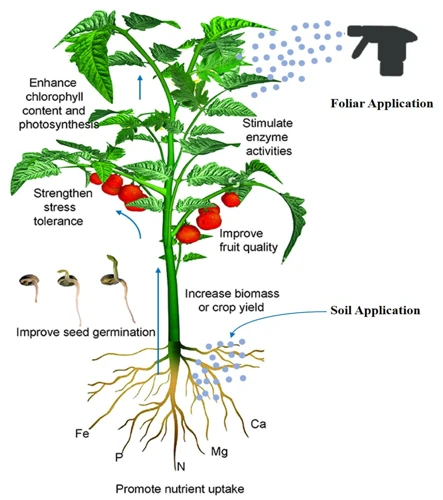
How to Monitor Nutrient Levels When Using Foliar Sprays on Cannabis Plants
As cannabis cultivation becomes increasingly popular, growers are exploring various techniques to improve the quality and yield of their plants. One such technique is foliar spray, a method of feeding cannabis plants through their leaves rather than the soil. While foliar sprays offer several benefits, including faster nutrient uptake and increased resistance to pests and diseases, they can also be risky if not used correctly. Over-fertilization, in particular, can result in stunted growth, nutrient deficiencies, and even plant death. In this article, we’ll explore how to monitor nutrient levels when using foliar sprays on cannabis plants, to avoid the dangers of over-fertilization and ensure the health and vitality of your crop.
What are Foliar Sprays?
Contents
Have you ever heard of foliar sprays? They are a type of fertilizer that is applied directly to the leaves of plants in liquid form. This method of fertilizer application has gained popularity in recent years due to its effectiveness and efficiency. Foliar sprays can provide numerous benefits to cannabis plants, such as faster growth, increased nutrient uptake, and improved resistance to pests and diseases. In this section, we will delve deeper into the world of foliar sprays and explore their various types, advantages, and potential risks.
Types of Foliar Sprays
Foliar sprays are an effective way to deliver essential nutrients directly to the leaves of cannabis plants. There are different types of foliar sprays available on the market, each designed to meet different plant needs.
1. Nitrogen-based foliar sprays: These sprays contain high levels of nitrogen, which is one of the essential macronutrients cannabis plants need for growth. Nitrogen-based foliar sprays can help boost plant growth and increase yields, but they need to be used carefully to avoid over-fertilization.
2. Phosphorus-based foliar sprays: These sprays contain high levels of phosphorus, which is essential for root development, flowering, and fruit production. Phosphorus-based foliar sprays can help increase the number of flowers and fruits produced but should be used sparingly to avoid harming the plant.
3. Potassium-based foliar sprays: These sprays contain high levels of potassium, which is essential for maintaining plant health, increasing the resilience of the plant, and improving photosynthesis. Potassium-based foliar sprays can help plants withstand environmental stress and produce more abundant yields.
4. Micronutrient foliar sprays: These sprays contain essential micronutrients, such as iron, zinc, manganese, and copper, which are necessary for plant growth and development. Micronutrient foliar sprays can help correct nutrient deficiencies and improve plant health.
It is important to choose the right type of foliar spray based on the plant’s needs and growth stage. Using the wrong type of spray or overusing any type of spray can lead to over-fertilization, which can damage the plant and reduce yields.
Advantages of Using Foliar Sprays
Using foliar sprays to fertilize cannabis plants can offer many advantages over traditional methods like root fertilization. Here are some of the benefits of using foliar sprays:
| Advantages | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Quick absorption | Because foliar sprays are applied to the leaves, the nutrients they contain can be absorbed quickly and efficiently by the plant. |
| Targeted application | Foliar sprays can be applied directly to the leaves that need the most nutrients, allowing for targeted fertilization. |
| Reduced water usage | Since foliar sprays are applied directly to the leaves, there is no need to water the entire plant, which can reduce water usage. |
| Increased nutrient availability | By bypassing the roots and applying the nutrients directly to the leaves, you can increase the availability of certain nutrients that may be limited by soil pH or other factors. |
| Decreased risk of nutrient lockout | When nutrients are applied to the soil, they can sometimes become locked up and unavailable to the plant due to chemical reactions. Foliar sprays can help avoid this problem. |
While foliar sprays can offer many benefits, it’s important to use them properly and monitor nutrient levels to avoid over-fertilization.
Potential Risks of Using Foliar Sprays
It’s important to understand that using foliar sprays on cannabis plants does come with some potential risks. One of the biggest risks is over-fertilization, which can cause damage to the plant and even death in severe cases. In addition to over-fertilization, there are other risks associated with using foliar sprays on cannabis plants.
| Risk | Description |
|---|---|
| Leaf Burn | Applying foliar sprays in direct sunlight or during extreme temperatures can cause the leaves to burn due to the fertilizer’s concentration. This can result in decreased photosynthesis, which can negatively impact the plant’s growth and yield. |
| Microbial Growth | When using foliar sprays, there is a risk of microbial growth on the leaves, especially in areas with high humidity. This can lead to mold and other diseases that can damage the plant and reduce its yield. |
| Nutrient Lockout | Using too much fertilizer or using the wrong type of fertilizer can cause a nutrient lockout, which means that the plant is unable to absorb the necessary nutrients it needs. This can lead to stunted growth and lower yield. |
| Pesticide Residue | If pesticides are used in conjunction with foliar sprays, there is a risk of pesticide residue on the plant’s leaves. This can be dangerous for human consumption and can lead to other issues such as resistance to pesticides. |
To mitigate these risks, it’s important to follow proper application techniques and use balanced fertilizers. It’s also important to pay attention to the plant’s response after each application and adjust accordingly.
Why Is Over-Fertilization a Concern?
Maintaining the right balance of nutrients is crucial for the healthy growth of cannabis plants. However, over-fertilization is a common problem faced by many growers. This occurs when plants receive an excess of nutrients, leading to various issues that can be detrimental to their overall health. It is important for growers to understand the potential risks associated with over-fertilization, in order to prevent any harm to their plants and ensure optimal growth conditions. Let’s dive deeper into this concern and explore the effects of over-fertilization on cannabis plants.
Effects of Over-fertilization on Cannabis Plants
Over-fertilization can have serious negative effects on cannabis plants. Here are some of the potential issues that can arise:
1. Root Damage: When plants receive too many nutrients, it can cause root damage which in turn affects the plant’s ability to absorb water and nutrients.
2. Stunted Growth: Over-fertilization can lead to stunted growth in cannabis plants. This is because the excess nutrients can cause the plant to focus more on foliage growth rather than producing flowers.
3. Nutrient Burn: When plants receive too many nutrients, it can cause the leaves to become yellow and dry out. This is commonly known as nutrient burn and can make the leaves curl up and fall off.
4. pH Imbalance: Over-fertilization can cause the pH levels of the soil or growing medium to become too acidic or too alkaline, which can also negatively affect plant growth.
5. Lowered Quality: Over-fertilization can negatively affect the quality of the cannabis buds. The buds may become less potent or have an unpleasant taste and smell.
It is important for growers to properly monitor and manage nutrient levels to avoid these negative effects and ensure healthy plant growth.
Common Causes of Over-fertilization
Over-fertilization, which occurs when too much fertilizer is applied to the cannabis plants, can result in a host of problems, including decreased yields, stunted growth, and even death of the plants. It’s important for cannabis growers to be aware of the common causes of over-fertilization in order to avoid this common problem. Some common causes of over-fertilization include:
- Inaccurate measuring: Not measuring the correct amount of fertilizer can lead to over-fertilization.
- Using too much: Using more fertilizer than recommended on the label can lead to over-fertilization.
- Applying too often: Over-application of fertilizer can cause a buildup of nutrients in the soil, leading to over-fertilization.
- Not flushing the plants: Failing to flush the plants with water in between feedings can cause nutrient buildup and over-fertilization.
- Not adjusting for soil pH: Soil pH affects nutrient uptake, so failing to adjust the pH levels can cause over-fertilization.
- Using the wrong type of fertilizer: Not all fertilizers are created equal, and using the wrong type of fertilizer can lead to over-fertilization.
By being aware of these common causes of over-fertilization, cannabis growers can take steps to prevent this problem and promote healthy growth of their plants.
How to Identify Over-fertilization
One common sign of over-fertilization in cannabis plants is leaf burn. This occurs when the tips and edges of the leaves are discolored and appear crispy, dry, or scorched. Another sign of over-fertilization is the yellowing of leaves, which can be a result of nutrient imbalances or accumulation of excess salts in the soil.
Beyond these visual cues, there are a few other signs that may indicate over-fertilization. For instance, if the roots of the plant appear to be discolored or have a foul odor, this may be a sign of nutrient toxicity or excess fertilization. Additionally, if the plant is growing slower than expected, despite receiving ample light and water, this could also be a sign of over-fertilization.
It’s important to note that these symptoms can also be caused by other factors, such as pests or diseases, so it’s important to properly identify the underlying cause before taking any action.
If you suspect that your cannabis plants are experiencing over-fertilization, you should take steps to remediate the issue immediately to prevent further damage to the plant. This may include flushing the soil with water or using a specialized product designed to remove excess nutrients. It’s important to approach the issue with care and to avoid making sudden, drastic changes, as this could further shock the plant and lead to additional problems.
How to Monitor Nutrient Levels
As a cannabis grower, it’s crucial to maintain the proper nutrient levels in your plants to ensure optimal growth and quality. However, monitoring these levels can be a daunting task, especially when it comes to foliar sprays. You want to avoid under-fertilizing your plants, which can lead to stunted growth and poor yields, but you also want to avoid over-fertilizing, which can be just as detrimental. In this section, we’ll explore the best ways to monitor nutrient levels when using foliar sprays, so you can ensure your plants receive the right amount of nutrients without causing harm.
Understanding Nutrient Uptake
Nutrient uptake is the process by which plants absorb and use nutrients from the soil or foliar sprays to support growth and development. In order to effectively monitor nutrient levels when using foliar sprays on cannabis plants, it’s important to understand how nutrient uptake works.
Nutrient Forms
Plants can absorb nutrients in different forms, including:
| Nutrient Form | Examples |
|---|---|
| Minerals | Calcium, magnesium, iron, copper, zinc |
| Organic Compounds | Carbohydrates, amino acids, proteins, vitamins |
Nutrient Mobility
Different nutrients have different mobility within the plant, which can affect where and how they are absorbed. Some nutrients are more mobile than others and can easily move throughout the plant, while others are less mobile and tend to stay in one location.
| Nutrient Mobility | Examples |
|---|---|
| Mobile Nutrients | Nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium |
| Less Mobile Nutrients | Calcium, magnesium, sulfur |
Nutrient Interactions
The presence of one nutrient can influence the absorption of another nutrient, which is why it’s important to maintain a balance of different nutrients in the soil or foliar spray.
| Nutrient Interaction | Examples |
|---|---|
| Synergistic Interactions | Nitrogen and phosphorus, calcium and magnesium |
| Antagonistic Interactions | Calcium and potassium, iron and manganese |
By understanding nutrient uptake and how different nutrients interact with each other, growers can effectively monitor nutrient levels and provide their cannabis plants with the necessary nutrients for healthy growth and development.
Tools for Measuring Nutrient Levels
To ensure that you are not over-fertilizing your cannabis plants when using foliar sprays, it is important to monitor nutrient levels regularly. There are various tools that can be used to measure nutrient levels in the soil and the plant tissue. Here are some of the most commonly used tools:
| Tool | Measurements | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Soil Test Kit | pH, N, P, K, Ca, Mg | Simple and easy to use, relatively inexpensive | May not provide accurate results for all nutrients, limited range of detection |
| Electrical Conductivity (EC) Meter | Salinity of soil or nutrient solution | Provides quick and easy measurements, can indicate nutrient imbalances or excesses | May not indicate specific nutrient deficiencies, calibration is required |
| Tissue Analysis | Concentration of N, P, K, Ca, Mg, and other trace elements in plant tissue | Provides accurate measurement of nutrient levels in the plant, can detect hidden deficiencies | Expensive, time-consuming, may not provide immediate results |
| Visual Symptoms | Leaf color, shape, and texture | Can provide indications of nutrient deficiencies or excesses | Not always reliable, symptoms may overlap, may not detect hidden deficiencies |
It is important to note that no tool is perfect, and a combination of methods may be necessary to get an accurate picture of your plant’s nutrient levels. In addition to measuring nutrient levels, it is also important to monitor pH levels, as the availability of nutrients is often affected by soil pH. By regularly monitoring nutrient and pH levels, you can adjust your fertilization strategy to ensure that your cannabis plants are healthy and productive.
How to Collect Samples for Testing
When it comes to monitoring nutrient levels in your cannabis plants, collecting samples for testing is an important step. This helps you to identify any imbalances or deficiencies in the plant’s nutrients and adjust your fertilization accordingly. Follow these steps to collect samples for testing:
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Step 1: | Choose plants to sample that accurately represent the overall health of your crop. Ideally, you want to select plants from various locations throughout the growing area. |
| Step 2: | Take samples from both the leaves and the soil. For leaf samples, choose healthy leaves from the middle of the plant, as these are the most accurate representation of the plant’s overall nutrient levels. For soil samples, take samples from multiple areas of the growing area to ensure accuracy. |
| Step 3: | Use clean tools to take your samples. This means using sanitized scissors for taking leaf samples and a clean trowel for taking soil samples. |
| Step 4: | Take multiple samples from each location and mix them together. This helps to ensure accuracy and reduce the risk of skewed test results. |
| Step 5: | Label each sample clearly and store them in separate bags or containers to avoid cross-contamination. |
Taking the time to collect and test cannabis plant samples can help you to avoid over-fertilization and ensure that your plants receive the nutrients they need for healthy growth.
Recommended Nutrient Levels for Cannabis Plants
Strong and healthy cannabis plants need a balanced supply of essential nutrients. The recommended levels of these nutrients vary throughout the plant’s lifecycle, and it’s essential to monitor them closely to avoid over-fertilization. Here are the recommended nutrient levels for cannabis plants:
- Nitrogen (N): Nitrogen is essential for vegetative growth. During this stage, cannabis plants need a higher concentration of nitrogen, typically around 200-400 ppm. During the flowering stage, the nitrogen requirement drops to around 100-150 ppm.
- Phosphorus (P): Phosphorus is necessary for root growth and flower development. During the vegetative stage, cannabis plants need around 100-200 ppm of phosphorus, while during the flowering stage, the requirement increases to around 200-400 ppm.
- Potassium (K): Potassium is essential for overall plant health and helps with stress tolerance. During the vegetative stage, cannabis plants need around 200-400 ppm of potassium, while during the flowering stage, the requirement increases to around 400-600 ppm.
- Calcium (Ca): Calcium plays a crucial role in cell formation and strengthens the cell walls of the plant. Cannabis plants need a consistent supply of calcium throughout their lifecycle, typically around 150-200 ppm.
- Magnesium (Mg): Magnesium is essential for chlorophyll production, and a deficiency can lead to yellowing leaves. Cannabis plants need around 50-100 ppm of magnesium throughout their lifecycle.
- Sulfur (S): Sulfur plays a role in the formation of enzymes and proteins, and a deficiency can lead to reduced growth. Cannabis plants need around 50-100 ppm of sulfur throughout their lifecycle.
- Iron (Fe): Iron is essential for photosynthesis and helps the plant produce chlorophyll. Cannabis plants need around 1-3 ppm of iron throughout their lifecycle.
It’s important to note that nutrient levels can vary depending on the growing medium, pH balance, and the specific strain of cannabis being grown. Always monitor nutrient levels closely and adjust as needed to ensure healthy and flourishing cannabis plants.
Tips for Using Foliar Sprays Safely
When it comes to using foliar sprays on cannabis plants, safety should always be a top priority. While these sprays can be highly effective in delivering much-needed nutrients to your crops, using them incorrectly can lead to potentially harmful consequences such as over-fertilization. In this section, we’ll look at some important tips and best practices for using foliar sprays safely and effectively. By following these guidelines, you’ll be better equipped to help your plants grow and thrive without putting them at risk.
Read Labels and Instructions Carefully
When using foliar sprays on your cannabis plants, it’s important to always read the labels and instructions carefully before proceeding. This will help prevent any accidental misuse of the product and help you achieve the desired results.
One way to ensure that you are using the spray correctly is to check the label for the recommended dosage and application frequency. Be sure to follow these instructions precisely, as overuse or misuse of the product can harm your plants.
In addition to dosage and frequency, the label may also contain information about the specific nutrients that the spray provides. Be sure to match the nutrient needs of your plants to the nutrients provided by the spray in order to avoid over-fertilization.
Another important aspect of reading labels is to check for any warnings about the product. Some sprays may be hazardous if ingested, inhaled or if it comes into contact with your skin. Take appropriate precautions to keep yourself and your plants safe.
Always store your foliar sprays properly, preferably out of reach of children and pets, and away from direct light or extreme temperatures. This can help maintain the quality and effectiveness of the product.
By reading labels and instructions carefully, you can ensure that you are using the correct amount of product and can avoid any potential risks or negative effects on your cannabis plants.
Choose a Balanced Fertilizer
When choosing a fertilizer to use as a foliar spray, it’s important to select a balanced fertilizer that contains the right proportion of nutrients to ensure optimal growth and prevent over-fertilization. A balanced fertilizer contains a relatively equal proportion of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium (NPK).
Nitrogen (N) is an essential nutrient required for the growth of leaves, stems, and flowers. It is responsible for the green color of plants and plays a vital role in photosynthesis. However, overusing nitrogen can lead to excessive vegetative growth and reduce the potency of the buds.
Phosphorus (P) is an essential nutrient required for root development, fruit and flower production, and overall plant health. Lack of phosphorus can lead to stunted growth, whereas overuse can lead to nutrient imbalances and harm the plant.
Potassium (K) is an essential nutrient that plays a crucial role in regulating plant water balance and promoting disease resistance. It also helps to enhance flower production and improve the overall quality of buds.
When selecting a balanced fertilizer, it’s essential to consider the specific growth stage of the plants. Cannabis plants have different nutrient requirements during different growth stages. For instance, during the vegetative stage, the plant requires a fertilizer with a higher proportion of nitrogen to support leaf and stem growth. On the other hand, during the flowering stage, the plant requires less nitrogen and more phosphorus and potassium to support bud growth.
It’s also crucial to consider the pH level of the fertilizer. Cannabis plants need a pH level between 6.0-7.0 for optimal nutrient uptake. Using a fertilizer with a pH level outside this range can cause nutrient deficiencies and lead to other problems. It’s important to choose a balanced fertilizer with a pH level that’s compatible with cannabis plants.
To ensure that you’re using a balanced fertilizer, it’s recommended to read the label and check the NPK ratio. You can also consult with a cannabis cultivation expert or a reputable grow store for guidance.
Avoid Spraying In Direct Sunlight or Extreme Temperatures
When using foliar sprays on cannabis plants, it is important to avoid spraying in direct sunlight or extreme temperatures. This is because both heat and intense light can cause the spray to evaporate too quickly, reducing its effectiveness and potentially damaging the plant.
Direct sunlight can be particularly problematic because it can cause the spray to dry too quickly, leaving residues on the leaves that can interfere with photosynthesis and respiration. Additionally, if the spray gets too hot, it can become more concentrated and potentially burn the plant tissue. To avoid these issues, it is best to spray in the early morning or late afternoon when the sun is less intense.
Extreme temperatures can also pose a risk when using foliar sprays. If the spray is applied when temperatures are too high, it can cause the plant to wilt and become stressed. On the other hand, if the temperature is too low, the spray may not be absorbed by the plant as effectively, reducing its overall effectiveness.
To help ensure optimal results, it is recommended to spray cannabis plants when the temperature is between 65-80°F (18-27°C). If the temperature is expected to be outside this range, it may be best to wait until conditions improve before spraying.
Avoiding direct sunlight and extreme temperatures is an important consideration when using foliar sprays on cannabis plants. By taking these precautions, growers can help ensure their plants absorb the maximum amount of nutrients and minimize the risk of damage or stress.
| Issue | Risks | Best Time to Spray |
|---|---|---|
| Direct Sunlight | Evaporation, Reduced Effectiveness, Residue Buildup, Concentration of Spray | Early Morning or Late Afternoon |
| Extreme Temperatures | Wilting, Stress, Reduced Effectiveness | 65-80°F (18-27°C) |
Apply Sprays in Short Bursts
When applying foliar sprays to cannabis plants, it’s important to apply them in short bursts. This means that instead of continuously spraying the leaves, you should spray for a few seconds, pause for a few seconds, and then spray again.
The reason for this is twofold:
- Firstly, it allows the spray droplets to settle on the leaves before applying more. If you spray continuously, the droplets may run off the leaves before they have a chance to be absorbed.
- Secondly, spraying in short bursts allows you to monitor how much spray you are using. If you continuously spray for an extended period of time, you may end up over-applying the fertilizer, which can lead to over-fertilization and plant damage.
Here are some tips for applying sprays in short bursts:
- Use a spray bottle with a nozzle that allows you to control the flow of the spray.
- Spray each plant individually, giving each one enough time to absorb the spray before moving on to the next plant.
- If you’re using a pump sprayer, pump it slowly to control the flow of the spray.
- If you’re using a hose-end sprayer, adjust it so that the spray comes out in short bursts.
By applying sprays in short bursts, you can help ensure that your plants get the nutrients they need without risking over-fertilization. It’s always better to err on the side of caution when it comes to fertilizing cannabis plants, and spraying in short bursts is one way to do that.
Don’t Overuse Foliar Sprays
One of the most important things to keep in mind when using foliar sprays on cannabis plants is to avoid overuse. While these sprays can be effective in promoting healthy growth and addressing nutrient deficiencies, using them too frequently or in excessive amounts can actually harm the plants.
Overuse of foliar sprays can lead to several issues:
| Issue | Description |
|---|---|
| Burnt Leaves | The leaves may suffer from burn caused by too much fertilizer. This can result in discoloration, wilting, and scorching of the foliage. |
| Mineral Buildup in Soil | Foliar sprays can also lead to mineral buildup in the soil, which can interfere with the plant’s nutrient uptake and cause toxicity. |
| Negative Impact on Yield and Quality | Constant use of foliar sprays can diminish the quality and yield of the crop by increasing the risk of nutrient burn or toxicity. |
To prevent overuse, it’s crucial to follow the instructions provided by the manufacturer, which often includes recommended application rates and frequency. It’s also important to monitor the plants’ responses to the sprays and adjust the application accordingly. If a plant shows signs of nutrient deficiency, it may be wise to apply foliar sprays, but not too frequently or in excessive amounts.
When deciding whether or not to use a foliar spray, consider the following:
- The current nutritional state of the plant
- The type of fertilizer used
- The stage of growth the plant is in
- The overall health of the plant
Remember, less is often more when it comes to using foliar sprays. It’s always better to err on the side of caution and use them sparingly, rather than risk overuse and damage to the plants. With proper use and monitoring, foliar sprays can be an effective tool for maintaining healthy cannabis plants.
Conclusion
In conclusion, it is important to monitor nutrient levels when using foliar sprays on cannabis plants in order to avoid over-fertilization. Over-fertilization can have a negative impact on the health and overall growth of cannabis plants.
To prevent over-fertilization, it is important to understand the potential risks of using foliar sprays and choose a balanced fertilizer that provides the necessary nutrients for healthy plant growth without causing nutrient imbalances.
Monitoring nutrient levels can be done through the use of various tools and by collecting samples for testing. It is recommended to follow guidelines for nutrient levels specific to cannabis plants to ensure optimal growth and health.
In addition to monitoring nutrient levels, there are steps that can be taken to use foliar sprays safely. This includes reading labels and instructions carefully, avoiding spraying in direct sunlight or extreme temperatures, applying sprays in short bursts, and not overusing foliar sprays.
Overall, with proper attention to nutrient levels and safe use, foliar sprays can provide significant benefits to cannabis plants, including increased growth and productivity. By following these guidelines, growers can ensure the health and success of their cannabis crops.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the different types of foliar sprays available for cannabis plants?
There are several types of foliar sprays available for cannabis plants, including macronutrient sprays, micronutrient sprays, kelp sprays, and compost teas.
What are the advantages of using foliar sprays?
Foliar sprays are an effective way to quickly deliver nutrients to the plant, they are easily absorbed by the leaves, and can also increase yield and overall plant health.
What are the potential risks of using foliar sprays?
Foliar sprays can potentially lead to over-fertilization, which can cause harm to the plant, as well as harm to the environment if excess nutrients leach into water sources. They can also increase the risk of pests and diseases if used incorrectly.
What are the effects of over-fertilization on cannabis plants?
Over-fertilization can cause nutrient burn, root damage, stunted growth, and decreased harvest yields.
What are some common causes of over-fertilization in cannabis plants?
Over-fertilization can occur due to incorrect dosing, using the wrong type of fertilizer, or not adjusting fertilizer amounts based on plant growth stage.
What are some tools that can be used to measure nutrient levels in cannabis plants?
Nutrient test kits, pH testers, and conductivity meters are commonly used tools to measure nutrient levels in cannabis plants.
How do you collect samples for nutrient level testing?
Collect samples from multiple areas of the plant, including the top, middle, and bottom leaves. Take samples from both healthy and unhealthy-looking leaves for the most accurate results.
What are the recommended nutrient levels for cannabis plants?
The recommended nutrient levels for cannabis plants vary depending on the growth stage, but typically include a balance of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, as well as micronutrients like calcium and magnesium.
Can foliar sprays be harmful to humans?
Foliar sprays can potentially be harmful to humans if ingested or inhaled. It is important to follow safety instructions and use protective gear when applying foliar sprays.
Should foliar sprays be used as the sole source of nutrients for cannabis plants?
No, foliar sprays should not be used as the sole source of nutrients for cannabis plants. They are meant to supplement traditional soil-based fertilization methods, not replace them entirely.