The Importance of Micronutrients in Cannabis Cultivation
For cannabis cultivators, achieving optimal yield and potency of their crop is essential. However, many factors can impede their success, one of which is the lack of essential nutrients that cannabis plants require to thrive. One group of these essential nutrients is called micronutrients, which are frequently overlooked and underestimated by growers. Understanding the role of micronutrients in cannabis cultivation is imperative for obtaining high-quality yields. In this article, we will delve into the significance of micronutrients, how to identify and correct their deficiencies, and how to maximize their potential to produce the best possible outcome for your cannabis crop.
What Are Micronutrients?
Contents
As a cannabis cultivator, it’s essential to have a basic understanding of the different types of nutrients your plants need to thrive. While macronutrients like nitrogen, potassium, and phosphorus are often the focus of many feeding schedules, micronutrients are equally important for healthy plant growth. Micronutrients are essential plant nutrients that are required in much smaller quantities than macronutrients but are nonetheless crucial for plant development. They include elements such as iron, zinc, nickel, manganese, and copper, among others. Let’s delve deeper into the importance of micronutrients in cannabis cultivation.
Why are they important?
Micronutrients are essential for the proper growth and development of cannabis plants. They are called “micro” because they are required in small quantities, but that does not diminish their importance. Here are some reasons why they are important:
- Enzyme activity: Micronutrients are involved in the production and activity of enzymes that carry out various metabolic processes in the plant.
- Chlorophyll production: Micronutrients such as iron (Fe) and magnesium (Mg) are important components of chlorophyll, the pigment that gives plants their green color and is necessary for photosynthesis.
- Cell division and expansion: Micronutrients like boron (B) and zinc (Zn) are required for proper cell division and expansion, which are necessary for plant growth.
- Resistance to stress: Micronutrients help plants resist environmental stressors such as extreme temperatures and drought.
- Disease resistance: Micronutrients play a crucial role in the plant’s ability to defend against pests and diseases.
Micronutrients are critical to the overall health and growth of cannabis plants. Without them, plants can become stunted, weak, and vulnerable to pests and diseases. Understanding the role of micronutrients in cannabis cultivation is essential for growers to produce high-quality and abundant yields.
The role of micronutrients in cannabis cultivation
Micronutrients play a crucial role in cannabis cultivation, as they are essential for the proper growth, development, and overall health of the plant. Without an adequate supply of micronutrients, the cannabis plant cannot reach its full potential and may experience stunted growth, reduced yields, and even death.
In the table below, we’ll explore the specific roles of each micronutrient and their importance in cannabis cultivation.
| Micronutrient | Role | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Boron (B) | Facilitates cell division and membrane function | Important for reproductive growth and seed production |
| Iron (Fe) | Necessary for chlorophyll synthesis and energy production | Essential for photosynthesis and overall plant growth |
| Manganese (Mn) | Involved in the breakdown of carbohydrates and nitrogen metabolism | Aids in root development and stress tolerance |
| Zinc (Zn) | Needed for proper enzyme function and protein synthesis | Improves plant immunity and resistance to disease |
| Copper (Cu) | Assists in photosynthesis, respiration, and protein metabolism | Regulates the absorption and utilization of other nutrients |
| Molybdenum (Mo) | Required for nitrogen fixation and enzyme activity | Enhances plant growth and overall yield |
| Chlorine (Cl) | Involved in photosynthesis and water regulation | Helps maintain proper turgor pressure and osmotic balance |
As you can see, each micronutrient serves a specific function in the cannabis plant, and a deficiency in any one of them can cause problems with growth and overall health. Micronutrients are especially important during the flowering stage, when the plant is producing buds and requires extra nutrients to support increased growth and resin production. It is crucial to provide your cannabis plants with a balanced and complete nutrient regimen that includes all essential micronutrients.
Common Micronutrient Deficiencies
As a cannabis cultivator, it’s essential to understand the various micronutrient deficiencies that can occur in your plants. These deficiencies can affect the growth, yield, and overall health of your cannabis crop. Without proper attention to micronutrient levels, your plants may become stressed, discolored, and stunted. But how can you identify these deficiencies and what causes them in the first place? In this section, we’ll delve into the intriguing topic of micronutrient deficiencies, explore their visual identification, and discuss how nutrient lockout can affect your yields. We’ll also uncover the causes of these deficiencies in both soil and hydroponic mediums. So, let’s dive deep into the fascinating world of micronutrients in cannabis cultivation.
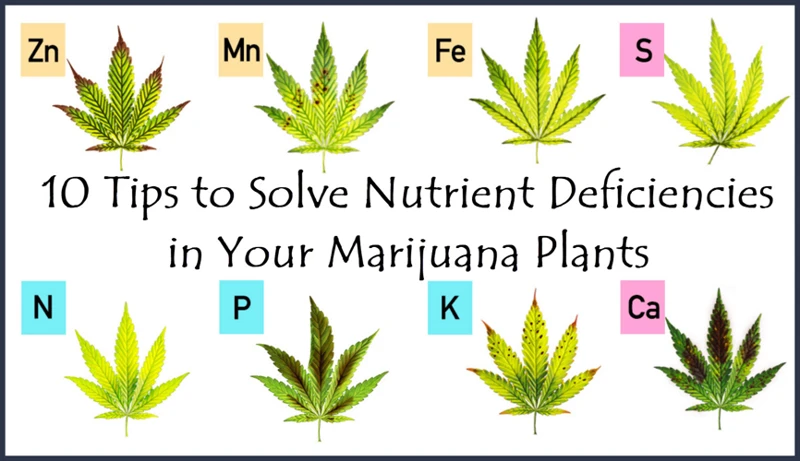
Visual identification of micronutrient deficiencies
One way to identify micronutrient deficiencies in cannabis plants is by visually inspecting the leaves for certain symptoms. Here is an overview of the symptoms associated with common micronutrient deficiencies:
| Micronutrient | Deficiency Symptoms |
|---|---|
| Iron (Fe) | Yellowing between the veins of new growth leaves (interveinal chlorosis) |
| Manganese (Mn) | Yellowing between the veins of old growth leaves |
| Zinc (Zn) | Yellowing between the veins of new growth leaves, stunted growth and distorted leaves |
| Boron (B) | Brittle stems, distorted growth, yellowing of leaves, and necrosis |
| Molybdenum (Mo) | Yellowing of leaves (similar to nitrogen deficiency) |
It is important to note that the symptoms of micronutrient deficiencies can be similar to other types of nutrient deficiencies or plant stress. It is important to also rule out other potential causes of plant stress before assuming a micronutrient deficiency is the issue. Identifying micronutrient deficiencies visually may not always be accurate, so soil and water testing is recommended for more accurate results.
Nutrient lockout and how it affects yields
Nutrient lockout is a phenomenon that occurs when a plant is unable to absorb essential micronutrients due to an excess of other minerals in the soil or water. This can lead to plant stress, reduced growth rates, and ultimately, lower yields.
To understand how nutrient lockout works, it’s important to know that plants can only absorb nutrients in certain forms. For example, iron is only available to plants in the ferrous form (Fe2+), but in alkaline soil (pH above 7.0), it can become oxidized to the ferric form (Fe3+), which is unavailable to plants. Similarly, an excess of calcium or magnesium can compete with other micronutrients for absorption, leading to deficiencies.
Here’s an example html table that shows some common causes and effects of nutrient lockout:
| Cause of Nutrient Lockout | Effect on Plant |
|---|---|
| High pH levels | Iron deficiency |
| Excess calcium or magnesium | Zinc or iron deficiency |
| Excess nitrogen | Phosphorus deficiency |
| Over-watering | Reduced root growth |
To avoid nutrient lockout, it’s important to monitor the pH level of your soil or water regularly and make adjustments as needed. Additionally, over-fertilization should be avoided, as excess nutrients can build up and compete with micronutrient absorption.
If you suspect nutrient lockout, it’s important to take action quickly to prevent further damage to your plants. pH adjustments, flushing the soil or growing medium with water, and applying chelated micronutrients can all be effective strategies for correcting nutrient imbalances.
Nutrient lockout is an important consideration for cannabis cultivators looking to maximize their yields and maintain healthy plants. By understanding the causes and effects of nutrient lockout, growers can take steps to prevent deficiencies and ensure their plants have access to the micronutrients they need to thrive.
Causes of micronutrient deficiencies in soil
In soil cultivation, a range of factors can cause micronutrient deficiencies in cannabis plants. Here are some of the most common causes and how they affect plant growth:
| Cause | Description |
|---|---|
| Soil pH | If the soil pH is too high or too low, the plant may not be able to absorb certain micronutrients. For example, a pH level of below 6.0 can lead to iron deficiency, while a pH level of above 7.0 can cause zinc and copper deficiencies. |
| Overfertilization | When too much fertilizer is added to the soil, it can cause a nutrient imbalance in the plant. Excess nitrogen can cause deficiencies in other micronutrients, as well as inhibit the uptake of phosphorus and potassium. |
| Underfertilization | If the soil lacks essential nutrients, it can affect the plant’s ability to grow and develop properly. This is especially true of micronutrients, which are required in smaller quantities but are still crucial for plant health. |
| Soil texture | Certain soil types, such as clay soils, may bind micronutrients and prevent them from being available for plant uptake. Sandy soils, on the other hand, may drain too quickly and not hold onto micronutrients for long enough. |
| Water quality | Water that is high in salts, chlorine, or other contaminants can affect the plant’s ability to absorb micronutrients. This can lead to deficiencies even if the soil contains adequate amounts of the necessary nutrients. |
By understanding the causes of micronutrient deficiencies in soil, growers can take steps to mitigate these issues and ensure that their cannabis plants have access to all the nutrients they need for healthy growth. pH management, proper fertilization, soil amendment, and water quality testing are all important considerations for avoiding micronutrient deficiencies in soil-grown cannabis.
Causes of micronutrient deficiencies in hydroponics
When it comes to hydroponic systems, there are a few different factors that can lead to micronutrient deficiencies. Here are some of the most common causes to be aware of:
- Incorrect pH Levels: One of the key factors in preventing micronutrient deficiencies in hydroponics is maintaining the correct pH levels. If the pH is too high or too low, the plant may struggle to absorb certain nutrients, including micronutrients.
- High Levels of Other Nutrients: In a hydroponic system, it’s important to carefully monitor the levels of all nutrients, not just micronutrients. If levels of other nutrients like nitrogen or potassium are too high, it can create competition for micronutrients, leading to deficiencies.
- Unstable Water Conditions: Hydroponic systems rely on a stable water supply to deliver nutrients to plants. If conditions like water temperature, oxygenation, or flow rate are inconsistent or unstable, it can lead to issues with nutrient uptake and micronutrient deficiencies.
- Low-Quality Nutrient Solution: The nutrient solution used in hydroponic systems should contain all of the micronutrients a plant needs. If the solution is low-quality or doesn’t contain the right ratios of nutrients, it can lead to deficiencies.
- Contaminated Water or Nutrient Solution: Finally, it’s important to ensure that the water and nutrient solution used in a hydroponic system are free from contaminants like bacteria or heavy metals. These can interfere with nutrient uptake and lead to deficiencies.
These are just a few examples of the various factors that can contribute to micronutrient deficiencies in hydroponics. It’s crucial to carefully monitor all aspects of a hydroponic system and take steps to correct any issues that arise in order to maximize plant growth and health.
How to Identify Micronutrient Deficiencies
As a cannabis cultivator, it’s important to keep a watchful eye for any signs of nutrient deficiencies that could harm your plants. Micronutrients play a crucial role in the growth and development of your crops, and even a small deficiency can have a big impact on your final yield. That’s why it’s important to learn how to properly identify micronutrient deficiencies to effectively address them. In this section, we will explore various ways to identify micronutrient deficiencies ranging from visual cues to soil and water testing, so you can take proactive measures to keep your cannabis healthy and thriving.
Visual cues
One of the easiest ways to identify micronutrient deficiencies in your cannabis plants is by paying close attention to their physical appearance. Here are some visual cues to look out for:
- Chlorosis: This is a condition where the leaves of the plant turn yellow or pale, indicating a lack of chlorophyll. Depending on the specific micronutrient deficiency, the chlorosis may appear in different areas of the plant. For example, iron deficiency typically causes chlorosis in new growth, while sulfur deficiency affects older leaves first.
- Necrosis: This refers to the death of plant tissue, characterized by brown or black spots or patches on the leaves or other parts of the plant. Micronutrient deficiencies can cause necrosis in different ways; for example, a boron deficiency can cause small, round necrotic spots, while a zinc deficiency can cause a more diffuse browning of the leaf tissue.
- Stunting: If your plants seem undersized or are growing more slowly than expected, this could be a sign of micronutrient deficiencies. For example, a copper deficiency can lead to stunting in the early stages of growth.
- Distortion: If your plants are exhibiting unusual shapes or growth patterns, this could be a sign of micronutrient deficiencies. For example, a manganese deficiency can cause leaves to curl downwards, while a calcium deficiency can cause distorted or misshapen new growth.
It is important to note that these visual cues can be easy to misinterpret or misdiagnose, so it is important to confirm your suspicions with additional testing.
Soil and water testing
Soil and water testing is an important step in identifying micronutrient deficiencies in cannabis plants. It can help growers determine which micronutrients are lacking or present in excess, allowing for the appropriate adjustments to be made to the grow environment.
Soil Testing: Soil testing involves taking a sample of the soil and sending it to a lab for analysis. The lab will provide a detailed report on the soil’s pH level, nutrient levels, and any potential toxicities. This information can help growers determine which micronutrients are lacking and which may need to be adjusted.
Water Testing: Water testing is another important aspect of identifying micronutrient deficiencies. Cannabis plants require a specific pH range for optimal growth and nutrient absorption. If the water pH is not within this range, it can lead to nutrient deficiencies. A water test can determine the pH level and other parameters such as dissolved oxygen, electrical conductivity, and total dissolved solids.
Benefits of Soil and Water Testing: Testing soil and water can help prevent micronutrient deficiencies before they occur. By identifying potential deficiencies early on, growers can adjust their feeding regimen and prevent nutrient lockout. Additionally, soil and water testing can help save money and resources by preventing over-fertilization or over-watering.
| Benefits of soil and water testing: |
|---|
| Identify potential micronutrient deficiencies |
| Prevent nutrient lockout |
| Prevent over-fertilization and over-watering |
Soil and water testing is an essential tool for any cannabis grower looking to optimize their crop’s growth and yield. By identifying micronutrient deficiencies and making the necessary adjustments, growers can ensure that their plants are getting everything they need to reach their full potential.
Eliminating other potential causes of plant stress
When trying to diagnose a micronutrient deficiency, it’s important to eliminate other potential causes of plant stress. There are several factors that can cause stress to a cannabis plant, including:
- Environmental stressors: such as temperature fluctuations or high humidity levels
- Pest infestations: such as spider mites or aphids
- Diseases: such as powdery mildew or root rot
- Root problems: such as over or under watering, or improper drainage
All of these factors can contribute to stunted growth, discoloration or spotting on leaves, and other symptoms that may mimic a micronutrient deficiency. To ensure that you’re correctly identifying the issue, it’s important to address any other potential causes of stress.
For example, if the leaves are showing signs of discoloration, it could be a result of over or under watering, or even root rot. In this case, it may be necessary to adjust the watering schedule or address any drainage issues before adding any additional nutrients to the soil or water.
Similarly, if there are signs of pest infestations, it’s important to address the infestation before introducing additional nutrients. Pests can cause significant stress to the plant and may also introduce diseases, which can cause additional damage.
By eliminating other potential causes of stress, you can ensure that you’re accurately diagnosing a micronutrient deficiency and properly addressing the issue.
Correcting Micronutrient Deficiencies
One of the most significant challenges in cannabis cultivation is managing micronutrient deficiencies. These deficiencies can arise due to various factors, including soil quality, water quality, pH imbalances, and nutrient imbalances. When left unaddressed, micronutrient deficiencies can lead to stunted plant growth, decreased yields, and poor quality buds. In this section of the article, we will explore the different methods for correcting micronutrient deficiencies and maximizing the growth and yield of cannabis plants.
Should you use synthetic or organic nutrients?
When it comes to choosing between synthetic and organic nutrients for your cannabis plants, there are various factors to consider. Let’s compare these two types of nutrients side by side in the table below:
| Synthetic Nutrients | Organic Nutrients | |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Chemically formulated nutrients with precise ratios of macronutrients and micronutrients. | Nutrients derived from natural sources such as compost, bone meal, and fish emulsion. |
| Availability of Nutrients | Quick and immediate availability of nutrients, but can also cause nutrient lockouts and imbalances. | Nutrients are released slowly over time and may be less immediately available to plants, but promote healthy soil and microbial activity. |
| Impact on Flavor and Potency | Synthetic nutrients may result in larger yields, but can also reduce flavor and potency of the final product if overused. | Organic nutrients can enhance the aroma and flavor of the final product, but may result in lower yields if not used correctly. |
| Environmental Impact | Synthetic nutrients can have negative environmental impacts if not properly disposed of, and may contribute to harmful run-off and water pollution. | Organic nutrients are typically more environmentally sustainable, but must still be used responsibly and with consideration for localized environmental factors. |
Ultimately, the choice between synthetic and organic nutrients comes down to personal preference and the specific needs of your plants. Consider the above factors and weigh the pros and cons carefully before making a decision. It is also important to note that a combination of both types of nutrients can be beneficial for maximizing plant growth and yield.
Applying micronutrients through the soil or foliar spray
When it comes to applying micronutrients to your cannabis plants, there are two main methods: through the soil or via foliar spray. Each method has its own benefits and drawbacks, and choosing the right method depends on your specific goals and cultivation practices.
Applying micronutrients through the soil
One of the most common ways to apply micronutrients to your cannabis plants is through the soil. This is done by adding the nutrients directly to your grow medium, either by using fertilizers that contain micronutrients or by adding them to the soil separately. When using this method, it’s important to ensure that the nutrients are well-mixed and distributed evenly throughout the soil to avoid burning or over-fertilizing your plants in certain areas.
Applying micronutrients via foliar spray
Another method of applying micronutrients is through foliar spray. This involves spraying a micronutrient solution directly onto the leaves of your cannabis plants using a sprayer. The leaves absorb the micronutrients, and they are then transported throughout the plant via the vascular system. This method is particularly beneficial for quickly correcting micronutrient deficiencies, as it allows for rapid absorption and utilization by the plant.
However, it’s important to note that foliar sprays can also be less effective than soil applications in some cases, as some micronutrients are less mobile in the plant and may not be distributed as evenly via foliar spray. Additionally, foliar sprays can sometimes result in burns or damage to the leaves if not applied properly.
Choosing the right method
Ultimately, the method you choose for applying micronutrients will depend on a variety of factors, including the specific micronutrient deficiencies you’re trying to correct, your growing medium and cultivation practices, and your overall goals for your cannabis plants. Consulting with a reputable cannabis cultivation expert or doing your own research can help you make the best decisions for your own unique situation.
Dosage and application timing
When it comes to dosing and timing the application of micronutrients, there are a few key things to keep in mind:
- Follow nutrient package instructions: Each brand of micronutrients will have slightly different instructions for dosing and application timing. It is important to follow these instructions carefully to avoid over or under-dosing your plants.
- Start with a low dose: Even if the package instructions recommend a certain dose, it is a good idea to start with a lower amount and gradually increase it over time. This will help you avoid over-dosing your plants, which can cause nutrient burn and other problems.
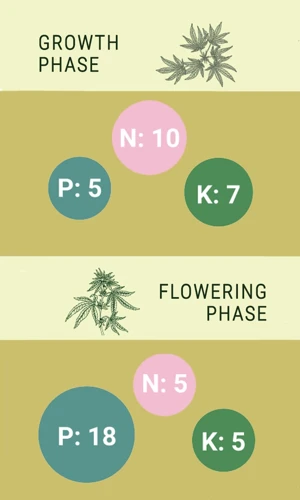
- Consider the stage of growth: Different micronutrients are needed at different stages of your plants’ growth. For example, during the vegetative stage, plants need more nitrogen, while during the flowering stage, they need more phosphorus and potassium. Make sure you are using the right micronutrients for each stage of growth.
- Apply at the right time: The timing of micronutrient application can also affect how well they work. For example, foliar sprays are most effective when applied early in the morning or late in the evening, when the stomata of the leaves are open. Applying micronutrients too late in the day can result in them evaporating before they can be absorbed by the plant.
- Monitor your plants: Keep a close eye on your plants to ensure they are responding well to the micronutrient supplements. Look for signs of over- or under-dosing, such as burnt or wilted leaves, and adjust your dosing or timing accordingly.
By following these tips for dosing and application timing, you can help ensure that your plants are getting the micronutrients they need to thrive without risking damage from over-dosing or improper application.
Maximizing Your Yield with Micronutrients
As a cannabis cultivator, you likely want to maximize your yields while also improving the quality of your harvest. One crucial strategy for achieving these goals is by utilizing micronutrients. By providing your plants with the necessary trace elements they need, you can help your crop reach its full potential. In this section, we will explore several ways in which you can leverage micronutrients to boost your cannabis yield, potency, and flavor. From preventative measures to optimizing growth and combining with other supplements, we will cover a range of techniques to help you get the most out of your cultivation efforts.
Preventative measures to avoid micronutrient deficiencies
To prevent micronutrient deficiencies in your cannabis plants, it’s crucial to establish a proper nutrient management plan. Here are some preventative measures you can take to ensure your plants get all the micronutrients they need:
1. Start with quality soil or hydroponic system: Make sure your growing medium is nutrient-rich and pH balanced. This will provide your plants with a good foundation and reduce the risk of deficiencies.
2. Use a balanced nutrient system: Choose a nutrient system that contains all the necessary micronutrients, in addition to macronutrients. Be sure to follow the manufacturer’s instructions for mixing and application rates to avoid over or underfeeding.
3. Monitor pH levels: Micronutrient availability is heavily influenced by the pH level of the soil or hydroponic solution. Keep a close eye on pH levels and adjust as necessary to keep them within the optimal range for your plants.
4. Avoid overwatering: Overwatering can lead to nutrient leaching and create an environment that is unfavorable for nutrient uptake. Make sure your plants are receiving adequate water, but not so much that the soil or growing medium becomes waterlogged.
5. Ensure proper lighting and temperature: Light and temperature can also impact nutrient uptake. Make sure your plants are receiving the appropriate amount and intensity of light for their growth stage, and that the temperature is within the optimal range for your strain.
By implementing these preventative measures, you can significantly reduce the risk of micronutrient deficiencies in your cannabis plants. Remember to monitor your plants regularly for any signs of nutrient deficiencies and adjust your nutrient management plan accordingly.
Using micronutrients to improve potency, flavor, and aroma
In addition to preventing micronutrient deficiencies, cannabis cultivators can use these elements to enhance the qualities of their crop. Micronutrients such as iron, magnesium, and sulfur have a direct impact on the aroma and flavor profiles of the plant. Iron is especially important for the production of terpenes, compounds responsible for the distinctive scent of each strain. Magnesium is involved in the production of chlorophyll and helps to improve the overall health of the plant.
Moreover, calcium, boron, and zinc have been shown to increase the potency of cannabis. Calcium and boron play a role in cell wall formation and strengthening, which can lead to higher resin production. Zinc is involved in the production of enzymes responsible for synthesizing THC, the primary psychoactive compound in cannabis.
Using micronutrients to enhance aroma, flavor, and potency is a nuanced process that requires careful attention to dosage and application timing. Cultivators should conduct soil and water tests to determine which micronutrients are already present and adjust their supplementation accordingly. Combining micronutrients with other supplements, such as beneficial bacteria or mycorrhizal fungi, can also help to maximize their effects.
By prioritizing the use of micronutrients in their cultivation process, cannabis growers can not only prevent deficiencies and improve the health of their plants but also enhance the sensory experience and the potency of their final product.
Combining micronutrients with other supplements to optimize growth
One way to optimize growth in cannabis cultivation is by combining micronutrients with other supplements. This can provide a comprehensive approach to plant nutrition, ensuring that all necessary elements are delivered to the plant in the appropriate quantities.
Beneficial microbes: Adding beneficial microbes to the growing medium can help improve nutrient uptake and plant health, as well as enhance soil structure and fertility. For example, mycorrhizal fungi can form a symbiotic relationship with the plant roots, facilitating the uptake of micronutrients.
Hormones and enzymes: Supplements such as hormones and enzymes can stimulate root growth and nutrient uptake, improving overall plant growth and yield. For instance, cytokinins can stimulate cell division and promote healthy foliage, while enzymes like chitinase can help protect the plant from pests and diseases.
Organic matter: Incorporating organic matter into the soil can improve soil structure, water retention, and nutrient availability. Compost, for example, can provide a source of micronutrients as well as beneficial microbes for the plant.
Foliar sprays: Applying micronutrients as a foliar spray can improve nutrient uptake and photosynthesis, leading to greater plant growth and yield. Combining micronutrients with other supplements, such as kelp extract or humic acid, can further enhance plant health and vigor.
Combining micronutrients with other supplements can be an effective strategy for optimizing growth in cannabis cultivation, but it’s important to use these products in moderation and follow the manufacturer’s instructions for application. Overuse of supplements can lead to nutrient imbalances or toxicity in the plant, so it’s important to monitor the plant’s response and adjust accordingly.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the role of micronutrients in cannabis cultivation is crucial for maximizing yields and improving potency, flavor, and aroma. Micronutrient deficiencies can significantly impact the growth and health of cannabis plants, leading to stunted growth, reduced yields, and even plant death.
Visual identification of micronutrient deficiencies is a valuable tool, but soil and water testing can also provide valuable insights into plant health. Additionally, eliminating other potential causes of plant stress can help identify micronutrient deficiencies more accurately.
Correcting micronutrient deficiencies requires careful consideration, as the use of synthetic or organic nutrients may have different effects on plant growth and yield. Proper dosage and application timing are also crucial to avoid nutrient lockout and prevent other issues.
Preventative measures such as regular testing, proper pH monitoring, and using quality soil or hydroponic solutions can help avoid micronutrient deficiencies. Using micronutrients in combination with other supplements, such as beneficial microbes and enzymes, can provide a comprehensive approach to optimizing plant growth.
In conclusion, proper understanding and application of micronutrients can enhance the overall productivity and quality of your cannabis garden. By addressing and correcting micronutrient deficiencies, you can ensure that your plants receive the necessary nutrients to thrive and produce the desired yield and quality.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the most common micronutrients needed for cannabis growth?
The most common micronutrients needed for cannabis growth are iron, zinc, manganese, copper, boron, and molybdenum.
What is the role of iron in cannabis cultivation?
Iron is a crucial micronutrient in the production of chlorophyll and plays a vital role in photosynthesis.
Can a lack of micronutrients cause stunted growth in cannabis plants?
Yes, the absence of micronutrients can lead to stunted growth, decreased yields, and even death of the plant.
What is the optimal pH range for cannabis plants to absorb micronutrients?
The optimal pH range for cannabis plants to absorb micronutrients is between 5.5 and 6.5.
What causes nutrient lockout in cannabis cultivation?
Nutrient lockout is caused by imbalanced pH levels, excessive use of fertilizers, or mineral build-up in the soil, which prevents nutrients from being taken up by the plant.
What is the difference between synthetic and organic micronutrients?
Synthetic micronutrients are chemically derived and can be quickly absorbed by plants, while organic micronutrients are naturally occurring and slower to release but can provide long-term benefits to the soil.
Is foliar spray an effective method of applying micronutrients to cannabis plants?
Yes, foliar spray is a useful method of applying micronutrients as it allows for quick absorption through the leaves, which can provide immediate relief to the plant.
What is the recommended dosage for applying micronutrients to cannabis plants?
The recommended dosage for applying micronutrients varies depending on the nutrient and the stage of growth. It is essential to follow the manufacturer’s instructions and avoid overfeeding the plant.
What can be done to prevent micronutrient deficiencies in cannabis plants?
Regular soil and water testing, maintaining balanced pH levels, and providing a nutrient-rich growing environment can help prevent micronutrient deficiencies.
Can micronutrients be used to enhance the flavor and aroma of cannabis buds?
Yes, using micronutrients such as magnesium, sulfur, and calcium can help enhance the flavor and aroma of cannabis buds.