Why Proper Sanitation is Critical for Integrated Pest Management in Cannabis Grow Rooms
The Basics of Integrated Pest Management
Contents
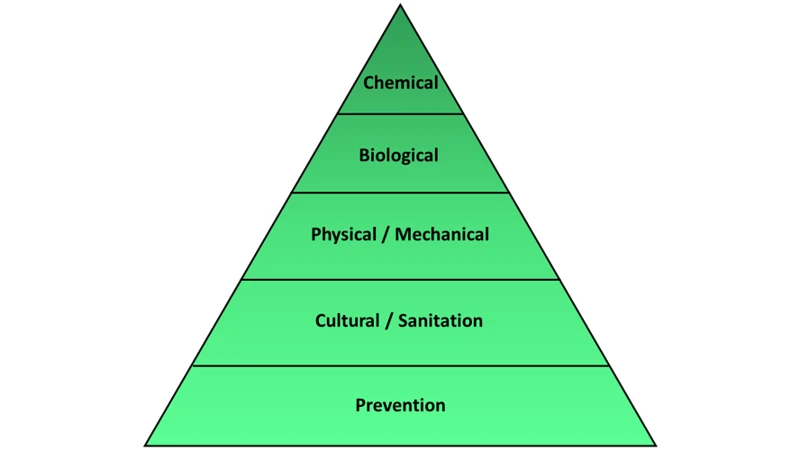
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is a proactive approach to pest control that aims to prevent pest infestations rather than dealing with them after the damage has been done. It’s a comprehensive strategy that combines different pest control methods, including biological controls, cultural controls, physical controls, and chemical controls, to manage pest populations effectively. In this section, we’ll delve deeper into the basics of IPM for cannabis cultivation, exploring why it’s essential and how it works.
What is Integrated Pest Management (IPM)?
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is a __sustainable__ approach to managing pests that combines multiple strategies to __prevent__ and __control__ infestations.
The key elements of IPM include:
- Monitoring and identifying pests and their life cycles
- Setting __action thresholds__ to determine when control measures are necessary
- Using a combination of __cultural__, __biological__, and __chemical__ control measures
- Regularly __evaluating__ the effectiveness of the IPM program and making necessary adjustments
Rather than relying solely on pesticides, IPM focuses on __preventing__ pest problems through sanitation, cultural practices, and environmental management. When control measures are necessary, they are chosen based on their __effectiveness__, __target specificity__, and __environmental impact__.
IPM is a __holistic__ approach to pest management that seeks to reduce the use of pesticides and __minimize__ their impact on the environment and human health.
Why is IPM Essential in Cannabis Cultivation?
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is a crucial component of cultivating high-quality cannabis. IPM involves using a combination of different strategies to manage pests and diseases in a way that is both environmentally and economically sustainable. Here are some reasons why it is essential to incorporate IPM into your cannabis cultivation practices:
- Efficiency: IPM is a proactive approach to pest management that helps identify and address pest problems early on, reducing the need for reactive treatments that can be costly and time-consuming.
- Cost-Effective: Programs that integrate multiple pest control methods can be more cost-effective than using only one method, especially in the long-term. It can also help minimize crop damage and yield loss.
- Pesticide Reduction: IPM can help reduce the use of pesticides, which can lead to environmental contamination and safety concerns. By using strategies such as crop rotation, biological controls, and sanitation, growers can significantly reduce the need for harsh chemicals.
- Quality Control: By taking a holistic approach to pest management, cannabis growers can ensure the safety and quality of their product, which is essential to creating a successful and reputable business.
- Eco-Friendly: IPM methods are often less harmful to the environment than traditional pesticide treatments, making it a sustainable option for growers who want to minimize their environmental footprint. By using biological controls such as predatory insects, beneficial nematodes, and microbials, growers can create a healthy and balanced ecosystem in their grow room or garden.
Integrated Pest Management is an essential practice for cannabis growers who want to grow high-quality crops while minimizing their environmental impact and maintaining a profitable business. By combining various methods of pest control, including sanitation, growers can create a healthy and sustainable growing environment that produces bountiful, healthy harvests.
The Role of Sanitation in IPM for Cannabis
When it comes to integrated pest management (IPM) in cannabis cultivation, proper sanitation practices are crucial. Without effective sanitation measures, pests and diseases can easily spread and wreak havoc on your plants, leading to significant crop losses. That’s why it’s important to understand the role that sanitation plays in IPM and ensure that you’re implementing the best practices to keep your grow room clean and free from potential threats. In this section, we’ll delve deeper into what sanitation means in the context of IPM, why it’s important, and how to practice proper sanitation in your cannabis grow room.
What is Sanitation in IPM?
Sanitation in integrated pest management (IPM) for cannabis refers to the practice of maintaining a clean and sterile environment to prevent the proliferation of pests and diseases.
Sanitation involves a combination of physical cleaning, sterilization, and waste management techniques that aim to reduce the primary conditions that pests thrive in, such as moisture, food sources, and shelter.
In simpler terms, sanitation is all about keeping your grow room clean and tidy to reduce the risk of pest and disease outbreaks.
Some common sanitation practices include:
- Cleaning regularly: This involves sweeping, dusting, and wiping down surfaces to remove any debris or organic matter that can attract pests. Regular cleaning can also help you identify any signs of pest activity and take action before they get out of hand.
- Starting with a sterile environment: Before you start cultivating, make sure to thoroughly clean and disinfect your grow room and equipment. This will help prevent the introduction of unwanted pests and pathogens.
- Managing plant waste: Properly disposing of plant debris, dead leaves, and other waste can help prevent the buildup of moisture and organic matter, which attract pests. Use sealable bags or bins and dispose of waste outside your grow room.
- Using proper techniques for handling and discarding soil: Soil can harbor pests and diseases, so it’s crucial to use sterile soil mixes and avoid reusing old soil. When discarding soil, seal it in a bag and dispose of it outside your grow room.
- Avoiding cross-contamination: Sanitation also involves preventing the spread of pests and diseases from one plant to another. Use separate tools for each plant, and if you need to handle multiple plants, wash your hands thoroughly in between.
- Quarantining new plants: New plants can introduce pests and diseases into your grow room. Quarantine new plants for several days to monitor them for any signs of infestation before moving them to your main grow area.
- Using protective gear: Wearing gloves, masks, and other protective gear can prevent the spread of pests and diseases and protect you from any chemicals you may use in your sanitation process.
By implementing these sanitation practices in your cannabis cultivation, you can significantly reduce the risk of pest and disease outbreaks and maintain a healthy and productive grow room.
Why is Sanitation Important in Cannabis Growing?
Maintaining proper sanitation practices in your cannabis grow room is crucial for successful integrated pest management (IPM). Here are some reasons why sanitation is so important in cannabis cultivation:
- Prevention of pest infestations: A clean grow room with no excess plant material or standing water can discourage pests from taking up residence in your cannabis crop.
- Prevention of diseases: Plant matter left in the grow room can lead to the growth of harmful microorganisms that could infect your cannabis plants.
- Elimination of breeding grounds: Clean growing spaces reduce the risk of creating a breeding ground for pests and diseases by removing their habitat.
- Maintaining plant health: When plants are grown in dirty and unhygienic conditions, they may not grow as healthy as they should. Sanitation practices like cleaning and sterilizing containers and tools can help promote plant growth and vigor.
In a cannabis grow room, it is essential to prevent the spread of pests and diseases from one plant to another. Sanitation practices like regular cleaning, managing plant waste, and avoiding cross-contamination can help control the growth of pests and diseases. By following these guidelines, you can keep your cannabis plants healthy and happy throughout their growth cycle.
How to Practice Proper Sanitation in Your Grow Room
When it comes to managing pests in your cannabis grow room, sanitation plays a crucial role. Proper sanitation involves keeping your grow room clean and free of debris, as well as using the right techniques for handling and discarding soil and plant waste. By following these practices, you can greatly reduce the chances of pests invading your space and damaging your crops. In this section, we will explore the steps you can take to practice proper sanitation in your cannabis grow room.
Clean Regularly
Regular cleaning is an essential part of maintaining a sanitary environment in your cannabis grow room. Here are some steps to follow:
1. Clear the Room
Before you start cleaning, remove all plants, equipment, and debris from the grow room. This will make it easier for you to clean every nook and cranny.
2. Sweep or Vacuum the Floor
Start by sweeping or vacuuming the floor to remove any dirt, dust, and debris. It’s crucial to clean the floor thoroughly as pests can hide under debris.
3. Scrub Surfaces with Soap and Water
Using a mixture of warm water and soap, clean all surfaces, including walls, floors, and equipment. Pay close attention to areas that are often overlooked, such as corners, crevices, and hard-to-reach spots.
4. Disinfect Surfaces
After cleaning, spray disinfectant on all surfaces to kill microbes and prevent the growth of harmful bacteria. Be sure to follow the instructions on the label to ensure proper use.
5. Clean Growing Containers and Tools
Growing containers and tools can harbor pests and pathogens, so it’s essential to clean them thoroughly. Scrub pots, trays, and tools with soap and water, and disinfect them before reusing them.
6. Dispose of Plant Debris Properly
Dispose of all plant debris properly to prevent the spread of diseases and pests. Seal it in a plastic bag and dispose of it off-site or in a compost bin.
By following these cleaning steps regularly, you can prevent the buildup of pests and diseases in your grow room, creating a healthy and productive environment for your cannabis plants.
Start with a Sterile Environment
To practice proper sanitation in your grow room, it is important to start with a sterile environment. This means ensuring that all surfaces, tools, and equipment are free from any harmful microorganisms that could lead to pest infestations or plant diseases. Here are some tips on how to create a sterile environment:
1. Clean surfaces and tools with disinfectants: Before starting your cannabis cultivation, make sure to clean all surfaces and tools with a disinfectant solution to kill any harmful microorganisms. Use a disinfectant that is designed for cannabis cultivation and follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully.
2. Use sterilized soil: Start with sterilized soil to limit the risk of harmful microorganisms. You can sterilize soil at home by using an oven or pressure cooker. Alternatively, you can also purchase sterilized soil from a reputable supplier.
3. Wear gloves: Wear gloves when handling soil or plants to avoid transferring microorganisms from your hands to the plants. Make sure to change gloves regularly or between different tasks.
4. Use a separate set of tools for each stage of cultivation: Use a separate set of tools for each stage of your cultivation to avoid cross-contamination. Make sure to clean and sterilize your tools between uses.
5. Avoid overcrowding: Overcrowding your grow room can lead to increased humidity levels and a higher risk of pest infestations and plant diseases. Make sure to space your plants out properly and avoid overcrowding.
By starting with a sterile environment, you can limit the risk of harmful microorganisms and pests in your grow room. This will help ensure the health and productivity of your cannabis plants.
Manage Plant Waste
Proper management of plant waste is crucial in maintaining a clean and healthy environment for your cannabis plants. This is because plant waste can attract pests and serve as a breeding ground for harmful pathogens. Additionally, leaving plant waste lying around can create a messy and unsanitary growing space.
To effectively manage plant waste, follow these tips:
- Remove Dead Leaves and Stems: Dead plant material should be removed regularly to reduce the likelihood of pests and diseases taking hold. Use sterilized scissors or pruning shears to trim off dead leaves and stems and dispose of them in a sealed container outside of the growing area.
- Collect Fallen Leaves and Debris: Any leaves or debris that falls onto the ground should be collected and removed from the area. Make sure to use a clean dustpan or broom and dispose of the waste in a sealed container.
- Store Pruned Material Correctly: When pruning your cannabis plants, make sure to store any pruned material in a sealed container away from your growing area. This will prevent pests from accessing the material and potentially infesting your plants.
- Compost Plant Waste Carefully: Composting can be a great way to dispose of plant waste while also improving soil health, but it should be done carefully to avoid introducing pests or pathogens. Use a proper compost bin and make sure to follow guidelines for temperature and moisture levels.
- Dispose of Plant Waste Properly: If you are not composting your plant waste, make sure to dispose of it properly. Seal it in a plastic bag and dispose of it in a covered trash bin. Avoid leaving plant waste lying around where it can attract pests.
By following these tips for managing plant waste, you can help keep your grow room clean and free from pests and diseases.
Use Proper Techniques for Handling and Discarding Soil
When it comes to sanitation in integrated pest management for cannabis cultivation, proper handling and discarding of soil is crucial. This process involves using appropriate techniques to avoid cross-contamination, as well as disposing of the soil in the correct manner to prevent the spread of pests and diseases.
One of the most important aspects of handling soil is using protective gear to avoid contamination from pathogens and pests. Gloves, masks, and coveralls should be worn when handling soil, and they should be changed regularly to avoid spreading any contaminants.
Once the soil has been removed from the growing area, it’s important to manage the waste properly. This means disposing of it in a way that prevents contamination of other areas and minimizes the risk of spreading pests and diseases. One option is to use a composting system that is specifically designed for cannabis waste.
It’s also important to avoid cross-contamination by using separate tools and equipment for each batch of soil. For example, a separate shovel and bucket should be used for each batch, and they should be cleaned and disinfected before using them again.
Another important technique is quarantining new plants. When new plants are introduced to the growing area, they should be isolated and monitored for signs of pests or diseases before being added to the main crop. This helps to prevent the introduction of contaminates into the entire growing area.
Using proper techniques for handling and discarding soil can help minimize the risk of pests and diseases in a cannabis cultivation operation. By following these best practices, growers can avoid cross-contamination, manage waste responsibly, and create a sterile environment for their plants to thrive in.
| Techniques for Handling and Discarding Soil |
|——————————————–|
| – Use protective gear to avoid contamination |
| – Manage soil waste properly |
| – Avoid cross-contamination by using separate tools and equipment |
| – Quarantine new plants and monitor for pests and diseases |
| – Dispose of soil waste in a responsible manner |
Avoid Cross-Contamination
It is important to avoid cross-contamination in order to maintain a clean and healthy environment for your cannabis plants. Cross-contamination occurs when you transfer pathogens or pests from one area to another. This can happen through contact with contaminated tools, equipment, clothing, or surfaces. To avoid cross-contamination, consider the following measures:
- Designate tools and equipment for specific tasks: Use different tools and equipment for different tasks to prevent the transfer of pests and pathogens. For example, use one pair of scissors for pruning and another pair for harvesting.
- Wash your hands: Proper hand hygiene is essential in preventing the spread of pests and pathogens. Wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water or use hand sanitizer before entering your grow room.
- Wear clean clothing: Change into clean clothing, such as a jumpsuit or lab coat, before entering your grow room. Avoid wearing the same clothes outside of your grow room to prevent the transfer of pests and pathogens.
- Clean and disinfect: Clean and disinfect all tools, equipment, and surfaces before and after use. Use a disinfectant solution to kill any lingering pathogens or pests.
- Control air flow: Make sure your grow room has proper ventilation and air filtration systems to prevent the spread of pests and pathogens through the air.
By taking these steps to avoid cross-contamination, you can help maintain a healthy and pest-free environment for your cannabis plants. Remember to always prioritize sanitation as a crucial part of your integrated pest management plan.
Quarantine New Plants
When introducing new plants to your grow room, it is important to quarantine them before allowing them to mingle with your other plants. This process helps to prevent the introduction of pests and diseases into your grow room.
Here are some steps to follow:
- Designate an area in your grow room for new plants to be quarantined. This area should be separate from your other plants and should have limited contact with other items in the grow room.
- Inspect the new plants for any signs of pests or diseases before bringing them into the designated quarantine area. Look for yellowing leaves, discoloration or deformities, as well as any pests such as spider mites or aphids.
- Keep the new plants in quarantine for at least 1-2 weeks to allow any pests or diseases to reveal themselves. During this time, closely monitor the plants for any signs of problems.
- While in quarantine, treat the new plants with preventative measures such as beneficial insects or organic pest control sprays to ensure any potential pests are eliminated.
- After the quarantine period has ended and the new plants have been deemed healthy, they can be introduced to the rest of your plants in the grow room.
By properly quarantining new plants before mixing them with your existing plants, you can take a proactive approach to preventing the spread of pests and diseases in your grow room. This simple step can greatly reduce the risk of an infestation and ultimately lead to a healthier crop.
Use Protective Gear
When practicing proper sanitation in your cannabis grow room or facility, it is important to use protective gear to minimize the risk of introducing pests or diseases. Protecting yourself from exposure to pesticides and other chemicals is also essential. Here are some examples of the protective gear you should consider using:
| Protective Gear | Description |
|---|---|
| Gloves | Wearing gloves can help prevent the transfer of pests and diseases to your plants. They can also protect your hands from exposure to harsh chemicals and fertilizers. |
| Masks | A mask can prevent you from inhaling harmful chemicals, dust, or spores that can cause respiratory irritation or other health problems. Choose a mask that is designed for the chemicals you’re working with and replace it regularly to ensure maximum protection. |
| Goggles | Goggles can protect your eyes from exposure to pesticides, fertilizers, and other chemicals. Make sure they fit properly and are designed for the specific hazards you’re working with. |
| Aprons or Coveralls | Wearing an apron or coveralls can protect your skin and clothing from exposure to pesticides, fertilizers, and other chemicals. Make sure they are made of materials that are resistant to the chemicals you’re working with and launder them frequently to minimize any cross-contamination. |
| Shoe Covers or Boots | Wearing shoe covers or boots can prevent the transfer of pests or diseases from your shoes to your plants. Choose a pair that is easy to clean and disinfect and make sure to change them before entering a new area. |
Remember, using protective gear is an essential part of practicing proper sanitation in your cannabis cultivation facility. Not only does it help protect your plants from pests and diseases, it also protects you from exposure to harmful chemicals and other hazards. Make sure to choose the appropriate gear for the specific tasks you’re performing and replace them as needed to ensure maximum protection.
Other Best Practices for IPM in Cannabis Cultivation
As an experienced cannabis grower or cultivator, you understand that pest management is an essential part of the process. Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is a well-known approach to controlling pests in cannabis cultivation, and proper sanitation is a crucial aspect of this method. However, there are other best practices that can also contribute to an effective IPM system. So, let’s explore some of these additional methods and techniques for managing pests in your cannabis crops. By implementing these strategies, you can ensure healthy plants, high yields, and a successful harvest.
Choose Resistant Varieties
One of the best practices for Integrated Pest Management (IPM) in cannabis cultivation is to choose resistant varieties. This means selecting strains that have natural resistance or tolerance to certain pests or diseases.
Advantages of Choosing Resistant Varieties
When you choose resistant varieties, you can reduce the risk of pest and disease outbreaks in your cannabis garden. This is because resistant plants can withstand attacks from specific pests or diseases without suffering significant damage. Resistant varieties require less pesticide use, which in turn can reduce the risk of pesticide residue on your cannabis flowers.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Resistant Varieties
When selecting resistant varieties, there are several factors to consider. First, you need to know which pests and diseases are prevalent in your area. This will help you choose a strain that is specifically resistant to those threats. Second, you should consider the growing conditions in your garden, such as temperature, humidity, and soil type. Some strains may be more susceptible to certain pests or diseases in certain growing conditions. Finally, you should also consider the potency and other desirable characteristics of the strain, as pest resistance alone may not be enough to meet your needs.
List of Resistant Varieties
Here are some examples of cannabis strains that are known for their resistance to certain pests and diseases:
- Blueberry – resistant to powdery mildew
- Californian Orange – resistant to spider mites
- OG Kush – resistant to pests and diseases in general
- Afghan Kush – resistant to pests and diseases in general
- White Rhino – resistant to spider mites
Note: It’s important to remember that resistance does not mean immunity. Even resistant varieties can still fall prey to pests or diseases if the conditions are right. Regular monitoring and preventative measures, such as sanitation and biological controls, are still necessary to maintain a healthy garden.
Monitor Your Plants Regularly
Regular monitoring of your cannabis plants is crucial for effective integrated pest management. This involves inspecting your plants for signs of infestation or disease on a regular basis. Here are some tips for monitoring your plants effectively:
- Check every part of the plant: When you’re inspecting your plants, be sure to look at every part of the plant, including the leaves, stems, and buds. Pests and diseases can hide in small crevices or under leaves, so a thorough inspection is important.
- Look for signs of pests: Keep an eye out for signs of pests such as webs, holes in leaves, or discoloration. You may also see the pests themselves, such as spider mites or aphids.
- Watch for signs of disease: Diseases can cause discoloration or spots on leaves, and can also cause wilting or stunted growth. If you notice any abnormal growth patterns in your plants, you may want to investigate further to see if disease is the cause.
- Keep track of your observations: It’s a good idea to keep a record of your observations, so you can track changes over time. You can use a notebook or a spreadsheet to record things like the date, the plant affected, and the type of pest or disease you observed.
- Act quickly: If you do notice an infestation or disease, it’s important to act quickly to prevent it from spreading to other plants. Depending on the severity of the problem, you may need to remove affected plants or treat them with pesticides or other treatments.
By monitoring your plants regularly, you can catch pests and diseases early, before they have a chance to cause serious damage to your plants. This can help you to protect your crop and maintain a healthy, vibrant garden.
Use Biological Controls When Possible
In addition to practicing proper sanitation measures, using biological controls can be an effective way to manage pests in cannabis cultivation. Biological controls involve the use of natural predators or parasites to keep pest populations under control, and they can be a valuable tool in an integrated pest management program.
Here are some examples of biological controls that can be used in cannabis cultivation:
- Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt): This naturally occurring bacterium produces toxins that are deadly to many types of pests, such as caterpillars and mosquitoes. Bt can be applied as a spray or dust to target areas where pests are present. It is safe to use and does not harm beneficial insects or humans.
- Predatory mites: These tiny insects feed on other mites, such as spider mites, that can damage cannabis plants. They are often used in greenhouses and indoor grows to control mite populations. Predatory mites are not harmful to humans or plants and can be purchased from biological control companies.
- Ladybugs: These colorful beetles are voracious eaters of aphids and other soft-bodied insect pests. They can be released into the growing area to control pest populations. Ladybugs can be purchased from biological control companies or collected from nature.
- Nematodes: These microscopic worms are natural parasites that feed on the larvae of many insect pests, such as fungus gnats and thrips. They can be applied to the soil or growing medium and are safe for plants and humans.
- Beneficial fungi: Certain types of fungi, such as Trichoderma and Beauveria, can be used to control pest populations. These fungi either kill pests directly or make them less able to eat or reproduce. They can be applied as a spray or in the growing medium and are safe for plants and humans.
Using biological controls can offer several advantages:
- They are generally safe to use and do not harm beneficial insects, plants, or humans.
- They are often more targeted in their pest control, meaning they only affect the pests they are intended to control, rather than a broad spectrum of insects.
- They can be more environmentally friendly than traditional pesticide applications.
- They can reduce the risk of pests developing resistance to pesticides.
Incorporating biological controls into an integrated pest management program can be an effective and sustainable way to manage pest populations in cannabis cultivation. By using natural predators and parasites to keep pests under control and practicing proper sanitation measures, growers can maintain a healthy and pest-free growing environment for their cannabis plants.
Avoid Overfertilization
Overfertilizing plants can be a common mistake made by novice and experienced cannabis growers alike, and it can lead to a host of problems including nutrient burn, nutrient lockout, and susceptibility to pest and disease infestations. To avoid overfertilization, it is crucial to have a good understanding of your plant’s nutrient needs as well as the quality and composition of your soil or growing medium.
What is Overfertilization?
Overfertilization occurs when plants are given too much fertilizer, either in terms of quantity or frequency. This can happen in both soil and hydroponic setups, and the excess nutrients can accumulate in the soil or growing medium, which can lead to root damage and cause the plant to become less healthy overall.
Why is Overfertilization a Problem?
Overfertilizing can cause a variety of problems for your cannabis plants, including:
– Nutrient burn: Too much nitrogen, phosphorus, or potassium can cause the tips of leaves to turn yellow or brown and curl up, which can eventually kill the plant if not corrected.
– Nutrient lockout: Overfertilizing can cause excess nutrients to accumulate in the soil, which can make it more difficult for the plant to absorb the nutrients it needs to grow and develop properly.
– Increased susceptibility to pests and diseases: Overfertilized plants are more vulnerable to pests and diseases because their weakened state makes it harder for them to fight off these threats.
– Poor flavor and aroma: Overfertilization can leave behind residual chemicals in cannabis flowers, which can affect their flavor and aroma and make them less appealing to consumers.
How to Avoid Overfertilization
To avoid overfertilizing your cannabis plants, here are some tips to keep in mind:
| Tip | Description |
| 1. Conduct soil tests | Before adding fertilizer, test your soil to determine what nutrients it lacks and adjust accordingly. |
| 2. Use high-quality fertilizers | Invest in high-quality fertilizers that are designed specifically for cannabis plants, and follow the manufacturer’s recommended dosage instructions. |
| 3. Stick to a feeding schedule | Establish a feeding schedule and stick to it, but be sure to avoid feeding your plants more frequently or with higher doses than recommended. |
| 4. Monitor plant health | Regularly check your plant’s health to ensure that it is not showing signs of nutrient burn or lockout, and adjust accordingly. |
| 5. Flush plants before harvest | Several days before harvest, flush your plants with water to remove any excess nutrients that may be present in the soil or growing medium. |
By following these simple tips, you can help prevent overfertilization and ensure that your cannabis plants remain healthy and robust throughout their growing cycle. Remember, less is often more when it comes to cannabis cultivation, so it’s important to be mindful of the nutrients you are providing your plants and to give them only what they need to thrive.
Rotate Your Crops
Rotating your crops is a crucial part of preventing pest infestations in your cannabis cultivation. This simple technique involves alternating the placement of your plants in your grow room or outdoor garden each season. By doing so, you can help to prevent the buildup of soilborne diseases and pests which can become problematic over time.
Here are some steps to follow to rotate your crops properly:
- First, determine which plants can be rotated. Certain cannabis strains may not be suitable for crop rotation due to their specific growth needs or other factors.
- Next, choose a new location for your plants that is far enough away from their previous location. This helps to ensure that any pests or diseases that may be present won’t spread to the new crop.
- Prepare the soil in the new location. It’s important to maintain a healthy soil environment in your grow room or garden, so consider adding compost or other organic matter to help enrich the soil.
- Maintain proper watering and fertilization schedules as you plant your new crop.
- Monitor your new crop regularly for signs of infestations or disease. Catching any issues early can help prevent them from spreading to your entire crop.
- Once the new crop reaches maturity, harvest it and begin the process again with a new location for your next crop.
By rotating your crops regularly, you can help to prevent the buildup of pests and diseases while also maintaining a healthy soil environment for your cannabis plants. This simple technique, combined with proper sanitation and other best practices for integrated pest management, can go a long way in ensuring a successful and thriving cannabis cultivation.
The Bottom Line: Sanitation is Key in Integrated Pest Management for Cannabis
Proper sanitation plays a critical role in successful Integrated Pest Management (IPM) for cannabis. By implementing good sanitation practices, cannabis growers can prevent the spread of pests and diseases, reduce the risk of infestations, and ultimately produce healthier plants.
Sanitation is Key
Sanitation is an essential aspect of IPM and involves a range of practices to maintain a clean and healthy growing environment. It includes regularly removing plant debris and other materials that can harbor pests, disinfecting equipment and tools, and implementing proper waste management techniques.
Effective sanitation practices can help prevent and control common cannabis pests such as spider mites, aphids, and thrips. It can also reduce the occurrence of diseases such as fungal infections that can spread rapidly through a grow room.
Implementing Proper Sanitation Practices
There are several key sanitation practices that cannabis growers should follow to promote a healthy growing environment and reduce the risk of pest and disease infestations.
One critical practice is to regularly clean and disinfect all equipment, surfaces, and tools used in the grow room. This includes hand tools, propagation trays, and grow tents. Regular cleaning not only helps keep pests and diseases at bay, but it can also improve plant growth and overall yield.
Growers should also start with a sterile environment by thoroughly cleaning and disinfecting the grow room before starting a new crop. This can help prevent pests and diseases from carrying over from one crop to the next.
Proper waste management is also essential in maintaining proper sanitation. Growers should dispose of plant debris and other waste in sealed bags and remove them from the grow room daily. This can help reduce the risk of pests and diseases spreading throughout the grow room.
Additionally, growers should use proper techniques for handling and discarding soil, as poorly managed soil can harbor pests and diseases. They should also avoid cross-contamination by using separate tools or disinfecting tools between use.
To prevent introducing pests or diseases to an established crop, growers should quarantine new plants for a minimum of two weeks in a separate area before introducing them to the rest of the room.
Conclusion
Sanitation is a critical aspect of IPM in cannabis cultivation. By implementing good sanitation practices, growers can help prevent and control pests and diseases, ultimately producing healthier plants. Effective sanitation reduces the risk of pest and disease infestations and can improve plant growth and yields. By following proper sanitation practices, growers can help ensure the long-term success of their crops.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are some common pests found in cannabis cultivation?
Common pests include spider mites, thrips, whiteflies, aphids, and fungus gnats.
Can pests affect the quality of cannabis?
Yes, pests can damage the plant, reduce yields, and infect the final product with harmful bacteria and viruses.
What are some signs of pest infestation in cannabis plants?
Signs include yellow or wilted leaves, small webs or fluffy white spots on the plant, and pest droppings on leaves or around the base of the plant.
What is the best way to prevent pest infestation in a cannabis grow room?
The best way to prevent pest infestation is through proper sanitation and hygiene practices, regular monitoring of plants, and using biological controls when possible.
What is the difference between sanitation and disinfection?
Sanitation involves cleaning and removing visible debris while disinfection involves using chemical solutions to kill microbes on surfaces.
How important is proper ventilation in an IPM program?
Proper ventilation is important in removing excess heat and humidity and preventing the growth of mold and fungi, which can attract pests.
What should be done with plant waste to prevent pest infestation?
Plant waste should be properly disposed of or composted away from the growing area to prevent attracting pests.
Why is cross-contamination a concern in cannabis cultivation?
Cross-contamination can spread pests and diseases from one plant to another, leading to a larger infestation that’s harder to control.
What are some effective biological controls for pest management in cannabis?
Effective biological controls include ladybugs, predatory mites, nematodes, and parasitic wasps.
Can overfertilization attract pests?
Yes, overfertilization can attract pests as it creates an environment of excess nutrients that pests thrive on.