Growing Cannabis: Optimizing Light Schedule
For cannabis growers, finding the perfect balance of light exposure can be a mystery. With so many different strains with diverse requirements, it can be challenging to optimize light schedules for maximum growth and yield. Understanding the principles of photoperiodism and light cycles is crucial to creating an environment that is conducive to the needs of each plant. In this article, we will explore the optimal light schedules for different cannabis strains, as well as the factors that impact these schedules, and ways to troubleshoot common problems that can occur. By the end of this article, you will have a better understanding of how to create the perfect light schedule for your cannabis garden.
Understanding Light Schedule for Cannabis Plants
Contents
One of the most critical factors that contribute to the healthy growth and development of cannabis plants is the light schedule. However, understanding the effect of light on cannabis plants can be perplexing, especially for novice growers. Nevertheless, it’s vital to master this concept to ensure that your plants thrive and produce high-quality yields. In this section, we’ll delve into the nitty-gritty of how light works for cannabis plants, focusing on photoperiodism, light cycles, and their influence on plant growth.
Photoperiodism
Photoperiodism is a natural biological response of plants to the amount of daylight and darkness they receive, affecting their growth and development. Cannabis plants are classified into two types based on their photoperiodism response: photoperiodic and auto-flowering. Photoperiodic strains require specific light schedules to progress through their growth stages, while auto-flowering strains do not depend on light cycles and will flower on their own, regardless of light schedules.
The length of light and darkness a photoperiodic plant receives determines its stage of growth. During the vegetative stage, cannabis plants require approximately 18 hours of light per day and 6 hours of darkness. This promotes optimal growth and development of the plant’s foliage and roots. During the flowering stage, the light cycle is changed to provide the plant with 12 hours of light and 12 hours of uninterrupted darkness, which triggers the plant to produce flowers.
To better understand how photoperiodism works, refer to the table below:
| Light Cycle | Plant Response |
|---|---|
| 18 hours light / 6 hours darkness | Vegetative growth and development |
| 12 hours light / 12 hours darkness | Flowering stage – triggers flower production |
It’s important to note that the photoperiodic response may vary slightly among different cannabis strains. Some strains may require 16 hours of light during the vegetative stage, while others may require 20 hours. Similarly, some strains may require 11 hours of darkness during the flowering stage, while others may require 13 hours. It’s essential to research the specific light requirements for the cannabis strain you plan to grow to optimize its growth and yield.
Light Cycles for Cannabis Plants
When it comes to optimizing the light schedule for cannabis plants, one important factor to consider is the light cycle. The light cycle refers to the amount of light and darkness that the plants receive within a 24-hour period. The specific light cycle that works best for your cannabis plants will depend on several factors, including the strain you are growing and the stage of growth.
Here is an overview of the different light cycles commonly used for cannabis plants:
| Light Cycle | Duration of Light | Duration of Darkness |
|---|---|---|
| 18/6 | 18 hours | 6 hours |
| 16/8 | 16 hours | 8 hours |
| 14/10 | 14 hours | 10 hours |
| 12/12 | 12 hours | 12 hours |
The most common light cycle used for cannabis plants is the 18/6 cycle, which involves providing the plants with 18 hours of light and 6 hours of darkness each day. This cycle is ideal for the vegetative stage of growth, allowing the plants to develop strong roots and branches.
As the plants move into the flowering stage, many growers switch to a 12/12 light cycle. This involves providing the plants with 12 hours of light and 12 hours of darkness each day. This change in light cycle stimulates the plants to begin producing buds.
Some growers choose to use a 24/0 light cycle, which involves providing the plants with constant light. While this may seem like a good idea, it is not recommended for novice growers, and can actually have negative effects on the plants. A period of darkness is essential for cannabis plants to develop properly.
It is important to note that the ideal light cycle can vary depending on the specific strain you are growing. Some strains may require more or less light, or may respond differently to changes in light cycle. Additionally, some growers may choose to experiment with different light cycles to see what works best for their individual plants.
By understanding the different light cycles for cannabis plants and experimenting to find the optimal cycle for your strain, you can help ensure the healthy growth and development of your plants.
Optimizing Light Schedule for Different Cannabis Strains
As a cannabis grower, one of the most critical factors to consider when optimizing the growth of your plants is their light schedule. It’s important to understand that different strains of cannabis have unique requirements when it comes to light exposure. To achieve the best results, you need to develop a tailored light schedule for each strain. In this section, we will explore the factors that you should consider when optimizing light schedules for various cannabis strains, such as Indica, Sativa, Hybrid, and Auto-Flowering strains. Additionally, we will discuss some common problems that you may encounter when optimizing light schedules and offer solutions to help you troubleshoot these issues.
Indica Strains
When it comes to optimizing the light schedule for Indica strains, it is important to understand their natural habitat and growth characteristics. Indica strains originate from the mountainous regions of India, Afghanistan, and Pakistan where they grow in short, bushy plants. As a result, they have adapted to shorter growing seasons and need less light than Sativa strains to reach maturity.
To optimize the light schedule for Indica strains, a 12/12 light cycle is recommended during the flowering stage. This means that the plants receive 12 hours of light and 12 hours of darkness each day. During the vegetative stage, a 16/8 light cycle is recommended for optimal growth. This allows the plants to receive ample light for growth and development.
It is also important to provide a low-intensity light source during the flowering stage. This helps to stimulate resin production and increase potency in the buds. High-intensity light can actually have the opposite effect and decrease potency.
During the vegetative stage, a higher intensity light source can be used to promote growth and development. LED grow lights or metal halide lights are popular choices for providing the ideal light spectrum for Indica strains.
When it comes to timing and duration of light exposure, consistency is key. The light cycle should remain the same throughout the growth cycle to prevent light stress and ensure a healthy crop.
Here is a summary of the recommended light schedule for Indica strains:
| Growth Stage | Light Cycle | Light Intensity |
|---|---|---|
| Vegetative | 16/8 | High Intensity |
| Flowering | 12/12 | Low Intensity |
By following these guidelines for optimizing the light schedule for Indica strains, growers can ensure a healthy and potent crop.
Sativa Strains
Sativa strains of cannabis require a slightly different light schedule than Indica strains. These strains come from tropical regions and are adapted to receiving intense sunlight for long periods of time. They have thinner leaves and grow taller than Indicas. Here are some tips for optimizing light schedule for Sativa strains:
- Longer Light Exposure: Sativa strains require a longer light exposure than Indicas – around 14 to 18 hours of light per day during the vegging phase.
- Adjusting Light Cycles: During the flowering phase, Sativa strains require around 12 hours of light and 12 hours of darkness. However, some growers prefer to switch to an 11-13 or 10-14 light cycle to encourage faster flowering.
- Gradually Increase Light Exposure: Sativa strains can be more sensitive to sudden changes in light exposure. It’s recommended to gradually increase light exposure by 15 to 30 minutes each week to avoid stressing the plants.
- Use High-Intensity Lighting: Due to their adaptation to strong sunlight, Sativa strains can benefit from using high-intensity lighting such as LEDs or HIDs.
- Supplemental UV Lighting: Some growers incorporate supplemental UV lighting during the later stages of growth to encourage resin production, which can enhance the potency of Sativa strains.
Keep in mind that these are general guidelines, and factors such as the specific Sativa strain being grown and environmental conditions can impact the optimal light schedule. Experimentation and observation are also key to finding the best light schedule for your Sativa plants.
Hybrid Strains
When it comes to hybrid strains, the light schedule can vary depending on the specific genetics of the plant. This is because hybrid strains are a combination of both indica and sativa genetics, resulting in different growth patterns and characteristics.
To optimize the light schedule for hybrid strains, it is important to consider the dominant genetics of the plant. For example, if the hybrid strain is indica-dominant, it may require less light during the flowering stage compared to a sativa-dominant hybrid. On the other hand, if the hybrid strain is sativa-dominant, it may require more light for optimal growth and development.
It is recommended to start with a light schedule that is balanced between the needs of both indica and sativa genetics. A common light cycle for hybrid strains during the vegetative stage is 18 hours of light and 6 hours of dark. During the flowering stage, a light cycle of 12 hours of light and 12 hours of dark is typically used.
However, as every hybrid strain is unique, a grower should always pay close attention to the plant’s growth and adjust the light schedule accordingly. Experimentation and observation are essential when growing hybrid strains to ensure the best possible growing conditions for each individual plant.
Additionally, factors such as the growth stage of the plants, available light sources, and growing environment should also be considered when optimizing the light schedule for hybrid strains. By taking these factors into account and being attentive to the needs of each individual plant, growers can successfully grow healthy and high-yielding hybrid cannabis plants.
Finding the optimal light schedule for hybrid strains requires patience, experimentation, and attention to detail. With a little bit of trial and error, growers can ensure that their hybrid strains receive the ideal amount of light to thrive and produce high-quality buds.
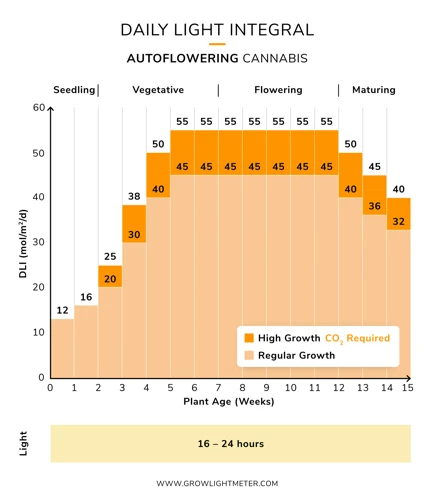
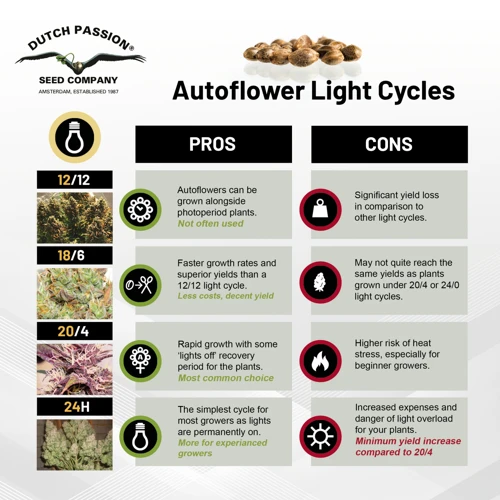
Auto-Flowering Strains
Auto-flowering strains are unique cannabis strains that do not rely on a specific light cycle to start flowering. Rather, they automatically start flowering based on their age. These strains are ideal for growers looking for a more flexible and convenient option.
When growing auto-flowering strains, there are a few things to keep in mind. Here are some tips for optimizing light schedule for auto-flowering strains:
- Light schedule: Auto-flowering strains typically do best with a minimum of 18 hours of light per day throughout their entire life cycle. Some growers may choose to provide a full 24 hours of light per day to maximize growth and yield.
- Light intensity: Auto-flowering strains can be sensitive to intense light. Be sure to keep the light source at an appropriate distance to avoid “light burn”.
- Nutrient schedule: Since auto-flowering strains tend to have a shorter life cycle, they require a well-timed nutrient schedule. Be sure to provide the appropriate amount of nutrients at the right time to ensure optimal growth and yield.
- Experimentation: As with any cannabis strain, it’s important to experiment with different light schedules and techniques to find the best fit for your specific auto-flowering strain. Keep a close eye on your plants and adjust your light schedule accordingly.
Remember, auto-flowering strains are unique and require a different approach to light scheduling than traditional photoperiod strains. By following these tips and experimenting with different techniques, you can optimize your light schedule for your auto-flowering strain and achieve optimal growth and yield.
Factors to Consider When Optimizing Light Schedule
When it comes to optimizing light schedules for cannabis plants, there are a number of important factors to consider. These can include the growth stage of the plants, the available light sources, the growing environment, the timing and duration of light exposure, and even the process of experimentation and observation. It can be perplexing to determine the appropriate approach for each individual scenario, but taking the time to carefully think through each of these factors is essential for ensuring the success of your cannabis grow operation. Let’s take a closer look at each of these considerations and how they can impact your light schedule optimization efforts.
Growth Stage of Plants
It is important to consider the growth stage of cannabis plants when optimizing their light schedule. Different growth stages require different amounts of light and specific light wavelengths to encourage healthy growth and flowering. Here is an overview of suggested light schedules for each growth stage:
| Growth Stage | Hours of Light per day | Light Spectrum |
|---|---|---|
| Seedling Stage | 18-24 hours | Cool white fluorescent or LED lights (preferably in the blue spectrum) |
| Vegging Stage | 18-24 hours | Full-spectrum fluorescent or LED lights (preferably with a higher ratio of blue to red wavelengths) |
| Pre-Flowering Stage | 12-16 hours | Full-spectrum fluorescent or LED lights (preferably with an equal ratio of blue to red wavelengths) |
| Flowering Stage | 12 hours on, 12 hours off | Full-spectrum LED lights (preferably with a higher ratio of red to blue wavelengths) |
During the seedling stage of growth, cannabis plants require a lot of light to promote healthy root and stem growth. Cool white fluorescent or LED bulbs in the blue spectrum are ideal for this stage as they help prevent stretching and encourage sturdy growth.
In the vegging stage, plants require a similar amount of light, but with a higher ratio of blue to red wavelengths. Full-spectrum fluorescent or LED lights are recommended during this stage as they help promote strong vegetative growth.
The pre-flowering stage requires a shorter amount of light per day, around 12-16 hours, with an equal balance of blue and red wavelengths to prepare the plants for the next stage.
During the flowering stage, which usually lasts 8-10 weeks, cannabis plants require a 12-hour light schedule with a higher ratio of red to blue wavelengths. Full-spectrum LED lights are ideal for the flowering stage as they help to promote optimal bud development and THC production.
It is important to note that different strains may have slightly different requirements in terms of light during each stage, so it is important to research and adjust accordingly.
Available Light Sources
When optimizing the light schedule for cannabis plants, the available light sources play a crucial role in determining the growth and quality of the plants. The type and intensity of light can vary depending on the source. Thus, it is important to choose the best light sources that suit your particular strain of cannabis plants. Consider the following options:
- Fluorescent bulbs: These are a popular choice among many growers because they are efficient and emit low heat, reducing the risk of light burn. They are ideal for seedlings or plants in the vegetative stage.
- High Intensity Discharge (HID) lamps: These lights have a high output, making them ideal for plants in the flowering stage. However, they emit a lot of heat and require adequate ventilation to avoid light stress on the plants.
- Light Emitting Diode (LED) lamps: These are a newer type of grow light that are energy-efficient and produce very little heat. They are ideal for both vegetative and flowering stages of growth.
- Ceramic Metal Halide (CMH) lamps: These are a newer type of HID lamp that emit a full spectrum of light, similar to natural sunlight. They are efficient and effective for both the vegetative and flowering stages of growth.
When considering the available light sources, it is important to also think about the size of your grow space and the number of plants you are growing. The type and intensity of light needed will depend on the size of your space as well as the number of plants you have.
Ultimately, the best light source for your cannabis plants will depend on your unique situation. Consider the available options and choose one that is best suited for your particular strain and growing environment.
Growing Environment
The growing environment plays a crucial role in optimizing the light schedule for cannabis plants. The table below highlights some of the key factors to consider for the best growth environment.
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Temperature | The ideal temperature range for cannabis plants is between 65-80°F (18-27°C). Lower or higher temperatures can negatively impact plant growth. |
| Humidity | Cannabis plants require a humid environment but not too much. The ideal range is between 40-60% humidity during vegetative growth and 40-50% during flowering. |
| Air circulation | Good air circulation is essential to prevent mold and pests. Fans can be used to stimulate strong stems, which helps cannabis plants support heavy buds. |
| CO2 levels | Cannabis plants thrive in environments with high carbon dioxide levels, between 800-1500 ppm. High CO2 concentrations can enhance photosynthesis rates and stimulate plant growth. |
| pH level | The ideal pH level for cannabis plants is between 6.0-7.0. The soil or hydroponic solution should be tested regularly to ensure proper nutrient absorption by the plants. |
Creating a favorable growing environment not only helps cannabis plants grow optimally, but it also ensures that growers can achieve the best yields possible. Temperature, humidity, air circulation, CO2 levels, and pH level are all key factors that need to be monitored to ensure a healthy growing environment. By paying attention to these factors and minimizing any negative impact on the plants, growers can optimize their light schedules for the best results.
Timing and Duration of Light Exposure
One of the most important factors to consider when optimizing light schedules for cannabis plants is timing and duration of light exposure. This refers to the specific periods of time when your plants are exposed to light, as well as how long they receive that light each day.
Different strains of cannabis have varying preferences when it comes to the number of hours of light they need each day, so it’s important to understand the requirements of the specific strain you’re growing. Generally, cannabis plants require between 12 and 18 hours of light per day during the vegetative stage, followed by 12 hours of light and 12 hours of darkness during the flowering stage.
To give you an idea of the specific light schedules recommended for different strains, here’s a table outlining the typical timing and duration of light exposure for four popular types of cannabis:
| Cannabis Strain | Vegetative Stage | Flowering Stage |
|---|---|---|
| Indica | 18 hours of light per day | 12 hours of light per day |
| Sativa | 12-16 hours of light per day | 12 hours of light per day |
| Hybrid | 16-18 hours of light per day | 12 hours of light per day |
| Auto-flowering | 18-24 hours of light per day | 18-24 hours of light per day |
It’s important to note that these are just general guidelines, and there may be some variation depending on the specific strains you’re growing. It’s always a good idea to do some research on the specific light requirements of your strains before creating a light schedule.
In addition to the number of hours of light per day, it’s also important to pay attention to the timing of your light exposure. During the vegetative stage, you’ll want to give your plants their light during the daytime hours, while providing them with a period of total darkness during the night.
During the flowering stage, it’s important to ensure that your plants receive their 12 hours of light and 12 hours of darkness on a consistent schedule each day. This means avoiding any interruptions to the dark period, such as opening the grow room door or shining a light on your plants during their “nighttime.”
By carefully considering the timing and duration of light exposure for your cannabis plants, you can ensure that they receive the optimal light schedule for their specific needs.
Experimentation and Observation
When it comes to optimizing the light schedule for different cannabis strains, experimentation and observation is key. There are a lot of factors to consider, and what works for one strain may not work for another. Here are some tips for experimenting and observing to determine the best light schedule for your plants:
- Start with a baseline: Begin by following the recommended light cycle for the specific strain you are growing. This will give you a starting point to work with.
- Make small adjustments: Rather than drastically changing the light schedule all at once, make small adjustments and observe the plants’ response. For example, if you want to increase the amount of light your plants are getting each day, try adding just 15 minutes at a time and monitor their growth.
- Keep detailed records: Take notes on any changes you make to the light schedule, as well as the plants’ response. This will help you identify patterns and make more informed decisions moving forward.
- Observe plant behavior: Look for signs of stress or growth. If plants are becoming too tall and spindly, this may indicate they need more light. Conversely, if you notice burning or yellowing of leaves, the plants may be getting too much light.
- Consider environmental factors: Remember that other factors like temperature, humidity, and air flow can also impact the plants’ response to light. Be sure to keep these factors consistent as you experiment with the light schedule.
- Be patient: Remember that plants can take time to respond to changes in light schedule, so be patient and give them time to adjust before making further adjustments.
By consistently experimenting, keeping detailed records, and observing your plants’ response, you can fine-tune the light schedule to optimize growth and yield for the specific cannabis strains you are growing.
Troubleshooting Common Light Schedule Problems
As much as we strive for the perfect light schedule for our cannabis plants, problems can still arise. Despite our best efforts, issues like light burn, lack of light, and light stress can hinder plant growth and diminish yields. It can be frustrating to encounter these problems, but they can be overcome with the right approach. In this section, we will discuss common light schedule problems and how to troubleshoot them effectively. By understanding these issues and how to address them, we can maintain healthy plants and achieve optimal results.
Light Burn
One common problem that growers may encounter when optimizing light schedules for cannabis plants is light burn. This occurs when plants are exposed to too much light, resulting in damage to the leaves and stunting of growth.
Light burn can be identified by yellowing and browning of the leaves, as well as curling and crisping of the edges. In some cases, the burnt leaves may also have white patches or blisters.
To prevent light burn, it is important to select appropriate light sources and adjust the distance between the plants and the light as needed. This can be done by measuring the intensity of the light using a lux meter and keeping it below the recommended level for the specific stage of growth.
It is important to gradually increase the duration and intensity of light exposure over time instead of exposing the plants to high levels of light immediately. This allows the plants to adapt to the light and prevent damage from occurring.
If light burn does occur, it is important to address the issue immediately by adjusting the light schedule and/or distance from the light to prevent further damage. Affected leaves may need to be trimmed or pruned to prevent the spread of damage to other parts of the plant.
It is also important to address any underlying issues that may be contributing to light burn, such as nutrient deficiencies, heat stress, or pest infestation. By addressing these issues, growers can prevent future occurrences of light burn and promote healthy growth of their cannabis plants.
Below is a table summarizing the causes, symptoms, and solutions of light burn in cannabis plants:
| Cause | Symptom | Solution |
| Excessive light intensity | Yellowing, browning, curling, crisping, white patches or blisters | Adjust distance from light, gradually increase exposure over time, trim/prune affected leaves |
| High temperature | Brown spots or patches, dry and brittle leaves | Lower temperature, improve ventilation and air flow |
| Nutrient deficiency | Yellowing, browning, spots, stunting of growth | Adjust nutrient mix, pH levels and feeding schedule |
| Pest infestation | Yellowing, spotting, curling, stunting of growth, visible pests | Identify and eliminate pests, improve plant hygiene and pest prevention |
Lack of Light
When it comes to growing cannabis, one of the most common problems that cultivators face is a lack of light. This can happen for a variety of reasons, such as a failure in the lighting system, plants being grown in a location with insufficient natural light, or simply not providing the cannabis plants with enough light.
Signs of Lack of Light
If your cannabis plants are not receiving enough light, they may exhibit a number of signs. One of the most noticeable indications of a lack of light is stunted growth. Plants that are not receiving sufficient light will fail to grow at their expected rate, resulting in smaller plants with thinner stems and fewer leaves.
Another sign that your cannabis plants may be experiencing a lack of light is yellowing of the leaves. This is because plants require light to create chlorophyll, which is a crucial component of photosynthesis. Without enough chlorophyll, the leaves will begin to turn yellow and eventually die.
Addressing Lack of Light
If you notice signs of a lack of light in your cannabis plants, there are several steps you can take to try and remedy the situation.
One of the easiest solutions is to simply adjust the light source. If you are using artificial grow lights, make sure they are positioned correctly and are emitting the proper amount of light for the stage of growth your plants are in. If you are relying on natural light, consider moving your plants to a sunnier location or investing in supplemental lighting.
Another step you can take is to adjust the timing and duration of light exposure. Cannabis plants have different light requirements depending on their stage of growth, so make sure you are providing the appropriate amount of light for the plant’s current needs.
Finally, it’s important to ensure that your cannabis plants are receiving adequate nutrients, as healthy plants are better able to tolerate the stress of a lack of light. Consider using fertilizers that are specifically formulated for cannabis, and monitor your plants closely for any signs of distress.
Preventing Lack of Light
Of course, the best way to address a lack of light in cannabis plants is to prevent it from occurring in the first place. This means carefully planning your grow setup to ensure that your plants are receiving the appropriate amount of light throughout their growth cycle.
Consider investing in quality grow lights that are appropriate for the type of cannabis you are growing, and make sure they are positioned correctly and emitting enough light for your plants’ needs. If you are growing outdoors, choose a location that receives ample sunlight throughout the day.
By being proactive in optimizing your light schedule, you can help ensure that your cannabis plants receive the light they need to thrive and produce a bountiful harvest.
Light Stress
Light stress can occur when plants receive too much light, which can lead to bleaching or burning of the leaves. On the other hand, insufficient light can cause stretched out and weak stems. It’s crucial to strike a balance and ensure that the light schedule is optimized for the specific strain being grown.
| Signs of Light Stress | Causes of Light Stress |
|---|---|
| Bleached leaves | Too much light intensity |
| Brown or burned spots on leaves | Light source too close to plants |
| Wilting or drooping leaves | High temperatures caused by too much light exposure |
| Slow growth or stunted plants | Insufficient light intensity or duration |
To avoid light stress, it’s important to monitor the plants regularly and adjust the light schedule accordingly. If signs of light stress are noticed, the grower may need to reduce the light intensity or distance from the light source, or decrease the duration of light exposure. It’s also important to ensure that the growing environment is properly ventilated to prevent heat buildup.
When optimizing the light schedule, it’s crucial to consider the growth stage of the plants, the available light sources, and the growing environment. Experimentation and observation are also key to finding the ideal light schedule for each specific strain. By avoiding light stress and optimizing the light schedule, growers can ensure a healthy and abundant harvest.
Conclusion
In conclusion, optimizing the light schedule for different cannabis strains plays a crucial role in achieving maximum growth and yield. Understanding photoperiodism, light cycles, growth stages, available light sources, growing environments, timing, and duration of light exposure are all important factors to consider when developing a light schedule for your cannabis plants.
It’s important to note that different strains have different light requirements, which is why it’s essential to research and understand your particular strain’s needs. Indica strains, for example, typically require more darkness during their flowering stage, while sativa strains may require a longer period of light exposure to reach their full potential.
It’s also important to experiment and observe your plants as they grow under different light schedules to determine what works best for your specific environment and strain. Troubleshooting common light schedule problems such as light burn, lack of light, and light stress is also important to ensure your plants remain healthy and productive.
In conclusion, optimizing the light schedule for your cannabis plants can take some trial and error but is well worth the effort in achieving optimal growth and yield. Remember to keep an open mind, research your strain, observe your plants, and adjust your light schedule accordingly. With a little effort and patience, you can achieve a bountiful and healthy crop.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is photoperiodism in cannabis plants?
Photoperiodism is the response of cannabis plants to changes in the amount of light they receive. It influences the plant’s growth and development, especially during the flowering stage.
What are the different light cycles for cannabis plants?
The most common light cycles for cannabis plants are 18/6 (18 hours of light and 6 hours of darkness) for vegetative growth and 12/12 (12 hours of light and 12 hours of darkness) for flowering.
What is the optimal light schedule for indica strains?
Indica strains thrive with a 12/12 light cycle during the flowering stage, while a 18/6 light cycle is ideal for vegetative growth.
What is the optimal light schedule for sativa strains?
Sativa strains require more light than indica strains. A 12/12 light cycle during the flowering stage, and a 20/4 or even 24/0 light cycle during the vegetative stage can boost their growth and productivity.
What is the optimal light schedule for hybrid strains?
Hybrid strains are a blend of indica and sativa genetics, so their ideal light schedule will depend on which side is dominant. In general, a 12/12 light cycle during the flowering stage and a 18/6 or 20/4 light cycle during vegetative growth can work for most hybrid strains.
What is the optimal light schedule for auto-flowering strains?
Auto-flowering strains require less light than photoperiod strains since they do not depend on light cycle to trigger the flowering stage. A 18/6 light cycle is suitable for the entire life cycle of auto-flowering strains.
How do I determine the growth stage of my cannabis plants?
The growth stage of cannabis plants can be determined by observing their physical characteristics such as the number of nodes, the shape and size of leaves, and the presence of buds. A plant can be in the vegetative stage or flowering stage.
What are some available light sources for indoor cannabis growing?
LED, fluorescent, and HID lights are popular options for indoor cannabis growing. Each has its pros and cons regarding spectrum, intensity, and energy efficiency.
What should I consider when choosing a light schedule for my cannabis plants?
Factors to consider include the growth stage of your plants, environmental conditions, available light sources, timing and duration of light exposure, and experimentation and observation. Each strain has a specific light requirement, but some strains may also have different phenotypes that could affect their response to light.
How do I troubleshoot light schedule problems in my cannabis plants?
Light burn, lack of light, and light stress are common problems that can result from improper light schedule. To address these issues, you may need to adjust the distance between your plants and light sources, improve the quality and intensity of light, provide better ventilation and humidity control, and reduce or increase the light exposure duration.