Hydroponic vs Soil-Based Nutrient Delivery Systems for Cannabis Cultivation: Which One is Right for You?
Introduction
Contents
Embarking on the journey of growing cannabis can be both exciting and daunting. One of the most important decisions you’ll need to make is choosing between a hydroponic or soil-based nutrient delivery system. Both methods have their own unique advantages and disadvantages, and it’s important to consider each carefully before making the final decision. In this article, we’ll take an in-depth look at both systems, explore the different types of hydroponic and soil-based systems, compare their yield, growth rate, cost, and complexity, and help you decide which system is best suited for your needs.
What is Hydroponics?
Hydroponics is a method of growing plants without soil. Instead of soil, plants are grown in a nutrient-rich water solution. This method of growing has become increasingly popular in recent years, especially in the cannabis industry. With hydroponics, plants are able to grow faster and yield more compared to traditional soil-based methods.
One of the main advantages of hydroponics is that it allows growers to have greater control over the nutrient intake of their plants. This means that plants can be given exactly the right amount of nutrients to encourage healthy growth and higher yields. Additionally, hydroponic systems use less water than soil-based systems, making them more efficient and environmentally-friendly.
However, there are also some disadvantages to using hydroponics. One of the main downsides is that they can be more expensive and complex to set up compared to soil-based systems. Additionally, hydroponic systems require more maintenance and can be less forgiving of mistakes compared to soil-based systems.
Below is a table summarizing the pros and cons of hydroponic systems for cannabis cultivation:
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Allows greater control over nutrient intake | Higher initial set-up cost |
| Uses less water than soil-based systems | Can be more complex to set up |
| Faster plant growth and higher yields | Requires more maintenance |
| More environmentally-friendly | Less forgiving of mistakes |
Whether or not to use hydroponic systems is an important decision for cannabis growers. In the next sections, we will explore some of the different types of hydroponic systems as well as soil-based systems to help growers make an informed decision.
What is Soil-Based Nutrient Delivery System?
Soil-based nutrient delivery systems are the more traditional method of growing plants, where a plant is planted directly into the soil. The soil itself acts as a natural source of nutrients for the plant. This method is a more hands-off and natural approach to growing cannabis. However, it is important to note that not all soils are created equal and some may lack the necessary nutrients for optimal plant growth. This is where fertilizers come in.
Fertilizers are used to supplement the soil’s nutrient content, which can vary depending on the region or location of the grow. There are two main types of fertilizers: organic and synthetic. Organic fertilizers are made from organic matter, such as decomposed plant and animal material, and release nutrients slowly over time. Synthetic fertilizers, on the other hand, are made from chemical compounds and deliver nutrients more quickly, but can have negative effects on the environment if overused.
Soil-based nutrient delivery systems have some pros and cons:
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Natural source of nutrients | Soil quality can vary, affecting plant growth |
| Potential for greater flavor in cannabis due to the soil’s influence | Requires more effort in terms of plant maintenance and soil testing |
| Organic fertilizers can promote healthy microbial activity in the soil | Slow nutrient release may not provide sufficient nutrients for fast-growing cannabis strains |
Soil-based nutrient delivery systems can be a good option for those who prefer a more natural and hands-on approach to growing cannabis. However, it does require more effort in terms of soil testing and plant maintenance. Additionally, the quality of the soil can have a big impact on plant growth, so it is important to choose the right soil and fertilizers to ensure the best results. For those who are environmentally conscious, choosing organic fertilizers can also help promote healthy microbial activity in the soil and reduce the negative impact of synthetic fertilizers on the environment.
Hydroponics
When it comes to cultivating cannabis, one of the most innovative and highly-regarded methods is hydroponics. This system utilizes a nutrient solution to feed the plants instead of traditional soil. With hydroponic systems, plant roots sit in a solution of water and carefully portioned nutrients, which are delivered directly to the roots. This allows for precise control of the nutrient uptake and delivery, as well as faster and more abundant growth. However, since differences exist between synthetic and organic inputs, deciding between hydroponics or soil-based systems requires considering all relevant factors. To learn more about nutrient types, you may want to check our ORG vs. SYN Nutrients for Cannabis: Which Is Better? guide.
Pros
When it comes to Hydroponic systems, there are several pros that make them a viable option for cannabis cultivation. Here are some of the advantages:
| Advantages | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Increased Yield | With hydroponics, plants are given the exact amount of water and nutrients they need, resulting in faster and stronger growth. This often leads to higher yields compared to soil-based systems. |
| Water Conservation | Hydroponic systems use up to 90% less water compared to traditional soil-based systems. This is because the water is recycled and reused, resulting in less waste. |
| No Soil Needed | Since hydroponic systems use water and nutrient solutions instead of soil, there is no need for soil, which can lead to savings in terms of space and cost. |
| Control Over Nutrient Delivery | In soil-based systems, it can be difficult to ensure that plants are receiving the right balance of nutrients. With hydroponics, however, the grower has complete control over the nutrient delivery, resulting in healthier, more robust plants. |
| Less Chance of Soil-Borne Diseases | Soil can carry a variety of pests and diseases that can harm plants. In hydroponics, there is no soil, so the chance of soil-borne diseases affecting the plants is greatly reduced. |
These are just a few of the many advantages of using hydroponic systems for cannabis cultivation. However, it’s important to consider the potential cons as well before making a decision.
Cons
While hydroponic systems have their advantages, there are also several drawbacks that growers should consider. These include:
- More upfront costs: Setting up a hydroponic system can cost more initially as it requires specialized equipment such as pumps, timers, and grow lights.
- Higher electricity costs: Hydroponic systems rely heavily on artificial lighting which can lead to higher electricity bills.
- Higher risk of equipment failure: Due to the complexity of hydroponic systems, there is a greater risk of equipment failure which can be costly and time-consuming to fix.
- Potential for nutrient imbalances: While hydroponic systems are designed to provide precise nutrient delivery, it can be difficult to achieve balance and avoid nutrient deficiencies or toxicities.
- Increased responsibility: Hydroponic systems require more maintenance and monitoring than traditional soil-based systems, which might not be ideal for growers who have limited time or resources.
Despite these challenges, many growers still choose to leverage hydroponics due to their potential for higher yields, faster growth rates, and greater control over growing conditions.
Types of Hydroponic Systems
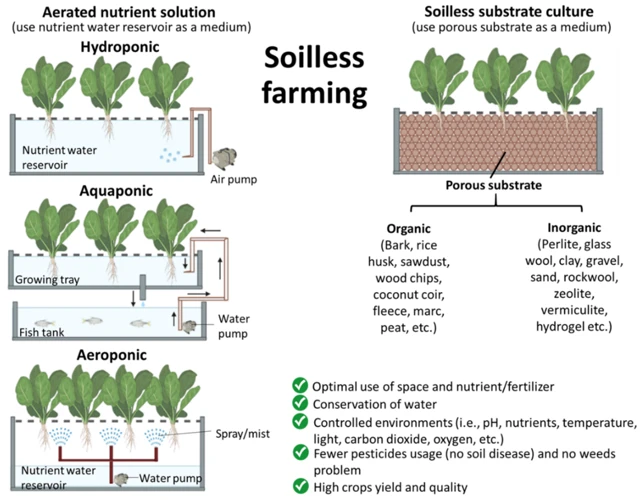
Hydroponics is a method of growing cannabis without soil, using water and nutrient solutions to deliver essential minerals and nutrients directly to the plant’s roots. There are several different types of hydroponic systems that offer growers different levels of control, efficiency, and complexity.
Deep Water Culture (DWC)
This is one of the easiest and most common types of hydroponic systems. It involves suspending the plants’ roots in nutrient-rich water using a platform or net. This allows the roots to absorb water and nutrients while also providing ample oxygen. DWC systems require constant monitoring of pH levels and nutrient levels to ensure optimal growth.
Drip System
A drip hydroponic system involves dripping nutrient solution onto the base of each plant through tubing or drippers. This system is relatively simple to set up and allows growers a high degree of control over nutrient delivery. The drip system can operate on a timer, which means growers don’t need to constantly monitor their plants’ progress.
Flood and Drain System
This hydroponic system involves flooding the growing medium, usually a tray filled with stones, with nutrient-rich water at regular intervals. The system drains the nutrient solution back into a reservoir through a tube, ensuring the roots have enough oxygen to thrive. This cycle repeats every few hours or so, ensuring the roots don’t become waterlogged.
Nutrient Film Technique (NFT)
An NFT system works by flowing a thin film of nutrient solution over a sloping channel, which supports the plants’ roots. The roots absorb the necessary minerals and nutrients as they grow. NFT systems are relatively cheap to set up and maintain, but they require regular monitoring to ensure a steady flow of water.
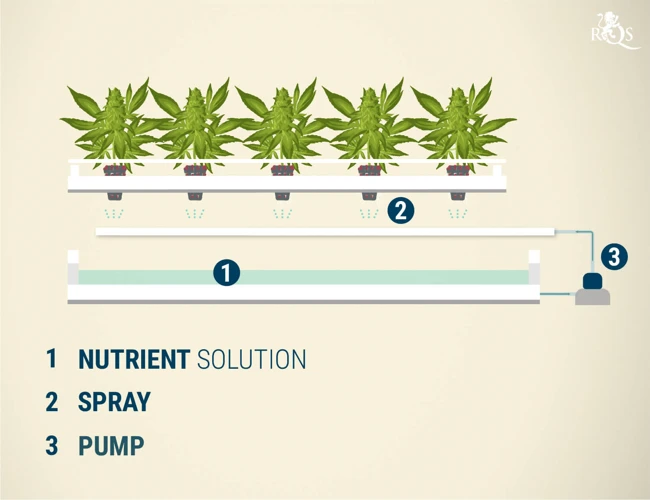
AeroPonics
AeroPonics involves suspending the plants’ roots in a mist of nutrient-rich water using a platform or net. This system allows growers to deliver nutrients and oxygen in a precise and controlled manner. AeroPonics is a relatively expensive and complex system to set up, but it can offer higher yields than other hydroponic systems.
Each of these hydroponic systems has its own advantages and disadvantages, and choosing the right system for your cannabis cultivation depends on your preferences, resources, and goals. The following section will go into further detail on the pros and cons of hydroponic systems as well as soil-based nutrient delivery systems.
Soil-Based Nutrient Delivery Systems
When it comes to growing cannabis, soil-based nutrient delivery systems remain a popular choice for many cultivators. These systems rely on the traditional method of growing in soil and have been used for centuries for agriculture. Soil-based systems can be straightforward and easy to maintain, making it a common choice for beginners or those looking for a simpler grow setup. However, there are also drawbacks to using soil-based systems that should be considered before making a decision. In this section, we’ll discuss the pros and cons of using soil-based nutrient delivery systems for cannabis cultivation, as well as the different types available.
Pros
When it comes to the pros of hydroponic systems for cannabis cultivation, there are several key advantages.
One major advantage is that hydroponic systems typically use less water than traditional soil-based systems, making them more environmentally friendly. Because hydroponic systems use nutrient-rich water instead of soil, there is greater control over the nutrients and pH levels that the plants receive. This can lead to faster growth rates and higher yields.
Another benefit of hydroponic systems is their versatility. They can be set up indoors or outdoors, and they can be configured to fit a wide range of spaces and budgets. Additionally, many hydroponic systems are designed to be low-maintenance, which can save time and effort compared to traditional soil-based systems.
Finally, because hydroponic systems are designed to be highly controlled and precise, they can be ideal for growing cannabis in a consistent and repeatable way. This can be especially important for larger-scale operations where consistency and quality are key priorities.
The advantages of hydroponic systems for cannabis cultivation are clear. By using nutrient-rich water and a controlled environment, growers can achieve faster growth rates, higher yields, and greater control over the nutrient and pH levels of their plants.
| Pros | Description |
| Water Efficiency | Hydroponic systems use less water than traditional soil-based systems |
| Nutrient Control | Greater control over the nutrients and pH levels that the plants receive |
| Versatility | Can be set up indoors or outdoors and can be configured to fit a wide range of spaces and budgets |
| Low-Maintenance | Many hydroponic systems are designed to be low-maintenance |
| Consistency | Hydroponic systems can be ideal for growing cannabis in a consistent and repeatable way, especially for larger-scale operations |
Cons
It is important to consider the drawbacks of using hydroponic systems for cannabis cultivation. These include:
- Cost: Hydroponic systems are typically more expensive to set up than soil-based systems, as they require specialized equipment such as pumps, timers, and grow lights.
- Complexity: Hydroponic systems can be more complex to maintain, requiring monitoring and adjustments to pH and nutrient levels to ensure optimal plant growth.
- Dependency on Technology: Since hydroponic systems rely on technology such as pumps and timers, power outages or equipment malfunctions can cause damage to the plants if not addressed quickly.
- Vulnerability to Disease: Hydroponic systems are often more susceptible to disease outbreaks due to the water-based growing environment. If one plant becomes infected, it can quickly spread to others in the system.
- Environmental Impact: Hydroponic systems require electricity to power grow lights and pumps, which contributes to carbon emissions and may not be sustainable in the long term.
While hydroponic systems have their drawbacks, it is important to note that with proper care and maintenance, many of these issues can be mitigated. It ultimately comes down to the individual grower’s preferences and priorities when choosing between hydroponic and soil-based systems.
Types of Soil-Based Systems
Soil-based nutrient delivery systems rely on the use of soil to provide nutrients to the plant. There are various types of soil-based systems, each with its own unique characteristics and requirements. Here are some of the most common types:
- Standard Container Gardening: This is the most basic type of soil-based system, which involves planting directly in a container filled with soil. It can be done indoors or outdoors, and is a good option for beginners who want to start small.
- Raised Bed Gardening: Similar to standard container gardening, but with the use of a raised bed. This allows for better drainage, increased soil depth, and less strain on the gardener’s back.
- Lasagna Gardening: Also known as sheet composting, this method involves layering organic materials, such as leaves and compost, on top of the soil to create a nutrient-rich environment. This is a great option for those looking to start a garden without tilling the soil.
- Container Gardening with Mulch: This involves planting in containers but using mulch on top of the soil to retain moisture and reduce weed growth. It can be a low-maintenance option for those with limited gardening space.
- Hybrid Soil-Based Systems: These combine aspects of different types of soil-based systems, such as raised bed gardening with lasagna gardening or container gardening with mulch. This allows for a customizable and adaptable approach to gardening depending on the specific needs of the plants.
Soil-based systems can be a great option for those who prefer a more traditional approach to gardening and want to work with soil as a natural source of nutrients for their plants. However, they may require more maintenance and attention than hydroponic systems, and the type of soil used and its nutrient composition can greatly impact the success of the plants.
Comparison
Now it’s time to compare the two nutrient delivery systems for cannabis cultivation: hydroponics and soil-based systems. Both systems have their advantages and drawbacks, so it’s important to carefully evaluate them on several metrics. In the following sections, we will compare the yield, growth rate, cost, and complexity of hydroponic and soil-based systems to help you determine which system is best for your needs. Keep in mind that the optimal choice may vary depending on various factors, such as budget, available space, and skill level, among others.
Yield
When it comes to yield, both hydroponic and soil-based systems have their advantages and disadvantages. Let’s take a closer look at each:
| Hydroponic System | Soil-Based System | |
|---|---|---|
| Advantages | With a well-designed hydroponic system, plants can have access to nutrients without any competition from weeds or other plants. This can lead to faster growth and larger yields compared to some soil-based systems. | Plants grown in soil-based systems tend to have deep root growth and can potentially uptake more nutrients from the soil over time, resulting in a higher overall yield. Additionally, certain strains may be better suited to soil-based systems. |
| Disadvantages | If the hydroponic system is not properly maintained, it can lead to plant stress and reduced yield. Additionally, hydroponic systems can have a steeper learning curve and initial setup costs can be higher. | If the soil is not properly balanced with nutrients and amendments, it can lead to reduced yield. Additionally, soil-based systems can be more susceptible to nutrient runoff and contamination issues. |
The yield of a cannabis cultivation system depends on numerous factors, including genetics, light source, and environmental conditions. It’s important to carefully consider all aspects of the system and choose the one that best fits your needs and resources.
Growth Rate
When it comes to growth rate, hydroponic systems tend to produce faster growth compared to soil-based nutrient delivery systems. In hydroponic systems, the roots of the plants have constant access to nutrients and oxygen which allows them to grow rapidly without being constrained by the limitations of soil. This, in turn, allows hydroponic systems to produce a higher yield at a faster rate.
In contrast, soil-based systems can be slower due to a variety of factors, such as the presence of pests or diseases, nutrient imbalances, or the need to wait for soil to dry out between waterings. However, soil-based systems may also have the advantage of producing plants that are more robust and better able to handle environmental stressors.
Here’s a comparison of the growth rate for hydroponic and soil-based systems:
| Hydroponic Systems | Soil-Based Systems |
| Faster growth rate due to constant access to nutrients and oxygen | Potentially slower growth rate due to soil constraints and other factors |
| May produce a higher yield at a faster rate | May produce more robust plants that are better able to handle environmental stressors |
While hydroponic systems may have the advantage when it comes to growth rate and yield, soil-based systems may have their own unique benefits depending on the specific needs and goals of the grower. It’s important to consider all factors and choose a system that will work best for your individual circumstances.
Cost
When it comes to the cost, both hydroponic and soil-based systems have their own advantages and disadvantages. Here are some points to consider:
Hydroponic Systems
- Higher Startup Cost: Hydroponic systems generally require a higher initial investment to get started due to the need for specialized equipment such as pumps, grow lights, and nutrient solutions.
- Lower Maintenance Cost: Once the initial setup is completed, hydroponic systems require less maintenance such as watering, fertilization, and weeding, leading to lower ongoing costs over time.
- Electricity Costs: Hydroponic setups can require more energy to run, which can lead to higher electricity bills.
Soil-Based Systems
- Lower Startup Cost: Soil-based systems typically require less upfront investment as they do not require as many specialized pieces of equipment compared to hydroponic setups.
- Higher Maintenance Cost: Soil systems require more maintenance such as watering, fertilization, and pest control. This means that the ongoing maintenance costs may be higher.
- Soil Amendments: Soil-based systems often require regular amendments to maintain healthy soil, which can also add to the ongoing costs of maintaining the system.
While hydroponic systems have a higher startup cost, they can offer lower ongoing maintenance costs, while soil-based systems may have lower startup costs but require more ongoing maintenance, leading to higher ongoing costs. The choice between the two will ultimately come down to your budget and preferences.
Complexity
When it comes to complexity, hydroponic systems tend to be more complex than soil-based systems. This is because hydroponics requires more equipment and technical know-how to set up and maintain.
Hydroponic systems require a tight control over the nutrient solution, temperature, humidity, and pH levels in order to achieve optimal plant growth. This can be achieved through the use of pumps, timers, pH testing and regulating equipment, and other specialized tools.
In contrast, while soil-based systems still require attention to these factors, they are generally less complex and require less specialized equipment. Soil-based systems allow for a more traditional approach to growing, involving the use of natural soils and fertilizers.
| Hydroponics | Soil-Based Systems |
|---|---|
| Tight control over nutrient solution, temperature, humidity, and pH levels | Less need for precise monitoring |
| Requires more specialized equipment and technical know-how | More traditional approach to growing, using natural soils and fertilizers |
| More complex set up and maintenance | Generally less complex and requires less specialized equipment |
This added complexity in hydroponic systems can be a disadvantage for those who are new to growing, or those who prefer a more hands-off approach to cultivation. However, for those who are willing to put in the time and effort to learn and maintain their hydroponic system, the rewards can be significant in terms of yield and growth rate.
It’s worth noting that there are varying levels of complexity within both hydroponic and soil-based systems. Some hydroponic systems, such as deep water culture, can be relatively simple and easy to maintain, while some soil-based systems, such as organic or biodynamic farming, can require more knowledge and attention to detail. Ultimately, the level of complexity will depend on the specific system and approach chosen.
Choosing a System
As you venture into cannabis cultivation, it’s important to choose the right system that matches your needs and goals. With so many options for hydroponic and soil-based nutrient delivery systems, it can be overwhelming to decide which one to go for. However, by understanding the factors that influence your choice, you can make an informed decision and optimize your yields. In this section, we’ll explore these factors and help you determine the best system for your cannabis cultivation journey.
Factors to Consider
When considering which type of system to use for cannabis cultivation, there are several factors to take into account. These include:
- Grow Space: The amount of space available for the plants will greatly affect the choice of system. Hydroponic systems can be more compact and take up less space than soil-based systems.
- Water and Nutrient Management: Hydroponic systems generally require more attention and monitoring, as the water and nutrient levels need to be carefully maintained. Soil-based systems may be less intensive in terms of monitoring, but may require more frequent watering.
- Cost: Hydroponic systems can have higher upfront costs compared to soil-based systems, but can potentially save money in the long run due to higher yields and faster growth rates.
- Yield Goals: If the goal is to maximize yield, hydroponic systems may be the better choice due to their ability to provide precise control over nutrient delivery and environmental factors.
- Growth Goals: If the goal is to achieve a specific flavor or aroma profile, soil-based systems may be preferable due to their ability to affect the plant’s natural terroir.
- Experience Level: Hydroponic systems can be more complex and may require more experience and knowledge to set up and maintain. Soil-based systems may be more beginner-friendly and easier to set up and manage.
By carefully considering these factors, growers can make an informed decision about which type of system is best suited for their specific needs and goals.
Which System is Best for You?
Choosing the best nutrient delivery system for your cannabis cultivation depends on a variety of factors. Consider the following when making your decision:
- Growing Experience: If you are a beginner, a soil-based system may be easier to manage. Hydroponic systems require more attention to detail and may require a bit more experience.
- Growing Location: Consider the location of your grow room or greenhouse. If you have limited space, a hydroponic system may allow you to maximize your growing area. If you have ample space, soil-based systems may be more manageable.
- Budget: Hydroponic systems can be more expensive to set up and maintain, so if you are on a tight budget, a soil-based system may be a better option for you.
- Time: Hydroponic systems require more frequent monitoring and maintenance, while soil-based systems can be more forgiving if you have a busy schedule.
- Environmental Impact: Soil-based systems are generally considered more environmentally friendly, as they rely on natural resources like soil and compost for nutrients. Hydroponic systems, on the other hand, rely on synthetic fertilizers and may produce more waste.
Ultimately, the decision between a hydroponic or soil-based nutrient delivery system for cannabis cultivation depends on your individual needs and preferences. Consider the above factors and do your research before making a decision.
Conclusion
In conclusion, choosing between a hydroponic or soil-based nutrient delivery system for cannabis cultivation largely depends on personal preference and specific needs. Both systems have their pros and cons, and ultimately, it’s up to the cultivator to decide which system is best for their operation.
While hydroponic systems offer faster growth rates, higher yields, and better control over nutrient delivery, they can be more complex and expensive to set up and maintain. However, the potential benefits may outweigh these drawbacks for growers who are willing to invest in a high-quality hydroponic setup and have the necessary knowledge and skills to use it effectively.
On the other hand, soil-based systems are generally more affordable and easier to set up and maintain, making them a great option for novice growers or those on a budget. While they may not offer the same level of control over nutrient delivery or growth rates as hydroponic systems, they can still produce high-quality cannabis and may be a better fit for those who prefer a more traditional approach to cultivation.
When choosing a system, it’s important to consider factors such as your budget, level of experience, desired yield, and overall goals for your operation. Ultimately, the system that is best for you will depend on your individual needs and preferences.
Whether you choose hydroponics or a soil-based system, the key to successfully growing cannabis is staying informed and constantly refining your skills and techniques. With the right knowledge and tools, you can create the ideal environment for your plants to thrive and produce top-quality yields year after year.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the advantages of hydroponic systems for cannabis cultivation?
Hydroponic systems offer faster growth rates, higher yields, and the ability to closely control nutrient delivery to plants.
What are the disadvantages of hydroponic systems for cannabis cultivation?
Hydroponic systems can be more expensive to set up and maintain, and require more attention to monitoring nutrient levels and pH.
What are the advantages of soil-based systems for cannabis cultivation?
Soil-based systems are generally more affordable and require less maintenance than hydroponic systems.
What are the disadvantages of soil-based systems for cannabis cultivation?
Soil-based systems may produce lower yields and require more space for roots to grow.
What are the different types of hydroponic systems?
There are several types of hydroponic systems, including deep water culture, drip irrigation, nutrient film technique, and aeroponics.
What are the different types of soil-based systems?
Soil-based systems include traditional potting soil, super soil, and amended soil mixes such as coco coir or perlite.
Which system produces higher yields?
Hydroponic systems generally produce higher yields due to optimal nutrient delivery and faster growth rates.
Which system has a faster growth rate?
Hydroponic systems typically have faster growth rates due to the ability to closely control nutrient delivery and environmental factors.
Which system is more expensive?
Hydroponic systems are generally more expensive to set up and maintain than soil-based systems.
Which system is best for first-time growers?
Soil-based systems are generally more forgiving for first-time growers due to the ability to buffer nutrient levels and the lower cost of equipment and supplies.