Implementing Integrated Pest Management for Your Cannabis Plants
What is Integrated Pest Management?
Contents
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is a proactive and eco-friendly approach to pest control that involves the use of various techniques and methods to manage pests while minimizing the negative impact on the environment and human health. In other words, IPM aims to prevent and control pest infestations by combining the use of various pest management techniques in a targeted and strategic manner.
The core principle of IPM is prevention, which involves creating an environment that is unfavorable to pests by removing their sources of food, water, and shelter. Another important aspect of IPM is the monitoring of pest populations to detect infestations early and prevent them from spiraling out of control.
When an infestation is detected, intervention strategies may be implemented, which involve the targeted and often localized application of pest control methods. Evaluation is also an important element of the IPM approach, as it helps growers assess the effectiveness of their pest management strategies over time.
IPM is an important tool for cannabis growers because pests, such as spider mites and whiteflies, can significantly damage crops, reduce yield, and even ruin entire harvests. Additionally, the use of chemical pesticides in cannabis cultivation can be problematic due to legality issues and concerns about the potential health effects of exposure to pesticides. IPM offers an eco-friendly and more sustainable option for managing pests in commercial cannabis production.
Why is Integrated Pest Management Important for Cannabis Growers?
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is a crucial aspect for every cannabis grower in the industry. This is because, without proper pest management techniques, cannabis plants are at risk of being attacked by a wide range of pests, from aphids to spider mites, which can cause stunted growth, yield reduction, and even plant death. By implementing IPM techniques, cannabis growers can prevent and control pests by focusing on long-term prevention strategies that mitigate problems before they begin.
One of the biggest benefits of implementing IPM techniques is the reduction of chemical pesticide use. Many pesticides pose serious health risks to humans and can contaminate the environment. By utilizing IPM techniques, growers can minimize the need for harmful pesticides, thus reducing their environmental impact and promoting more sustainable growing practices. Additionally, reducing pesticide use can improve the overall quality of the cannabis harvest, creating healthier and more potent products.
IPM can greatly benefit a grower’s bottom line. Investing in pest prevention methods may require some upfront costs, but in the long run, it can save growers a great deal of money. By preventing pest infestations, growers can avoid costly damages and loss of product, which would otherwise result in significant financial losses.
Finally, implementing IPM techniques can also improve the reputation of the cannabis industry as a whole. By using environmentally friendly and sustainable practices, cannabis growers can build a positive brand image, which can ultimately lead to increased consumer trust and loyalty. This is especially important as the cannabis industry continues to gain widespread acceptance and adoption around the world.
How to Implement Integrated Pest Management Techniques for Cannabis Growers
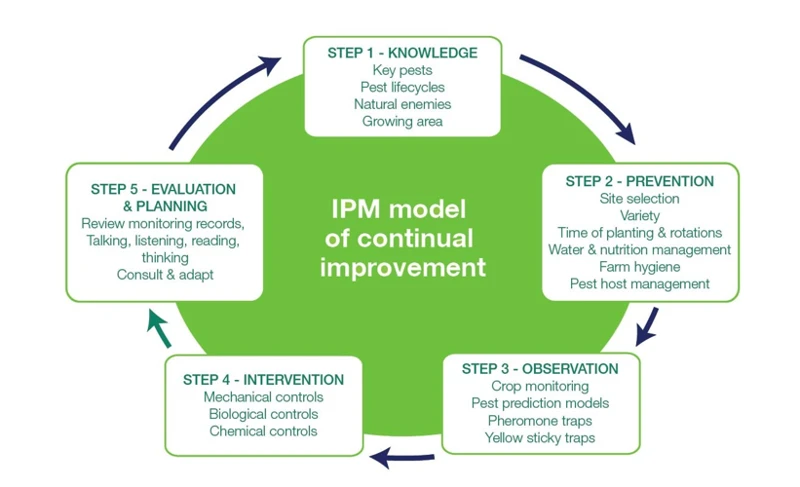
As a cannabis grower, implementing Integrated Pest Management (IPM) techniques is crucial to ensure a healthy and high-quality crop. IPM is a proactive and ecological approach to pest control that emphasizes prevention and focuses on both the pest and its environment. The process is broken down into four main steps: prevention, monitoring, intervention, and evaluation. By following these steps, growers can effectively address pest issues without relying solely on expensive and potentially harmful chemical pesticides. In this section, we will delve deeper into how to implement each step of the IPM process.
1. Prevention
Prevention is the first and most important step in Integrated Pest Management (IPM) for cannabis growers. It involves creating a healthy growing environment that is less conducive to pests and diseases. This can be achieved through a variety of methods, including:
| Prevention Techniques | Description |
|---|---|
| Cleanliness | Keep the grow room clean and free of clutter. Regularly remove any dead plant material or debris from the space to eliminate potential breeding grounds for pests. |
| Quarantine | New plants or clones should be quarantined for at least a week, and checked regularly for signs of pests or disease. This helps to prevent the introduction of unwanted pests into the grow room. |
| Airflow | Good air circulation in the grow room is essential for preventing fungal growth and other pests. Installing fans or other air movement devices can significantly reduce the risk of pest infestations. |
| Temperature and Humidity | Maintain appropriate temperature and humidity levels in the grow room. Pests are less likely to survive in a space that is too hot or too cold, and proper humidity levels can prevent fungal growth. |
| Nutrition | Plants that are well-nourished and healthy are less susceptible to pest infestations. Proper fertilization and watering practices can help to promote plant health. |
| Sanitation | Wash your hands and tools regularly to prevent the spread of pests and disease. Use only clean tools and equipment to avoid introducing pests into the space. |
Using these prevention techniques will reduce the chances of pest infestations and diseases in your cannabis growing environment. By keeping the grow room clean and providing proper nutrition and environmental conditions, you can create a healthy space for your plants to thrive. This step is essential in minimizing the need for more drastic intervention measures that are less environmentally-friendly and potentially more costly.
2. Monitoring
As a crucial step in integrated pest management (IPM), monitoring involves regular inspections and observations of the cannabis plants to detect any signs of pest or disease infestations before they become severe enough to cause significant damage or spread. This helps growers to take early preventive or corrective actions, reducing the likelihood of crop losses.
The monitoring process should include:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Regular inspections | Plants should be inspected every few days, especially during the early growth stages or flowering. Growers should look for signs of pest activity, such as visible insects or damage to leaves, stems, or flowers. They should also check for any signs of disease, such as fungal growths, yellowing or wilting leaves, or unusual spots. |
| Record-keeping | Growers should keep a record of their monitoring activities, noting the date, location, and nature of any observations. This helps them to detect patterns of pest or disease activity, identify potential sources of infestations, and track their success in controlling them over time. |
| Thresholds | Growers should establish pest and disease thresholds that trigger interventions based on the severity and type of infestation. They should base these thresholds on the specific crop, strain, and growth stage of the plants, as well as the environment and climate conditions. |
| Sampling techniques | To accurately monitor pest and disease populations, growers should use appropriate sampling techniques such as sticky traps, yellow cards, or visual scans. They should also use magnifying glasses or microscopes to identify the type and stage of the pests or diseases, as well as their life cycle and behavior. |
| Data analysis | Growers should use the data collected from monitoring to analyze the effectiveness of their IPM program, identify any gaps or weaknesses, and make adjustments as needed. They should also communicate the results to their team members or consultants to ensure everyone is up-to-date on the latest developments. |
Monitoring is a critical component of IPM as it enables growers to detect and respond promptly to pest and disease problems, reducing the need for costly and harmful interventions. With careful monitoring and planning, cannabis growers can successfully implement IPM techniques that promote healthy and robust plants while protecting the environment and human health.
3. Intervention
During the intervention step of integrated pest management (IPM), pest control measures are taken to manage the pest population if they exceed the action threshold previously set during the monitoring step. The intervention step should be proportional to the pest population and the potential damage they could cause to the cannabis crop. The following table shows some examples of interventions and their potential impact on beneficial insects and the environment.
| Intervention Method | Potential Impact on Beneficial Insects | Potential Impact on Environment |
|---|---|---|
| Biological control agents (e.g. predatory mites) | Low impact as they target specific pests and do not harm beneficial insects | Low impact as they do not leave harmful residues and do not contribute to long-term environmental problems |
| Botanical pesticides (e.g. neem oil) | Moderate impact as they may also kill beneficial insects | Low impact as they break down quickly and do not have long-term effects on the environment |
| Chemical pesticides (e.g. pyrethroids) | High impact as they do not discriminate between pest and beneficial insects and may disrupt the balance of the ecosystem | Moderate impact as they can leave toxic residues and contribute to long-term environmental problems |
It is important to note that chemical pesticides should only be used as a last resort and in accordance with local laws and regulations. Additionally, the use of cultural practices such as crop rotation and sanitation can help reduce the need for interventions.
4. Evaluation
Once interventions have been implemented, it is crucial for cannabis growers to evaluate the effectiveness of their integrated pest management techniques. This step allows for adjustments to be made and for the prevention of future infestations. Evaluation can be done through various methods, such as visual inspection or the use of monitoring tools.
Visual Inspection: This involves regularly checking plants for signs of pest damage, such as holes in leaves, discolored spots or markings, and unusual growth patterns. If pest activity is observed, the grower can take immediate action to address the issue.
Monitoring Tools: There are a variety of monitoring tools available to help growers track pest populations. Sticky traps are commonly used to catch flying insects like whiteflies or fungus gnats. Pheromone traps can be used to attract and trap male insects, preventing them from mating with females and reproducing. Growers can also use magnifying lenses or microscopes to identify pests that are too small to see with the naked eye.
Once the monitoring or inspection has been done, growers can then evaluate the effectiveness of their integrated pest management techniques. If the infestation has been successfully controlled, the grower should continue to monitor the plants to ensure that the pests do not return. If the infestation persists, the grower may need to use additional intervention techniques or modify their pest management strategy. Evaluation is an ongoing process that allows growers to continually improve their pest management techniques and ensure the health and quality of their cannabis crops.
To summarize, evaluation is a critical step in integrated pest management for cannabis growers as it allows for adjustments to be made and for the prevention of future infestations. Both visual inspection and monitoring tools can be used to evaluate the effectiveness of pest management techniques. Ongoing evaluation ensures that growers are consistently improving their strategies to maintain healthy, high-quality cannabis crops.
| Evaluation Method | Description and Purpose |
|---|---|
| Visual Inspection | Regular checking of plants for signs of pest activity to identify and address issues early. |
| Monitoring Tools | Use of tools such as sticky traps or magnifying lenses to track pest populations and identify specific pests. |
| Analysis and Modification | Evaluation of the effectiveness of pest management techniques and modification of strategies as needed to prevent future infestations. |
Specific Integrated Pest Management Techniques for Cannabis Growers
As a cannabis grower, it’s crucial to have a strategy in place for managing pests that can wreak havoc on your plants. Integrated Pest Management (IPM) offers a comprehensive approach to pest control that involves a combination of preventative measures, monitoring, intervention, and evaluation. Now, let’s take a closer look at some specific techniques you can use as a cannabis grower to implement an effective IPM program and keep your plants healthy and thriving.
1. Beneficial Insects
One of the effective integrated pest management techniques for cannabis growers is the use of beneficial insects. These insects prey on the harmful pests that can cause damage to cannabis plants. By introducing beneficial insects, cannabis growers can minimize the use of chemical pesticides and maintain a healthier and more natural environment for cannabis cultivation.
Here are some of the commonly used beneficial insects and the pests they target:
| Beneficial Insect | Target Pests |
|---|---|
| Ladybugs | Aphids, mealybugs, spider mites, whiteflies, thrips, and scale insects |
| Parasitic wasps | Caterpillar, leafminer, and whitefly larvae; spider mites; and thrips |
| Praying mantis | Caterpillars, flies, mosquitoes, aphids, grasshoppers, and other insects |
| Predatory mites | Spider mites and other mites |
It’s important to note that beneficial insects should be introduced early in the stage of cannabis growth and in sufficient numbers to provide effective pest control. Growers should also provide an adequate environment for the insects to thrive, such as providing enough food and moisture.
In addition to beneficial insects, some cannabis growers also use microbial products that contain beneficial bacteria or fungi. These products can help control pests and diseases in a natural way, without using harmful chemicals.
The use of beneficial insects and plant-based products can be a more sustainable and environmentally friendly way to manage pests in cannabis cultivation, while also reducing the risks of harmful residues in the final product.
2. Plant-Based Products
Plant-based products are a common and effective solution for pest management in cannabis cultivation. These natural products are typically derived from plant extracts or oils and offer a safer and more eco-friendly alternative to synthetic pesticides. Plant-based products are often less harmful to beneficial insects and do not typically leave residues on cannabis plants.
Below is a table that showcases several commonly used plant-based products for cannabis pest management:
| Plant-Based Product | Pest Targeted | Effectiveness | Application Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Neem Oil | Spider Mites, Whiteflies, Aphids, Thrips | High | Spray on leaves |
| Pyrethrum Extracts | Spider Mites, Aphids, Thrips | High | Spray on leaves |
| Garlic Oil | Spider Mites, Aphids, Thrips | Medium | Spray on leaves |
| Cinnamon Oil | Ants, Gnats | Medium | Spray on soil |
| Pepper Spray | Mites, Caterpillars, Beetles | Low-Medium | Spray on leaves |
While plant-based products can be highly effective, they often require more frequent applications and can have varying levels of efficacy depending on the pest being targeted. It’s important to research and choose products that are best suited for the specific pests present in your cannabis cultivation environment. As with any pest management solution, it’s recommended to test small areas before applying more broadly to ensure that the product does not harm your cannabis plants.
3. Chemical Pesticides
When it comes to controlling pests in cannabis crops, chemical pesticides may be an option for growers. However, their use requires careful consideration and planning.
Benefits:
- Effective against a wide range of pests
- Fast-acting
Drawbacks:
- May harm non-target organisms, including beneficial insects and the crop itself.
- May leave harmful residues on the plant, which can impact the quality and safety of the final product.
- Resistance can develop quickly in pest populations, rendering the pesticide ineffective.
- Regulations may restrict the use of certain pesticides in cannabis cultivation.
It is important for growers to understand the proper application of chemical pesticides, including dosage, timing, and application method. Improper application can lead to inadequate pest control, accidental contamination, and potential harm to the environment.
To minimize the risks associated with chemical pesticide use, growers should consider other pest management techniques, such as beneficial insects and plant-based products, before turning to chemical pesticides. If chemical pesticides are deemed necessary, it is important to consult with a pest management professional and carefully select a product that is appropriate for the pest and stage of infestation, while adhering to all legal requirements and safety regulations.
Integrated Pest Management Challenges for Cannabis Growers
As with any agricultural enterprise, cannabis cultivation faces a variety of challenges when it comes to pest management. However, marijuana growers face several unique obstacles that make it difficult to implement integrated pest management techniques effectively. These challenges range from legal restrictions on pesticides to the specific varieties and strains of cannabis grown, as well as environmental factors such as climate and humidity. In this section, we will explore some of the most pressing challenges of integrated pest management for cannabis growers and how they can be overcome.
1. Legal Restrictions
The implementation of Integrated Pest Management techniques for cannabis growers can be hindered by a number of legal restrictions. The legal status of cannabis is a complex issue and varies depending on the country, state or region. In some places, the cultivation and use of cannabis may be completely legal, while in others it may be illegal or with strict regulations.
Here are some legal restrictions that cannabis growers may face when implementing Integrated Pest Management techniques:
- Illegal Status: In places where cannabis cultivation is illegal, growers may face severe penalties and legal consequences if discovered. This may discourage them from using safe IPM techniques that could be perceived as incriminating evidence.
- Limited Options: In some jurisdictions, cannabis growers may have limited access to certain Integrated Pest Management tools, such as beneficial insects or pesticides, due to legal or regulatory restrictions. This can make it difficult to implement an effective IPM strategy.
- Quality Control: If cannabis growers are required to disclose their use of Integrated Pest Management techniques, this information can be subject to quality control and compliance measures. This may increase the burden on growers to ensure that their IPM techniques are effective and meet legal standards.
- Testing and Certification: In some places, cannabis growers may be required to undergo testing and certification to demonstrate that they are using safe and effective IPM techniques. This can be time-consuming and costly, and may deter some growers from adopting IPM strategies altogether.
- Public Perception: The use of pesticides or other chemicals can be a controversial issue in the cannabis industry, where many consumers prefer natural or organic products. Implementing IPM strategies that involve chemical pesticides may damage a grower’s reputation or cause negative perceptions among customers.
Legal restrictions can make it challenging for cannabis growers to implement Integrated Pest Management strategies, but with careful planning and compliance, it is possible to develop an effective and legal IPM program that promotes sustainable and healthy cannabis cultivation practices.
2. Crop Varieties and Strains
One of the main challenges that cannabis growers face when implementing Integrated Pest Management techniques is the wide variety of crop varieties and strains. Each strain has its own unique characteristics, including different levels of resistance to pests and diseases.
1. Resistance to Pests
Certain strains may be more resistant to certain pests than others. For example, some strains are more resistant to spider mites, while others may be more resistant to whiteflies or thrips. Understanding the resistance of each strain can help growers select the right strains to grow in order to minimize the likelihood of pest infestations.
2. Susceptibility to Diseases
Similarly, different strains may have varying levels of susceptibility to different diseases. For example, some strains may be more prone to developing powdery mildew, while others may be more prone to root rot. Growers need to be aware of the diseases that are most common in their area and choose strains that are less susceptible to those specific diseases.
3. Growth Characteristics
Different strains may also have different growth characteristics, such as height, width, and overall growth rate. This can impact the type and placement of monitoring devices, as well as the selection of beneficial insects and plant-based products for pest control.
4. Nutrient Requirements
Different strains may also have different nutrient requirements, which can impact the overall health and resistance of the plant. Growers need to ensure that they are providing each strain with the appropriate level of nutrients to maintain optimum health and resistance to pests and diseases.
5. Harvest Timing
Finally, different strains may have different harvest timing, which can impact the overall lifecycle of pests and the effectiveness of pest control measures. Growers need to be aware of the harvest timing for each strain to select the appropriate pest control measures and avoid any negative impacts on the quality or quantity of their crop.
Crop varieties and strains present a unique challenge for cannabis growers implementing Integrated Pest Management techniques. To address this challenge, growers need to carefully consider the unique characteristics of each strain when selecting the right pest control measures and overall management strategies for their crop.
3. Climate and Environment
The climate and environment in which cannabis is grown can greatly affect the types of pests that are attracted to the plants. The following are some factors to consider:
- Temperature: Certain pests thrive in warmer temperatures while others prefer cooler temperatures. It is important to understand the ideal temperature range for the specific strain of cannabis being grown.
- Humidity: High humidity can create the perfect environment for pests such as mites, while low humidity can cause stress on the plants and make them more susceptible to infestations.
- Altitude: Higher altitudes can decrease the number of pests due to cooler temperatures and lower air pressure. However, this can also lead to other issues such as decreased sunlight and wind damage.
- Location: The location of the grow operation can also have an impact on the types of pests that are prevalent. Outdoor grows in rural areas may be more susceptible to pest infestations from wildlife, while indoor grows in urban areas may face issues with pests such as cockroaches and rodents.
It is important for cannabis growers to understand the climate and environment in which their plants are being grown in order to implement effective integrated pest management techniques. Adjustments may need to be made based on these factors to truly create a successful and pest-free growing operation.
4. Cost
One of the major challenges for cannabis growers when it comes to implementing integrated pest management techniques is the cost. Here are some cost-related factors that need to be considered:
- Initial Investment: Switching to an integrated pest management approach often requires an initial investment that can be daunting to many cannabis growers. This might entail purchasing equipment such as sticky traps, pheromone traps, and predator insects as well as expenses associated with implementing a new crop management plan. However, it is important to note that these costs will likely prove to be lower in the long run than those of relying on chemical pesticides.
- Cost of Alternative Methods: While chemical pesticides may be cheaper than some of the alternatives, such as biocontrol agents and plant-based products, there is a significant risk with their use, such as toxic residues on the end product, development of resistance by the pests, and contaminating the surrounding environment, including the ground, air, and water. These risks may ultimately result in a higher cost for the grower in terms of reapplication or crop loss.
- Labor Costs: Implementing an integrated pest management system often requires additional labor such as frequent monitoring, managing beneficial insects, and applying plant-based products. This increased labor can add to the cost of pest management.
- Potential Losses: While the initial costs of an integrated pest management system may be higher, the potential losses from a pest outbreak can also be quite significant. A complete loss of a crop can result in a considerable financial setback for a grower, which is why adopting an integrated pest management strategy can be seen as an investment in the long-term sustainability of the operation.
There is no one-size-fits-all solution when it comes to pest management in cannabis cultivation, but growers need to evaluate the potential benefits and drawbacks of different pest control methods to find a solution that fits their budget and agricultural practices.
5. Knowledge and Experience
One of the major challenges that cannabis growers face in implementing integrated pest management techniques is the need for extensive knowledge and experience. Successful pest management requires a deep understanding of pest life cycles, crop anatomy, and ecological interactions between different plant and animal species. Without proper training and experience, growers may struggle to recognize the early signs of pest infestations, identify beneficial insects and organisms, and choose the appropriate intervention strategies.
To overcome this challenge, it is important for cannabis growers to invest in ongoing education and training programs. This may involve attending workshops and conferences, studying relevant literature and research, and seeking guidance and advice from experienced growers and pest management experts. Fortunately, there are many resources available to cannabis growers who wish to expand their knowledge and expertise in pest management.
Growers should also consider partnering with pest management professionals, such as entomologists and agronomists, who can provide specialized knowledge and support. Additionally, by working closely with other growers and industry professionals, cannabis growers can gain valuable insights into the particular challenges and best practices for pest management in the cannabis industry.
Ultimately, success in integrated pest management requires ongoing learning and adaptation, as pests and plants evolve over time. Through a commitment to education and innovation, cannabis growers can overcome the knowledge and experience challenge and implement effective pest management strategies for their crops.
Some practical steps that growers can take to improve their knowledge and experience include:
- Attending regular training and education events, such as webinars, seminars, and workshops focused on integrated pest management.
- Reading relevant literature and research papers focused on pest biology and management.
- Networking with other growers and pest management professionals to learn from their experiences and insights.
- Partnering with a pest management specialist or consultant to provide expert advice and support.
- Experimenting with different pest management techniques to learn what works best for their specific crops and growing conditions.
Conclusion
In summary, implementing Integrated Pest Management techniques is crucial for cannabis growers in order to maintain healthy and fruitful plants while minimizing potential harm to the environment and consumers. Through Prevention, Monitoring, Intervention, and Evaluation, growers can effectively manage and prevent pest problems.
While there are several techniques available to help with pest control, including the use of beneficial insects, plant-based products, and chemical pesticides, it is important to consider the potential legal restrictions, crop varieties and strains, climate and environment, cost, and knowledge and experience associated with each approach.
Growers must take a proactive approach to pest management by regularly monitoring their plants and implementing preventative measures, such as proper sanitation and hygiene practices. In the event that pests do become a problem, intervention strategies should be carefully considered, with an emphasis on using the least toxic option possible.
Ultimately, by implementing an Integrated Pest Management approach, cannabis growers can ensure that their plants remain healthy and productive while minimizing the risk of harm to the environment and consumers. With careful attention to best practices and a commitment to ongoing education and development, growers can successfully navigate the challenges and reap the rewards of a successful cannabis crop.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are some common pests that affect cannabis plants?
Some of the most common pests that affect cannabis plants include spider mites, thrips, aphids, whiteflies, mealybugs, and fungus gnats.
How do pests typically impact cannabis plants?
Pests can damage the leaves, stems, and roots of cannabis plants, which can negatively affect their growth and yield. They can also spread diseases, which can be particularly harmful for indoor grows where plants are in close proximity to each other.
What are some preventative measures growers can take to avoid pest infestations?
Growers can take several preventative measures to avoid pest infestations, including practicing good hygiene and sanitation, using sterilized growing mediums, and keeping a separate area for quarantine and isolation of infected plants.
How do growers monitor for pests?
Growers can monitor for pests by regularly inspecting their plants, using sticky traps or tape to capture flying insects, and examining leaves and soil under a microscope to identify any signs of infestation.
What are some plant-based products that can be used as part of an integrated pest management plan?
Plant-based products such as neem oil, garlic oil, and peppermint oil can be effective as part of an integrated pest management plan for cannabis plants.
What are some beneficial insects that can be used to control pest populations in cannabis grows?
Beneficial insects such as ladybugs, Lacewings, and predatory mites can be used to control pest populations in cannabis grows.
Are chemical pesticides effective for cannabis pest control?
While chemical pesticides can be effective for cannabis pest control, they should be used as a last resort due to potential health risks and harm to the environment.
What are the legal restrictions around pesticide use in cannabis cultivation?
Legal restrictions around pesticide use in cannabis cultivation vary by region, but many jurisdictions have strict regulations around the use of chemical pesticides due to potential health risks and environmental damage.
What role does climate and environment play in integrated pest management for cannabis growers?
Climate and environment can have a significant impact on pest populations and the effectiveness of pest control measures, so it’s important for growers to take these factors into consideration when developing an integrated pest management plan.
Why is knowledge and experience important for successful implementation of integrated pest management techniques?
Knowledge and experience are important for successful implementation of integrated pest management techniques because it requires a deep understanding of plant biology, pest identification and behaviour, and the various control methods available.