong earthy or compost-like smell
Synthetic Nutrients:
- Synthetic nutrients are often highly concentrated and provide a precise balance of nutrients, which can lead to a uniform and consistent flavor and aroma
- The absence of impurities in synthetic nutrients can prevent unwanted flavors or aromas from being introduced to the plants
- However, some growers believe that synthetic nutrients can result in a less complex and less flavorful end product
- Synthetic nutrients can also potentially leave behind residue or chemical flavors in the finished cannabis
Ultimately, the effect of organic vs synthetic nutrients on flavor and aroma can vary depending on the specific nutrient mix used and the growing conditions. Some growers may prefer the complex and unique flavors of organic nutrients, while others may prefer the consistency and uniformity of synthetic nutrients.
Environmental Impact
Both organic and synthetic nutrients have an impact on the environment. However, the extent of their impact differs significantly.
Organic Nutrients: These nutrients are derived from natural sources such as animal waste, compost, and bone meal. Organic nutrients tend to have a lower environmental impact compared to synthetic nutrients. This is because they are renewable, biodegradable, and they release fewer pollutants into the environment. However, obtaining these nutrients may require land use for animal rearing and transportation, which contributes to greenhouse gas emissions.
Synthetic Nutrients: These nutrients are derived from artificial sources and may contain chemical compounds such as nitrates and heavy metals. They tend to have a higher environmental impact than organic nutrients because their production requires significant amounts of energy and they release pollutants into the environment during their production and use. Additionally, the accumulation of synthetic nutrients in soil, water, and other ecosystems can be harmful to aquatic life and can contribute to the formation of harmful algal blooms.
To highlight the environmental impact of organic versus synthetic nutrients, we have summarized the main points in the table below:
| Organic Nutrients | Synthetic Nutrients | |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Natural sources | Artificial sources |
| Renewability | Yes | No |
| Biodegradability | Yes | No |
| Production impact | Requires land use and transportation | Requires significant amounts of energy and releases pollutants |
| Environmental impact | Lower | Higher |
| Accumulation in soil/water | Less harmful | Can be harmful to aquatic life and contribute to harmful algal blooms |
While both organic and synthetic nutrients have an impact on the environment, the use of organic nutrients tends to have a lower environmental impact. This is because they are renewable, biodegradable, and release fewer pollutants into the environment. However, the production and transportation of organic nutrients may still contribute to greenhouse gas emissions. It is important to consider the environmental impact when choosing between organic and synthetic nutrients for cannabis cultivation.
Cost
When it comes to cost, the choice between organic and synthetic nutrients for cannabis can vary depending on a few factors.
Here are some considerations for cost:
- Upfront costs: Organic nutrients tend to have higher upfront costs compared to synthetic nutrients. This is because they are often made from natural sources and require more processing before they can be sold. Synthetic nutrients, on the other hand, are easier and cheaper to produce and can be sold at a lower cost.
- Long-term costs: While organic nutrients may have higher upfront costs, they can actually be more cost-effective in the long run. This is because they tend to have a slower release, meaning that they provide nutrients to the plant over a longer period of time. Synthetic nutrients, while cheaper upfront, may need to be used more frequently and in higher quantities, which can lead to more frequent purchases and higher long-term costs.
- Yield: The yield of the cannabis plant can also affect the cost. While organic nutrients may have higher upfront costs, they may also lead to higher yields and a better quality product. Synthetic nutrients may lead to lower yields, which can ultimately affect the cost per gram of cannabis produced.
It’s important to consider both the upfront and long-term costs, as well as the potential yield, when deciding between organic and synthetic nutrients for cannabis. Ultimately, the choice will depend on the individual needs and preferences of the grower.
Conclusion
After exploring the differences between organic and synthetic nutrients for cannabis, it’s clear that each has its own unique set of advantages and disadvantages for growers to consider.
On the one hand, organic nutrients offer a natural way to nourish cannabis plants, using materials such as bone meal, fish meal, and kelp. These nutrients tend to be slower-acting, but they can provide a range of micronutrients and improve soil health over time. Additionally, organic nutrients are often more sustainable than synthetic options, making them an appealing choice for environmentally-conscious growers.
On the other hand, synthetic nutrients are formulated in a lab and can be more precisely tailored to suit a grower’s specific needs. They work quickly and can produce impressive yields, but often come with a higher price tag. There are also concerns about the environmental impact of synthetic fertilizers, which can contribute to water pollution and other issues.
When it comes down to it, the choice between organic and synthetic nutrients for cannabis will depend on a grower’s individual priorities and resources. It’s important to weigh the pros and cons of each option carefully, and to experiment with different nutrients to see what works best for your plants. No matter what you choose, it’s essential to take a thoughtful and responsible approach to cannabis cultivation, prioritizing the health of your plants and the environment alike.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the benefits of using organic nutrients for cannabis cultivation?
Organic nutrients provide a more balanced diet for the plant, can improve soil health, and offer a more natural taste and smell to the final product.
Can synthetic nutrients be as effective as organic nutrients?
Synthetic nutrients can provide a quick and efficient source of nutrients, but they don’t have the same diversity of micronutrients and can lead to salt buildup in the soil.
Can organic nutrients be harmful to the environment?
No, organic nutrients are produced from natural sources, and their use generally has a positive impact on the environment. Fertilizers made with chemicals or fossil fuels, on the other hand, can have negative effects on the environment.
Are organic nutrients more expensive than synthetic nutrients?
Organic nutrients may be more expensive initially, but they can improve soil health and result in higher yields over time, making them more cost-effective in the long run.
Can synthetic nutrients be harmful to the plant?
Overuse of synthetic nutrients can lead to a buildup of salts in the soil, which can be harmful to the plant.
What are some examples of organic nutrients?
Bone meal, fish emulsion, compost, and worm castings are all examples of organic nutrients.
What are some examples of synthetic nutrients?
Miracle-Gro, General Hydroponics, and Fox Farm are examples of synthetic nutrients.
Do organic nutrients have a different taste than synthetic nutrients?
Yes, organic nutrients can result in a more natural and nuanced taste and smell than synthetic nutrients.
Do synthetic nutrients require more maintenance than organic nutrients?
Synthetic nutrients require more frequent flushing to avoid salt buildup in the soil, while organic nutrients are more forgiving in this regard.
Is it possible to use a combination of organic and synthetic nutrients?
Yes, it is possible to use a combination of organic and synthetic nutrients, which can provide the benefits of both approaches.