A Comprehensive Guide to Fertilizing Cannabis for Optimal Growth
Growing cannabis can be a challenging yet rewarding experience. As a cannabis grower, you want to ensure that your plants are receiving the right nutrients to thrive and produce high-quality buds. Fertilizers play a crucial role in the growth and development of cannabis plants. However, with so many different types of fertilizers available, it can be overwhelming to know which one to choose. In this article, we will explore the basics of fertilizers, including the essential nutrients for cannabis plants, and the different types of fertilizers, such as organic, synthetic, and biological. We will also discuss the effects of fertilizers on cannabis growth, understanding NPK, and foliar feeding. By the end of this article, you will have a better understanding of fertilizers and how to use them to achieve optimal cannabis growth.
The Basics of Fertilizers
Contents
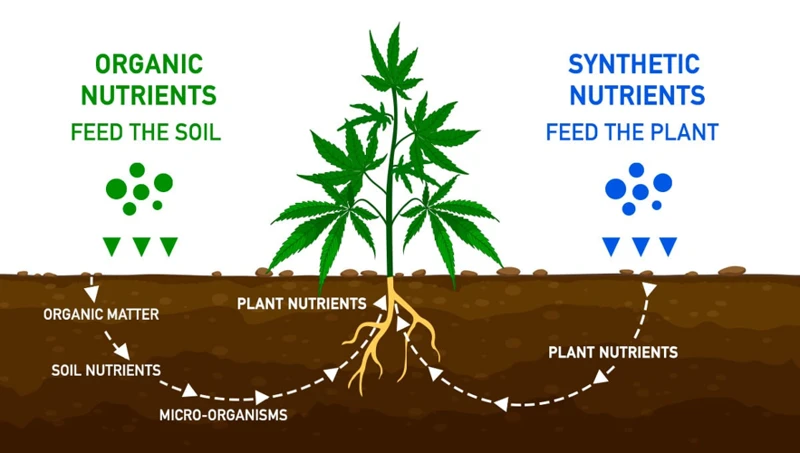
When it comes to growing cannabis, proper nutrition is essential for achieving healthy and vigorous plants. One of the most important aspects of plant nutrition is the use of fertilizers. Fertilizers are substances that provide essential nutrients to plants and help them grow. However, with so many types of fertilizers available, it can be difficult to determine which one is right for your cannabis plants. In this section, we will explore the basics of fertilizers, including the different types, essential nutrients, and how to read fertilizer labels. Understanding the fundamentals of fertilizers is crucial in maximizing the potential of your cannabis growth. To learn more about the differences between organic and synthetic nutrients, check out our article on organic vs. synthetic nutrients for cannabis.
What are fertilizers?
Fertilizers are important substances used to improve soil fertility and to provide essential nutrients to plants. They are designed to provide plants with the necessary elements to support their growth and development, thus promoting healthy and fruitful plant growth.
Fertilizers can be broken down into two main categories: organic and synthetic fertilizers. Organic fertilizers are made up of natural materials, such as compost, manure, and bone meal. Synthetic fertilizers, on the other hand, are made from inorganic materials and are typically manufactured in large-scale chemical plants.
Both organic and synthetic fertilizers contain essential nutrients that plants need to grow, including nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. Nitrogen is essential for plant growth and is typically responsible for the development of leaves and stems. Phosphorus supports root growth and helps plants to develop healthy flowers and fruits. Potassium promotes strong stem growth and is essential for the overall health of the plant.
Fertilizers come in many different forms, including granular, liquid, and sprayable. Granular fertilizers are typically applied to the soil and are slowly broken down over time, providing a long-lasting source of nutrients for plants. Liquid fertilizers, on the other hand, can be applied directly to the plant’s leaves or roots for quick absorption. Sprayable fertilizers are similar to liquid fertilizers, but they are typically applied as a fine mist over the plant’s leaves for quick absorption.
Regardless of the type of fertilizer used, it is essential to follow the instructions carefully to ensure proper application and avoid over-fertilization, which can lead to burnt leaves and stunted plant growth. With proper use, fertilizers can be an effective way to promote healthy and abundant plant growth.
The different types of fertilizers
Fertilizers are essential for providing the necessary nutrients to cannabis plants. There are three main types of fertilizers available: organic, synthetic, and biological fertilizers.
Organic Fertilizers: Organic fertilizers are derived from organic materials such as animal manure, bone meal, and compost. These fertilizers provide slow-release nutrients to the soil, promoting the growth of healthy plants. Organic fertilizers also improve soil health, making it easier for plants to absorb nutrients. Some common types of organic fertilizers include:
- Compost
- Blood meal
- Bone meal
- Fish emulsion
- Feather meal
- Manure
Synthetic Fertilizers: Synthetic fertilizers are made from chemical compounds and are formulated to provide specific nutrients to plants. These fertilizers are easy to use and provide quick results. However, overuse can lead to chemical build-up in the soil, which can harm soil health and plant growth. Some common types of synthetic fertilizers include:
- Ammonium nitrate
- Calcium nitrate
- Superphosphate
- Potassium sulfate
- Urea
Biological Fertilizers: Biological fertilizers contain living microorganisms such as bacteria or fungi, which help to break down organic matter into nutrients that plants can absorb. These fertilizers help to promote soil health and can improve the overall growth of cannabis plants. Some common types of biological fertilizers include:
- Mycorrhizae
- Rhizobia
- Azotobacter
- Actinomycetes
- Bacillus subtilis
Each type of fertilizer has its own advantages and disadvantages, so it’s important to choose the one that best fits your needs and growing conditions.
What are the essential nutrients for cannabis plants?
Cannabis plants require a variety of nutrients to grow and thrive. These nutrients are classified into two categories: macronutrients and micronutrients.
Macronutrients are required in relatively large quantities and include nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), potassium (K), calcium (Ca), magnesium (Mg) and sulfur (S). These nutrients play important roles in plant growth and development, such as building cell walls, photosynthesis, and enzyme function.
Micronutrients, on the other hand, are required in smaller quantities and include iron (Fe), manganese (Mn), zinc (Zn), copper (Cu), boron (B), molybdenum (Mo), and chlorine (Cl). Despite their minimal quantity requirements, these nutrients are crucial for maintaining the overall health of cannabis plants and helping them reach their maximum potential.
The table below highlights the essential nutrients for cannabis plants along with their corresponding functions.
| Nutrient | Function |
|---|---|
| Nitrogen (N) | Building blocks for amino acids, enzymes, and chlorophyll; promotes foliage growth |
| Phosphorus (P) | Plays a crucial role in photosynthesis, energy transfer, and root development |
| Potassium (K) | Responsible for enzyme activation, cell division, and water uptake |
| Calcium (Ca) | Important for cellular structure and function, as well as regulating pH levels and nutrient uptake |
| Magnesium (Mg) | Essential for photosynthesis and chlorophyll development, as well as enzyme activation and stress tolerance |
| Sulfur (S) | Important for amino acid production and protein synthesis, as well as overall plant health and nutrient uptake |
| Iron (Fe) | Key component of photosynthesis and chlorophyll production |
| Manganese (Mn) | Crucial for enzyme activation, chlorophyll production, and nitrogen metabolism |
| Zinc (Zn) | Important for hormone production and growth regulation, as well as enzyme activation and chlorophyll synthesis |
| Copper (Cu) | Essential for photosynthesis and lignin formation, as well as enzyme activation and iron uptake |
| Boron (B) | Important for cell wall synthesis, reproductive development, and calcium uptake |
| Molybdenum (Mo) | Necessary for nitrogen metabolism and enzyme function |
| Chlorine (Cl) | Helps maintain proper osmotic pressure, regulates stomatal function, and plays a role in photosynthesis and ion transport |
It’s important to note that a deficiency or excess of any of these nutrients can have detrimental effects on cannabis growth and development, leading to reduced yield or even plant death. It’s crucial to understand the needs of your cannabis plants and provide them with the appropriate nutrients through fertilization.
Organic Fertilizers
When it comes to growing cannabis, many growers prefer to use organic fertilizers due to concerns about the potential harmful effects of synthetic fertilizers. Organic fertilizers are made from natural sources such as plant and animal matter, making them a more environmentally friendly choice. However, with so many options available, it may be difficult to know which type of organic fertilizer is best for your cannabis plants. In this section, we will explore the basics of organic fertilizers, their types, how they work, and their effects on cannabis growth. Additionally, we will provide tips on using organic fertilizers effectively to help you achieve optimal results.
What are organic fertilizers? How do they work?
Organic fertilizers are made from natural plant and animal materials, and they do not contain synthetic chemicals. They are rich in organic matter and contain all essential elements that a plant needs for healthy growth, such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium (NPK).
How do they work?
Organic fertilizers work by breaking down slowly, releasing nutrients over time, and improving the soil structure. They promote healthy microbial activity in the soil, which helps to create a nutrient-rich environment for plant growth. Organic fertilizers improve the physical properties of the soil, making it more aerated and better able to hold moisture, which is important for plant growth.
Advantages of using organic fertilizers
– Environmentally-friendly
– Improve soil structure
– Long-lasting effects
– Safe for humans and pets
– Promote healthy microbial activity in soil
– Reduce the risk of nutrient leaching
Disadvantages of using organic fertilizers
– Slow-release of nutrients means slower growth
– Difficult to measure the nutrient content
– May contain weeds and pathogens if not properly composted
– May not have as high of an NPK ratio as synthetic fertilizers
Despite their disadvantages, many growers prefer to use organic fertilizers because of their long-lasting effects and environmental benefits.
Types of organic fertilizers
Organic fertilizers can be classified into different types based on their source and nutrient composition. Here are some of the most common types of organic fertilizers and their characteristics:
| Fertilizer Type | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Manure-based fertilizers | Composed of animal feces and bedding material. Generally high in nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. | Chicken manure, cow manure, bat guano |
| Compost-based fertilizers | Created through the decomposition of organic matter such as food waste, leaves, and yard trimmings. Generally rich in micronutrients. | Worm castings, leaf mold, mushroom compost |
| Bone meal fertilizers | Created by grinding animal bones, which are then processed to remove any fat and meat. High in phosphorus and calcium. | Bone char, blood meal |
| Fish-based fertilizers | Created from leftover fish waste, bones, and scraps. High in nitrogen, phosphorus, and micronutrients. | Hydrolyzed fish fertilizer, fish emulsion |
| Kelp-based fertilizers | Created from seaweed and kelp, which are dried and processed into a powder or liquid. High in micronutrients and growth hormones. | Kelp meal, liquid kelp |
| Cottonseed meal fertilizers | Created from the seeds of the cotton plant after the cotton fibers have been removed. High in nitrogen and potassium. | Cottonseed meal |
It’s important to note that organic fertilizers may not provide the same amounts of nutrients as their synthetic counterparts. They also tend to release nutrients more slowly over time, which means they may not have an immediate effect on plant growth. However, they can improve soil health and promote microbial activity, which can lead to long-term benefits for plant growth and overall plant health.
The effects of organic fertilizers on cannabis growth
Organic fertilizers can have different effects on cannabis growth depending on their composition and application method. Some of the benefits of using organic fertilizers include promoting soil health, increasing microbial activity, improving nutrient absorption, and producing higher yields. Here are some specific effects of organic fertilizers on cannabis growth:
- Slow-release of nutrients: Organic fertilizers contain nutrients that are released slowly over time, providing a steady supply of essential elements for cannabis plants. This gradual release prevents over-fertilization and helps maintain a more balanced nutrient profile in the soil.
- Rich in micronutrients: Organic fertilizers often contain a wide range of micronutrients that are essential for plant growth but may be lacking in synthetic fertilizers. These micronutrients can help improve the overall health and vitality of cannabis plants.
- Improvement of soil structure: Organic fertilizers can help improve soil structure by increasing the organic matter content, improving soil aeration and water retention, and promoting the growth of beneficial soil microorganisms.
- Reduced environmental impact: Organic fertilizers are generally considered more environmentally friendly than synthetic fertilizers because they are made from natural materials and are less likely to contribute to water pollution or soil degradation.
- Increased terpene and cannabinoid production: Some organic fertilizers, such as worm castings or bat guano, are high in micronutrients that can help increase the production of terpenes and cannabinoids in cannabis plants, resulting in a more flavorful and potent end-product.
However, it’s important to note that organic fertilizers can also have some downsides. They may be less effective in correcting specific nutrient deficiencies, may be more difficult to apply evenly, and can have a strong odor that may not be desirable in some settings. Additionally, they may contain pathogens or pests if not properly composted or sterilized. It’s important to choose high-quality organic fertilizers and use them according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
Tips for using organic fertilizers
When using organic fertilizers, there are some tips that can help you achieve the best results while ensuring the health of your cannabis plants. Here are some important tips to keep in mind:
| Tips for Using Organic Fertilizers |
|---|
| 1. Choose the right type of organic fertilizer for your plants. |
| Some organic fertilizers are better for certain types of plants than others, so it’s important to choose one that’s appropriate for cannabis. Look for one that contains the essential nutrients that cannabis needs. |
| 2. Use the correct dosage. |
| Organic fertilizers are often more concentrated than synthetic fertilizers, so be sure to follow the instructions carefully. Using too much can harm your plants or cause nutrient burn. |
| 3. Consider using compost tea. |
| Compost tea is a popular organic fertilizer that can provide nutrients and beneficial microbes to your plants. It’s easy to make and can promote healthy plant growth. |
| 4. Don’t overwater your plants. |
| Organic fertilizers often work best when the soil is slightly dry. Overwatering can cause the nutrients to leach out of the soil, which can lead to nutrient deficiencies. |
| 5. Use organic fertilizers in conjunction with other growing techniques. |
| Organic fertilizers work best when used in conjunction with other growing techniques, such as proper lighting, ventilation, and pruning. Using a combination of techniques can help you achieve optimal plant growth and yield. |
By following these tips, you can ensure that your cannabis plants are getting the nutrients they need to thrive, while minimizing the risk of nutrient burn or other problems that can occur when using fertilizers.
Synthetic Fertilizers
Synthetic fertilizers are a popular choice for many cannabis growers due to their convenience and quick results. These fertilizers are man-made and are formulated to provide specific nutrients needed for plant growth. However, their use is often a topic of controversy among growers and enthusiasts, leaving many people perplexed about their effects on cannabis growth. In this section, we’ll explore the different types of synthetic fertilizers, how they work, and their potential effects on cannabis plants.
What are synthetic fertilizers?
Synthetic fertilizers, also known as chemical fertilizers, are man-made products that are formulated to provide plants with the essential nutrients needed for their growth and development. They are generally composed of inorganic compounds and are usually faster acting than organic fertilizers.
The Advantages of Synthetic Fertilizers:
| Advantages | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Quick Release | Synthetic fertilizers release nutrients quickly and can provide fast results for plants. |
| Easy to Use | They can be easily applied to plants through soil or foliar application. |
| Versatile | Synthetic fertilizers can be tailored to meet the specific nutrient requirements of different plants and can be used in a variety of soil types and growing conditions. |
| Reliable Quantity | They are produced in large quantities and can be easily purchased from gardening centers. |
The Disadvantages of Synthetic Fertilizers:
| Disadvantages | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Environmental Pollution | Synthetic fertilizers can leach into the soil and nearby bodies of water, causing environmental pollution and harm to aquatic life. |
| Salt Accumulation | Overuse of synthetic fertilizers can lead to salt accumulation in the soil, which can harm plants and reduce soil productivity. |
| High Cost | Synthetic fertilizers can be more expensive than organic fertilizers due to the manufacturing and transportation costs involved. |
| Limited Soil Health | Excessive use of synthetic fertilizers can negatively impact soil health over time, as they do not contribute to building up the organic matter content in soil in the same way that organic fertilizers do. |
Synthetic fertilizers can be a useful tool in cannabis cultivation when used in moderation and with proper care. However, it is important to consider their potential negative impacts and to use them in conjunction with organic and biological fertilizers in order to maintain soil health and minimize environmental harm.
Types of synthetic fertilizers
Synthetic fertilizers are man-made fertilizers that are created to provide the essential nutrients for plants to grow. These fertilizers are typically made using chemicals and other synthetic materials. There are several different types of synthetic fertilizers which are used for cannabis growth. Let’s explore these types in detail in the table below.
| Types of Synthetic Fertilizers | Description |
|---|---|
| Nitrogen Fertilizers | Nitrogen fertilizers are used to promote vegetative growth and help the plant produce more foliage. They are commonly used during the vegetative stage of growth. |
| Phosphorous Fertilizers | Phosphorous fertilizers are used to promote root growth and flower development. They are commonly used during the flowering stage of growth. |
| Potassium Fertilizers | Potassium fertilizers are used to promote overall plant growth, increase resistance to disease, and improve water uptake. They are commonly used throughout all stages of growth. |
| Compound Fertilizers | Compound fertilizers are a combination of nitrogen, phosphorous, and potassium. These fertilizers are created to provide a balanced mix of nutrients that are required for overall plant growth. |
| Slow-Release Fertilizers | Slow-release fertilizers are designed to release nutrients over an extended period of time. These fertilizers are used to ensure that the plant receives a steady supply of nutrients without the risk of nutrient burn. |
It is important to note that synthetic fertilizers can be harmful to the environment and can have negative effects on the soil’s health. It is recommended to use synthetic fertilizers in moderation and to follow manufacturer instructions carefully to avoid overuse.
The effects of synthetic fertilizers on cannabis growth
When it comes to synthetic fertilizers, the effects on cannabis growth can vary depending on the specific type of fertilizer used. Here are some examples of the potential effects:
| Type of Synthetic Fertilizer | Effect on Cannabis Growth |
|---|---|
| Nitrogen-based fertilizers | Can promote stem and leaf growth, but may inhibit flower development if overused |
| Phosphorus-based fertilizers | Can promote root growth, flower development, and overall plant health, but may build up in soil over time |
| Potassium-based fertilizers | Can improve plant stress tolerance, disease resistance, and flower development, but may cause nutrient burn if overused |
| Micronutrient fertilizers | Can provide essential trace minerals like iron, zinc, and magnesium, but may be unnecessary in soil with sufficient nutrients |
It’s important to note that while synthetic fertilizers can provide a quick boost of nutrients to cannabis plants, they may also have negative impacts on soil health and the environment if overused. Additionally, some growers prefer to use organic or biological fertilizers to avoid synthetic additives and promote a more sustainable growing environment.
Tips for using synthetic fertilizers
When using synthetic fertilizers on your cannabis plants, there are a few tips to keep in mind to ensure their growth and health. Here are some important tips to consider:
| Tips for using synthetic fertilizers |
|---|
| Always follow the instructions on the label. |
| Be careful not to over-feed your plants, as this can lead to nutrient burn and other problems. |
| Only use synthetic fertilizers during the vegetative growth stage, as they can be too harsh for the flowering stage. |
| Avoid using synthetic fertilizers during the last two weeks of the flowering stage, as this can affect the taste and quality of your buds. |
| Flush your plants with clean water before harvesting to remove any excess nutrients from the soil. |
| Consider using a pH meter to ensure the pH level of your soil is within the appropriate range for the specific fertilizer you are using. |
| Store your synthetic fertilizers in a cool, dry place away from sunlight to prevent them from degrading. |
| Wear gloves and other protective gear when handling synthetic fertilizers, as they can be harsh chemicals that can be harmful to your skin and health. |
Following these tips can help you achieve the best results with your synthetic fertilizers and ensure the health and vitality of your cannabis plants. Remember to always read and follow the instructions on the label and use caution when handling fertilizers.
Biological Fertilizers
When it comes to fertilizing cannabis plants, there are many options to choose from. In addition to synthetic and organic fertilizers, there are also biological fertilizers. These fertilizers use living organisms to provide essential nutrients to the plant. But what exactly are biological fertilizers, and how do they work? Let’s dive in and explore this fascinating type of fertilizer that can offer unique benefits to your cannabis plants.
What are biological fertilizers? How do they work?
Biological fertilizers are made up of living organisms like bacteria, fungi, and algae. These fertilizers have become more popular with cannabis growers due to their ability to promote soil health and increase nutrient uptake in plants.
How do biological fertilizers work?
Biological fertilizers work by colonizing the roots and rhizosphere of the plant, forming a symbiotic relationship. This fosters an environment where beneficial microorganisms break down organic matter and release essential nutrients that the plant can easily absorb. This mutualistic relationship can increase the plant’s resistance to pests and diseases, while also improving soil structure and water retention.
Types of biological fertilizers
There are several types of biological fertilizers, each containing different bacteria or fungi strains. Here are some examples:
| Type of Biological Fertilizer | Description |
|---|---|
| Mycorrhizae | A fungus that forms a relationship with the plant roots and can increase nutrient uptake by as much as 700%. |
| Rhizobia | Bacteria that can fix atmospheric nitrogen, converting it into a form that plants can use. |
| Actinomycetes | Bacteria that break down organic matter and release nutrients like phosphorus and potassium. |
| Compost Tea | A mixture of beneficial bacteria and fungi that can be brewed to create a liquid fertilizer. |
The effects of biological fertilizers on cannabis growth
When applied correctly, biological fertilizers can have a positive impact on cannabis growth. They promote healthy root growth and increase nutrient uptake, which leads to larger yields and stronger, more resilient plants. Additionally, biological fertilizers can improve soil structure and fertility, which can improve soil health over time, reducing the need for synthetic fertilizers.
Tips for using biological fertilizers
Here are some tips for using biological fertilizers:
- Make sure to follow the manufacturer’s recommended dosage rates.
- Avoid using chemical fertilizers in combination with biological fertilizers, as the chemicals can harm the beneficial microorganisms.
- Apply biological fertilizers at the beginning of the growing season to give the microorganisms time to establish themselves.
- Store biological fertilizers in cool, dry locations to preserve the living microorganisms.
Types of biological fertilizers
Biological fertilizers are derived from living organisms and contain beneficial microorganisms that help improve soil health and nutrient availability for plants. There are different types of biological fertilizers available for cannabis plants, each with its unique benefits.
1. Mycorrhizal Inoculants:
Mycorrhizal inoculants contain beneficial fungi that form a symbiotic relationship with the plant roots. They help increase nutrient uptake, water absorption, and overall plant health. Mycorrhizae works particularly well with phosphorus uptake, making it a valuable addition during the vegetative stage.
2. Beneficial Bacteria:
Beneficial bacteria promote soil health and increase nutrient availability for plants. These bacteria are responsible for converting nutrients into a form that plants can absorb. There are many different strains of beneficial bacteria that each have their unique benefits, including improving soil texture, nitrogen fixation, and disease suppression.
3. Compost Tea:
Compost tea is a microbe-rich fertilizer that is made by steeping compost in water. The resulting solution is teeming with beneficial microorganisms that promote soil health, nutrient availability, and plant growth. Compost tea is known to improve the soil structure, boost plant immunity, and increase yields.
4. Fish Emulsion:
Fish emulsion is made by processing fish waste and blending it with water. It is a great source of nutrients, particularly nitrogen, and is easy to apply. Fish emulsion is readily absorbed by plants and stimulates growth, making it a popular choice for the vegetative stage.
5. Worm Castings:
Worm castings are a rich source of nutrients, beneficial bacteria, and microorganisms. They improve soil structure, increase water retention, and promote strong root development. Worm castings are ideal for soil amendments, as they help create a healthy growing environment for cannabis plants.
Biological fertilizers offer a natural and sustainable way of improving soil health and nutrient availability for cannabis plants. From mycorrhizal inoculants to compost tea, each type of biological fertilizer has its unique benefits that can help improve plant growth and yields.
The effects of biological fertilizers on cannabis growth
Biological fertilizers, which use organic materials and microorganisms to promote healthy plant growth, have several positive effects on cannabis growth:
- Improved soil structure: Biological fertilizers encourage healthy soil structure by adding organic matter, improving water retention, and promoting soil microbial activity. This creates optimal conditions for cannabis root development, leading to stronger and healthier plants.
- Better nutrient uptake: The microorganisms in biological fertilizers can break down nutrients in the soil, making them more available for cannabis plants to absorb. This improves nutrient uptake and can help prevent nutrient deficiencies.
- Increased resistance to disease and pests: The use of biological fertilizers can help create a balanced and diverse soil ecosystem, which can improve the plant’s natural defenses against disease and pests.
- Enhanced aroma and flavor: Biological fertilizers can improve the taste and smell of cannabis buds, as they can help promote terpene production.
The use of biological fertilizers can lead to healthier, more vibrant cannabis plants, with improved resistance to disease and pests, as well as increased aroma and flavor. However, it’s important to note that biological fertilizers may not provide as immediate and noticeable results as synthetic fertilizers and may require more time and patience.
Tips for using biological fertilizers
When using biological fertilizers for cannabis growth, it is important to keep in mind the following tips:
- Choose the right type of fertilizer: Different biological fertilizers have different compositions and nutrient ratios, so it is important to choose the right one for your specific cannabis strain and growth stage.
- Mix the fertilizer properly: Biological fertilizers tend to have a concentrated texture, thus they need to be mixed well with water in order to be properly distributed in the soil.
- Apply according to the growth stage: Depending on the stage of growth, it is important to adjust the application of the biological fertilizer in terms of dosage and frequency, to avoid overfeeding or underfeeding.
- Keep the soil healthy: Biological fertilizers work best when the soil is well balanced and rich in organic matter, so it is important to maintain soil health through natural means such as composting, crop rotation and avoiding the use of artificial pesticides.
- Avoid chemical use: Biological fertilizers rely on natural processes to work, and many chemicals such as bleach or chlorine can harm the beneficial bacteria and fungi required for the fertilizer to work properly.
- Monitor plant growth: Regular monitoring of plant health, flowering and nutrient absorption can help fine-tune the application of biological fertilizers and adjust any imbalances before they cause any major issues.
By following these tips, growers can ensure that their cannabis plants receive the best possible nutrients and achieve optimal growth and yields.
Understanding NPK
As a cannabis grower, understanding the role of fertilizers in promoting plant growth is crucial. One essential aspect to consider is the NPK ratio, which stands for the three primary nutrients required by cannabis plants: nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K). Each nutrient plays a vital role in different stages of plant growth, ranging from seedlings to flowering. It’s essential to have a basic comprehension of NPK ratios to provide the right nutrients during each stage of cannabis growth. In this section, we will discuss the importance of understanding NPK and how it influences cannabis growth.
What is NPK?
NPK stands for Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Potassium, which are three essential nutrients that plants need in order to grow and thrive. These nutrients play a crucial role in the development of healthy roots, stems, leaves, flowers, and fruits.
Each of the three nutrients has a specific function:
| Nitrogen (N) | Phosphorus (P) | Potassium (K) |
|---|---|---|
| Helps with leaf and stem growth | Aids in root growth and flower development | Promotes overall plant health and helps with disease resistance |
| Enhances photosynthesis | Assists with energy transfer within the plant | Regulates water balance and improves stress tolerance |
| Increases chlorophyll production | Helps with seed formation and crop yields | Improves overall plant vigour and strength |
It’s important to note that each nutrient is necessary in a different amount, depending on the stage of growth the plant is in. For example, during the vegetative stage, cannabis plants require higher amounts of Nitrogen in order to promote leaf and stem growth. During the flowering stage, however, cannabis plants require higher amounts of Phosphorus in order to produce abundant flower buds.
NPK ratios are often displayed on fertilizer labels as a series of three numbers. These numbers represent the percentage of each nutrient that is present in the fertilizer. For example, a fertilizer with an NPK ratio of 20-10-10 contains 20% Nitrogen, 10% Phosphorus, and 10% Potassium.
Understanding NPK is crucial when it comes to selecting the right fertilizer for your cannabis plants. By choosing an appropriate NPK ratio, you can ensure that your plants are getting the nutrients they need in the right amounts at the right stage of growth.
The importance of NPK in cannabis growth
Cannabis plants require certain essential nutrients to grow, and the most important of these are nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, commonly referred to as NPK. These three nutrients play a critical role in the growth, development, and overall health of cannabis plants.
Nitrogen (N) is vital for vegetative and foliage growth. It aids in the creation of amino acids and protein synthesis, which are fundamental building blocks for various structures within the plant. Nitrogen deficiencies can lead to yellowing of leaves and stunted growth.
Phosphorus (P) is essential for healthy root development and assists in energy transfer within the plant. It is also crucial in the later stages of flowering as it helps with the creation of essential oils and sugars. A lack of phosphorus can result in slow growth, weak stems, and an overall reduction in yield.
Potassium (K) is crucial for the plant’s overall health, including water usage, disease resistance, and stress tolerance. It also impacts the size and quality of buds and flowers. A deficiency in potassium can cause leaf burn, brown spots on leaves, and stunted growth.
Understanding and balancing the NPK ratio is essential for maximizing cannabis growth and achieving high-quality yields. Different stages of growth require different ratios of nutrients, and it is important to choose a fertilizer product that matches the stage of growth.
It is also important to note that too much of any nutrient can be harmful to the plant, which is why it is important to read and follow the instructions on the fertilizer label. Overfeeding can cause nutrient burn, toxic build-up, and other negative effects.
NPK is crucial for the growth and development of cannabis plants, and understanding the importance of balancing these nutrients can lead to a successful and rewarding harvest.
How to read NPK labels on fertilizers
When shopping for fertilizers, it’s important to understand how to read NPK labels as they provide vital information about the nutrient content of the fertilizer. NPK stands for nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K), and these three nutrients are essential for the growth and development of cannabis plants.
Here are some steps to follow when reading NPK labels on fertilizers:
- Find the three numbers: The three numbers on the fertilizer label represent the NPK ratio. For example, a label with 10-5-5 indicates that the fertilizer contains 10% nitrogen, 5% phosphorus, and 5% potassium.
- Understand the ratio: The NPK ratio indicates the proportion of each nutrient in the fertilizer. For instance, a 10-10-10 fertilizer has an equal proportion of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, while a 3-1-2 fertilizer has more nitrogen than phosphorus and potassium.
- Consider the plant’s growth stage: Different growth stages of cannabis require different ratios of NPK. For example, during the vegetative stage, plants require higher levels of nitrogen, while during the flowering stage, they need more phosphorus and potassium.
- Check for additional nutrients: Fertilizers may also contain other essential nutrients, such as calcium, magnesium, and sulfur. Make sure to check the label for these additional nutrients.
- Watch out for filler ingredients: Some fertilizers may also contain filler ingredients, such as sand or clay, which do not contribute to the nutrient content of the fertilizer. Be sure to check the label for the percentage of filler ingredients.
By understanding how to read NPK labels, cannabis growers can choose the appropriate fertilizer for their plants and ensure that they receive the necessary nutrients for optimal growth and development.
NPK ratios for different stages of cannabis growth
When it comes to cannabis growth, different stages require different ratios of NPK (nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium) nutrients to ensure healthy plants and maximum yields. It’s important to understand these ratios and apply them correctly. Here’s a breakdown of the ideal NPK ratios for each stage of cannabis growth:
| Growth Stage | N (nitrogen) | P (phosphorus) | K (potassium) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Seedling/Clone | 2 | 1 | 2 |
| Veg | 3 | 1 | 2 |
| Pre-Flower | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| Flowering | 1 | 4 | 5 |
| Ripening | 0 | 1 | 6 |
During the seedling and clone stage, cannabis plants require a higher ratio of potassium to ensure strong root development. In the vegetative stage, plants require more nitrogen for leafy growth. When plants enter pre-flower, the ratio of phosphorus needs to increase to promote healthy bud development. During the flowering stage, the ratio of potassium needs to be higher to support flower growth, and as the plant ripens, it requires less nitrogen and more potassium.
It’s important to note that NPK ratios can vary between different fertilizers and growing methods. It’s essential to follow the instructions provided by the manufacturer and monitor plant health to adjust the ratios as necessary. Over-fertilizing or under-fertilizing can lead to nutrient deficiencies or toxicities, which can harm the plant’s growth and overall quality. Proper management of NPK ratios during different stages of cannabis growth will help achieve maximum yields and high-quality buds.
Foliar Feeding
As cannabis growers continue exploring various methods to promote plant growth and health, foliar feeding has become a popular technique. Foliar feeding is the process of feeding plants by applying liquid fertilizer directly to their leaves. While some growers swear by this method, others are perplexed by its benefits and potential risks. In this section, we will take a deep dive into foliar feeding, examining its advantages, drawbacks, and best practices for application.
What is foliar feeding?
Foliar feeding is the process of applying fertilizers directly to the leaves of a cannabis plant. This method of fertilization allows for quick absorption of essential nutrients by the plant.
Below is a table highlighting some of the benefits and potential risks of foliar feeding cannabis plants:
| Benefits of Foliar Feeding | Potential Risks of Foliar Feeding |
|---|---|
|
|
It’s important to note that foliar feeding should not be the sole method of fertilization for a cannabis plant. It’s simply a way to supplement the plant’s nutrient intake, and should be done in moderation to avoid over-fertilization. Additionally, it’s important to avoid foliar feeding during the heat of the day as this can cause leaf burn.
Foliar feeding can be a helpful tool in promoting optimal growth for cannabis plants, as long as it’s done correctly and in conjunction with other fertilization methods.
The benefits and risks of foliar feeding cannabis plants
Foliar feeding involves spraying a nutrient-rich liquid directly on the leaves of cannabis plants. This technique has both benefits and risks that cannabis growers must consider in their practices.
| Benefits | Risks | |
|---|---|---|
| Effectiveness | The nutrients are absorbed quickly and efficiently through the leaves, improving the overall health and appearance of the plant. | Overapplication can lead to nutrient burn or damage to the leaves, and not all nutrients are effective when applied through the leaves. |
| Targeted application | Foliar feeding allows growers to target specific nutrient deficiencies in the leaves, rather than waiting for the nutrients to be absorbed through the roots. | If not done correctly, foliar feeding can lead to uneven distribution of nutrients and result in uneven growth or nutrient lockout. |
| Cost-effective | Foliar feeding is a cost-effective way to supplement nutrients and can reduce the overall use of fertilizers. | Improperly mixed solutions or using low-quality fertilizers in the spray can lead to plant damage and higher long-term costs. |
Foliar feeding can be an effective way to quickly and precisely provide nutrients to cannabis plants, but it requires careful attention and knowledge to ensure that it is done correctly and safely.
How to properly apply foliar feeding
Proper application of foliar feeding can greatly enhance the overall growth of your cannabis plants. Here are some tips on how to properly apply foliar feeding:
- Choose the right time: It’s best to apply foliar feeding during the early morning or late afternoon when the leaves are not exposed to direct sunlight. This will allow the leaves to fully absorb the nutrients without causing any harm to the plant.
- Use the right solution: It’s important to use a solution that is specifically designed for foliar feeding. This can be either a premixed solution or a custom solution that you create yourself. Make sure to properly dilute the solution according to the instructions.
- Apply the solution evenly: Using a spray bottle or a pump sprayer, apply the solution evenly to the top and bottom of the leaves. Be sure not to oversaturate the leaves as this can lead to nutrient burn.
- Monitor the plants: Keep a close eye on your plants after foliar feeding. If you notice any signs of stress or damage, adjust your foliar feeding schedule or solution accordingly.
- Combine with soil feeding: Foliar feeding should not replace regular soil feeding, but rather supplement it. Use in combination with a nutrient-rich soil and regular feeding schedule for optimal growth.
Following these tips can help ensure that your cannabis plants receive the proper nutrients through foliar feeding without any negative effects on their growth.
Conclusion
After exploring the different types of fertilizers and their effects on cannabis growth, it is clear that there is no one-size-fits-all approach when it comes to fertilizing cannabis plants. Each type of fertilizer has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice ultimately depends on the grower’s preferences and goals.
Organic fertilizers are a great option for those who prioritize sustainability and want to avoid synthetic chemicals. They work by slowly releasing nutrients into the soil, providing a more balanced and gentle approach to fertilization. Some popular types of organic fertilizers include compost, worm castings, and bone meal. While organic fertilizers may not provide immediate growth results, they can lead to healthier and more resilient plants in the long run.
Synthetic fertilizers, on the other hand, are more suitable for growers who want fast and reliable results. Synthetic fertilizers are designed to quickly provide plants with the necessary nutrients, but they may also come with some risks. Overuse of synthetic fertilizers can lead to nutrient burn or damage to the soil’s microbial ecosystem. That being said, synthetic fertilizers have been extensively researched and can provide consistent results.
Biological fertilizers offer a unique approach to fertilization by using beneficial microorganisms to enhance plant growth. They work by establishing symbiotic relationships between microorganisms and plant roots, allowing for improved nutrient uptake and disease resistance. Some common types of biological fertilizers include mycorrhizae and rhizobia. While biological fertilizers may take longer to produce noticeable effects, they can lead to more resilient and vigorous plants.
Understanding NPK ratios is crucial for any cannabis grower. The three macronutrients, nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K), play a critical role in plant growth and development. Each stage of the cannabis plant’s lifecycle requires different ratios of NPK, and it is important to choose a fertilizer that matches these needs. NPK ratios can be found on the labels of fertilizers and can be used to make informed decisions when selecting a fertilizer.
Foliar feeding can also be used as a supplement to traditional fertilization methods. Foliar feeding involves spraying a nutrient solution directly onto the leaves, allowing for quick and targeted absorption. While foliar feeding can provide immediate results, it can also be risky and should be done sparingly.
In summary, selecting the right fertilizer for cannabis plants depends on the grower’s priorities and goals. Whether it be organic, synthetic, or biological fertilizers, each type has its own unique advantages and disadvantages. Understanding NPK ratios and considering foliar feeding as a supplement can also lead to healthier and more productive plants.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are some natural alternatives to chemical fertilizers?
Some natural alternatives to chemical fertilizers include compost, manure, bone meal, fish emulsion, and seaweed.
How often should I fertilize my cannabis plants?
It depends on the type of fertilizer you’re using and the stage of your cannabis plant’s growth. Follow the instructions on the fertilizer label and adjust as needed based on your plant’s needs.
What happens if I use too much fertilizer on my cannabis plants?
Using too much fertilizer can lead to nutrient burn, stunted growth, or other health issues in your cannabis plants. It’s important to follow instructions carefully and avoid overfeeding.
Can I use the same fertilizer for all stages of cannabis growth?
It depends on the fertilizer. Some fertilizers are meant for specific growth stages, while others are designed to be used throughout the plant’s life cycle. Check the label or consult with a gardening expert for advice.
Are organic fertilizers better for cannabis growth than synthetic fertilizers?
It depends on personal preference and growing conditions. Both organic and synthetic fertilizers can be effective, but organic fertilizers are often preferred by those who prioritize natural and sustainable growing methods.
What is the best NPK ratio for cannabis growth?
The best NPK ratio will vary based on the particular stage of growth your cannabis plant is in. Consult with a gardening expert or follow guidelines provided by the fertilizer manufacturer.
Can I make my own organic fertilizer at home?
Yes, there are several DIY organic fertilizer recipes available. These can include compost, worm castings, and other natural materials.
Foliar feeding is the process of applying liquid fertilizer directly to a plant’s leaves. This can help provide a quick nutrient boost to the plant.
How can I tell if my cannabis plant is getting too much or too little fertilizer?
Signs of over-fertilization can include burned or discolored leaves, stunted growth, and root damage. Signs of under-fertilization can include yellow or slow-growing leaves. Monitor your plant’s growth and appearance carefully to avoid nutrient issues.
Are there any risks associated with using fertilizers on cannabis plants?
Overuse or misuse of fertilizers can lead to plant health issues or even environmental damage. However, when used properly, fertilizers can be a valuable tool in promoting healthy cannabis growth.