Adjusting Macronutrient Levels for Cannabis Growth
Growing cannabis can be both exciting and overwhelming, especially if you are new to the process. One of the key factors to achieving a successful harvest is mastering the nutrient levels of your plants. This is where macronutrients, the primary nutrients that are required in large quantities for plant growth, come into play. Adjusting macronutrient levels throughout the different stages of cannabis growth is crucial to achieving optimal growth and yield. In this guide, we will break down the different stages of cannabis growth and their unique macronutrient needs, as well as provide tips on how to troubleshoot common macronutrient problems. By the end of this article, you will be equipped with the knowledge to confidently adjust macronutrient levels and grow healthy, thriving cannabis plants.
Understanding Macronutrients and Cannabis Growth
Contents
As a cannabis grower, understanding the importance of macronutrients is crucial for a successful harvest. Macronutrients are the essential elements that plants need in large quantities to grow and produce their own energy through photosynthesis. Without an appropriate balance of macronutrients, cannabis plants may suffer from stunted growth, poor yield, and even death. In this section, we will delve into the world of macronutrients and their role in cannabis growth, so you can ensure your plants receive the right balance throughout their lifecycle. It is important to note that macronutrients differ from micronutrients, which are required in smaller quantities. To learn more about the difference between the two, check out our article on macronutrients vs. micronutrients.
What are Macronutrients?
Macronutrients are the essential elements required in large quantities by cannabis plants to complete its life cycle. In fact, there are primary macronutrients as well as secondary macronutrients that have crucial roles in plant health and development.
The primary macronutrients are the three elements that are most important for cannabis plants in larger quantities. They are:
- Nitrogen (N): Nitrogen plays a critical role in the growth and development of the cannabis plant’s leaves, stems, and shoots. It is essential for the creation of chlorophyll, which is responsible for photosynthesis. A lack of nitrogen leads to severe stunted growth, yellowing or browning of the leaves, and weak stems.
- Phosphorus (P): Phosphorus is vital to the production of plant cell membranes, DNA, and RNA. It also plays a significant role in how the plant uses and stores energy. Phosphorus deficiency shows up as slow growth, purple or brown-colored leaves, and poor flowering.
- Potassium (K): Potassium is necessary for the cannabis plant’s stress response, root development, and water regulation. It is also essential for the production of sugars and the transportation of nutrients throughout the plant. A lack of potassium leads to weaker branches, yellowing or browning of leaves, and reduced size and quality of buds.
The secondary macronutrients are the elements required by plants in a lesser amount than the primary ones. They are:
- Calcium (Ca): Calcium is essential for the formation and maintenance of healthy cell walls, and it also contributes to the development of strong roots. Calcium deficiency leads to the death of young leaves, yellowing between the veins, root decay and stunted growth.
- Magnesium (Mg): Magnesium is a crucial component of chlorophyll and plays a role in how the plant uses and stores energy. Magnesium deficiency is characterized by yellowing between the leaf veins starting at the leaf base, leaf drop and stunted growth.
- Sulfur (S): Sulfur is essential for the production of amino acids, enzymes, and vitamins. Sulfur deficiency leads to yellowing of young leaves, stunted growth, and abnormal growth patterns.
Understanding macronutrients is crucial to attain maximum cannabis yield and health in a grow setup.
Macronutrients for Cannabis Growth
Macronutrients play a crucial role in the growth and development of cannabis plants. These are the primary nutrients that are needed in large amounts, and are necessary for overall plant health and development. There are three macronutrients that are essential for cannabis growth, and they include:
- Nitrogen: Nitrogen is essential for the production of chlorophyll, the green pigment that enables photosynthesis. It is also needed for the production of amino acids, which are the building blocks of proteins. Without sufficient nitrogen, cannabis plants will have stunted growth and yellowing leaves.
- Phosphorous: Phosphorous is necessary for the development of roots, stems, and flowers, and plays a vital role in photosynthesis. It is also needed for the production of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is the primary source of energy for plants. A deficiency of phosphorous can lead to slow growth and a lack of flowering.
- Potassium: Potassium is essential for the growth and development of cannabis plants, and is heavily involved in the regulation of water uptake and distribution. It also helps to regulate the opening and closing of stomata, which are the tiny pores on the leaves that allow for the exchange of gases. A lack of potassium can lead to slow and stunted growth, as well as lower yields.
It is important to note that there are other macronutrients that cannabis plants need, such as calcium, magnesium, and sulfur, but they are not required in as large quantities as nitrogen, phosphorous, and potassium. Keeping a careful balance of all the necessary macronutrients is essential to achieving healthy and vigorous cannabis plants.
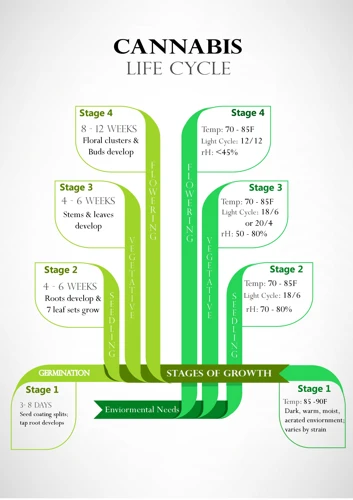
The 3 Cannabis Growth Stages and Macronutrient Needs
As a cannabis grower, it’s important to understand the different stages of plant growth and their corresponding macronutrient needs. Each stage presents unique challenges and requires specific attention to ensure optimal growth and yield. From the delicate seedling stage to the budding flowering stage, adjusting macronutrient levels is essential for successful cultivation. In this section, we will delve into the three distinct stages of cannabis growth and explore the specific macronutrient requirements for each.
Seedling Stage
During the seedling stage, your cannabis plants are delicate and vulnerable. They require a specific balance of macronutrients to establish strong root systems and healthy foliage. Here are the optimal macronutrient levels to focus on during this stage:
- Nitrogen: Nitrogen is crucial during the seedling stage, as it helps build the foundational structure of the plant. Aim for a ratio of 3:1:2 (N:P:K) for a balanced ratio that won’t overload your plant with too much nitrogen. Avoid nitrogen toxicity, which can lead to stunted growth and burned leaves.
- Phosphorus: Phosphorus aids in root development, which is critical during the seedling stage. Ensure your soil or hydroponic solution has ample phosphorus for your cannabis plants to thrive. Look for a ratio of 3:1:2 (N:P:K).
- Potassium: While potassium is important throughout all cannabis growth stages, it’s less critical during the seedling stage. Focus on nitrogen and phosphorus, but don’t ignore potassium entirely. A 3:1:2 (N:P:K) ratio will suffice.
During this stage, it’s important to avoid overfeeding your cannabis plants. They don’t require as many nutrients as they will in the vegetative and flowering stages. Keep a close eye on your plants and adjust your nutrient levels as needed based on their growth and development. Remember, in the seedling stage, less is often more.
Vegging Stage
During the vegging stage, cannabis plants require higher levels of nitrogen to support their rapid growth and development of foliage. However, it is important not to over-fertilize the plants during this stage as it can lead to a deficiency in other macronutrients such as potassium and phosphorus.
When using soil as the growing medium, a macronutrient ratio of 3:1:2 (N-P-K) is recommended for the vegging stage. This means that plants should receive three parts nitrogen, one part phosphorus, and two parts potassium. It is important to monitor the plants closely during this stage to ensure they are not showing signs of nutrient deficiencies or excesses.
In hydroponics systems, the recommended macronutrient ratio for the vegging stage is slightly different. A ratio of 5:1:2 (N-P-K) is often used to promote healthy growth and development of the plants. This means that the plants should receive five parts nitrogen, one part phosphorus, and two parts potassium.
The following table provides an overview of the recommended macronutrient ratios for the vegging stage in both soil and hydroponics systems:
| Nitrogen (N) | Phosphorus (P) | Potassium (K) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Soil | 3 parts | 1 part | 2 parts |
| Hydroponics | 5 parts | 1 part | 2 parts |
It is also important to maintain the proper pH levels during the vegging stage, as nutrient uptake can be affected by pH imbalances. The ideal pH range for soil is between 6.0 and 7.0, while for hydroponics systems it should be between 5.5 and 6.5.
The vegging stage is a crucial time for cannabis plants to establish a strong foundation for healthy growth and development. By providing the proper macronutrient ratios and pH levels, growers can ensure optimal growth and a high yield during the flowering stage.
Flowering Stage
During the Flowering Stage, cannabis plants start to produce buds. At this stage, the nutrient needs of the plant change dramatically. The plant needs less nitrogen and more phosphorus and potassium to support proper bud development. Below are the specific macronutrient needs and ratios for the Flowering Stage of cannabis growth:
- Phosphorus: Phosphorus is essential for the development of healthy buds. It also helps regulate energy transfer in the plant. During the Flowering Stage, the plant’s need for phosphorus increases. A phosphorus deficiency during this stage can result in slow or stunted bud growth. The recommended ratio of phosphorus to nitrogen during the Flowering Stage is 1:2.
- Potassium: Potassium is critical to the development of strong, sturdy stems and branches. It also helps regulate water balance in the plant. During the Flowering Stage, the plant’s need for potassium increases significantly. A potassium deficiency can result in weak stems, improper bud development, and reduced yield. The recommended ratio of potassium to nitrogen during the Flowering Stage is 2:1.
- Nitrogen: While nitrogen is still necessary during the Flowering Stage, the plant requires significantly less of it. Too much nitrogen can lead to excessive vegetative growth and small buds. The recommended ratio of nitrogen to phosphorus and potassium during the Flowering Stage is 1:4.
- Calcium and Magnesium: Calcium and Magnesium are secondary macronutrients that are essential to plant growth and development. Calcium is necessary for strong cell walls, and Magnesium helps regulate photosynthesis. During the Flowering Stage, the plant’s need for both of these nutrients remains the same.
It’s important to monitor your plant’s nutrient needs during the Flowering Stage and adjust your feeding accordingly. Be sure to use a high-quality bloom fertilizer with an appropriate nutrient ratio to support healthy bud development and achieve optimal yields.
Adjusting Macronutrient Levels for Optimal Growth and Yield
As your cannabis plant grows, its macronutrient needs will change depending on its stage of growth. Adjusting the macronutrient levels will help you achieve optimal growth and yield. But how do you know when to adjust the nutrient levels, and how can you do it effectively? In this section, we’ll explore the signs of macronutrient deficiencies and excesses, and the best ways to modify nutrient levels in both soil and hydroponics systems. We’ll also discuss common macronutrient ratios used for cannabis growth and how to troubleshoot any nutrient problems that may arise.
Signs of Macronutrient Deficiencies and Excesses
Macronutrient deficiencies and excesses can greatly affect the growth and yield of cannabis plants. It’s important to know how to recognize and troubleshoot these issues in order to adjust nutrient levels accordingly. Here are some indicators of common macronutrient deficiencies and excesses:
| Macronutrient | Deficiency | Excess |
|---|---|---|
| Nitrogen | Yellowing of leaves, especially on lower part of the plant. Overall stunted growth. | Dark green leaves, delayed flowering, weakened stems. |
| Phosphorus | Purple or red stems, slowed growth, small leaves. | Burnt tips, stunted growth, reduced yield. |
| Potassium | Yellowing or necrosis (dead tissue) of leaf tips and edges. Weak stems, reduced size. | Stunted growth, reduced yield, burnt tips and edges. |
| Calcium | Brown spots on leaves, stunted growth, weakened stems. | Reduced uptake of other nutrients, salt buildup in soil. |
| Magnesium | Yellowing of leaves between veins, stunted growth. | Burnt tips, reduced uptake of other nutrients, reduced yield. |
| Sulfur | Yellowing of newer leaves, stunted growth. | Burnt tips, reduced uptake of other nutrients, reduced yield. |
Keep in mind that these are only general indicators and additional testing may be necessary to pinpoint the exact issue. It’s also important to note that over-fertilization can cause similar symptoms as nutrient deficiencies, so it’s important to properly diagnose the issue before adjusting nutrient levels.
Modifying Nutrient Levels in Soil
When it comes to modifying nutrient levels in soil, there are a few approaches you can take to ensure optimal growth and yield.
1. Add Nutrient-Rich Amendments: One way to adjust macronutrient levels in soil is to add nutrient-rich amendments, such as compost, aged manure, or worm castings. These organic amendments release nutrients slowly, providing a steady supply of macronutrients to your plants. Additionally, they improve soil structure and fertility, which can increase the soil’s ability to hold and release nutrients.
2. Adjust pH: Another important factor to consider is the soil pH. If the pH is too high or too low, plants won’t be able to absorb nutrients properly. Ideally, cannabis plants prefer a slightly acidic soil pH between 6.0 and 7.0. To adjust the pH, you can add soil amendments like lime to raise the pH or sulfur to lower it.
3. Use Macronutrient Supplements: In addition to amendments and pH adjustments, you may also want to consider using macronutrient supplements. These products are designed to provide a concentrated source of specific macronutrients, like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. They come in liquid or powder form and can be added to your soil mixture or used as a foliar spray.
4. Conduct Regular Soil Testing: To accurately monitor your soil’s macronutrient levels, it’s important to conduct regular soil testing. This will help you identify any deficiencies or excesses and adjust your nutrient levels accordingly. Soil testing kits can be purchased online or at garden centers.
5. Water Plants Properly: Proper watering is also crucial for maintaining healthy macronutrient levels in soil. Overwatering or underwatering can disrupt nutrient absorption in plants. Make sure to water your plants thoroughly but avoid saturating the soil. Let the top layer of soil dry before watering again.
By utilizing these methods, you can effectively modify macronutrient levels in soil to promote healthy cannabis growth and maximize your yield.
Modifying Nutrient Levels in Hydroponics Systems
When it comes to hydroponic systems, modifying nutrient levels can be a bit different than with soil. Here are some steps to follow to ensure your hydroponic system is properly adjusted for optimal cannabis growth:
- Check pH levels: In hydroponic systems, maintaining appropriate pH levels is crucial for nutrient absorption. Aim for a pH level between 5.5 and 6.5, as levels that are too high or too low can result in nutrient deficiencies or toxicities.
- Monitor EC levels: EC, or electrical conductivity, measures the concentration of nutrients in the water. This level should be adjusted based on the stage of growth. During the vegetative stage, aim for an EC level of 0.8-1.2, while the flowering stage requires a slightly higher level between 1.2-1.8.
- Add nutrients gradually: Just like with soil, it’s important to gradually introduce nutrients to avoid overwhelming the plant. Begin with a lower concentration and gradually increase the amount as the plant progresses through each stage of growth.
- Flush the system: Every few weeks, it’s important to flush the system with clean water for a few days. This helps to prevent nutrient buildup and allows the plant to absorb fresh nutrients more efficiently.
- Adjust nutrient ratios: As the plant moves from the vegetative to flowering stage, the ratios of macronutrients needed will change. Adjust the nutrient solution to reflect the appropriate ratios for each stage of growth.
Making sure your hydroponic system has the correct nutrient levels is key to producing healthy, thriving cannabis plants. With regular monitoring and adjustments, you can ensure your plant has the right balance of nutrients for optimal growth and yield.
Common Macronutrient Ratios for Cannabis Growth
Determining the right macronutrient ratios is crucial for achieving optimal growth and yield in cannabis plants. There are various established ratios for different growth stages and cultivation methods. However, with so many options to choose from, it’s natural to feel overwhelmed and unsure of which ratio to use. In this section, we’ll delve into common macronutrient ratios for cannabis growth and explore the standard ratios for soil and hydroponics. By the end of this section, you’ll have a better understanding of macronutrient ratios and will be able to make informed decisions about what ratio is best for your cannabis plants.
Standard Ratios for Soil
When it comes to cannabis growth in soil, there are certain macronutrient ratios that are commonly used to achieve optimal results. Here are some standard ratios for soil:
- Nitrogen (N): During the vegetative stage, a ratio of 3-1-2 (N-P-K) is commonly used. This means that there is three times more nitrogen than phosphorus and twice as much potassium as phosphorus. In the flowering stage, the ratio is typically decreased to around 1-2-2 to promote the growth of flowers.
- Phosphorus (P): Phosphorus is essential for root development, so higher levels of phosphorus are needed during the early stages of growth. A ratio of 1-3-3 or 2-3-3 (N-P-K) is commonly used during the first few weeks of the vegetative stage. As the plant matures and enters the flowering stage, the ratio is often lowered to around 1-2-2 to promote flower growth.
- Potassium (K): Potassium is important for overall plant health and stress resistance. During the vegetative stage, a ratio of 3-1-2 (N-P-K) is commonly used. In the flowering stage, the ratio is decreased to around 1-2-2 to promote flower development.
It’s important to note that these ratios are simply guidelines and may need to be adjusted based on the specific needs of your plants. Additionally, it’s important to regularly test your soil to ensure that the nutrient levels are within the appropriate range.
Standard Ratios for Hydroponics
When it comes to hydroponics, there are a few different macronutrient ratios that growers can use to optimize their cannabis growth. These ratios typically vary based on the specific type of hydroponic system being used, as well as the stage of growth the cannabis plants are in.
Here are some common macronutrient ratios for hydroponics:
- Vegetative Stage: During the vegetative stage, cannabis plants require higher levels of nitrogen to support leafy growth. A common ratio for this stage is 3-1-2 (nitrogen-phosphorus-potassium).
- Flowering Stage: As cannabis plants enter the flowering stage, they require less nitrogen and more phosphorus and potassium to support bud development. A common ratio for this stage is 1-3-2.
- Bloom Boosters: Some growers choose to add bloom boosters to their hydroponic systems in order to further enhance bud development. These boosters typically contain extra phosphorus and potassium, and may have a ratio of 0-50-30 or 0-39-25.
It’s important to note that these ratios are just a general guideline, and may need to be adjusted based on the specific needs of your cannabis plants. Additionally, it’s important to monitor the pH of your hydroponic system, as imbalances in pH can affect nutrient uptake and lead to nutrient deficiencies or toxicities.
Troubleshooting Macronutrient Problems
As you navigate through the stages of cannabis growth, you may encounter various issues related to macronutrient levels that can affect the health and yield of your plants. Keeping a close eye on your plants and identifying signs of macronutrient deficiencies or excesses is crucial to maintaining optimal growth. Troubleshooting these problems and finding the right balance of nutrients can be a daunting task for even the most experienced growers. In this section, we’ll explore common macronutrient problems and offer some solutions to help you get your plants back on track.
Over-Fertilization
Over-fertilization can be just as detrimental to your cannabis plants as under-fertilization. It occurs when too many macronutrients, particularly nitrogen and phosphorus, are added to the soil or hydroponic system. This can lead to a condition known as “nutrient burn,” where the tips of the leaves turn brown and eventually die off.
Signs of over-fertilization include:
- Brown or yellow tips on leaves
- Browning or yellowing of the edges of leaves
- Leaf tips curling downwards
- Slow growth
- Wilting
It is important to correct over-fertilization as soon as possible to prevent further damage to your plants. One solution is to flush the soil or hydroponic system with plain water to remove excess nutrients. This should be followed by a period of no fertilization to allow the plants to recover.
Preventing over-fertilization:
- Use a high-quality fertilizer that is specifically formulated for cannabis
- Monitor your plants closely and only fertilize when necessary
- Always follow the recommended dosage on the fertilizer packaging, and never exceed it
- Check the pH of your soil or hydroponic system regularly, as improper pH levels can lead to nutrient lockout and over-fertilization
Remember, over-fertilization can be just as harmful to your cannabis plants as under-fertilization. Keep a close eye on your plants and make adjustments as necessary to ensure optimal growth and yield.
Under-Fertilization
Under-fertilization can also cause problems for cannabis growth. When a plant is under-fertilized, it may not receive enough essential nutrients, which can lead to stunted growth and a decreased yield. Here are some signs of under-fertilization and ways to address it:
| Signs of Under-Fertilization | How to Address It |
|---|---|
| Yellowing leaves | Nitrogen deficiency – add a nitrogen-rich fertilizer |
| Slow growth | Phosphorus deficiency – provide a phosphorus-rich fertilizer |
| Poor root development | Potassium deficiency – add a potassium-rich fertilizer |
| Weak stems | Calcium deficiency – provide a calcium-rich fertilizer or increase the pH level |
By paying attention to these signs and making the necessary adjustments, growers can ensure that their plants receive the right amount of nutrients for optimal growth and yield. It’s important to remember that both over- and under-fertilization can harm cannabis plants, so finding the right balance is key.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding and adjusting macronutrient levels throughout the different stages of cannabis growth is crucial for achieving optimal growth and yield. Macronutrients, such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, are essential for healthy plant development and must be appropriately balanced based on the growth stage.
During the seedling stage, it is important to focus on providing ample amounts of phosphorus and potassium while limiting nitrogen intake. During the vegging stage, nitrogen becomes a primary focus as it promotes leaf growth and overall plant health. Lastly, during the flowering stage, an increase in phosphorus and potassium is necessary to support flower production.
Modifying nutrient levels in the soil or hydroponics system requires careful attention to avoid over-fertilization, which can lead to nutrient burn and plant damage. Signs of nutrient deficiency or excess, such as yellowing leaves or stunted growth, should be closely monitored to ensure appropriate adjustments are made.
Common macronutrient ratios for cannabis growth differ slightly between soil and hydroponic systems, but generally follow a 3:2:1 ratio of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. It is important to note that these ratios can be adjusted based on the unique needs of the individual plant and environmental factors.
In the event of nutrient problems, such as over or under-fertilization, corrective measures should be taken promptly. Proper pH levels and soil drainage are also essential for healthy plant growth.
Overall, properly understanding and adjusting macronutrient levels is a key factor in successful cannabis cultivation. By closely monitoring nutrient levels and making necessary adjustments, growers can ensure healthy growth and maximum yield.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the best macronutrients for cannabis growth?
The best macronutrients for cannabis growth are nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. They are essential for healthy plant growth, and deficiencies in any of these can negatively impact your yield.
What is the ideal N-P-K ratio for cannabis in the flowering stage?
The ideal N-P-K ratio for cannabis in the flowering stage is 1:3:2, with a slightly higher phosphorus to promote flowering and potassium levels to increase bud growth.
Can you use the same macronutrient ratios for both soil and hydroponic systems?
No, the macronutrient ratios should be adjusted based on the growing medium. Soil has natural nutrients, so less fertilizer is required, while hydroponic systems need a more precise nutrient balance for optimal growth.
What happens if you over-fertilize your cannabis plants?
Over-fertilizing can lead to nutrient burn and damage to the roots, which results in stunted growth, yellowing leaves, and decreased yield. It’s essential to follow the recommended guidelines and adjust nutrient levels as needed.
Can you adjust macronutrient levels during the different stages of growth?
Yes, adjusting macronutrient levels is crucial for optimal cannabis growth and yield. The nutrient needs of the plant vary during each stage of growth, so adjusting the macronutrient ratios can help promote healthy growth and increased yield.
How do you modify nutrient levels in hydroponics systems?
To modify nutrient levels in hydroponic systems, you can add or reduce the amount of nutrients in the water. It’s essential to monitor the pH levels and adjust if necessary, as high or low pH levels can impact nutrient uptake.
What are the signs of macronutrient deficiencies in cannabis plants?
The signs of macronutrient deficiencies in cannabis plants can manifest in different ways, such as yellowing leaves, stunted growth, and brown or brittle leaves.
What is the macronutrient ratio for the seedling stage?
The macronutrient ratio for the seedling stage is 2:1:1, with a higher ratio of nitrogen to promote healthy leaf and stem growth.
Is it possible to have too much macronutrients in cannabis plants?
Yes, having too much macronutrients can lead to nutrient toxicity, which results in burnt leaves, slowed growth, and decreased yield. It’s crucial to follow the recommended nutrient guidelines and adjust as needed.
Can you use organic macronutrients for cannabis growth?
Yes, you can use organic macronutrients for cannabis growth. Organic macronutrients come from natural sources and can provide essential nutrients for healthy plant growth.