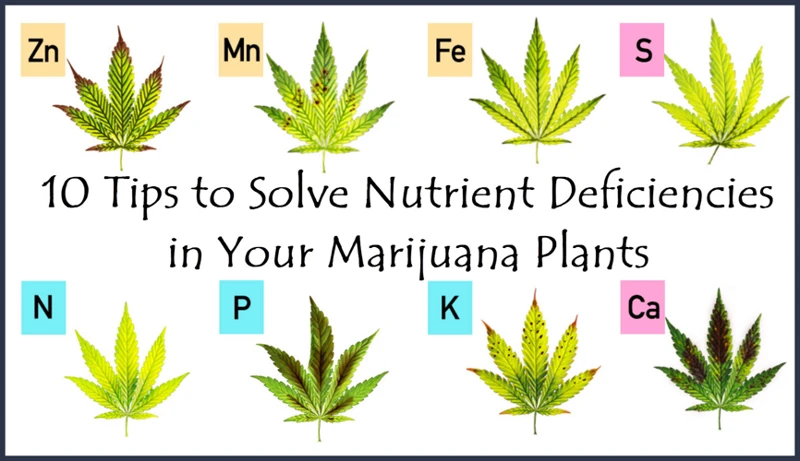
The Top Macronutrient Deficiencies to Watch Out for in Cannabis Plants
As a cannabis grower, seeing your plants suffer from poor health can be frustrating and perplexing. While there are several factors that can affect plant growth, one of the most significant is the availability of macronutrients. These vital nutrients are responsible for providing the foundation of plant growth and development, but if they’re not present in sufficient amounts, your plants may suffer from a range of deficiencies. In this article, we’ll dive into the world of macronutrient deficiencies in cannabis plants, exploring the most common deficiencies, how to recognize them, and what you can do to fix them. So, let’s take a closer look at what macronutrients are and why they’re so important for healthy cannabis growth.
What Are Macronutrients?
Contents
As an aspiring cannabis grower, you’ve probably heard the term “macronutrients” thrown around a lot. But what exactly are macronutrients and why are they so crucial to the growth of healthy cannabis plants? Simply put, macronutrients are the essential nutrients that plants need in large quantities in order to thrive. These nutrients are responsible for everything from the plant’s overall growth and development to its ability to produce potent buds. In this section, we’ll take a closer look at the three main macronutrients and why they’re so important to your cannabis plants.
The Three Macronutrients
There are three main macronutrients that are essential for the growth and development of cannabis plants. These nutrients are required in large amounts and play a critical role in the plant’s overall health and productivity.
1. Nitrogen: Nitrogen is a vital macronutrient that is required for plant growth and development. It is responsible for the production of chlorophyll, which is needed for photosynthesis. Nitrogen deficiency can cause yellowing of leaves and stunted growth in cannabis plants.
2. Phosphorus: Phosphorus is another essential macronutrient that plays a critical role in cannabis growth and development. It is necessary for the formation of healthy roots, stems, flowers, and fruits. Phosphorus deficiency can lead to poor root development and slow growth in plants.
3. Potassium: Potassium is the third vital macronutrient that is essential for cannabis growth and development. It plays a critical role in the regulation of water balance and nutrient uptake in plants. Potassium deficiency can cause slow growth, weak stems, and poor quality flowers in cannabis plants.
All three macronutrients: nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, are critical for the growth and development of healthy cannabis plants. Deficiencies in any of these nutrients can have negative effects on plant growth and productivity, and therefore it is crucial to ensure that plants receive adequate levels of these macronutrients throughout their growth cycle.
The Top Macronutrient Deficiencies in Cannabis
As a cannabis grower, it is essential to understand the importance of macronutrients and their role in the growth and overall health of your plants. Unfortunately, even with the best care and attention, macronutrient deficiencies can still occur, leading to stunted growth, reduced yields, and in severe cases, plant death. In this section, we will explore some of the most common macronutrient deficiencies that cannabis plants can experience and discuss their causes and symptoms in detail. By the end of the section, you will have a comprehensive understanding of how to diagnose and treat macronutrient deficiencies in your cannabis plants.
Nitrogen Deficiency
Nitrogen is one of the most essential macronutrients required for the growth and development of cannabis plants. A deficiency of this critical nutrient can cause stunted growth, yellowing of leaves, and a reduction in the overall yield of the plant. A Nitrogen deficiency can also be mistaken for other nutrient deficiencies, so it’s important to correctly identify the problem before attempting any solutions.
Here’s an overview of the signs and symptoms of a Nitrogen deficiency in cannabis plants:
| Sign/Symptom | Description |
|---|---|
| Yellowing leaves | One of the most common and obvious signs of a Nitrogen deficiency is the yellowing of the cannabis plant’s leaves. In many cases, the yellowing will begin at the bottom of the plant and will gradually move up toward the top. |
| Stunted growth | Cannabis plants that are lacking Nitrogen will often experience stunted growth. This stunted growth can lead to weaker and smaller plants that are more susceptible to pests and diseases. |
| Pale leaves | In addition to yellowing, the leaves of a Nitrogen-deficient cannabis plant may also appear pale or even white in some cases. This is because Nitrogen is essential for the production of chlorophyll, which is responsible for the green color in plants. |
| Lower leaf drop | As a Nitrogen deficiency progresses, the lower leaves of the cannabis plant may begin to drop off. This is due to the plant cannibalizing itself in order to obtain the necessary Nitrogen for growth. |
| Weak stems | Cannabis plants lacking Nitrogen may also have weak stems that are unable to support the weight of the plant. This can cause the plant to tip over or break, further stunting its growth and development. |
If left untreated, a Nitrogen deficiency can severely impact the health and yield of the cannabis plant. It’s important to take steps to address the problem as soon as possible.
Phosphorus Deficiency
Phosphorus is one of the three primary macronutrients required by cannabis plants. It plays a vital role in photosynthesis, energy transfer, and nutrient uptake. A deficiency in this nutrient can lead to stunted growth, weak stems, and poor flower production.
| Symptoms | Description |
|---|---|
| Poor root development | A phosphorus deficiency can cause the roots to become stunted and underdeveloped. This can lead to poor nutrient uptake and weak plants. |
| Purple stems | One of the most visible symptoms of a phosphorus deficiency is purple stems. This discoloration is caused by the accumulation of anthocyanin pigments. |
| Delayed flowering | Phosphorus is essential for flower development. A deficiency in this nutrient can delay flowering and reduce the overall yield of the plant. |
| Poor bud formation | Buds that lack density and are smaller than normal can be a sign of a phosphorus deficiency. This nutrient is required for the growth and development of healthy buds. |
To address a phosphorus deficiency, it may be necessary to add a phosphorus-rich fertilizer to the soil or nutrient solution. It’s important to make sure the fertilizer is compatible with the growing medium and the plant’s stage of growth. Adjusting the pH level of the soil or nutrient solution may also help improve phosphorus uptake by the plant.
It’s essential to monitor the macronutrient levels in cannabis plants and address any deficiencies promptly to ensure healthy growth and a bountiful yield.
Potassium Deficiency
Potassium is an essential macronutrient that is essential for plant growth and development. It plays a crucial role in regulating water movement, maintaining turgor pressure, activating enzymes, and promoting photosynthesis. A potassium deficiency can cause stunted growth, leaf curling and browning at the margins, and low yields.
|Symptoms: |Description: |
|—————————|——————————-|
|Yellowing leaves with dead spots.| A potassium deficiency first appears in the lower leaves with a yellowish tinge that develops into a burnt or crispy look.|
|Weak stems and stalks.| Plants with potassium deficiency grow weak stems that cannot support the weight of the flowers and leaves. |
|Delayed flowering time.| The flowering stage of plants with a potassium deficiency is delayed, which affects its growth cycle.|
|Reduced yields.| The final result of potassium deficiency is the reduced size and quality of the buds. |
To fix a potassium deficiency in cannabis plants, you need to add fertilizers that are high in potassium. One effective way is to use a potassium-rich liquid nutrient solution, which can be dissolved in water and applied directly to the soil. Another way is to use potash, which is a potassium-based fertilizer that is highly soluble in water. You can apply it to the soil or mix it with the nutrient solution for a more effective delivery.
Besides adding nutrients, you can also adjust the pH level of the soil. Potassium is better absorbed when the pH level ranges between 6.0 and 7.0. Use pH testing kits to check the pH level and adjust it using pH buffers.
Lastly, flushing the soil with water to remove any excess salts and minerals, which could interfere with absorption. Check for root problems such as damage or poor drainage since this could also cause a potassium deficiency.
Potassium is an essential nutrient that plays a vital role in promoting the growth and development of cannabis plants. A deficiency in potassium can impact the quality and size of your buds, which can lead to disappointing yields. It’s important to pay attention to the symptoms and take prompt action to fix the deficiency.
Calcium Deficiency
Calcium is one of the essential macronutrients that cannabis plants require in moderate amount. It plays a critical role in maintaining the structural integrity of the cell walls and regulates various enzymatic reactions within the plant. Calcium deficiency can lead to a broad range of problems, including stunted growth, leaf deformation, and poor yield.
What causes calcium deficiency in cannabis plants?
- High concentrations of potassium, magnesium, and sodium make it difficult for the plant to absorb calcium from the soil, leading to calcium deficiency.
- Excessive use of fertilizers rich in nitrogen or phosphorus can lead to competition between nutrients, leading to inadequate absorption of calcium.
- Irregular watering habits can also contribute to calcium deficiency.
- Soil that is too acidic (low pH) or too alkaline (high pH) can hinder the uptake of calcium from the soil.
How to identify calcium deficiency in cannabis plants?
- The leaves will start to curl, and their tips will turn brown or black.
- You may notice brown spots appearing around the edges of the leaves, which may spread to the entire leaf surface with time.
- The stems of the plant may start to appear weak and brittle.
- The growth of the plant may be stunted, and the leaves may seem smaller than usual.
How to fix calcium deficiency in cannabis plants?
- The first step towards addressing calcium deficiency is to check the pH level of the soil. If the soil is too acidic or alkaline, try to adjust the pH level to 6.0-7.0 to make it easier for the plant to absorb calcium.
- Use calcium-rich fertilizers that contain calcium nitrate or calcium carbonate to provide the plant with an adequate amount of calcium.
- Add crushed eggshells, bone meal, or dolomite lime to the soil to supplement the calcium content.
- Make sure to water the plant regularly, allowing the soil to remain moist but not waterlogged.
By identifying and addressing the calcium deficiency in cannabis plants, you can help them grow healthy and produce a better yield. Remember to maintain a balance between all the essential macronutrients in the soil for the plants to grow healthy and strong.
Magnesium Deficiency
One of the top macronutrient deficiencies that cannabis plants can experience is a lack of magnesium. Magnesium is an essential element needed for several processes in the plant, including chlorophyll production and protein synthesis. Without enough magnesium, the plant will show signs of yellowing or discoloration, especially in the older leaves. Here is a table summarizing the symptoms, causes, and solutions for magnesium deficiency in cannabis plants:
| Symptoms | Causes | Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Yellowing of leaves, especially in between veins | Low levels of magnesium in soil or water; high levels of potassium or calcium that can block magnesium uptake; pH imbalances that prevent the plant from absorbing magnesium | Use a fertilizer that contains magnesium; adjust pH levels to ensure proper nutrient uptake; use supplements or additives specifically designed to address magnesium deficiency |
| Stunted growth | Magnesium deficiency can slow down or stunt growth as it is needed for many metabolic processes, including the activation of enzymes. | Identify the cause of the deficiency and address it as soon as possible. This can involve adding nutrients to the soil, adjusting pH levels, or flushing the plant to remove excess nutrients. |
| Poor quality buds and low yields | When a plant is deficient in magnesium, it is unable to produce chlorophyll effectively, which can reduce the quality and quantity of buds. | Using a fertilizer that contains a balanced mix of macronutrients, including magnesium, can help prevent deficiencies and promote healthy plant growth. |
It is important to note that while correcting magnesium deficiency can improve the health of your cannabis plants, adding too much magnesium can also have negative effects. Always follow the recommended dosage guidelines provided by your nutrient manufacturer and use caution when supplementing with additional nutrients.
Sulfur Deficiency
Sulfur is one of the essential macronutrients required by cannabis plants, and its deficiency can cause stunted growth and reduced plant vigor. Sulfur is particularly important for the formation of chlorophyll, which is critical for photosynthesis.
Symptoms of sulfur deficiency can be similar to those of nitrogen deficiency, but the difference is that the leaves show yellowing starting from the center of the leaves, and veins may also appear darkened or even blackened. The leaves may also become brittle and curl downwards.
A sulfur deficiency can be remedied by adding a suitable fertilizer containing sulfur. Here are some common sources of sulfur fertilizer:
| Fertilizer | Sulfur Content |
|---|---|
| EPSOM salt (magnesium sulfate) | 13-14% sulfur |
| Ammonium sulfate | 20-24% sulfur |
| Gypsum (calcium sulfate) | 19% sulfur |
It’s important to note that adding too much sulfur can lead to toxicity and negatively affect plant growth. It’s recommended to follow the instructions on the fertilizer package and not exceed the recommended dosage.
Additionally, it’s also essential to ensure that the growing medium is at the right pH level to facilitate the absorption of sulfur. The optimal range is typically between 6.0 to 7.0. Too high or too low pH levels can affect the plant’s ability to take up the nutrients it needs from the soil.
Sulfur deficiency in cannabis plants is a crucial issue that can lead to decreased growth and yield. Proper identification of the problem and adding the necessary nutrients is critical for the plant’s health and development.
How to Recognize Macronutrient Deficiencies in Cannabis
For any cannabis grower, recognizing macronutrient deficiencies in your plants is crucial to maintaining healthy and strong growth. Without the right balance of nutrients, plants can experience stunted growth or even die. To ensure your plants are getting everything they need, it’s important to know how to identify deficiencies both visually and through testing. Here, we’ll explore some methods for recognizing macronutrient deficiencies in your cannabis plants.
Visual Symptoms
One of the most common ways to identify macronutrient deficiencies in cannabis plants is through visual symptoms. Here are some signs to look out for:
- Nitrogen deficiency: Leaves turn yellow starting from the bottom of the plant and working up. The leaves may also become weak and thin.
- Phosphorus deficiency: Leaves may appear dark green or blue-tinted, and may develop red or purple stems. The leaves may also become stiff and brittle.
- Potassium deficiency: Leaves develop yellow or brown spots, particularly at the edges, and may curl or twist. The plant may also experience slower overall growth.
- Calcium deficiency: Young leaves and buds may appear distorted or twisted. The tips and edges of leaves may also develop brown or black spots.
- Magnesium deficiency: Leaves will turn yellow, starting at the edges and moving inward. In severe cases, leaves may become brittle and curl or twist.
- Sulfur deficiency: Leaves become yellow starting from the bottom of the plant and working up. The leaves may also become small and thin.
It is important to note that these visual symptoms can also be caused by other issues such as pests or diseases, so it is important to investigate thoroughly to confirm the cause of the problem. Additionally, some nutrients, such as iron or zinc, may show similar symptoms to macronutrient deficiencies, so it is important to have a comprehensive understanding of cannabis plant nutrition. pH and EC testing can also be helpful in identifying specific nutrient deficiencies.
pH and EC Testing
One of the most effective ways to determine macronutrient deficiencies in cannabis plants is by conducting a pH and Electrical Conductivity (EC) test on the soil.
The Importance of pH Testing
The pH level of soil plays a crucial role in determining the availability of macronutrients to the cannabis plant. The pH scale ranges from 0 to 14, with 7 being neutral. A pH level of 6.5 to 7.5 is ideal for cannabis plants as it allows for optimal nutrient uptake. A pH level that is too high or too low can result in nutrient deficiencies or toxicities that can have a negative impact on the growth and development of cannabis plants.
The Role of EC Testing
EC measures the amount of nutrients or salts that are present in the soil solution. In other words, it determines the concentration of the solution. Plants require a specific range of EC for healthy growth and development. If the EC is too low, there may not be enough nutrients available to the plant, and if it is too high, the soil may become toxic and damage the roots of the plant.
Using pH and EC Testers
To test the pH and EC levels of the soil, a pH tester and EC meter can be used. These tools are available at most gardening stores and are relatively easy to use.
To perform a pH test, a small amount of soil is mixed with water and the pH tester is inserted into the solution. The pH tester will give a reading of the pH level of the soil.
For EC testing, a small sample of soil is mixed with water and the EC meter is inserted into the solution. Similar to the pH tester, the EC meter will provide a reading of the concentration of salts in the soil.
Interpreting pH and EC Readings
Once the readings are obtained, they should be compared to ideal ranges for cannabis plants. If the pH and EC levels are not within the ideal range, adjustments should be made to address the specific deficiencies or toxicities.
It is important to note that pH and EC levels can vary depending on the stage of growth, soil type, and nutrients being used. Regular testing is necessary to ensure optimal plant health and growth. The following table provides an overview of ideal pH and EC ranges for cannabis plants.
| Stage of growth | Ideal pH Range | Ideal EC Range (in ms/cm) |
|---|---|---|
| Seedling | 6.0-6.5 | 0.4-0.7 |
| Vegging | 5.5-6.5 | 0.8-1.5 |
| Flowering | 6.0-6.8 | 1.5-2.0 |
How to Fix Macronutrient Deficiencies in Cannabis Plants
Now that you’ve learned about the top macronutrient deficiencies in cannabis plants and how to recognize them, it’s important to know how to fix these issues. Correcting macronutrient deficiencies in cannabis plants can be perplexing, especially for new growers who are still learning the ropes. However, it’s crucial to understand how to fix these deficiencies in order to ensure your plants remain healthy and continue to thrive. In this section, we’ll cover several methods for fixing macronutrient deficiencies in cannabis plants. From adding nutrients and adjusting pH and EC levels to flushing the soil and checking for root problems, we’ll guide you through the steps to bring your plants back to good health.
Adding Nutrients
When it comes to addressing macronutrient deficiencies in cannabis plants, one of the most common solutions is adding nutrients. This involves supplying the plant with additional nutrients that it may be lacking in order to promote healthy growth and development.
To do this, growers can use various types of fertilizers that are specifically formulated to address macronutrient deficiencies. These fertilizers contain high levels of the deficient nutrient, allowing the plant to quickly absorb the necessary nutrients and recover.
Fertilizers come in different types, including organic and synthetic fertilizers. Organic fertilizers are derived from natural sources, such as compost, manure, and bone meal, while synthetic fertilizers are chemically formulated to provide specific nutrients.
When selecting a fertilizer, it’s important to choose one that is appropriate for the specific deficiency and growth stage of the plant. Additionally, some fertilizers may be better suited for specific growing mediums, such as soil or hydroponic systems.
To properly add nutrients to the plant, fertilizer should be mixed into the growing medium, either by top dressing the soil or mixing it into the nutrient solution in hydroponic systems. Care should be taken to avoid over-fertilization, which can damage the plant’s roots and lead to further issues.
Adding nutrients is a key method for addressing macronutrient deficiencies in cannabis plants. By selecting the appropriate fertilizer and properly applying it, growers can help promote healthy growth and development, resulting in a bountiful harvest.
Adjusting pH and EC Levels
Maintaining the correct pH and EC levels of your cannabis plants is crucial for preventing macronutrient deficiencies. pH refers to the acidity or alkalinity of the soil, while EC (electrical conductivity) measures the concentration of nutrients in the soil solution.
Adjusting pH levels: Cannabis plants thrive in soil with a pH between 6.0 and 7.0. If the pH is too high or too low, it can result in nutrient deficiencies. To adjust the pH level, you can use pH-up or pH-down solutions, which are available at most grow stores. Before applying any solutions, it’s essential to test the pH level of your soil using a pH test kit. Once you’ve determined the current pH level, add small amounts of pH-up or pH-down until you reach the desired range. Re-test the soil after adjustments to ensure the pH level is in the optimal range.
Adjusting EC levels: High or low EC levels can cause nutrient deficiencies in cannabis plants. If the EC is too high, it means there are too many nutrients in the soil, and the plant may experience nutrient burn. Conversely, if the EC is too low, the plant may suffer from nutrient deficiencies. To adjust EC levels, you may need to flush the soil with plain water to remove excess nutrients or add nutrient solution to increase nutrient levels. It’s essential to use an EC meter to accurately measure the concentration of nutrients in the soil solution before making any adjustments.
Adjusting pH and EC levels is an important step in preventing macronutrient deficiencies in cannabis plants. By using pH-up or pH-down solutions and monitoring the EC levels, growers can ensure their plants are getting the nutrients they need to thrive. Proper monitoring and maintenance of pH and EC levels can result in healthy, robust plants with high yields.
| Step | Process |
|---|---|
| Step 1 | Test the pH level of the soil using a pH test kit. |
| Step 2 | If the pH is too high, add pH-down solution in small amounts until it reaches the optimal range. If the pH is too low, add pH-up solution in small amounts until you reach the optimal range. |
| Step 3 | Re-test the soil after adjustments to ensure the pH level is in the desired range. |
| Step 4 | Measure the EC level of the soil using an EC meter. |
| Step 5 | If the EC is too high, flush the soil with plain water to remove excess nutrients. If the EC is too low, add nutrient solution to increase nutrient levels. |
| Step 6 | Re-measure the EC level after adjustments to ensure it is in the optimal range. |
Flush the Soil
Flush the soil is the process of thoroughly watering the plant with plain, pH-balanced water for a certain period of time. This is done to remove any excess nutrients from the soil that can cause nutrient lockout or toxicity in the plant. Flushing the soil can also help to reduce the overall salt buildup in the soil and improve the plant’s overall health.
Here are the steps to flush the soil:
- Step 1: Prepare enough plain, pH-balanced water to thoroughly water the plant. The amount of water needed will depend on the size of the plant and the size of the container it is in.
- Step 2: Water the plant with the plain, pH-balanced water until it flows out of the bottom of the pot. Make sure to get all areas of the soil.
- Step 3: Wait for the water to drain from the bottom of the pot.
- Step 4: Water the plant again with the plain, pH-balanced water until it flows out of the bottom of the pot again.
- Step 5: Wait for the water to drain from the bottom of the pot.
- Step 6: Repeat steps 4 and 5 as necessary until the soil is thoroughly flushed.
It is recommended to flush the soil every few weeks or whenever there is a nutrient buildup in the soil. Flushing the soil can also help to prevent nutrient deficiencies by ensuring that the plant has access to all the necessary nutrients. However, it’s important to not over-flush the soil, as this can strip the soil of essential nutrients and harm the plant.
In conclusion, flushing the soil is an effective way to remove excess nutrients and improve the overall health of a cannabis plant. It’s important to follow the steps carefully and not over-do it to avoid causing harm to the plant.
Check for Root Problems
One important step in fixing macronutrient deficiencies in cannabis plants is to check for root problems. If the plant roots are not healthy, they may not be able to absorb the necessary nutrients. Here are some steps to take when checking for root problems:
- Inspect the Roots: Carefully remove the plant from the soil and check the roots for any signs of damage, rot, or discoloration. Healthy roots should be white and firm to the touch, while unhealthy roots will be discolored, soft or mushy.
- Check for Overwatering: Overwatering can cause root problems, such as rot or mold, so check to make sure the soil is not overly moist. You can also use a moisture meter to check the water level in the soil.
- Ensure Proper Drainage: Make sure the pot or container has proper drainage holes to allow excess water to flow out of the bottom. Improper drainage can cause the soil to become waterlogged and lead to root problems.
- Trim Damaged Roots: If you find any damaged roots, trim them off with clean, sharp scissors or a knife. Be sure to sterilize your tools beforehand to prevent the spread of disease.
- Repot the Plant: If the root problems are severe or you suspect the soil is contaminated, consider repotting the plant in fresh soil.
By taking the time to check for root problems, you can identify and address any issues that may be affecting the plant’s ability to absorb the macronutrients it needs to grow and thrive.
Conclusion
After going through the detailed information on top macronutrient deficiencies in cannabis plants, it’s apparent how crucial it is to ensure that your plants receive the necessary nutrients to prevent such deficiencies.
Macronutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, magnesium, and sulfur are all essential for the healthy growth of cannabis plants. They play a significant role in the structure and development of plants, and their importance should not be taken for granted.
Macronutrient deficiencies can lead to a host of problems that affect plant growth, development, and yield. Understanding how to identify and fix these deficiencies is essential for any cannabis grower.
Visual symptoms are the easiest way to identify nutrient deficiencies, although pH and EC testing can help determine which nutrient is lacking. Adding nutrients, adjusting pH and EC levels, flushing the soil, and checking for root problems are all ways to fix macronutrient deficiencies in cannabis plants.
In conclusion, ensuring that your cannabis plants receive the necessary macronutrients is essential to their proper growth and development. By understanding how to recognize and fix these deficiencies, growers can ensure that their plants receive the essential nutrients they need to thrive. Remember, healthy plants equal a healthier yield!
Frequently Asked Questions
What are micronutrients?
Micronutrients are essential elements that are required by cannabis plants in very small amounts for healthy growth and development.
Why are macronutrients important for cannabis plants?
Macronutrients are important for cannabis plants because they provide the essential building blocks that the plant needs for healthy growth and development.
What are some common symptoms of macronutrient deficiencies in cannabis plants?
Common symptoms of macronutrient deficiencies in cannabis plants include yellowing or discoloration of leaves, stunted growth, and poor plant health overall.
How can I determine if my cannabis plants are suffering from a macronutrient deficiency?
You can determine if your cannabis plants are suffering from a macronutrient deficiency by observing visual symptoms and testing soil pH and EC levels.
What are some common causes of macronutrient deficiencies in cannabis plants?
Common causes of macronutrient deficiencies in cannabis plants include poor soil quality, over or under watering, and nutrient imbalances.
What is the best way to fix a macronutrient deficiency in my cannabis plants?
The best way to fix a macronutrient deficiency in your cannabis plants is to add the necessary nutrients, adjust pH and EC levels, flush the soil, and check for root problems.
Is it possible to overfeed cannabis plants with macronutrients?
Yes, it is possible to overfeed cannabis plants with macronutrients, which can lead to nutrient burn and other plant health problems.
How often should I fertilize my cannabis plants with macronutrients?
It is important to follow the recommended fertilization schedule for your particular strain of cannabis, as over or under fertilization can lead to nutrient imbalances.
What are some natural sources of macronutrients for my cannabis plants?
Some natural sources of macronutrients for cannabis plants include compost, manure, bone meal, and fish emulsion.
Can macronutrient deficiencies be prevented in my cannabis plants?
Yes, macronutrient deficiencies can be prevented in your cannabis plants by providing proper soil drainage, testing and adjusting pH and EC levels, and following a recommended fertilization schedule.