Organic vs Synthetic Macronutrients: What Are the Pros and Cons?
Macronutrients are crucial for the growth and development of any plant, and cannabis is no exception. However, growers face a perplexing choice when it comes to deciding between organic and synthetic macronutrient sources. There’s no easy answer to this question, and it can cause confusion and frustration for those new to cultivating cannabis. In this article, we’ll explore the pros and cons of both organic and synthetic macronutrient sources, and provide you with the information you need to make an informed decision for your cannabis plants. From the role of macronutrients in cannabis growth to considerations when choosing a macronutrient source, we will guide you through the key factors to keep in mind. So, whether you’re a seasoned grower or new to cannabis cultivation, let’s dive into the world of macronutrients and discover the best way to support your plants’ health and vitality.
What Are Macronutrients and Why Are They Important?
Contents
Macronutrients are the essential elements required by plants to grow and thrive. They are called macronutrients because they are needed in large amounts. There are three primary macronutrients – nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium – that play crucial roles in cannabis plant growth. These macronutrients are necessary for the development of healthy leaves, roots, and flowers. Without the proper balance of macronutrients, cannabis plants can become stunted, weak, and even die. In this section, we will explore the importance of macronutrients and their role in cannabis growth.
The Role of Macronutrients in Cannabis Growth
Cannabis plants require certain macronutrients in order to grow properly. Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Potassium are three of the most important macronutrients for cannabis growth.
| Nitrogen | Phosphorus | Potassium |
|---|---|---|
| Nitrogen is one of the building blocks of amino acids, which are used to build proteins. | Phosphorus is necessary for photosynthesis and encourages root development. | Potassium is important for water uptake and the overall health of the plant, as it helps to regulate many important processes such as photosynthesis, respiration, and protein synthesis. |
| The role of nitrogen in cannabis growth: Nitrogen helps to increase leaf growth and overall plant size. | The role of phosphorus in cannabis growth: Phosphorus is important for flower formation and early root development. | The role of potassium in cannabis growth: Potassium helps to strengthen the plant’s roots and stems, and also plays a crucial role in the production of terpenes and cannabinoids. |
Without these three macronutrients, cannabis plants will not be able to grow properly and may result in stunted growth or even death. It is important to ensure that cannabis plants are receiving the proper balance of these macronutrients throughout their growth cycle.
The Three Macronutrients: Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Potassium
Macronutrients are essential for the growth and development of cannabis plants. The three primary macronutrients required by cannabis plants are nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. Each of these macronutrients serves a unique role in the plant’s growth and development.
Nitrogen: Nitrogen is responsible for promoting vegetative growth in cannabis plants. It helps in the development of leaves, stems, and overall plant structure. Nitrogen is also essential for the production of chlorophyll, which is necessary for photosynthesis.
Phosphorus: Phosphorus is responsible for promoting root development and aiding in the transfer of energy throughout the plant. It is essential for proper flower development and the production of essential oils in the plant.
Potassium: Potassium is responsible for regulating water and nutrient uptake in cannabis plants. It also aids in the development of strong stems and helps the plant resist disease.
It is essential to ensure that cannabis plants receive the appropriate levels of these three macronutrients throughout their growth cycle to ensure healthy growth and maximum yield. Both organic and synthetic macronutrients can provide these essential nutrients to the plants.
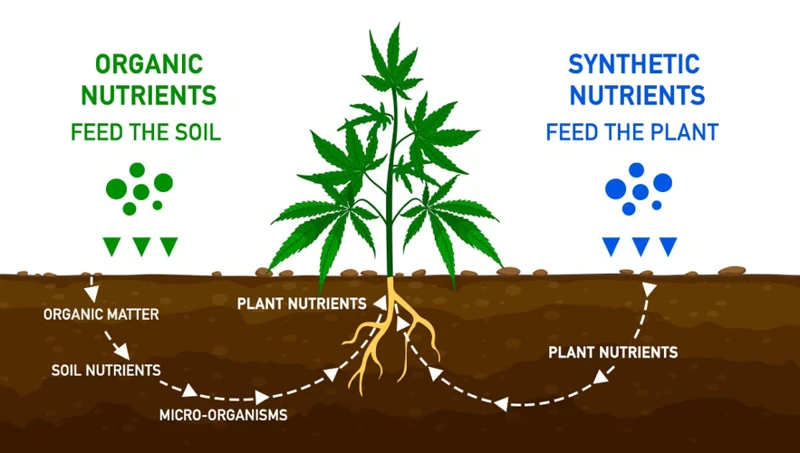
Organic Macronutrient Sources
When it comes to growing cannabis, choosing the right macronutrient source is crucial for ensuring healthy and robust plant growth. While synthetic fertilizers have been a go-to choice for many growers, some are turning to organic options for a more sustainable and natural approach. Organic macronutrient sources are derived from natural materials, such as compost, bone meal, and bat guano. Not sure which option is right for you? Let’s dive into the pros and cons of organic macronutrient sources to help you make an informed decision.
Examples of Organic Macronutrients
Organic macronutrients are derived from natural sources and undergo little to no processing before being applied to cannabis plants. Here are some examples of organic macronutrients:
- Blood meal: considered a high-nitrogen fertilizer, blood meal is made from the blood of animals and can be quickly broken down by cannabis plants.
- Bone meal: made from ground-up bones, bone meal is a slow-release fertilizer that provides both nitrogen and phosphorus.
- Fish emulsion: made from decomposed fish, fish emulsion is a liquid fertilizer that provides a range of macronutrients and micronutrients.
- Manure: typically sourced from cows, horses, or other animals, manure is a high-nitrogen fertilizer that can release macronutrients slowly over time.
- Bat guano: bat droppings are often transformed into a high-phosphorus fertilizer that can be particularly useful during the flowering stage of cannabis growth.
- Compost: created by breaking down organic matter such as leaves, twigs, and food scraps, compost provides a range of nutrients to cannabis plants and can also improve soil structure.
While these organic macronutrients can be effective for cannabis growth, they do come with some drawbacks that should be considered.
Pros of Organic Macronutrient Sources
Organic macronutrient sources have several advantages over synthetic alternatives. Here are some of the benefits that organic macronutrient sources offer:
- Slow Release: Organic macronutrient sources are often slow-release, which means that the nutrients are released over time, providing a consistent and continuous supply of nutrients to the plant. This helps to prevent over-fertilization and reduces the risk of nutrient burn.
- Natural: Organic macronutrient sources are derived from natural materials, such as bone meal, fish meal, and compost, which means that they are less likely to contain harmful chemicals and toxins that may harm the plant or the consumer.
- Improves Soil Health: The use of organic macronutrient sources can improve soil health by increasing soil organic matter, improving soil structure, and increasing the soil’s ability to retain water and nutrients. This can lead to healthier plants, higher yields, and a more sustainable growing system.
- Better Taste and Aroma: Organic macronutrients can improve the taste and aroma of your harvest, resulting in a more flavorful and fragrant yield.
- Environmentally Friendly: Organic macronutrient sources are often produced in a sustainable and environmentally-friendly manner, reducing the overall impact on the environment.
Organic macronutrient sources offer a range of benefits that make them an attractive option for growers who are looking for a natural and sustainable way to provide their plants with the essential nutrients they need to thrive.
Cons of Organic Macronutrient Sources
While organic macronutrient sources have numerous benefits, they also have some downsides that growers need to consider. These cons include:
| Cons of Organic Macronutrient Sources |
|---|
| Slow Release: Organic macronutrient sources take longer to break down and be readily available for the plant to use. This means that the effects of organic fertilizers are not immediately visible and may take longer to produce noticeable results. |
| Inconsistent Formulations: The quantities of nutrients in organic macronutrient sources can vary depending on the source and quality of the product. As a result, it can be more difficult to get a precise balance of nutrients for optimal plant growth. |
| Potential for Overfeeding: Because the nutrients in organic sources are released slowly over time, it is possible to overfeed plants if too much fertilizer is applied. This can result in nutrient burn and other negative effects on plant health. |
| Insect and Pest Attraction: Organic fertilizers can attract insects and pests that may damage plants. This is especially true for products that contain animal or plant matter. |
| Odor: Some organic fertilizers have a strong odor that can be unpleasant for growers or those around the grow area. This can be especially problematic for those growing cannabis in indoor environments. |
Despite these drawbacks, many growers still prefer organic macronutrient sources for their effectiveness and the benefits they provide to the soil and environment. It ultimately comes down to personal preference and the specific needs of the plants being grown.
Synthetic Macronutrient Sources
When it comes to providing cannabis plants with the necessary macronutrients, there are two primary options: organic and synthetic sources. While organic sources come from natural materials, synthetic sources are artificially created. Some growers prefer synthetic options as they can provide more precise control over nutrient amounts and ratios. However, others may have concerns about the use of chemicals and additives in synthetic sources. In this section of the article, we will explore synthetic macronutrient sources, their pros and cons, and discuss considerations when choosing between organic and synthetic options.
Examples of Synthetic Macronutrients
Synthetic macronutrient sources are artificially created in a laboratory, usually in a highly concentrated form. They are designed to provide plants with precise ratios of macronutrients. Here are some examples of synthetic macronutrients:
| Macronutrient | Form | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Nitrogen | Ammonium Nitrate, Urea, Ammonium Sulfate | Quick release nitrogen sources that can burn plants if overused. |
| Phosphorus | Monoammonium Phosphate, Monopotassium Phosphate | Highly concentrated phosphorus sources that stimulate root growth and flower development. |
| Potassium | Potassium Chloride, Potassium Nitrate | Fast acting potassium sources that help plants regulate water and nutrient uptake. |
As you can see, synthetic macronutrients offer precise control over nutrient ratios and are highly concentrated. However, they can also be more expensive and potentially damaging to plants if not used correctly. It is important to carefully follow instructions and not overuse synthetic macronutrients.
Pros of Synthetic Macronutrient Sources
Synthetic macronutrient sources have several benefits over their organic counterparts. These benefits include:
- Efficiency: Synthetic macronutrients are more readily available for immediate use by plants when compared to organic macronutrients. This means that plants can absorb synthetic macronutrients faster and in larger quantities, leading to faster growth and increased yields.
- Precision: Synthetic macronutrients are formulated to contain specific ratios of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, which can be precisely adjusted to meet the unique needs of different plants at various stages of growth. This level of precision is often difficult to achieve with organic macronutrients.
- Purity: Synthetic macronutrients are manufactured under controlled conditions, which ensures that they are free of contaminants and pathogens that can harm plants or affect the quality of the final product.
- Long shelf life: Synthetic macronutrients can be stored for long periods of time without the risk of spoilage or loss of potency. This makes them a convenient option for growers who need to store a large supply of macronutrients for future use.
- Cost-effective: Synthetic macronutrients are often more affordable than their organic counterparts due to their simple manufacturing process and the high yields they can produce.
Despite these benefits, it is important to use synthetic macronutrients in moderation and with caution. Overuse of synthetic macronutrients can lead to nutrient burn and other complications that can harm plant growth and affect the quality of the final product. It is important to carefully follow manufacturer instructions and to monitor plant health closely to ensure that synthetic macronutrients are used safely and effectively.
Cons of Synthetic Macronutrient Sources
While synthetic macronutrient sources may have their benefits, there are also several cons to using them. The following are some potential drawbacks to consider:
- Potential for Salt Buildup: Synthetic fertilizers can contribute to salt buildup in the soil over time, which can lead to nutrient imbalances and damage to plant roots. This can be mitigated by regularly flushing the soil with water, but it is an additional task that growers have to manage.
- Harsh Chemicals: Synthetic fertilizers are often made with harsh chemicals that can be harmful to the environment and to human health if not handled properly. If not used correctly, they can cause burns, skin irritation, and respiratory issues. Additionally, many synthetic fertilizers are derived from non-renewable resources, which may not be sustainable in the long run.
- Less Microbial Activity: Synthetic fertilizers tend to have fewer micronutrients and beneficial microbes compared to organic fertilizers. This can result in a less diverse and potentially weaker microbiome in the soil, which can have negative impacts on plant health and overall crop yield.
- Increased Risk of Overfertilization: Since synthetic fertilizers are often highly concentrated, it can be easy for growers to apply too much of them, which can lead to overfertilization. This can cause nutrient lockout, plant burn, and other issues that can harm plant growth and productivity.
While synthetic macronutrient sources can be effective in certain situations, growers must also be aware of the potential downsides noted above. It’s crucial to weigh the pros and cons carefully when deciding which macronutrient source to use and to follow recommended usage guidelines to ensure plant health and maximum yield.
Which Macronutrient Source Should You Choose?
When it comes to choosing between organic and synthetic macronutrient sources for your cannabis plants, it can be a perplexing decision to make. Both options have their pros and cons, leaving growers wondering which one is the best for their specific needs. It’s important to understand the considerations that should be taken into account before making a decision, as well as the potential benefits of combining both organic and synthetic sources. Let’s take a closer look at these factors to help you make an informed choice.
Considerations When Choosing a Macronutrient Source
When choosing a macronutrient source for your cannabis plants, there are several factors to consider:
- Cost: One of the primary considerations when choosing between organic and synthetic macronutrient sources is the cost. Organic fertilizers tend to be more expensive than synthetic fertilizers, which can be a concern for those on a tight budget.
- Sustainability: Sustainability is another important factor to consider when choosing a macronutrient source. Organic fertilizers are often considered more sustainable because they are derived from natural sources and are less likely to harm the environment. Synthetic fertilizers, on the other hand, can be harmful to the environment if not used properly.
- Effectiveness: The effectiveness of a macronutrient source is also an important consideration. While organic fertilizers may be more sustainable, they may not be as effective as synthetic fertilizers. Synthetic fertilizers are often more concentrated and may provide more immediate results than organic fertilizers.
- Soil Health: The health of your soil is another important factor to consider when selecting a macronutrient source. Organic fertilizers can help improve soil health by increasing microbial activity and promoting a healthy soil structure. Synthetic fertilizers, on the other hand, can harm soil health if overused.
- Growth Stage: The growth stage of your cannabis plants is also an important consideration when selecting a macronutrient source. During the vegetative stage, cannabis plants require more nitrogen, while during the flowering stage, they require more phosphorus and potassium. Make sure to select a fertilizer that is appropriate for the growth stage of your plants.
By considering these factors, you can choose a macronutrient source that is best suited for your specific needs and goals.
Combining Organic and Synthetic Macronutrient Sources
Combining organic and synthetic macronutrient sources can help create a balanced nutrient profile for your cannabis plants. This allows you to take advantage of the benefits of both types of macronutrient sources, while mitigating their respective downsides.
One way to do this is to use a base nutrient solution that includes primarily synthetic macronutrients, and then add organic supplements as needed. For example, you might use a synthetic nutrient solution that provides a strong baseline of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, and then add organic supplements like kelp meal, bone meal or bat guano to provide additional micronutrients and trace elements.
Alternatively, you could use a primarily organic base nutrient solution and then supplement with synthetic macronutrients as needed. This can be especially useful if you’re growing cannabis in soil or other organic media, as these systems tend to benefit from a more diverse range of nutrient sources.
When combining organic and synthetic macronutrient sources, it’s important to pay attention to your plants’ specific needs. Be sure to monitor your plants regularly to ensure that they’re getting the right balance of nutrients, and adjust your feeding schedule as needed. Additionally, keep in mind that different strains of cannabis may have different nutrient requirements, so be sure to do your research and choose a combination of macronutrient sources that will work well for your particular strain.
Some potential benefits of combining organic and synthetic macronutrient sources include:
- Improved plant growth and development
- Increase in terpene production and flavor
- Increase in cannabinoid potency
- Reduced risk of nutrient imbalances or deficiencies
- Potentially reduced environmental impact, as organic sources tend to be more sustainable and eco-friendly
Combining organic and synthetic macronutrient sources can be a versatile and effective way to optimize the nutrient profile of your cannabis plants. By taking advantage of the strengths of both types of nutrient sources, you can provide your plants with the ideal balance of macronutrients, leading to healthier, more productive plants with higher yields of high-quality cannabis.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the choice between organic and synthetic macronutrient sources for cannabis growth is not a one-size-fits-all decision. Both options have their pros and cons, and ultimately, the decision should be based on the specific needs and preferences of the individual cultivator.
Organic macronutrient sources offer a range of benefits, including improved soil health, reduced environmental impact, and potentially higher-quality flavor in the final product. However, they can also be more complex to use and may require more time and attention to achieve the desired results. Additionally, organic sources may not provide the same level of control over nutrient ratios as synthetic sources.
Synthetic macronutrient sources offer precise control over nutrient ratios and are generally easier and more predictable to use. They are also often more cost-effective than organic sources. However, synthetic sources can degrade soil health over time and contribute to environmental pollution.
When choosing a macronutrient source, cultivators should consider factors such as their growing environment, the stage of growth their plants are in, and their personal values regarding organic vs. synthetic methods. It may also be beneficial to combine organic and synthetic sources for a hybrid approach that balances the strengths of each.
Overall, successful cannabis cultivation requires careful attention to macronutrient levels and a willingness to adjust and experiment with different sources in order to find the optimal solution for each unique growing situation.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I use both organic and synthetic macronutrient sources together?
Yes, combining both sources can provide a balanced nutrient profile for your cannabis plants.
What are some common examples of organic macronutrient sources?
Examples include fish emulsion, bone meal, blood meal, and composted manure.
What are some common examples of synthetic macronutrient sources?
Examples include ammonium nitrate, potassium sulfate, and triple superphosphate.
Which type of macronutrient source is more environmentally friendly?
Organic macronutrient sources are generally more environmentally friendly as they are derived from natural sources and promote soil health.
Can using too much macronutrient source harm my plants?
Yes, over-fertilization with either organic or synthetic macronutrient sources can lead to nutrient burn and harm your cannabis plants.
Is it necessary to use macronutrient sources during all stages of cannabis growth?
Yes, macronutrient sources are essential for healthy cannabis growth during all stages of development.
How do I know if my cannabis plants are deficient in a macronutrient?
Deficiencies in specific macronutrients can lead to characteristic visible symptoms such as yellowing leaves, stunted growth, and poor bud development.
Which macronutrient is most important for bud development?
Phosphorus is the macronutrient most important for bud development, as it promotes cell division and energy transfer within the plant.
Can I make my own organic macronutrient source at home?
Yes, composting food waste and other organic materials can create a nutrient-rich soil amendment to act as an organic macronutrient source.
Can synthetic macronutrient sources leach into groundwater and cause pollution?
Yes, overuse of synthetic macronutrient sources can result in leaching of excess nutrients into groundwater and cause pollution, making it important to use them responsibly.