Chemical Pest Control for Healthy Cannabis Growth
Introduction
Contents
As cannabis continues to gain popularity both for recreational and medicinal uses, it is important to understand the role of chemical pest control in ensuring healthy plant growth. By using pesticides, growers can protect their plants from various pests that can cause damage or even death to the plants. However, in order to use chemical pest control effectively, it is important to understand the different types of pesticides, factors to consider when using them, application methods, and alternative pest control methods. In this article, we will explore all of these aspects of chemical pest control and how they can be used to optimize cannabis growth.
What is Chemical Pest Control?
Chemical pest control refers to the use of certain chemicals to eliminate or curb the growth of pests in crops. This is a widely used method that is often preferred due to its effectiveness in managing pests. The use of chemicals in agriculture is not new and has been used for many years. However, with increased awareness of environmental sustainability, there has been an increase in the use of alternative pest control methods.
In chemical pest control, pesticides are used to control and manage pests. Pesticides contain chemicals that can be harmful to pests, but also have the potential to harm humans and beneficial insects if not used properly. There are different types of pesticides that are formulated to control specific pests, including insecticides, fungicides, and rodenticides.
Insecticides are chemicals that are used to control insects. They work by either killing the insects or interrupting their growth and reproduction. Fungicides, on the other hand, are used to control fungal infections that can affect the growth and development of crops. Rodenticides are used to control rodents that can destroy crops and contaminate food products.
While chemical pest control is effective, it is important to use it judiciously and responsibly. Overuse or misuse of pesticides can result in pest resistance and environmental contamination. It is important to choose the right type of pesticide for the target pest, apply it at the right time and in the right amount, and take necessary safety precautions.
In recent years, there has been increased interest in alternative pest control methods that are more environment friendly. These methods include organic pesticides, biological control, and cultural control. Nonetheless, chemical pest control remains an important tool for managing pests and ensuring healthy cannabis growth.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| – Effective in controlling pests | – Potential harm to beneficial insects |
| – Can be used to target specific pests | – Can result in pest resistance |
| – Quick results | – Environmental contamination if not used responsibly |
Why is Chemical Pest Control Important for Cannabis Growth?
Chemical pest control is crucial for cannabis growth due to several reasons:
- Pests can cause extensive damage to the plants, leading to stunted growth, decreased yield, and even plant death. This can result in significant financial losses for growers.
- Some pests can transmit diseases, both to the cannabis plant and to humans who consume the end product. This can pose a risk to public health and can have legal consequences for growers.
- Chemical pest control is often more effective and efficient than other methods, allowing growers to quickly address pest infestations and prevent further damage to their crops.
- Without proper pest control, growers may have difficulty achieving high-quality, consistent yields that meet industry standards.
Given the potential consequences of pest infestations, incorporating chemical pest control into a comprehensive pest management plan is essential for ensuring healthy cannabis growth and maximizing yields.
Types of Pesticides
Understanding the different types of pesticides available for pest control is an essential aspect of maintaining healthy cannabis growth. These chemicals are formulated to combat specific types of pests and diseases that can impact the plant’s growth and yield. Pesticides fall into three broad categories: insecticides, which target insects; fungicides, which combat fungal infections; and rodenticides, which are designed to control mice and other small rodents that can damage crops. Let’s explore each type of pesticide in more detail to gain a better understanding of their uses and effectiveness in cannabis cultivation.
Insecticides
Insecticides are chemical compounds that are specifically designed to kill or control insect pests that could harm the cannabis growers’ crops. These chemical substances are available in various forms such as sprays, baits, granules, and powders.
Contact insecticides act by killing insects upon contact with the pesticide. This type of insecticide is effective against pests like aphids and spider mites that remain on the plant’s surface.
Ingestion insecticides act upon being ingested by the pests. These types of insecticides are effective against chewing insects such as caterpillars and beetles.
Systemic insecticides are compounds that are absorbed by the plant and spread throughout the plant, protecting it from the inside out. These types of insecticides are known to be more effective and long-lasting than contact or ingestion insecticides.
When using insecticides, it is important to take note of the active ingredient of the pesticide. Different insecticides contain different active ingredients, and each has a specific target pest. It is recommended to use insecticides that have been specifically designed for cannabis plants and are safe for human consumption.
It is crucial to follow proper dosage, timing, and safety precautions when applying insecticides to cannabis plants. Overuse or misuse of insecticides can lead to pesticide buildup in the plants, rendering them unsafe for human consumption.
Lastly, it is essential to consider that some pests may develop a resistance to certain insecticides over time. In such cases, it is recommended to rotate the use of different types of insecticides to prevent resistance from developing.
Fungicides
Fungicides refer to chemicals designed to control fungal infections in cannabis plants. Fungal infections are a common problem in the cannabis cultivation process, and they can cause significant damage if left untreated. The use of fungicides in the early stages of a fungal infection can help prevent further spread and keep the plants healthy.
There are different kinds of fungicides available for use in cannabis cultivation. Contact fungicides act on fungal spores present on the surface of the plants, and they are applied as a spray directly on the leaves or stems. Systemic fungicides, on the other hand, are absorbed by the plant tissue and provide protection from fungal infections from the inside.
When applying fungicides in cannabis cultivation, it is crucial to consider the specific type of fungus affecting the plants. This will help in selecting the appropriate fungicide for use. Copper-based fungicides are particularly useful against powdery mildew, a common fungal infection in cannabis. Fungicides containing azoxystrobin are effective against botrytis, another fungal disease.
It is essential to read the instructions and follow the recommended dosage when using fungicides. Overuse or misuse of fungicides can lead to the development of resistance in the fungi, making it harder to control in the future. It is also worth noting that some fungicides may leave unwanted residues on the plants, which can affect their quality and safety.
In addition to using fungicides, it is helpful to implement preventive measures to minimize the risk of fungal infections. This includes keeping the grow area clean and hygienic, ensuring proper ventilation and air circulation, and avoiding overwatering the plants. These measures can help to create an environment less favorable for fungi to thrive.
The use of fungicides is an essential part of a comprehensive pest control strategy for cannabis cultivation. It helps to prevent the spread of fungal infections and ensure healthy plant growth. However, care must be taken to use the appropriate fungicides and follow the recommended dosage to avoid negative consequences.
Rodenticides
Rodenticides are chemical pesticides that are designed to control rodents such as rats and mice. These types of pesticides are highly effective in controlling rodent populations, but they can also pose a significant risk to other animals that may come into contact with the chemicals. When using rodenticides for cannabis growth, it is important to use them with caution and to follow all safety instructions.
There are several types of rodenticides available for use, including anticoagulants and non-anticoagulants. Anticoagulant rodenticides work by preventing blood from clotting, which ultimately leads to death. Non-anticoagulant rodenticides, on the other hand, affect the nervous system of rodents and can cause paralysis or death.
Factors to Consider:
When using rodenticides for cannabis growth, it is important to consider several factors to ensure their effectiveness and safety. These factors include:
- The type of rodent problem you are dealing with
- The location and severity of the infestation
- The potential risks to other animals and people in the area
- The type of rodenticide being used
- The dosage and application method
Application:
Proper application of rodenticides is essential to their effectiveness and safety. The dosage and application method will vary depending on the specific type of rodenticide being used, but it is important to follow all instructions carefully.
Safety Precautions:
When using rodenticides for cannabis growth, it is important to take appropriate safety precautions. These may include:
- Using protective equipment such as gloves and masks
- Keeping the rodenticides out of reach of children and pets
- Disposing of any leftover chemicals safely and responsibly
Rodenticides can be an effective tool for controlling rodent populations in cannabis growth, but they must be used with caution to avoid potential risks to other animals and people. It is important to carefully consider all factors before using rodenticides and to follow all safety instructions to ensure their effectiveness and safety.
Factors to Consider
When it comes to chemical pest control for cannabis growth, there are several factors that need to be taken into consideration before applying pesticides. Plant age, pest type, and growth environment are all important variables that can affect the effectiveness of the treatment. It’s crucial to determine the appropriate dosage, timing, and frequency of application in order to ensure the health and safety of both the plants and the individuals handling the pesticides. In this section, we will dive into these important factors and discuss their significance in more detail.
Plant Age
When it comes to chemical pest control for healthy cannabis growth, one important factor to consider is the age of the plant. Different types of pesticides can be used depending on the growth stage of the plant. Here are some things to keep in mind:
- Seedlings: Seedlings are very delicate and can be easily harmed by pesticides. Care must be taken to use pesticides that are safe for young plants, and to apply them carefully and sparingly.
- Vegetative Stage: During the vegetative stage, the plant is growing rapidly and can tolerate more pesticides. However, some pesticides can still harm the plant if not used correctly. It is important to follow the instructions carefully and not to use more than the recommended amount.
- Flowering Stage: During the flowering stage, the plant is more sensitive to pesticides, especially those that contain oils or other ingredients that can affect the quality of the buds. It is important to use pesticides that are specifically labeled for use on flowering plants, and to be careful not to damage the flowers or leave residue that could affect their potency.
In addition to the age of the plant, it is also important to consider the type of pest and the growth environment when choosing a pesticide. Different types of pests may require different types of pesticides, and factors such as temperature, humidity, and lighting can affect how well a pesticide works. By taking these factors into account, you can help ensure that your pesticide use is effective and safe for your cannabis plants.
Pest Type
When it comes to chemical pest control, understanding the type of pests that are affecting your cannabis plants is crucial in selecting the appropriate pesticide. There are various pests that can infest cannabis plants, including:
- Spider Mites: These tiny pests can cause significant damage to cannabis plants by sucking sap from the leaves, ultimately leading to discoloration and stunted growth.
- Aphids: Aphids can quickly reproduce and cause substantial damage to cannabis plants by feeding on the sap of leaves and stems.
- Thrips: Thrips are tiny insects that can severely damage cannabis plants by creating scars or silvering on the leaves, ultimately leading to deformed growth.
- Caterpillars: Caterpillars can chomp through cannabis leaves and buds, causing significant damage in a short amount of time.
- Whiteflies: Whiteflies can cause extensive damage to cannabis plants by feeding on the plant’s sap and carrying viruses.
Each of these pests requires a specific type of pesticide for effective control. For example, spider mites can be successfully countered by using miticides or a neem oil solution, while aphids can be controlled by using insecticidal soap or neem oil. Thrips, on the other hand, can be combated with insecticidal soap or neem oil, as well as pyrethrin-based insecticides.
It’s essential to correctly identify the type of pest on your cannabis plants to determine the most effective pesticide for control. Using the wrong pesticide can be ineffective and even harmful to your plants. It’s recommended that growers seek the advice of a professional if they are unsure of the pest type or the appropriate pesticide to use.
Growth Environment
The growth environment is one of the most important factors to consider when using chemical pest control for healthy cannabis growth. The environment in which the plant is grown can affect the effectiveness of the pesticide, as well as the safety of the plant and the surrounding area.
Temperature: The temperature of the grow room or outdoor environment can affect the efficacy of pesticide treatments. High temperatures can cause the pesticide to break down more quickly, leading to less effective control. On the other hand, extremely low temperatures can slow down the pests’ metabolism, leading to reduced pesticide absorption.
Humidity: Humidity is another important factor that can influence the effectiveness of pesticide treatments. High humidity can increase the chance of fungal diseases, which may require the use of fungicides. Conversely, low humidity can increase the risk of spider mite outbreaks, which require specific treatment.
Light: Light is another environmental factor that should be considered when using chemical pest control. Some pesticides degrade under intense light, which may affect their ability to control pests. Additionally, the amount and type of light the plant receives can affect its growth and vigor, which in turn can impact its ability to resist pest outbreaks.
Soil: The soil in which the cannabis plant is grown can also affect the efficacy of pesticides. For example, soil that is too dry or too wet can affect the absorption and distribution of the pesticide throughout the plant. Additionally, soil pH can impact the effectiveness of pesticides, as some pesticides work better in acidic soil while others are better suited for alkaline soil.
Air flow: The air flow in and around the growing environment can also impact pest control. Stagnant air can create pockets of humidity and encourage pest growth, while air that is too dry or too warm can impact pesticide effectiveness. Adequate ventilation can help to ensure that the pesticide is evenly distributed throughout the plant, while also reducing the risk of mold and mildew growth.
A careful consideration of the growth environment is crucial to ensure the safe and effective use of chemical pest control in cannabis cultivation. Proper management of environmental factors can help to prevent pest outbreaks and ensure that the pesticide is effective in controlling any pests that do occur.
Application
When it comes to chemical pest control in cannabis growth, proper application of pesticides is crucial for the safety and wellness of your plants. While pesticides are effective at eliminating pests, improper application can harm your plants and even pose health risks to those consuming the final product. It is vital to understand the right timing and frequency, dosage, and safety precautions when applying chemicals to your cannabis crops. In this section, we will cover everything you need to know about applying pesticides for cannabis growth.
Timing and Frequency
Timing and frequency are critical components of effective chemical pest control in cannabis cultivation. Different pests have different life cycles that make them more vulnerable to certain types of pesticides at specific times. Additionally, overuse of pesticides can lead to pests developing resistance and necessitating stronger, more toxic chemicals. It is important to carefully time and dose pesticide applications.
The timing and frequency of pesticide applications will depend on the pest being targeted and the pesticide being used. Generally, it is best to apply pesticides at the earliest signs of pest infestation to prevent them from spreading and causing damage. Frequent monitoring of plants is necessary to catch pests early and determine the appropriate course of action.
The table below provides some general guidelines for timing and frequency of pesticide applications for common pests in cannabis cultivation:
| Pest | Timing | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Spider Mites | During vegetative growth | Once weekly applications for 2-3 weeks |
| Aphids | At first sign of infestation | Two applications, 7-10 days apart |
| Thrips | During flowering stages | Two applications, 7-10 days apart |
| Caterpillars | During flowering stages | As needed, depending on infestation |
| Whiteflies | At first sign of infestation | Two applications, 7-10 days apart |
It is important to note that these guidelines are not comprehensive and that particular pesticide and pest combinations may require different timing and frequency adjustments. Additionally, it is important to follow the product label instructions and local regulations for safe and effective pesticide use.
Dosage
When it comes to chemical pest control for cannabis growth, the correct dosage is crucial. Using too much can not only harm the plant, but also leave harmful residues that can be dangerous to humans. On the other hand, using too little may not effectively control the pests and can also lead to the pests developing a resistance to the pesticide.
To determine the correct dosage, it is important to carefully read the label and follow the manufacturer’s instructions. The label should specify the amount of pesticide to be used per gallon of water or per plant. It is also important to calculate the amount of pesticide needed based on the size of the grow operation.
Factors that impact dosage include:
- The severity of the pest infestation
- The type of pesticide being used
- The size and age of the plant
- The environmental conditions of the grow operation
It is important to measure the pesticide accurately using graduated tools, such as a measuring cup or syringe. If using a foliar spray, it is recommended to test a small area of the plant before applying to the whole plant to ensure the correct dosage and to avoid any adverse effects.
Other dosage considerations:
- Never mix pesticides together: Mixing pesticides together can have unpredictable results and can be dangerous. Always use one type of pesticide at a time.
- Don’t exceed recommended dosage: Using more pesticide than recommended can lead to negative effects on the plant and environment.
- Time of day: It is important to apply pesticides during cooler parts of the day, such as early morning or late afternoon, to avoid potential damage to the plant.
- Wear protective gear: When applying pesticides, it is important to wear proper protective gear, such as gloves and a mask, to minimize exposure to the chemicals.
Determining the correct dosage of pesticide is crucial for effective pest control and the health of the plant. Careful attention to label instructions, measurement tools, and environmental factors can help ensure the correct dosage is applied.
Safety Precautions
When it comes to using chemical pesticides for cannabis growth, it is crucial to take safety precautions to avoid any risks to human health, environment, and other crops. Here are some of the essential safety precautions to follow:
| Precautions | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Wear Protective Clothing and Gear | Before handling any chemical pesticides, it is imperative to wear personal protective equipment such as goggles, gloves, masks, and full-body suits. This will protect your skin, eyes, mouth, and respiratory system from harmful chemicals. |
| Read Manufacturer’s Instructions Carefully | Always read the label and packaging of chemicals carefully to know how to use it, dosage, mixing instructions, and the risks it poses to human health and environment. Keep in mind that different pesticides have different instructions, and using them improperly can lead to hazardous results. |
| Store Pesticides Properly | Keep the pesticides in a safe, dry, cool place and out of reach of children and pets. Make sure to store them in their original containers and away from food, seed, and fertilizer. Do not mix different chemicals or reuse the containers. |
| Use Pesticides Outdoors | It is highly recommended to apply pesticides outdoors to reduce the risk of exposure and minimize the impact on the environment. If using indoors, make sure the area is well-ventilated, and keep people and pets away from the area. |
| Disposal of Excess Pesticides and Containers | After use, dispose of any excess pesticides and containers according to the manufacturer’s instructions and local regulations. Do not pour it down the drain, on soil, or in water bodies as it can contaminate the environment and harm other living organisms. |
| Wash Hands and Clothing Thoroughly | After using pesticides, wash your hands and clothing thoroughly with soap and water. Take a shower if possible. Launder your clothing separately from other clothes, and do not reuse the protective gear until it is thoroughly cleaned. |
Following these safety measures can help to reduce the risks while using chemical pesticides for cannabis growth. It is essential to always prioritize the safety of human health and the environment while maintaining the plant’s quality and yield.
Integrated Pest Management
When it comes to pest control, a more holistic and sustainable approach is always preferable. This is where Integrated Pest Management (IPM) comes in. Unlike traditional chemical pesticide use, IPM involves utilizing multiple strategies to prevent, control and eliminate pests. By combining various pest management techniques, growers can significantly reduce or even eliminate the need for chemical pesticides while still maintaining healthy and high-yielding cannabis plants. In this section, we’ll take a closer look at what IPM is, how it can be used in cannabis growth, and the many benefits it offers.
What is IPM?
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is a holistic and sustainable approach to pest control that aims to reduce the use of chemical pesticides. It is a preventive strategy that incorporates several methods to effectively manage pests while minimizing environmental and health risks. IPM involves regular monitoring and assessment of pest populations, identification of pest species, and selection of appropriate control methods.
IPM includes the following pest control methods:
- Biological control: Utilizing natural predators, parasites, and pathogens to control pest populations.
- Cultural control: Twisting plant leaves to make it difficult for insects to feed, planting companion crops or trap crops, maintaining proper irrigation, nutrition, and sanitation practices.
- Mechanical/physical control: Using physical barriers or traps to exclude or capture pests, handpicking or pruning infested plants, removing pest breeding sites or plant residues.
- Chemical control: Utilizing chemical pesticides when other methods have been deemed ineffective or inadequate.
IPM is becoming increasingly popular in the cannabis industry as growers work to minimize the use of chemicals and prioritize sustainable, environmentally friendly practices. By incorporating a range of pest control methods, growers can effectively manage pests while minimizing risks to the plant, the environment, and human health.
Using IPM for Cannabis Growth
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is a holistic approach to pest control, which combines various methods to minimize pest damage while reducing the use of chemicals. The following are steps to using IPM for healthy cannabis growth:
- Identify the Pest: Before taking action, it’s crucial to identify the type of pest affecting the plants. This can be done by inspecting the plants regularly, looking for physical signs of damage or insects, and using sticky traps or pheromone traps.
- Set action thresholds: Determine the highest level of pest damage that can be tolerated without causing significant economic damage. This helps growers decide when to take action.
- Monitor the plants regularly: It’s important to frequently check the plants for pests and damage, especially during critical growth stages such as flowering. Keeping records of pest populations and damages can help in making informed decisions.
- Implement preventative measures: Cultural methods, such as maintaining plant health through proper fertilization, watering, and pruning practices, can help minimize pest infestations. Additionally, physical barriers like nets, screens, or row covers can prevent insects from reaching the plants.
- Introduce natural enemies: Beneficial insects or organisms like ladybugs, lacewings, and nematodes can be introduced into the growing environment to help control pests. These natural enemies prey on and consume the pests that cause damage to the plants.
- Use chemical control as a last resort: While chemicals can be effective in controlling pests, they should only be used when all other options have failed. When using chemical pesticides, it’s essential to follow instructions and safety precautions to minimize damage to plants, people, and the environment.
By using an IPM approach, growers can effectively manage pests while reducing reliance on chemical pesticides. This leads to a healthier growing environment for the plants, the growers, and those who consume the cannabis.
Benefits of IPM
The Integrated Pest Management (IPM) technique brings a variety of benefits to the cannabis cultivation industry. Below is an overview in the form of an html table of the benefits associated with IPM:
| Benefits of IPM in Cannabis Growth |
|---|
| Reduced use of harmful pesticides |
| Increased plant resistance to pests |
| Targeted and strategic pest control |
| Improved overall plant health |
| Decreased risk of pesticide resistance development |
| Conservation of beneficial insects |
The table shows that the benefits of IPM approach goes beyond merely controlling pests. It also addresses how to create a healthy environment for cannabis growth while minimizing pesticide use. By doing so, this approach helps to increase the quality and yield of the plants. Through targeted and strategic pest control, it ensures that the cannabis plants don’t suffer from unnecessary effects of pesticide application. The IPM approach contributes to the conservation of the grower’s time, money, and energy by minimizing efforts in controlling the pests.
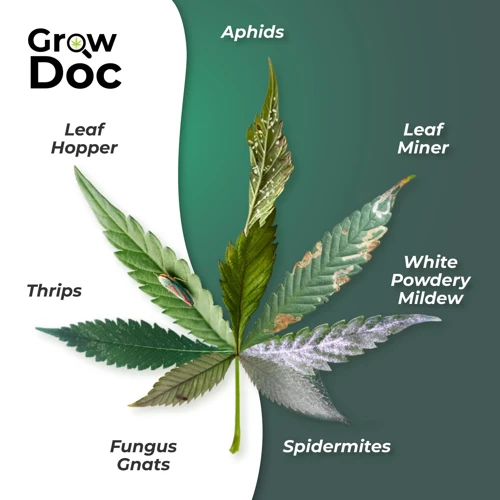
Common Pests and Their Control
One of the biggest threats to healthy cannabis growth is the presence of pests. These tiny creatures can quickly damage plants and reduce their overall yield. It’s important to understand the most common pests that affect cannabis plants and how to control them. In this section, we will explore some of the most prevalent pests and discuss various chemical and non-chemical methods of controlling them. By being aware of these potential threats and knowing how to deal with them, you can ensure the continued health and productivity of your cannabis plants.
Spider Mites
Spider mites are tiny pests that can be a real problem for cannabis growers. They are a common pest that can cause significant damage to your plants if not addressed promptly. These arthropods are related to ticks and spiders and are typically less than 1 mm in size. They are most commonly found on the underside of leaves, where they create a web-like structure.
| Pest | Appearance | Damage |
|---|---|---|
| Spider Mites | Very small – can be difficult to see with the naked eye. Typically yellow or green in color with eight legs. | They will suck the sap from the leaves of your cannabis plants, resulting in yellowing, drying, and browning of the leaves. You may also notice small webs on the underside of the leaves, which can make your plants look unsightly. |
Controlling spider mites can be a challenge, as they reproduce rapidly, and their small size can make them difficult to detect until they have caused significant damage. Fortunately, there are several chemical pest control options available to help you address the problem.
One effective option for control is the use of insecticides such as abamectin, which target the nervous system of arthropods. Another chemical option is pyrethrin, which targets the nervous system of insects and mites. Neem oil is also effective in controlling spider mites, as it disrupts their hormones and prevents them from reproducing.
It is important to apply these insecticides as soon as you notice the presence of spider mites. Additionally, you should rotate the types of insecticides you use, as spider mites can develop resistance to some chemicals over time.
Care should be taken with chemical pest control options, as spider mites can develop a resistance to certain pesticides over time. You should always follow the manufacturer’s instructions when applying any chemical, and you should wear protective gear such as goggles and gloves to prevent exposure to the product.
In addition to chemical pest control options, there are several non-chemical methods you can use to control spider mites. These include using a strong blast of water to knock the mites off your plants, pruning affected leaves, and increasing humidity to help your plant recover.
Spider mites are a common problem for cannabis growers, but with vigilance and attention to detail, it is possible to control them and protect your plants.
Aphids
Aphids are tiny insects that can cause major damage to cannabis plants. They have a soft, pear-shaped body and feed on the sap of the leaves, stems, and buds. As they feed, they secrete a sticky substance called honeydew that can attract other pests and lead to fungal growth.
Identification: Aphids can come in different colors, such as green, black, yellow, or brown. They can often be found in clusters on the undersides of leaves.
Control: There are several ways to control aphids on cannabis plants.
1. Manual removal: Use a pair of tweezers or a gentle stream of water to remove aphids from the plant.
2. Insecticidal soap: This is a non-toxic option for controlling aphids. It works by suffocating them. Be sure to follow the instructions on the package carefully.
3. Neem oil: This is a natural insecticide that is effective against aphids. It works by disrupting their feeding and reproductive systems. Be sure to dilute the neem oil according to instructions.
4. Predatory insects: Ladybugs and lacewings are natural predators of aphids. Release them into the garden to help control the aphid population.
5. Pyrethrin: This is a synthetic insecticide that is effective against aphids. Be sure to read the label carefully and follow instructions for safe use.
Prevention: Preventing an aphid infestation is easier than controlling one. Here are some preventive measures you can take:
– Inspect new plants before bringing them into your garden.
– Keep your plants healthy and well-fed to make them less susceptible to aphid damage.
– Practice crop rotation to avoid building up a large population of aphids in one area.
– Use reflective mulch or reflective barriers to create a physical barrier that can deter aphids.
Thrips
Thrips are tiny, slender insects that can cause serious damage to cannabis plants by feeding on the leaves, flowers and stems. These bugs have fringed wings and their feeding can cause silvering, scarring and distortion of the leaves, as well as incomplete flower formation. Thrips reproduce quickly and can spread from plant to plant with ease, making early detection and control critical for cannabis growers.
There are several chemical pesticides that can be used to control thrips on cannabis plants. These include insect growth regulators, which interfere with the growth and development of the thrips larvae by disrupting their hormonal balance, as well as contact insecticides, which work by entering the insects’ bodies and causing damage to their nervous systems. It’s important to note that certain insecticides can cause phytotoxicity, or plant damage, so it’s essential to carefully follow the manufacturer’s instructions when applying these chemicals.
In addition to chemical pesticides, there are several alternative methods for controlling thrips on cannabis plants. Biological control, or the use of natural predators to control the insect population, can be effective against thrips. Some beneficial insects that feed on thrips include predatory mites, lacewings, and ladybugs. Cultural control methods, such as removing infested plant material and improving overall plant health, can also help prevent thrips infestations. Finally, using sticky traps can help monitor thrips populations and alert growers to potential issues before they become major infestations.
Overall, the key to controlling thrips on cannabis plants is early detection and a combination of control methods, including chemical pesticides, alternative pest control methods, and cultural control measures. By taking a proactive approach to pest management, cannabis growers can minimize the damage caused by common pests like thrips and ensure healthy, high-quality yields.
Caterpillars
Caterpillars are one of the most common pests that can be found feeding on cannabis plants. There are many different species of caterpillars, but they all have a similar appearance with long bodies and numerous legs. Some common types of caterpillars that can be found on cannabis plants include the armyworm and the corn earworm. These pests can cause significant damage to the cannabis plants by consuming the leaves and buds.
To control caterpillars, there are several measures that can be taken:
- One of the most effective methods of controlling caterpillars is to physically remove them from the plant. This can be done by carefully inspecting the plants and picking off any caterpillars that are found.
- Another option is to use insecticides that are specifically designed to target caterpillars. However, it is important to choose an insecticide that is safe to use on cannabis plants and to follow the instructions carefully in order to avoid damaging the plants or exposing yourself to harmful chemicals.
- Some natural predators of caterpillars include parasitic wasps and certain species of birds. Encouraging these predators to frequent your garden can help reduce the population of caterpillars.
Preventive measures can also be taken to minimize the risk of caterpillar infestation. Some of these measures include:
- Keeping the garden area clean and free of debris that can provide a habitat for caterpillars and other pests.
- Using row covers or netting to protect the plants from adult female moths that lay their eggs on the plants.
- Introducing companion plants that repel caterpillars and other pests, such as marigolds or garlic.
It is important to monitor cannabis plants regularly for signs of pest infestation and to take action as soon as possible to prevent the pest population from becoming too large and causing significant damage to the plants. By following these measures and implementing an integrated pest management strategy, growers can successfully control caterpillar populations and ensure healthy cannabis growth.
Whiteflies
Whiteflies are a common pest that can cause severe damage to cannabis plants. They are small, winged insects that feed on plant sap, causing yellowing and stunted growth. They can also spread viral diseases, further compromising the health of the plant.
One way to control whiteflies is by using chemical pesticides. However, it is important to choose the right type of pesticide and follow proper application techniques to avoid harming the plant and the environment.
Types of pesticides
For whitefly control, some of the commonly used insecticides are imidacloprid, pyrethrins, and neem oil.
Application
For effective whitefly control, it is important to target both the adult flies and the larvae. Insecticides can be applied using a foliar spray or soil drench. Timing and frequency of application will depend on the severity of the infestation and the stage of plant growth.
Safety precautions
When applying chemical pesticides, it is important to always wear protective gear such as gloves and mask to avoid skin and respiratory exposure. It is also crucial to follow manufacturer’s instructions and dispose of any leftover pesticides properly.
Alternative pest control methods
Aside from chemical pesticides, there are also alternative methods for controlling whiteflies. These include the use of beneficial insects such as ladybugs and lacewings, as well as sticky traps that can catch the adult flies. Additionally, cultural practices such as regular pruning and weed management can also prevent whitefly infestations.
By understanding the biology of whiteflies and the different methods for their control, cannabis growers can effectively manage this pest and ensure the healthy growth of their plants.
Preventive Measures
Preventive measures are essential in keeping pests at bay and maintaining the overall health of cannabis plants. These measures can greatly reduce the need for chemical control methods, which may have potentially harmful effects on both the plant and its environment. Some common preventive measures are listed in the table below:
| Preventive Measure | Description |
|---|---|
| Cleanliness and sanitation | Regularly clean and sanitize all equipment, tools and surfaces. |
| Quarantine | Isolate new plants or plants returning from outdoor environments before introducing them to the indoor grow area. |
| Air circulation and humidity control | Ensure proper airflow and humidity control as stagnant air and high humidity create an ideal environment for pests. |
| Pest-resistant strains | Choose strains that have natural resistance to pests. |
| Regular monitoring | Regularly check plants for signs of pest infestation, especially on the bottom of leaves. |
| Physical barriers | Use physical barriers like screens and netting to prevent pests from entering the grow area. |
| Biocontrols | Use beneficial insects, such as ladybugs or predatory mites, to naturally control pests. |
| Rotation and crop selection | Rotate crops and alternate between cannabis and non-cannabis plants as some pests are specific to certain plant families. |
Incorporating these preventive measures into a grow operation can significantly reduce the need for chemical pest control methods while promoting healthy cannabis growth. It is important to note that preventive measures alone may not always suffice, and chemical pest control methods may still be necessary in certain cases.
Alternative Pest Control Methods
As more and more cannabis growers aim for sustainable and eco-friendly practices, alternative pest control methods have gained popularity to replace chemical pesticides. These methods use natural and biological approaches to prevent and control pests, without compromising the quality and yield of the cannabis plants. Let’s explore some of the most common alternatives to chemical pest control and their benefits.
Organic Pesticides
Using organic pesticides is another option for controlling pests in cannabis growth. These pesticides are derived from natural sources and are considered a safer alternative to chemical pesticides.
Types of Organic Pesticides
There are several types of organic pesticides that can be used in cannabis growth. These include:
| Pesticide | Description |
|---|---|
| Neem Oil | A natural insecticide derived from the neem tree. It disrupts the growth and development of pests and can also act as a fungicide. |
| Diatomaceous Earth | A fine powder made from the shells of tiny aquatic organisms called diatoms. It works by drying out the exoskeletons of pests, causing dehydration and death. |
| Pyrethrin | A natural insecticide derived from the chrysanthemum flower. It attacks the nervous system of pests, causing paralysis and death. |
| Essential Oils | Oil extracts derived from plants such as peppermint, rosemary, and thyme. They contain compounds that repel or kill pests. |
Benefits of Organic Pesticides
Using organic pesticides in cannabis growth has several benefits. Firstly, they are considered safer for human and animal health compared to chemical pesticides. They also have a lower environmental impact since they are made from natural sources and break down more easily in the environment. Additionally, pests are less likely to develop resistance to organic pesticides since they have a different mode of action compared to chemical pesticides.
Challenges of Organic Pesticides
While organic pesticides have many benefits, they also have some challenges. They may not be as effective as chemical pesticides in controlling pests, and may need to be applied more frequently. Some organic pesticides can also harm beneficial insects, such as bees and ladybugs, which can disrupt the natural balance of the ecosystem. Organic pesticides can also be more expensive compared to chemical pesticides, which can be a concern for some growers.
Organic pesticides can be a viable option for controlling pests in cannabis growth, but growers need to consider the benefits and challenges of each pesticide and choose the best one for their specific situation.
Biological Control
Biological control is another method of pest control that is gaining popularity in the cannabis industry. This method involves the use of natural enemies of pests to control their population. Some of the commonly used biological control agents include predatory mites, ladybugs, and nematodes.
Predatory mites: These are a type of beneficial mite that feed on other harmful mites, such as spider mites. They are effective in controlling the population of spider mites and other mite-related pests.
Ladybugs: These are popular and widely used biological control agents that feed on aphids, mites, and other small insects. They can be released in large numbers to control the pest population.
Nematodes: These are microscopic worms that live in the soil and feed on the larvae of many soil-dwelling pests. They are particularly effective in controlling the population of root pests such as grubs.
Biological control has several benefits over chemical pesticides. Since it uses natural enemies, there is no risk of chemical residues in the final product. It is also environmentally friendly and does not harm other beneficial insects. However, it can be less effective than chemical pesticides and requires careful monitoring to ensure that the natural enemies are effective in controlling the pest population.
It is important to note that biological control should not be used as a standalone method of pest control. It is most effective when used in combination with other methods such as cultural control and chemical pesticides. When using biological control, it is important to source the natural enemies from a reputable supplier and handle them carefully to avoid damage.
Biological control is an effective and sustainable method of pest control for cannabis growers. With careful monitoring and the use of multiple methods, growers can ensure a healthy and pest-free crop.
Cultural Control
Cultural control is a pest control method that aims to prevent pests from infesting the cannabis plant by creating an unfavorable environment for them. This method relies on the knowledge of pest ecology and behavior, as well as the use of cultural practices that disrupt their life cycle.
| Cultural Control Methods | Explanation |
|—————————|——————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————-|
| Crop Rotation | In this method, cannabis is grown in a different location every year to break the life cycle of pests that may have overwintered in the soil. This also allows for the soil to regenerate nutrients and microorganisms, making it more resistant to pests and diseases. |
| Sanitation | The removal of plant debris, weeds, and other organic matter prevents the buildup of pests and diseases. Cleaning and disinfecting gardening tools help prevent the spread of pests and diseases from plant to plant. |
| Mulching | Mulching is the process of covering the soil around the cannabis plant with a layer of organic material. This prevents the growth of weeds and helps retain soil moisture. Organic mulches such as straw, hay or leaves can also create a barrier against pests such as spider mites that cannot easily move across the rough surface of the mulch. |
| Companion Planting | Companion planting is the practice of growing two or more different plant species together for mutual benefit. For example, planting marigolds around cannabis can help repel spider mites, while intercropping with clover can increase soil nitrogen levels, improving plant growth and making it more resistant to pests and diseases. |
| Traps and Barriers | Physical barriers, such as sticky traps, can be used to reduce the number of pests in the area. Yellow sticky traps are effective at catching aphids, thrips, and whiteflies, while using blue sticky traps can attract and trap fungus gnats. Barriers like mesh or netting can help prevent pests from entering the garden. |
| Light and Temperature | Light and temperature can be manipulated to reduce the likelihood of pest infestations. For example, using bright, cool-white lights can discourage pests from entering the garden, as they prefer areas with low light. Lowering the temperature within the grow-room can also discourage pests such as spider mites and thrips, which thrive in warm, humid environments. |
Cultural control is an effective method for preventing pest infestations and maintaining a healthy cannabis crop. It is eco-friendly, cost-effective, and can be used in conjunction with other pest control methods for even better results. By incorporating practices such as crop rotation, sanitation, mulching, companion planting, traps and barriers as well as manipulating light and temperature, growers can reduce their reliance on chemical pesticides and promote a healthier and sustainable growing environment for their cannabis plants.
Conclusion
As we come to the end of our discussion on chemical pest control for healthy cannabis growth, it is important to reflect on the effectiveness of this method in maintaining the quality and quantity of cannabis yields. While chemical pesticides have their benefits in preventing and controlling pests, there are also cautionary measures that must be observed to ensure the safety of both the plant and the consumer. Let us delve deeper into the advantages and caveats of chemical pest control for cannabis cultivation.
Benefits of Chemical Pest Control
Chemical pest control offers several benefits to cannabis growers. Here are some of the most prominent benefits:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Effective | Chemical pesticides are designed to kill pests quickly and efficiently. They are formulated to target specific pests, ensuring that they do not harm other beneficial organisms in the growth environment. |
| Easy to Use | Chemical pesticides generally come in ready-to-use formulations, making them simple and easy to apply. This makes chemical pest control an attractive option for growers who lack the time or resources for more complex pest control methods. |
| Cost-Effective | Many chemical pesticides are affordable and readily available, making them a cost-effective option for growers. Additionally, chemical pest control can prevent extensive damage to crops, reducing the risk of costly losses. |
| Flexible Application | Chemical pesticides can be applied at any point in the growth cycle, making them a flexible option for growers. They can also be used as a preventative measure or to address existing pest problems. |
| Speedy Results | Chemical pest control products typically provide quick results, meaning growers can quickly address pest infestations and minimize damage to their crops. |
Despite these benefits, it is important to exercise caution when using chemical pesticides. Overuse or misuse can lead to negative effects on the health of the plant, the growth environment, and the ecosystem as a whole. As such, growers should carefully consider their pest control options and ensure they follow safe and responsible pesticide application practices.
Cautions for Chemical Pest Control
When using chemical pest control methods, there are certain precautions that must be taken to ensure the safety of both the plant and the applicator. It is important to wear protective gear such as gloves, goggles, and a respirator to avoid skin and eye irritation as well as inhalation of harmful chemicals.
Table: Precautions for Chemical Pest Control
| Precautions | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Read the label | Make sure to follow all instructions and recommended doses. Never apply higher doses than recommended, as this can be harmful to the plant and the surrounding environment. |
| Choose the correct pesticide | Using the wrong pesticide can be ineffective against the targeted pest, and can also harm beneficial insects, soil microorganisms or birds. |
| Store pesticides safely | Pesticides should be stored in their original containers, in a secure, cool, and dry location. Keep them out of reach of children and pets to avoid accidental ingestion. |
| Dispose of pesticides properly | Do not dump unused pesticides down the drain or in the trash. Follow local regulations for pesticide disposal, which often involve special hazardous waste collection. |
| Wait before harvest | Make sure to follow the recommended waiting period after application before harvest. This is to avoid harmful residues and ensure the safety of the consumer. |
| Rotate pesticides | Using a single pesticide repetitively against certain pests increases the likelihood that they will develop resistance to that chemical. Rotating pesticides can help avoid this resistance development and can ensure effective pest control over time. |
In addition to these precautions, it is important to keep in mind that chemical pest control is not always the best solution. Sometimes, natural or cultural methods may be more effective or sustainable. Always assess the situation and weigh the pros and cons before resorting to chemical pest control methods.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are some common pests that affect cannabis growth?
Some common pests that affect cannabis growth include spider mites, aphids, thrips, caterpillars, and whiteflies.
Why is chemical pest control important for healthy cannabis growth?
Chemical pest control helps to prevent and control the spread of pests that can damage the cannabis plant and lead to lower yields.
What are some factors to consider when using chemical pest control on cannabis plants?
Factors to consider include the age of the plant, the type of pests present, and the growth environment of the plant.
What are some alternative methods of pest control for cannabis plants?
Alternative methods include organic pesticides, biological control, and cultural control.
What is Integrated Pest Management (IPM)?
IPM is a method of pest control that uses a combination of techniques to prevent and control pests while minimizing the use of chemicals.
How can IPM be used for cannabis growth?
IPM can be used by integrating various pest control techniques such as biological control, cultural control, and chemical control to prevent and control pests in cannabis growth.
What are some benefits of using IPM for cannabis growth?
Benefits of IPM include reduced use of chemicals, more sustainable pest control, and reduced risk of developing pesticide resistance in pests.
How should chemical pesticides be applied to cannabis plants?
Chemical pesticides should be applied according to the dosage and timing recommended by the manufacturer, and with proper safety precautions.
What are some cautions to consider when using chemical pest control on cannabis plants?
Cautions include potential harm to human health and the environment, the development of pesticide resistance in pests, and the potential for pesticide residue in the final product.
How does cultural control work as a pest control method?
Cultural control involves altering the growing environment to discourage the growth and reproduction of pests, such as maintaining proper humidity levels or using reflective mulch to repel aphids.