Composting vs. Chemical Fertilizers: Which is Best for Your Cannabis Plants?
Growing cannabis plants can be a rewarding experience, but choosing the right nutrients can be daunting. With so many options available, it can be challenging to know which method to use for optimal growth. Composting and chemical fertilizers are two popular choices, each with their own pros and cons. Composting is a natural and sustainable approach to providing nutrients, while chemical fertilizers can offer faster and more precise results. In this article, we’ll examine the differences between composting and chemical fertilizers, their respective advantages and disadvantages, and discuss which method is best for your cannabis plants. Let’s dive in and explore the world of cannabis nutrients!
What are composting and chemical fertilizers?
Contents
Before we delve into the pros and cons of composting and chemical fertilizers for your cannabis plants, let’s first define what these terms mean. Composting is the process of breaking down organic matter into a nutrient-rich soil amendment. Chemical fertilizers, on the other hand, are synthetic or man-made nutrients that are added to the soil to provide plants with essential elements needed for growth. While both options aim to nourish your plants, there are significant differences between the two approaches that are worth exploring.
Composting
Composting is the process of breaking down organic matter into a nutrient-rich soil amendment. The resulting material, known as compost, is an essential component for organic gardening and sustainable agriculture. Composting involves using a combination of ‘green’ and ‘brown’ materials, which are then broken down through microbial activity.
The ingredients for composting can be broken down into two categories:
| Green Materials | Brown Materials |
| Grass clippings | Leaves |
| Vegetable scraps | Twigs and branches |
| Coffee grounds | Shredded paper and cardboard |
| Eggshells | Straw |
The benefits of composting for cannabis plants include:
- Improved soil structure
- Increased water holding capacity
- Enhanced nutrient availability
- Improved soil biodiversity
- Reduced need for chemical fertilizers
However, there are also some downsides to composting that must be considered:
- Composting can be time-consuming, as it can take several months for the materials to fully break down
- It may be difficult to maintain the proper balance of green and brown materials, which can impact the quality of the compost
- If not done properly, composting can attract pests and produce unpleasant odors
Despite these challenges, many organic cannabis growers still prefer using compost as a natural, sustainable method of fertilization. By using composting methods, they can reduce their environmental impact while still producing healthy, high-quality plants.
Chemical fertilizers
Chemical fertilizers are synthetic mixtures of nutrients that are designed to provide quick and effective plant growth. They are often made from inorganic sources, such as rocks and minerals, and are manufactured through a chemical process.
The Pros of Chemical Fertilizers:
| Pros | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Quick-acting | Chemical fertilizers are designed to work fast, providing a readily available source of nutrients for plants to absorb. |
| Precise nutrient formulation | Manufactured fertilizers contain a precise blend of nutrients that are tailored to specific types of plants, ensuring they get the correct balance of nutrients they require for optimal growth. |
| Cost-effective | Chemical fertilizers are often cheaper than organic alternatives and are widely available in nurseries and garden centers. |
The Cons of Chemical Fertilizers:
| Cons | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Harmful environmental impact | Some chemical fertilizers contain high levels of salts that leach into groundwater and cause pollution. Overuse can lead to soil acidification and make it difficult for beneficial organisms to thrive. |
| Can damage soil quality | Constant use of synthetic fertilizers can deplete the soil of its natural nutrients and organic matter, which are critical for healthy plant growth. This can lead to compacted and nutrient-deficient soil that is hard to work with and decreases yields over time. |
| Can be harmful to plants if over-applied | Applying too much chemical fertilizer can cause root burn, which can damage or kill plants. The high salt content in some fertilizers can also cause root dehydration and stunt growth. |
Chemical fertilizers offer quick and targeted nutrition for cannabis plants. However, they should be used judiciously and with caution to avoid harming the environment and plants themselves. It is recommended to use a blend of both organic and synthetic fertilizers to achieve optimal plant growth and maintain healthy soil.
The Pros and Cons of Composting
When it comes to growing cannabis plants, choosing the right nutrients is essential for a successful crop. One option is to use composting, which is the process of decomposing organic matter to create a natural fertilizer for plants. While composting has several benefits, it also has some drawbacks to consider. Let’s take a closer look at the pros and cons of using composting as a nutrient source for your cannabis plants.
Pros
Composting offers several benefits for cannabis plants compared to chemical fertilizers. Here are some of the top reasons to consider composting:
- Improves Soil Health: Composting adds organic matter to the soil, improving soil structure and water-holding capacity. This helps the plant absorb nutrients and water more efficiently.
- Provides Nutrients: Compost is rich in nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. These naturally occurring nutrients are released slowly over time, providing a steady supply of nutrition for the plants.
- Environmentally Friendly: Composting is a sustainable practice that reduces waste and greenhouse gas emissions. It also helps to prevent water pollution and soil contamination by reducing the use of chemical fertilizers.
- Reduces Costs: Composting can be done at home using kitchen scraps and yard waste, which helps to reduce the cost of buying chemical fertilizers.
- Improves Flavor and Aroma: Compost-grown cannabis is known to have a richer flavor and aroma compared to chemically fertilized cannabis.
Composting is a natural and sustainable way to provide the essential nutrients needed for healthy cannabis plants, while also improving soil and environmental health.
Cons
Composting has some drawbacks that may make it unsuitable for some cannabis growers. Some of the cons of composting are:
- Slow release: Composting is a slow process that can take several weeks to several months to produce nutrient-rich soil. This can be a major disadvantage for growers who need to provide nutrients quickly to their cannabis plants.
- Inconsistent nutrient levels: The nutrient levels in compost can vary depending on the sources of the organic materials used, making it difficult to know the exact nutrient content of the soil.
- Quality control: Composting requires proper monitoring to ensure that the soil is free from pathogens and harmful chemicals. If done incorrectly, composting can introduce pests, diseases, and toxins into the soil.
- Smell: Composting can produce an unpleasant odor that may be offensive to some people. This can be a concern for growers who live in areas with close neighbors or for those who need to maintain a discreet grow operation.
While composting may not be the best option for all cannabis growers, it can still provide many benefits for those willing to put in the time and effort to make their own compost.
The Pros and Cons of Chemical Fertilizers
When it comes to fertilizing your cannabis plants, chemical fertilizers have some benefits and drawbacks to consider. While they can be easier to use and provide quick results, they can also harm the environment and may not offer the same long-term benefits as natural composting. Let’s take a closer look at the pros and cons of chemical fertilizers for cannabis cultivation.
Pros
Composting has several advantages that make it a great option for growing healthy cannabis plants. Here are some of the pros of composting:
| Natural Soil Amendment | Composting is a natural way to amend the soil and provide essential nutrients to cannabis plants. Unlike chemical fertilizers, which may contain harmful toxins, compost is completely organic and safe for the environment. |
| Improves Soil Structure | Composting can improve the soil structure and increase its ability to retain water. This can help prevent soil erosion and improve drainage, which is essential for growing healthy cannabis plants. |
| Reduces Waste | Composting helps divert organic waste from landfills, reducing the amount of greenhouse gases produced by decomposing waste. By composting kitchen scraps and yard waste, cannabis growers can reduce their carbon footprint and contribute to a more sustainable future. |
| Cost-Effective | Composting is a cost-effective way to provide nutrients to cannabis plants. Instead of buying expensive chemical fertilizers, cannabis growers can create their own compost at home using everyday organic waste. |
Composting is a great way to provide natural, organic nutrients to cannabis plants while reducing waste and minimizing environmental impact. By improving soil structure and retaining water, compost can help ensure healthy growth and maximum yields.
Cons
While composting has many benefits, it also has some drawbacks that should be considered before deciding to use it as the primary method of fertilizing cannabis plants. The cons of composting can be summarized in the following table:
| Cons of Composting |
|---|
| Slow Release of Nutrients |
| Requires Space |
| May Contain Weed Seeds and Pathogens |
| Potentially Unpleasant Odors |
Slow Release of Nutrients: While composting is a great source of nutrients for cannabis plants, it releases these nutrients slowly over time. This can be problematic for plants that require more immediate attention and rapid uptake of nutrients.
Requires Space: Composting requires space, both for the compost pile itself and for the materials needed to create it. For those without access to outdoor space, composting may not be a viable option.
May Contain Weed Seeds and Pathogens: Composting relies on the breakdown of organic matter, which means that it can potentially contain weed seeds and pathogens that can harm cannabis plants. It is important to ensure that compost is thoroughly aged and pasteurized before using it as a fertilizer.
Potentially Unpleasant Odors: As organic matter breaks down during the composting process, it can produce unpleasant odors. While these odors are natural and usually harmless, they can be an issue for those living in close proximity to the compost pile.
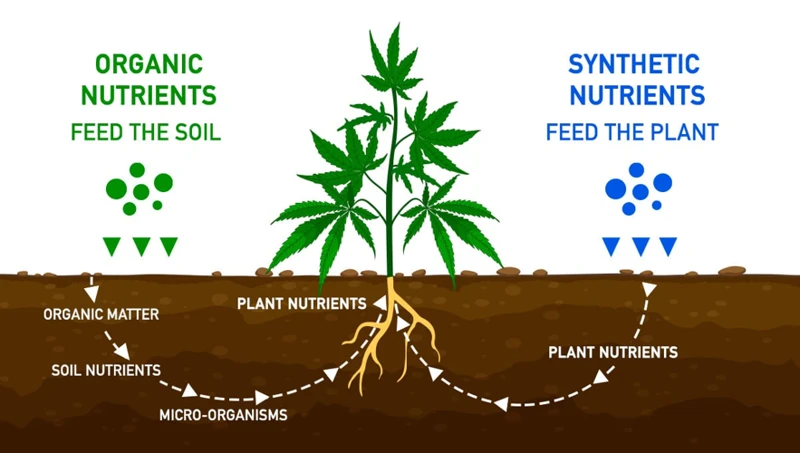
Organic vs. Synthetic Nutrients
When it comes to providing nutrients for your cannabis plants, there are two main options to consider: organic and synthetic nutrients. Each option has its own set of advantages and disadvantages, and deciding which one to use can be perplexing. Organic nutrients are derived from natural sources and can be an excellent way to promote healthy growth, but they can also be more challenging to use. On the other hand, synthetic nutrients are created using chemical processes and are generally easier to use, but they may not be as environmentally friendly. In this section, we will delve deeper into the differences between organic and synthetic nutrients to help you make an informed decision on which one is best for your cannabis plants.
Organic Nutrients
Organic nutrients are derived from natural sources such as animal waste, plant matter, and rock powders. These nutrients are often preferred by cannabis growers who prioritize producing high-quality, environmentally-friendly cannabis.
Here are a few examples of organic nutrients:
- Blood meal: This is a powerful source of nitrogen that is derived from animal blood.
- Bone meal: This organic fertilizer is made from ground animal bones and contains calcium and phosphorus.
- Compost: This is made from decomposed organic matter such as food scraps, leaves, and plant matter. It’s extremely rich in nutrients and can be used as a soil amendment or top dressing.
- Kelp meal: This is a type of seaweed that is high in micronutrients and minerals like potassium, magnesium, and iron.
- Rock phosphate: This is a type of mineral powder that is high in phosphorus and can improve plant growth and root development.
Advantages of using organic nutrients:
- Environmentally friendly: Organic nutrients break down slowly and don’t leach into the soil, which means they don’t contribute to environmental pollution in the same way that chemical fertilizers do.
- Boost soil health: Organic nutrients can help improve soil structure and fertility, which can lead to healthier cannabis plants with stronger root systems.
- Better taste: Many cannabis connoisseurs believe that organic-grown cannabis tastes better than cannabis that’s grown with chemical fertilizers.
Disadvantages of using organic nutrients:
- Slow release: Organic nutrients break down slowly, which can make it difficult to get nutrients to the plants quickly when they need them.
- Potential for pathogens: Using organic matter in soil can increase the likelihood of bacterial or fungal growth, which can be problematic for cannabis plants.
- More expensive: Organic nutrients are often more expensive than chemical fertilizers because they require more labor to produce and harvest.
Choosing organic nutrients is a personal preference for each cannabis grower. It’s important to consider the advantages and disadvantages before making a decision about what to use for your cannabis plants.
Synthetic Nutrients
Synthetic nutrients, also known as chemical fertilizers, are man-made and produced through various chemical processes. These nutrients are designed to provide specific ratios of essential nutrients to support plant growth. Synthetic nutrients usually come in a concentrated liquid or powder form, making them easy to mix with water and apply directly to the plant’s roots.
One advantage of synthetic nutrients is that they provide a precise and predictable ratio of essential nutrients that are important for plant growth. These nutrients are typically formulated to target specific growth stages, such as vegetative growth or flowering, which can help maintain optimal plant health and improve overall yield.
Another benefit of synthetic nutrients is that they are very efficient and easy to use. They are typically water-soluble, which means they can be easily absorbed by the plant’s roots, providing a quick nutrient uptake. Synthetic nutrients tend to have a longer shelf life than organic nutrients, which can save growers money in the long run.
However, there are also several disadvantages to using synthetic nutrients. One major concern is that they can be harmful to the environment if not used properly. Overuse of synthetic nutrients can lead to nutrient pollution, which can result in the depletion of oxygen in water bodies, causing harm to aquatic life.
Synthetic nutrients can also lead to a buildup of salts in the soil, which can lead to nutrient lockout, hindering nutrient uptake and creating a toxic environment for the plant.
Here is a table summarizing the pros and cons of using synthetic nutrients:
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Provides precise and predictable ratios of essential nutrients. | Can be harmful to the environment if not used properly. |
| Efficient and easy to use. | Can lead to nutrient lockout and toxic soil buildup. |
| Can improve overall yield. |
To sum up, while synthetic nutrients can offer efficient and precise ratios of essential nutrients to support plant growth, they can also be harmful to the environment if not used properly. It is important for growers to carefully follow application and dosage instructions and to be aware of the potential risks of overuse.
When to Use Composting and When to Use Chemical Fertilizers
Choosing between composting and chemical fertilizers can be a difficult decision for cannabis growers. Both have their advantages and disadvantages and the decision largely depends on the specific needs of the cannabis plants.
Composting is best used for long-term, slow-release nutrient supply. This means that it is ideal for outdoor grows in soil. The compost releases nutrients over time and helps to improve soil structure and water retention. Composting is also a great choice for organic growers who want to maintain an environmentally friendly approach to growing. It is a sustainable and cost-effective way to provide nutrients to plants.
Chemical fertilizers, on the other hand, are a more precise and customizable way of providing nutrients to cannabis plants. They are ideal for indoor growers who want to control every aspect of the grow, including nutrient intake. Chemical fertilizers can provide a significant boost to plant growth and can be adjusted to meet the changing needs of plants throughout the various stages of growth. However, chemical fertilizers can also potentially harm the environment if not used responsibly.
It’s important to consider the specific needs of the cannabis plants when deciding between composting and chemical fertilizers. Factors to consider include the type of growing environment (indoor vs. outdoor), growing medium (soil vs. hydroponics), and the desired outcome for the plants (increased yield or environmentally friendly approach). Ultimately, a combination of both composting and chemical fertilizers may be the best approach for some growers, as it allows for the benefits of both methods to be utilized.
How to Use Composting
When it comes to using composting for your cannabis plants, the process may seem intimidating at first. But with the right knowledge and techniques, composting can be a simple and effective way to provide your plants with the nutrients they need to thrive. In this section, we’ll break down the different composting methods and discuss how to properly apply compost to your cannabis plants. So, let’s get started on your journey towards healthier and happier plants!
Composting Methods
Composting Methods
There are several different methods of composting that you can try, depending on the materials you have available and the amount of time and effort you want to put into the process. Here are a few of the most popular methods:
- Traditional composting: This involves piling up your organic matter in a designated area, such as a compost bin or a corner of your garden. You can add a variety of materials, including kitchen scraps, yard waste, and shredded paper. Over time, the materials will break down naturally and turn into nutrient-rich compost that can be used to fertilize your cannabis plants.
- Vermicomposting: This method involves using worms to break down your organic matter. You can purchase a worm bin or make one yourself by drilling holes in a plastic container and adding bedding material, such as shredded newspaper. Then add your kitchen scraps and let the worms do their work. They will eat the scraps and excrete nutrient-rich castings, which can be used as fertilizer.
- Trench composting: If you prefer to avoid the hassle of turning and maintaining a compost pile, trench composting is a good option. Simply dig a trench in your garden and fill it with your organic matter. Cover it up with soil and let it decompose over time. You can then plant your cannabis directly over the decomposing material, which will continue to release nutrients into the soil as the plants grow.
- Composting with a tumbler: A compost tumbler is a cylindrical bin that you can rotate to mix and aerate your organic matter. This method can be faster than traditional composting, as you can create a more consistent mixture and speed up the decomposition process. However, tumblers can be expensive and may not be practical for large amounts of organic matter.
No matter which method you choose, it’s important to make sure your compost gets enough air and moisture to break down effectively. You can also add activators, such as compost starter or manure, to speed up the process. And always avoid adding any materials that could be harmful to your plants, such as treated wood or pet waste. By following these tips and experimenting with different methods, you can create high-quality compost that will help your cannabis plants thrive.
Application
To apply compost to your cannabis plants, there are a few methods you can use. It’s important to note that compost should be fully decomposed before application, otherwise it can harm your plants.
One common method is top-dressing, which involves sprinkling a thin layer of compost on top of the soil around your plants. This can be done every few weeks throughout the growing season to provide a slow-release of nutrients.
Another method is to mix the compost directly into the soil before planting. This ensures that the compost is evenly distributed and can provide nutrients to the roots as the plant grows. Mixing in a ratio of 1:3 (compost to soil) is recommended to avoid overloading the soil with nutrients.
Using compost tea is another option for application. To make compost tea, soak compost in water for a few days, strain the liquid, and dilute with water. This can then be used to water your plants and provide nutrients directly to the soil.
When applying chemical fertilizers, it’s important to follow the instructions carefully and avoid over-fertilizing. Too much fertilizer can lead to nutrient burn and damage to your plants.
One method is to mix the fertilizer into the soil before planting, similar to compost application. It’s important to measure and mix the fertilizer as instructed to avoid over-fertilizing.
Another method is to use a liquid fertilizer and apply it directly to the soil or as a foliar spray. This can provide a quick boost of nutrients to your plants.
It’s important to note that chemical fertilizers can be harmful to the environment if not used properly. Always follow the instructions and dispose of excess fertilizer responsibly.
Application Method | Composting | Chemical Fertilizers
— | — | —
Top-Dressing | Sprinkle a thin layer around the plant every few weeks | N/A
Mixing into Soil | Mix in a ratio of 1:3 (compost to soil) before planting | Mix as instructed before planting
Compost Tea | Soak compost in water for a few days, strain, and dilute with water to use as a nutrient-rich watering solution | N/A
Liquid Fertilizer | N/A | Apply directly to soil or as a foliar spray, according to instructions
How to Use Chemical Fertilizers
If you’ve decided to go the chemical fertilizer route for your cannabis plants, it’s important to understand how to use them correctly. While the application process itself may seem straightforward, there are a few important factors to keep in mind to ensure you’re not over-fertilizing or causing nutrient imbalances. In this section, we’ll cover the different types of chemical fertilizers available, how to properly apply them, and how to determine the correct dosage for your specific cannabis strain. So, let’s dive in and explore the world of chemical fertilizers!
Types of Chemical Fertilizers
There are several types of chemical fertilizers that can be used for cannabis plants. It is important to understand their differences in order to choose the right one for your specific needs. Here are some of the most common types:
- Nitrogen-based fertilizers: Nitrogen is one of the most important nutrients that cannabis plants need. Nitrogen-based fertilizers tend to be fast-acting and provide an immediate boost to the plant’s growth.
- Phosphorus-based fertilizers: Phosphorus is another essential nutrient for cannabis plants, particularly during the flowering phase. Phosphorus-based fertilizers can help promote stronger root growth and flower production.
- Potassium-based fertilizers: Potassium is important for overall plant health and can improve the plant’s ability to resist disease and pests. Potassium-based fertilizers can also help improve the plant’s stress tolerance.
- Compound fertilizers: Compound fertilizers typically contain a mix of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, as well as other micronutrients. These fertilizers are designed to provide a balanced nutrient profile and promote overall plant health.
- Time-release fertilizers: Time-release fertilizers, also known as slow-release fertilizers, are designed to release nutrients slowly over a period of time. These fertilizers can be useful for growers who want to provide a steady supply of nutrients without having to apply fertilizer as frequently.
- Foliar fertilizers: Foliar fertilizers are applied directly to the leaves of the plant. They can be a quick way to provide nutrients to the plant, but they may not be as effective as soil-based fertilizers in promoting long-term growth.
It is important to choose the right type of chemical fertilizer for your specific growing situation. Keep in mind that overuse of chemical fertilizers can lead to nutrient burn and other problems, so it is important to follow the recommended dosage and application instructions carefully. It may also be beneficial to incorporate organic fertilizers and other supplements into your feeding regimen to promote a healthier and more sustainable growing environment for your cannabis plants.
Application and Dosage
When using chemical fertilizers for cannabis plants, it is important to carefully follow the instructions on the label. Different types of fertilizers have different recommended dosage rates and application methods. Here are some general guidelines to keep in mind when using chemical fertilizers:
- Start with a small dose: It is always better to start with a smaller dosage than recommended and gradually increase it to avoid over-fertilization.
- Pay attention to the N-P-K ratio: N-P-K stands for Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Potassium, which are the three main nutrients required for plant growth. Make sure to choose a fertilizer with the right N-P-K ratio for your plants’ needs. For cannabis plants during the vegetative stage, a fertilizer with higher levels of nitrogen is usually recommended, while during the flowering stage, higher levels of phosphorus and potassium are preferred.
- Consider using a pH meter: Chemical fertilizers can alter the pH level of the soil, which can affect nutrient absorption. It is recommended to test the pH level of the soil before and after fertilizing and adjust it if necessary.
- Apply evenly: Follow the label instructions on how to apply the fertilizer and make sure to spread it evenly around the base of the plants to avoid over-fertilizing some areas and under-fertilizing others.
- Water properly: Watering your plants after applying the fertilizer can help distribute the nutrients evenly and prevent any potential burn or damage to the roots. Make sure to water the plants until the soil is moist but not waterlogged.
Remember that over-fertilizing can be harmful to your cannabis plants, so it is always better to err on the side of caution and start with a lower dosage. Pay attention to your plants and adjust the dosage accordingly if you notice any signs of nutrient deficiencies or excesses.
Composting vs. Chemical Fertilizers: Environmental Impact
As cannabis cultivation continues to expand, concerns about its environmental impact are becoming increasingly important. Both composting and chemical fertilizers have their own unique effects on the environment, and it’s important to understand how each method impacts the ecosystem. While composting is often touted as the more environmentally friendly option, the reality is a bit more complicated. On the other hand, chemical fertilizers have been criticized for their potential negative impact, but they also have their benefits. Let’s take a closer look at the environmental impact of composting and chemical fertilizers for cannabis cultivation.
Composting
Composting is a natural process of breaking down organic materials into a nutrient-rich soil amendment. This process is achieved through the use of microorganisms, such as bacteria and fungi, which break down the organic matter.
How to Compost?
There are several methods of composting, including hot composting, cold composting, and worm composting. Hot composting is the fastest method, where the compost pile is kept between 131-170°F (55-77°C) to speed up the decomposition process. Cold composting, on the other hand, is a slower process where organic matter is left to decompose naturally over time. Worm composting, also known as vermicomposting, is a method that involves using worms to break down the organic matter into compost.
Benefits of Composting
There are many benefits of using compost for growing cannabis plants. Compost is a natural fertilizer that provides a broad spectrum of nutrients to the plant, including nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. Compost also improves soil structure and water retention, making it easier for the plants to access the nutrients they need. Additionally, compost is an environmentally friendly alternative to chemical fertilizers, as it reduces waste and improves soil health.
Drawbacks of Composting
Composting does have some drawbacks, however. The process can take time, as the organic matter needs to break down properly before it can be used as compost. Additionally, compost may not provide specific nutrients in the exact ratios that cannabis plants need, making it difficult to achieve optimal growth if used as the sole source of nutrients. Finally, it can be difficult to control the exact nutrient profile of compost, as it relies on the breakdown of whatever organic matter is available.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Environmentally friendly | Takes time to produce |
| Improves soil structure and water retention | May not provide specific nutrient ratios |
| Reduces waste | Difficult to control nutrient profile |
Chemical Fertilizers
Chemical fertilizers are synthetic nutrients that are made from inorganic compounds. These fertilizers are designed to provide fast and efficient nutrients to plants. Chemical fertilizers can be either water-soluble or time-release fertilizers.
Advantages
One of the biggest advantages of chemical fertilizers is their ability to provide plants with the exact nutrients they need in the right amounts. This can result in faster growth and higher yields. Chemical fertilizers are often less expensive than organic fertilizers.
Disadvantages
There are several disadvantages to using chemical fertilizers. Because they are made from synthetic compounds, they can have negative effects on the environment. For example, excess nitrogen and phosphorous from chemical fertilizers can run off into waterways and cause algal blooms, which can be harmful to aquatic ecosystems. Overuse of these fertilizers can lead to soil degradation, making it more difficult for plants to grow in the future. Finally, chemical fertilizers can also have negative effects on the flavor and aroma of crops, especially cannabis.
Comparison with Composting
When it comes to choosing between chemical fertilizers and composting, it is important to consider the pros and cons of each method. While chemical fertilizers can provide plants with precise nutrients and are often less expensive, they can have negative effects on the environment and on the quality of the final product. On the other hand, composting can improve soil quality, promote healthy plant growth, and ultimately produce better-tasting and more flavorful cannabis. However, composting can be more time-consuming and may require more effort than simply applying chemical fertilizers.
Common Myths About Composting and Chemical Fertilizers
As with many topics related to agriculture and gardening, there are plenty of myths and misconceptions surrounding composting and chemical fertilizers. Some people may believe that composting is too complicated and time-consuming, while others may assume that chemical fertilizers are always harmful to the environment. However, the truth is not always so black and white. In this section, we will explore some of the most common myths about composting and chemical fertilizers, and shed light on what’s really fact versus fiction.
Myth #1: Composting is complicated and time-consuming
There is a common myth that composting is complicated and time-consuming but that is not entirely true. While it may require some effort and patience, the benefits of composting outweigh the initial investment of time and resources.
The truth about composting is that it is a natural process that occurs with the help of microorganisms and decomposition. By providing the right environment and ingredients, such as food scraps, yard waste and aeration, these microorganisms help break down organic matter into a rich, nutrient-dense soil amendment for your cannabis plants.
Here are some common misconceptions about composting:
| Myth | Reality |
|---|---|
| Composting takes too much time | While it may take some time for the compost to fully decompose, the process itself is relatively hands-off. Simply add your organic materials to a compost bin or pile, give it some air and water, and let nature do the rest. |
| Composting is messy and smelly | With proper management, composting should not produce any foul odors or attract pests. It is important to balance your compost with the right ratio of greens and browns, and to turn the compost regularly to increase airflow and prevent stagnation. |
| Composting requires a large outdoor space | While having a large outdoor space is certainly helpful, composting can be done on a smaller scale using a compost tumbler or even a worm bin. These methods are ideal for those with limited outdoor space or who live in apartments. |
| Composting is only for experienced gardeners | Composting is a simple and natural process that can be done by anyone, regardless of their gardening experience. There are plenty of resources available online or at your local gardening store to help guide you through the process. |
By debunking these myths about composting, we can see that it is an accessible and eco-friendly way to nourish your cannabis plants.
Myth #2: Chemical fertilizers are always bad for the environment
There is a common myth that chemical fertilizers are always bad for the environment. However, like most myths, this is not entirely accurate. While it is true that some chemical fertilizers can have negative effects on the environment, not all of them do. Some organic fertilizers can also have negative effects on the environment if they are not used properly.
To better understand the impact of chemical fertilizers on the environment, it is important to look at the different types of fertilizers and how they are used. Some fertilizers, such as nitrogen-based ones, can lead to an excessive amount of nutrients in the soil, which can be harmful to the environment. This can cause algae blooms and oxygen depletion in bodies of water, leading to what is commonly known as “dead zones”.
On the other hand, some chemical fertilizers can actually be beneficial to the environment. For example, there are fertilizers that contain micronutrients that can help plants grow more efficiently and even improve soil quality in the long term. Additionally, chemical fertilizers can be formulated to target specific deficiencies in the soil, allowing for more efficient use of resources.
When it comes to the environment, the impacts of organic fertilizers should also be considered. Organic fertilizers come from natural sources, but if they are overused, they can also lead to nutrient imbalances and negative effects on the environment. Some organic fertilizers may contain pathogens or heavy metals, which can be harmful to both the environment and human health.
It is important to use any type of fertilizer, whether organic or synthetic, in moderation and with proper understanding of how it affects the environment. By taking a balanced approach and using the right type of fertilizer at the right time, we can grow healthy plants while minimizing our impact on the environment.
| Myth | Reality |
|---|---|
| Chemical fertilizers are always bad for the environment | While some chemical fertilizers can have negative effects on the environment, not all of them do. Some chemical fertilizers can even be beneficial if used properly. Organic fertilizers can also have negative effects if overused or contain harmful substances. |
Myth #3: Chemical fertilizers are always more effective than composting
There is a common myth that chemical fertilizers are always more effective than composting for growing cannabis plants. However, this is not always the case.
It is true that chemical fertilizers can produce faster results and provide specific nutrients in exact ratios. They can also be easier to use for novice growers who are less familiar with composting. However, chemical fertilizers can negatively impact the environment and deplete soil nutrients over time.
On the other hand, composting may require more time and effort, but it can produce a healthier, more sustainable growing environment for cannabis plants. Composting is an all-natural process that adds organic matter to the soil and promotes microbial growth. This can improve soil structure, moisture retention and nutrient availability.
To illustrate the differences between chemical fertilizers and composting, we can use the following table:
| Chemical Fertilizers | Composting |
|---|---|
| Provides specific nutrients in exact ratios | Naturally adds organic matter to the soil |
| Can negatively impact the environment and deplete soil nutrients over time | Improves soil structure, moisture retention, and nutrient availability |
| Faster results | Slower process but creates a healthier, more sustainable growing environment |
| Easy to use for novice growers | May require more time and effort to maintain |
Ultimately, the choice between chemical fertilizers and composting will depend on the specific needs and preferences of the grower. However, it is important to recognize that the myth that chemical fertilizers are always more effective than composting is not always true.
Tips for Growing Healthy Cannabis Plants
Growing cannabis plants can be a challenging task that requires a lot of patience and attention to detail. To achieve the best results, it’s essential to understand the basic needs of your plants and provide them with the right growing environment. In this section, we will provide some helpful tips on how to grow healthy cannabis plants that are strong, potent, and free from pests and diseases. By following these tips, you can ensure that your plants will flourish and provide you with a bountiful harvest.
Tip #1: Understand the basic needs of cannabis plants
To grow healthy cannabis plants, it is important to understand their basic needs. This includes providing the right amount of water, nutrients, and light. Below is a table outlining the basic needs of cannabis plants:
| Need | Description | Optimal Range |
|---|---|---|
| Water | Cannabis plants require regular watering to stay healthy and hydrated. | Soil moisture should be maintained between 50-70%. |
| Nutrients | Cannabis plants require a balance of macronutrients (nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium) and micronutrients (calcium, magnesium, zinc, etc.) for optimal growth. | Depends on growth stage and strain, but generally: Nitrogen (N) – 1.0-1.5 mS/cm, Phosphorus (P) – 0.8-1.2 mS/cm, and Potassium (K) – 1.5-2.5 mS/cm. |
| Light | Cannabis plants require specific types and amounts of light to grow and flower properly. | Vegetative stage: 16-18 hours of light per day; Flowering stage: 12 hours of light per day; Intensity ranging from 600-1000 µmol/m²s. |
By understanding and addressing these basic needs, cannabis growers can ensure their plants have the best chance of success. It is also important to regularly monitor and adjust these factors as needed throughout the plant’s growth cycle to ensure optimal growth and yield.
Tip #2: Use high-quality soil and growing containers
When it comes to growing healthy cannabis plants, tip number two is to use high-quality soil and growing containers. This is because the soil and container you choose can have a significant impact on the overall health and growth of your plants.
First and foremost, it’s important to choose a soil that is well-draining and nutrient-rich. Using a nutrient-rich soil will provide your plants with the necessary nutrients to grow, while a well-draining soil will prevent over-watering and root rot. Make sure to avoid soils that are too dense or too sandy.
In addition to the soil, it’s important to choose a high-quality growing container that provides adequate drainage and enough space for your plants to grow. This means avoiding containers that are too small, as they can restrict the growth of the roots and limit nutrient uptake.
One option for growing containers is fabric pots, which allow for air pruning and better oxygenation of the roots. Another option is to use traditional plastic or ceramic containers, but make sure they have ample drainage holes for excess water to escape.
Investing in high-quality soil and growing containers can make a significant difference in the health and growth of your cannabis plants. It’s worth taking the time to research and choose the best options for your specific needs.
Tip #3: Keep the environment optimal for growth
To ensure that your cannabis plants grow healthy and strong, it’s important to keep the environment optimal for their growth. This includes regulating the temperature, humidity, light, and air circulation.
Temperature – Cannabis plants thrive in moderately warm temperatures between 68-77°F (20-25°C) during the day and slightly cooler temperatures between 62-72°F (17-22°C) during the night. The temperature should be consistent throughout the grow space and should not fluctuate too much.
Humidity – The ideal humidity level for cannabis plants depends on the stage of growth. During the seedling stage, humidity should be high (around 70%) to promote root growth. During the vegetative stage, humidity should be medium (around 50-70%) to prevent mold and mildew. During the flowering stage, humidity should be low (around 30-40%) to prevent bud rot.
Light – Cannabis plants require a minimum of 12 hours of light per day to grow properly. During the vegetative stage, they require full spectrum lighting for around 18 hours per day. During the flowering stage, they require 12 hours of light per day, with the remaining 12 hours being dark.
Air Circulation – Proper air circulation is essential for healthy cannabis plants. It helps to prevent mold and mildew, promotes healthy growth, and strengthens the stems. Investing in a fan or two to improve air circulation can make a big difference.
By keeping these environmental factors in check, you can ensure that your cannabis plants have the best chance of thriving and producing big, healthy buds.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the choice between composting and chemical fertilizers largely depends on personal preference and the specific needs of your cannabis plants. While both options have their respective pros and cons, it’s important to consider the environmental impact and long-term implications of your chosen method.
Composting offers a natural and sustainable approach to providing nutrients for your plants, with the added benefit of improving soil quality over time. However, it can be more time-consuming and less precise than chemical fertilizers, and may not provide sufficient nutrients in certain circumstances.
On the other hand, chemical fertilizers can be more convenient and effective, providing specific nutrients in consistent doses. However, they can also be harmful to the environment and may lead to a buildup of salts in the soil over time, potentially affecting the quality and yield of your cannabis plants.
Ultimately, the decision to use composting or chemical fertilizers should be based on careful consideration of the benefits and drawbacks of each method, as well as an understanding of the specific needs of your plants. Whichever method you choose, it’s important to prioritize the health and sustainability of your cannabis cultivation practices.
By following the tips for growing healthy cannabis plants, you can ensure that your plants thrive and produce high-quality yields, regardless of the nutrient source you choose. With careful attention to your plants’ needs and a commitment to sustainable cultivation practices, you can achieve a successful and rewarding cannabis cultivation experience.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is composting better for the environment than using chemical fertilizers?
Yes, composting is considered a more sustainable and eco-friendly option as it uses natural ingredients that do not harm the soil or surrounding environment.
Are chemical fertilizers more effective than composting?
Not necessarily. While chemical fertilizers may provide quicker results, composting can improve soil health and produce more nutrient-rich plants in the long run.
Can composting be used for growing cannabis plants?
Yes, composting can be a great option for growing cannabis plants, as it provides natural nutrients that can enhance growth and yield.
Are there any downsides to using composting for cannabis plants?
One potential downside is that composting requires time and effort to create, which may not be suitable for those who need quick results. Additionally, improper composting can lead to nutrient imbalances and other issues.
Can synthetic nutrients be used in combination with composting?
Yes, synthetic nutrients can be used alongside composting to enhance plant growth and ensure a balanced nutrient profile. However, it’s important to use them in moderation to prevent nutrient burn or other negative effects.
How often should compost be applied to cannabis plants?
This depends on various factors, such as the type of compost and the specific needs of the plants. As a general guideline, compost can be applied every few weeks or as needed based on the growth rate and nutrient requirements of the plants.
What types of chemical fertilizers are available for cannabis plants?
There are various types of chemical fertilizers available, including those that are high in nitrogen, phosphorus, or potassium. Some popular options for cannabis plants include nitrogen-rich urea and phosphorus-rich superphosphate.
Can chemical fertilizers harm the environment or surrounding wildlife?
Yes, improper use or disposal of chemical fertilizers can harm the environment and wildlife, as they may contain harmful chemicals or cause nutrient imbalances. It’s important to use these products responsibly and follow proper application guidelines.
What is the optimal environment for growing cannabis plants?
Cannabis plants thrive in warm, humid environments with plenty of sunlight and proper ventilation. It’s important to maintain a consistent temperature and humidity level throughout the growing cycle, and to avoid exposure to extreme temperatures or pollutants.
How can I ensure the best possible yield for my cannabis plants?
To ensure a healthy yield for cannabis plants, it’s important to provide optimal growing conditions, use high-quality soil and nutrients, and follow proper watering and fertilization schedules. Additionally, monitoring for pests and diseases and providing adequate support through trellising or other methods can help ensure strong, healthy growth.