Optimizing Nutrient Levels for Cannabis Growth
Growing cannabis can be a challenging but rewarding experience. One important aspect of successful cultivation is understanding the nutrient requirements of the plant at different stages of growth. The complexity of nutrient balancing may leave some growers perplexed, but fear not! Adjusting Nutrient Levels for Different Stages of Cannabis Growth is a step-by-step guide that will provide you with all the necessary information to ensure optimal nutrition for your plants. From understanding the primary macronutrients required, to knowing when and how to adjust levels during different growth stages, this guide will equip you with vital knowledge to help you grow healthy and thriving cannabis plants.
Understanding Cannabis Nutrient Requirements
Contents
Growing healthy and impressive cannabis plants requires an understanding of their nutrient requirements. Providing the right balance of macro and micronutrients is crucial for successful cannabis cultivation. In this section, we will dive into the essential nutrients that cannabis plants need to thrive and the role of N-P-K ratios in determining the right nutrient balance. We will also explore the importance of micronutrients in promoting plant growth and health. By the end of this section, you will have a solid understanding of the cannabis plant’s nutrient needs and be better equipped to adjust nutrient levels for optimal growth.
The Nutrients Cannabis Plants Need
Cannabis plants require a variety of nutrients to grow healthy and robust, such as Nitrogen (N), Phosphorus (P), Potassium (K), Calcium (Ca), Magnesium (Mg), and Sulfur (S). These nutrients are essential for various functions in the cannabis plant’s growth and development, such as building proteins, enzymes, and cell walls.
Additionally, cannabis plants also require micronutrients in small amounts, such as Boron (B), Copper (Cu), Iron (Fe), Manganese (Mn), Molybdenum (Mo), and Zinc (Zn). These micronutrients play a crucial role in various metabolic processes and activating enzymes in the plant.
Below is a more detailed breakdown of each nutrient’s function:
| Nutrient | Function |
|---|---|
| Nitrogen (N) | Essential for chlorophyll production and overall plant growth |
| Phosphorus (P) | Important in root development, flower formation, and overall plant growth |
| Potassium (K) | Helps regulate water uptake and is essential in flower formation and overall plant growth |
| Calcium (Ca) | Stimulates plant cell elongation and is essential in cell wall formation |
| Magnesium (Mg) | Essential for photosynthesis and chlorophyll production, improves overall plant vigor |
| Sulfur (S) | Involved in the production of amino acids and enzymes, improves overall plant growth |
| Boron (B) | Essential in cell division and the transport of sugars within the plant, crucial for flower and seed development |
| Copper (Cu) | Involved in the production of chlorophyll and activating enzymes in the plant, important in reproductive growth |
| Iron (Fe) | Participates in various metabolic processes and is essential for chlorophyll production |
| Manganese (Mn) | Helps activate enzymes and plays a role in chlorophyll production and photosynthesis |
| Molybdenum (Mo) | Involved in nitrogen metabolism and helps convert nitrates into usable forms for the plant |
| Zinc (Zn) | Important in the production of auxins, enzymes, and plant hormones, essential in overall plant growth |
A lack of one or more of these nutrients can lead to stunted growth, yellowing leaves, low yields, or even plant death. It’s essential to provide cannabis plants with the necessary nutrients to ensure optimal growth and maximize yields.
Understanding N-P-K Ratios
One of the most important things to understand when it comes to fertilizing cannabis plants is the N-P-K ratio. N-P-K stands for nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium – the three primary macronutrients that plants need to grow. Each of these elements plays a different role in cannabis growth and development.
The role of nitrogen: Nitrogen is essential for vegetative growth, as it helps build strong stems, leaves, and branches. It also plays a key role in photosynthesis, which is the process by which plants convert light energy into chemical energy to fuel their growth.
The role of phosphorus: Phosphorus is important for root development, as well as for the production of flowers and fruits. It also helps plants use and store energy, as well as transfer genetic information during reproduction.
The role of potassium: Potassium helps regulate water levels in plants, as well as increase their tolerance to stress and disease. It also helps with photosynthesis and the production of sugars, which are essential for plant growth.
The N-P-K ratio is expressed as a series of three numbers, such as 10-10-10 or 5-10-5. These numbers represent the percentage of each macronutrient in the fertilizer. For example, a bag of fertilizer labeled “10-10-10” contains 10% nitrogen, 10% phosphorus, and 10% potassium.
Understanding balanced vs. unbalanced ratios: In general, cannabis plants need more nitrogen during the vegetative stage and more phosphorus and potassium during the flowering stage. However, it’s important to maintain a balanced N-P-K ratio throughout each stage of growth to avoid nutrient deficiencies or toxicities.
A balanced N-P-K ratio for cannabis plants is typically around 4-2-4 or 7-4-10, but this can vary depending on the strain and growing environment. It’s important to research the specific N-P-K needs of your plants and adjust your fertilizer accordingly.
Choosing the right fertilizer: When selecting a fertilizer, be sure to read the label carefully to understand its N-P-K ratio and any other micronutrients it may contain. Choose a fertilizer with a balanced N-P-K ratio that matches the needs of your plants and growing medium.
By understanding the role of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, as well as the importance of a balanced N-P-K ratio, you can ensure that your cannabis plants receive the proper nutrients throughout each stage of growth.
The Role of Micronutrients
Micronutrients may be required in smaller amounts, but they are still crucial to the growth and development of cannabis plants. These essential elements aid in metabolic processes, enzyme activation, and overall plant health. They are often overlooked or forgotten about, but neglecting them can have detrimental effects on the final yield.
Here is a table detailing the various micronutrients and the role they play in cannabis growth:
| Micronutrient | Function | Symptoms of Deficiency |
|---|---|---|
| Iron (Fe) | Aids in chlorophyll production and enzyme activation | Yellowing of new growth along veins |
| Boron (B) | Aids in cell wall formation, pollen germination, and calcium absorption | Brittle stems, distorted growth, and poor flower development |
| Zinc (Zn) | Aids in enzyme activation and plant hormone production | Yellowing between veins, stunted growth, and poorly developed leaves |
| Copper (Cu) | Aids in photosynthesis and enzyme activation | Stunted growth, wilting leaves, and bluish-green coloration |
| Manganese (Mn) | Aids in photosynthesis, nitrogen metabolism, and enzyme activation | Yellowing between veins, stunted growth, and poor flower development |
| Molybdenum (Mo) | Aids in nitrogen fixation and enzyme activation | Chlorotic leaves and stunted growth |
| Chlorine (Cl) | Helps with osmosis and water movement in the plant | Browning of leaf tips and wilting |
It is important to note that while micronutrients are necessary for cannabis growth, they can also be harmful if overused. It is crucial to follow recommended dosages and to monitor plants for any signs of nutrient burn. Additionally, some nutrients can interact with each other and affect uptake. It is advisable to follow a balanced nutrient regimen and to adjust accordingly based on the specific needs of the plant.
Adjusting Nutrient Levels for Different Stages of Cannabis Growth
As a cannabis grower, it’s essential to understand that each stage of cannabis growth has unique nutrient requirements. Adjusting nutrient levels accordingly can make a significant difference in the health and yield of your plants. However, it can be challenging to determine what adjustments are necessary and when. In this section, we will explore how to adjust nutrient levels for each stage of cannabis growth, from seedling to flowering. By the end, you’ll have a clear understanding of the nutrients your plants need and when they need them.
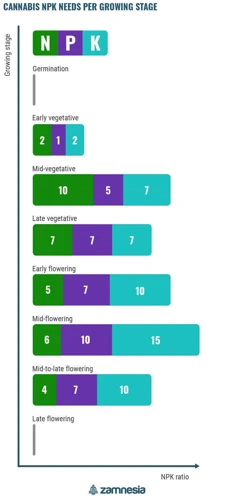
Seedling Stage
During the seedling stage, your cannabis plants are just beginning to develop their roots. This phase typically lasts for the first 2-3 weeks of the plant’s life. During this stage, it is important to provide your plant with the right amount of nutrients, as they are still very delicate and can easily be damaged.
Nutrient Requirements for Seedling Stage
| Nutrient | Ratio |
|———-|——-|
| Nitrogen | N/A |
| Phosphorus | 1 |
| Potassium | 2 |
During the seedling stage, your cannabis plants require a higher amount of phosphorus and potassium than nitrogen. Nitrogen levels should be kept relatively low, as high levels can inhibit the plant’s ability to absorb other nutrients. It is important to use a fertilizer specifically formulated for seedlings during this stage, as it will provide the appropriate ratio of nutrients.
Adjusting Nutrient Levels during Seedling Stage
It is important to monitor your plant’s growth during the seedling phase to determine if adjustments need to be made to nutrient levels. If your plant appears to be growing too slowly or is showing signs of nutrient deficiency, you may need to increase the amount of phosphorus and potassium in your fertilizer. However, it is important to avoid over-fertilizing during this stage, as it can damage the fragile roots of your plant.
Determining Nutrient Levels for Seedling Stage
When determining the appropriate nutrient levels for your cannabis plants during the seedling stage, it is important to take into account the type of growing medium you are using. Soil-based growing mediums may require different nutrient levels than hydroponic or coco coir-based growing mediums. Be sure to choose a fertilizer that is specifically designed for your chosen growing medium to ensure optimal results.
Using Supplements during Seedling Stage
While supplements are not always necessary during the seedling stage, adding beneficial bacteria and fungi supplements to your growing medium can help improve your plant’s overall health and growth. Compost tea is also a great supplement to add during the seedling stage, as it provides a natural source of nutrients to your plant. However, be sure to avoid over-supplementing during this stage, as it can lead to nutrient burn and other complications.
By providing your cannabis plants with the appropriate nutrient levels during the seedling stage, you can set them up for success throughout the rest of their growth cycle. Remember to monitor your plants closely and adjust nutrient levels as needed to ensure optimal growth and development.
Vegetative Stage
During the vegetative stage of cannabis growth, the plants are focused on developing foliage and establishing a sturdy structure. This phase usually lasts for a few weeks up to a few months, depending on the strain and growing conditions.
Nitrogen is one of the primary macronutrients that cannabis plants need during the vegetative stage to support leaf growth and overall vigor. The recommended N-P-K ratio for vegetative growth is usually around 3-1-2 or 4-1-3. However, it’s important to note that every strain may have slightly different nutrient requirements, so it’s always best to follow the guidance on the nutrient label and adjust as needed.
Phosphorous and potassium are also important nutrients during the vegetative stage, but in slightly lower concentrations compared to nitrogen. These nutrients help support root development, stem strength, and overall plant health. A good N-P-K ratio to aim for during this stage is 3-1-2 or 4-1-3.
Micronutrients are also essential during the vegetative stage. These include iron, magnesium, calcium, and others. Micronutrient deficiencies can cause yellowing or stunted growth, so it’s important to ensure that the plants are receiving a balanced nutrient mix.
It’s recommended to gradually increase the nutrient levels during the vegetative stage to avoid overfeeding the plants. Start with a lower concentration of nutrients and gradually increase over a period of several weeks. Monitoring pH levels and EC or PPM levels is also important during this stage to ensure that the plants are getting the proper balance of nutrients.
In addition to adjusting nutrient levels based on the plant’s needs, it’s also important to adjust the nutrient levels based on the type of growing medium used. Soil, hydroponic systems, and coco coir all have unique nutrient requirements, which should be taken into consideration when adjusting nutrient levels.
Flowering Stage
During the flowering stage, cannabis plants require a different nutrient balance than they did during the vegetative stage. This is because they are no longer focusing on growing new leaves and stems, but rather on producing buds. Here are some tips for adjusting nutrient levels during the flowering stage:
- Increase phosphorous and potassium: During the flowering stage, your plants will need more phosphorus and potassium to support bud growth. Look for a fertilizer with an NPK ratio of around 0-50-30.
- Reduce nitrogen: High levels of nitrogen during the flowering stage can lead to excessive vegetative growth and reduced bud production. Look for a fertilizer with a lower nitrogen content or switch to a bloom-specific fertilizer.
- Increase micronutrient supplements: Micronutrients are especially important during the flowering stage, as they help with the production of essential oils and terpenes. Look for a micronutrient supplement specifically formulated for the flowering stage.
- Adjust pH levels: Just as in the vegetative stage, it’s important to monitor and adjust the pH of your nutrient solution to ensure your plants can access the nutrients they need. Aim for a pH between 6.0 and 7.0 during the flowering stage.
- Use bud boosters: There are many different supplements and additives on the market that claim to boost bud production and potency. Look for products with high levels of phosphorus, potassium, and other micronutrients.
Remember that every strain of cannabis is different, and may require slightly different nutrient levels during the flowering stage. Keep an eye on your plants and adjust their nutrient levels accordingly. It’s also important to flush your plants with plain water in the last few weeks before harvest to ensure a smooth, clean smoke.
Determining Nutrient Requirements Based on Growing Medium
As a cannabis grower, it’s important to understand that the type of growing medium used will have an impact on the nutrient requirements of your plants. Different growing mediums have varying levels of nutrients and can affect the pH levels of the soil or solution. It’s essential to determine the specific nutrient requirements for your chosen growing medium to ensure healthy growth and optimum yields. Let’s explore the different types of growing mediums and how to adjust your nutrient levels accordingly.
Soil
One of the most common growing mediums for cannabis is soil. When it comes to adjusting nutrient levels in soil, there are several things to consider.
- pH levels: As with any growing medium, pH is an important factor to consider when adjusting nutrient levels. Cannabis plants thrive in a pH range between 6.0 and 7.0, so it’s important to keep the soil within this range to ensure optimal nutrient uptake.
- Nutrient levels: Soil typically contains some level of nutrients, but it’s important to supplement with additional nutrients at different stages of growth. During the seedling stage, cannabis plants require high levels of nitrogen (N) and lower levels of phosphorus (P) and potassium (K). During the vegetative stage, cannabis plants require higher levels of N and P, while reducing K levels. During the flowering stage, cannabis plants require lower levels of N and higher levels of P and K.
- Organic matter: Soil also contains organic matter, which can add some nutrients to the soil. However, it’s important to amend the soil with additional organic matter, such as compost or worm castings, to ensure that the soil has enough nutrients for the cannabis plant to grow and thrive.
- Watering: When adjusting nutrient levels in soil, it’s important to pay attention to how much water the cannabis plant is receiving. Overwatering can lead to nutrient deficiencies and can cause the roots to rot, while underwatering can cause the soil to become too concentrated with nutrients, leading to nutrient burn.
By considering these factors, growers can successfully adjust nutrient levels in soil for different stages of cannabis growth.
Hydroponics
Growing cannabis using hydroponic systems is becoming increasingly popular due to its many benefits. Hydroponic systems allow for precise control of nutrient levels and pH, resulting in faster growth rates and higher yields compared to soil-based growing. However, proper nutrient management is crucial for success with hydroponic cannabis growing, as plants in these systems rely solely on their nutrient solution for sustenance.
Choosing the Right Nutrients
When growing cannabis hydroponically, it’s important to select the right nutrient solution based on the plant’s stage of growth. During the vegetative stage, plants require higher levels of nitrogen to promote leafy growth, while the flowering stage requires higher levels of phosphorus and potassium for the development of buds. Many nutrient solutions cater specifically to these stages, as well as provide added micronutrients necessary for optimal growth.
Checking pH and EC Levels
In hydroponic systems, maintaining the proper pH and Electrical Conductivity (EC) levels is crucial for nutrient uptake and plant health. pH levels should be between 5.5 and 6.5, as nutrient availability decreases outside of this range. EC levels can vary depending on the strain and growing conditions, but in general, a range of 1.2-2.0 is suitable for most cannabis plants during the vegetative stage, while a range of 1.5-2.5 is suitable for the flowering stage.
Flushing
Just like with soil-based growing, hydroponic cannabis plants should be flushed periodically to remove excess buildup of salts and other minerals from the nutrient solution. This is typically done during the last week or two of the flowering stage and involves watering with pH-balanced water without any nutrients. This allows for a better taste and smoother smoking experience.
Dosage and Feeding Frequency
Cannabis plants in hydroponic systems require a constant flow of nutrients to thrive, so it’s important to check the nutrient solution daily and adjust as necessary. Dosage and feeding frequency will depend on factors such as the size of the plant, type of nutrient solution and growing conditions. Generally, hydroponic cannabis plants require feeding several times a day in small doses, as overfeeding can lead to nutrient burn and plant stress.
Benefits of Hydroponic Growing
Hydroponic growing has several benefits when it comes to growing cannabis. Not only does it allow for precise control of nutrients and pH, resulting in faster growth and higher yields, but it also takes up less space than soil-based growing and is less messy. Additionally, since the plants in hydroponic systems don’t have to search for nutrients like they would in soil, they are healthier and more resistant to pests and diseases.
Growing cannabis using hydroponic systems can be a great way to optimize growth and yields, but proper nutrient management is crucial. By choosing the right nutrients, maintaining proper pH and EC levels, flushing regularly, and paying attention to dosage and feeding frequency, you can successfully grow high-quality cannabis using hydroponics.
Coco Coir
Coco coir is a popular growing medium that can provide excellent results for cannabis growers. It is made from the fibrous husks of coconuts and is similar to peat moss, but with some important differences.
Advantages of Coco Coir
One of the biggest advantages of coco coir is its ability to hold onto water while still providing adequate drainage. This allows for a healthy root environment with plenty of oxygen, resulting in robust and fast-growing plants. Coco coir is also a renewable resource, unlike peat moss which is typically harvested from bogs and can take years to replenish.
Another advantage of coco coir is that it is naturally free of pests and diseases. This can be a big plus for cannabis growers who want to avoid the use of pesticides and other chemicals.
Nutrient Requirements for Coco Coir
Because coco coir is an inert medium, meaning it has no nutrients of its own, growers must provide all the necessary nutrients for their plants. This can be done using liquid nutrients specifically designed for coco coir, or by amending the coco coir with nutrients and minerals.
When amending coco coir, it is important to keep in mind that it has a tendency to retain calcium and potassium while leaching out magnesium. This means that growers may need to adjust their nutrient ratios accordingly.
Adjusting Nutrient Levels for Different Stages of Growth
Just like with other growing mediums, nutrient requirements for cannabis plants in coco coir will vary depending on the stage of growth. During the seedling stage, lower overall nutrient levels should be used to avoid burning the sensitive young plants. The vegetative stage will require higher levels of nitrogen, potassium, and calcium, while the flowering stage will require more phosphorus instead.
Common Coco Coir Supplements
There are a number of supplements available that can help boost cannabis growth when using coco coir. These include beneficial bacteria and fungi, which can help improve nutrient uptake and overall plant health. Organic supplements are often preferred by growers looking to avoid synthetic chemicals, but both organic and synthetic options will work in coco coir.
Monitoring Nutrient Levels
When growing in coco coir, it is important to monitor nutrient levels regularly to ensure that plants are not being over or underfed. This can be done using a pH meter and an EC or PPM meter. Adjustments can then be made as needed to keep plants healthy and thriving.
Coco coir can be an excellent option for cannabis growers looking for a sustainable and effective growing medium. With proper nutrient management and regular monitoring, growers can expect to see healthy and abundant yields from their cannabis plants.
| Advantages of Coco Coir |
|---|
| Ability to hold onto water while still providing adequate drainage. |
| Naturally free of pests and diseases. |
| Nutrient Requirements for Coco Coir |
|---|
| Coco coir is an inert medium, meaning it has no nutrients of its own, so growers must provide all the necessary nutrients for their plants. |
| Coco coir has a tendency to retain calcium and potassium while leaching out magnesium, so nutrient ratios may need to be adjusted. |
| Adjusting Nutrient Levels for Different Stages of Growth |
|---|
| Seedling stage: lower overall nutrient levels. |
| Vegetative stage: higher levels of nitrogen, potassium, and calcium. |
| Flowering stage: more phosphorus instead. |
| Common Coco Coir Supplements |
|---|
| Beneficial bacteria and fungi can help improve nutrient uptake and overall plant health. |
| Organic supplements are often preferred by growers looking to avoid synthetic chemicals, but both organic and synthetic options will work in coco coir. |
| Monitoring Nutrient Levels |
|---|
| Regular monitoring of nutrient levels using a pH meter and an EC or PPM meter can ensure that plants are not being over or underfed. |
| Adjustments can then be made as needed to keep plants healthy and thriving. |
Using Supplements to Boost Cannabis Growth
Now that you have a good understanding of the nutrient requirements for your cannabis plants and how to adjust them for different stages of growth, you may want to think about using supplements to give your plants an extra boost. A variety of supplements exist on the market that claim to improve plant growth and yield, but how do you know which ones to choose? In this section, we’ll explore the different types of supplements available and what the best options are for your cannabis plants based on your growing methods and personal preferences. Let’s dive in and see how to take your cannabis plants to the next level!
Beneficial Bacteria and Fungi
One way to boost the growth and health of your cannabis plants is to introduce beneficial bacteria and fungi to the soil or growing medium. These microorganisms can help break down nutrients and make them more available to the plant’s roots. Here are some types of beneficial bacteria and fungi that you can add to your cannabis grow:
- Bacillus subtilis: This bacterium can help the plant resist stress and disease, as well as improve nutrient uptake. It can be found in products like RootShield and Serenade.
- Mycorrhizal fungi: These fungi form a symbiotic relationship with the plant’s roots, helping it to absorb water and nutrients more efficiently. You can buy mycorrhizal inoculants like Great White or Mykos to add to the soil or planting holes.
- Trichoderma: This fungus can help control pathogens and improve plant growth. Products like Bonticare and RootShield Plus contain strains of Trichoderma.
- Nitrogen-fixing bacteria: Some bacteria, like Rhizobium and Azotobacter, can convert nitrogen from the air into a form that the plant can use. These can be found in products like BioAg’s VAM and Azos.
By adding these beneficial microorganisms to your cannabis grow, you can improve soil health and plant growth without relying solely on synthetic fertilizers. Keep in mind that it’s important to follow the manufacturer’s instructions for application and dosage, as too much of these additives can harm your plants.
Organic vs. Synthetic Supplements
When it comes to supplements for cannabis growth, there are two main types: organic and synthetic. Here’s a breakdown of the pros and cons of each:
Organic Supplements:
- Pros:
- Derived from natural materials, making them more environmentally friendly
- Tend to contain a wider range of micronutrients
- Encourage microbial activity in the soil
- Can improve overall plant health and taste
- Cons:
- Can be more expensive than synthetic supplements
- Slower release of nutrients, requiring more frequent applications
- Can be less precise, making it harder to adjust nutrient levels
- May contain unknown contaminants or pathogens
Synthetic Supplements:
- Pros:
- Less expensive than organic supplements
- Provide a more precise and uniform nutrient mix
- Can be tailored to specific nutrient requirements
- Low risk of contamination or pathogens
- Cons:
- Derived from synthetic materials, which can be harmful to the environment and human health
- Can negatively affect soil microbial activity
- May not improve plant health or taste as much as organic supplements
- Can cause nutrient imbalances if not used correctly
Organic supplements may be preferential for those looking for a more natural and sustainable approach, while synthetic supplements may be more suitable for those looking for precision and cost-effectiveness. Ultimately, the choice between organic and synthetic supplements will depend on your personal values, growing methods and goals for your cannabis plants.
Brewing Your Own Compost Tea
Compost tea is a natural and effective way to boost the levels of essential nutrients in your cannabis plants. It’s easy to make your own compost tea at home with just a few simple ingredients. Here’s how to do it:
- Choose High-Quality Ingredients: Start with high-quality compost as the base for your tea. You can also add other organic ingredients like worm castings, bat guano, kelp meal, and bone meal to boost the nutrient levels. Make sure to use a source of water that is free of chlorine and other harmful chemicals.
- Create the Tea Mixture: Combine your compost and other organic ingredients in a large container or compost tea brewer. Add water to create a mixture that is roughly 5-10% organic matter to water volume ratio.
- Aerate the Mixture: Aeration is essential to brewing compost tea. You can use an aquarium pump and air stone to oxygenate the mixture and help beneficial microorganisms to thrive. Make sure to keep the temperature of the mixture between 60-80 degrees Fahrenheit.
- Brew for the Right Time: The ideal brewing time for compost tea is between 24-48 hours. Any more than this, and the tea may become anaerobic and potentially harmful to your plants.
- Apply the Tea: Once the brewing process is complete, strain the mixture to remove any solids, and apply the resulting compost tea to your cannabis plants. You can use a spray bottle to apply the tea to the leaves and flowers or directly into the soil.
Using compost tea as a supplement for your cannabis plants can lead to healthier plants and better yields. It’s worth noting that compost tea should be used in combination with a proper nutrient regimen rather than as a sole source of nutrition for your plants. It’s important to monitor the nutrient levels of your plants and adjust as necessary to ensure optimal growth and health.
Monitoring and Adjusting Nutrient Levels
As a cannabis grower, monitoring and adjusting nutrient levels is an essential part of ensuring your plants grow healthy and strong. Without the proper balance of nutrients and pH levels, your cannabis may suffer from nutrient deficiencies or excesses, impacting the quality and yield of your harvest. In this section, we will explore the tools and techniques you need to effectively monitor pH, EC, and PPM levels, and adjust nutrient levels during flushing to ensure your cannabis thrives throughout each stage of growth.
Measuring pH Levels
Maintaining the proper pH level of the nutrient solution is crucial for healthy cannabis growth. The pH level directly affects the plant’s ability to absorb nutrients. A too high or too low pH level can result in nutrient deficiencies or toxicities that negatively impact plant growth and yield.
The following are steps to measure pH levels for cannabis growth:
- Prepare the nutrient solution: Before measuring the pH level, ensure that the nutrient solution is thoroughly mixed. Allow the solution to settle for 5-10 minutes before taking measurements.
- Calibrate the pH meter: Calibration is necessary to ensure accurate readings. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for calibration. Usually, a pH 7.0 buffer solution is first used for calibration, followed by a pH 4.0 or 10.0 solution, depending on the pH meter model.
- Measure the pH level: Dip the pH meter into the nutrient solution at a depth of at least 1 inch. Wait for the reading to stabilize and record the pH level. It is recommended to take multiple readings and average them out to ensure accuracy.
- Adjust the pH level: The ideal pH level for cannabis growth depends on the growing medium. Generally, the pH level should be between 5.5 and 6.5 for soil and 5.5 and 6.0 for hydroponics. To adjust the pH level, add pH up or pH down solutions in small increments, follow the manufacturer’s instructions and re-measure the pH until it reaches the desired range.
- Test the pH level regularly: pH levels can fluctuate rapidly in a nutrient solution, so it’s essential to test it regularly. Aim for daily testing in hydroponic systems and every other day for soil-grown plants.
Remember, maintaining the proper pH level is essential for healthy cannabis growth. Regular pH testing and adjustments are necessary to ensure optimal nutrient uptake and avoid nutrient imbalances that can negatively impact plant growth and yield.
EC and PPM Levels
EC and PPM Levels
EC and PPM levels are commonly used units of measurement to gauge the nutrient concentration in the growing medium. Here’s a closer look at each:
- EC (Electrical Conductivity): EC measures the ability of a solution to conduct an electrical current, and is an indicator of the amount of nutrients present in the water. In the context of cannabis growing, a higher EC reading indicates a higher concentration of nutrients in the solution.
- PPM (Parts Per Million): PPM is another unit of measurement used to indicate the nutrient concentration in a solution. It determines the total amount of dissolved minerals in the solution, and is calculated by multiplying the EC by a factor of 500 or 700, depending on the type of meter you’re using.
When adjusting nutrient levels, it’s important to keep a close eye on these readings. Cannabis plants require different nutrient levels during different stages of growth, and the wrong nutrient concentration can lead to issues with plant health and development.
Seedling Stage
Seedlings require lower EC and PPM levels to prevent nutrient burn, stunted growth, and other issues. Maintaining an EC of around 0.4-0.6 and a PPM of 200-300 is ideal for seedling growth.
Vegetative Stage
During the vegetative stage, cannabis plants require higher levels of nutrients to fuel healthy leaf and stem growth. Increasing the EC to around 1.0-1.5 and PPM to 500-800 is recommended for this stage.
Flowering Stage
In the flowering stage, cannabis plants require higher levels of phosphorus and potassium to facilitate bud development. During this stage, aim to maintain an EC of 1.5-2.2 and PPM of 800-1500 to maximize yields.
Remember, these recommendations may vary depending on the specific strain and growing conditions. Always monitor your EC and PPM levels closely, and adjust nutrient concentrations accordingly.
Adjusting Nutrient Levels During Flushing
During the final weeks of the cannabis plant’s life cycle, it’s important to flush out any excess nutrients that may have built up in the growing medium. This process allows the plant to use up its remaining nutrients and produce a cleaner, smoother smoke. Adjusting nutrient levels during flushing can be a delicate process, but it’s crucial for achieving a successful harvest.
Why Flush?
Before harvesting, the cannabis plant needs to be flushed with clean, pH-balanced water to remove any excess nutrients from the growing medium. When cannabis plants are given too many nutrients, they can become overfed and produce harsh, unpleasant-tasting smoke. This can also inhibit the plant’s ability to finish flowering and mature properly.
How to Flush
To flush the cannabis plant, stop feeding it nutrients and only give it clean, pH-balanced water for the final two weeks of its life cycle. In the first week of flushing, continue to water the plant as normal to allow the plant to start using up its stored nutrients. In the second week, reduce the amount of water given to the plant to help it finish using up any remaining nutrients.
| Timeframe | Steps |
|---|---|
| First week of flushing | Water the plant as normal |
| Second week of flushing | Reduce the amount of water given to the plant |
Monitoring Nutrient Levels During Flushing
While the cannabis plant is being flushed, it’s important to monitor the nutrient levels in the runoff water to ensure that there are no excess nutrients still present in the growing medium. Measure the pH and EC levels of the runoff water during each watering and adjust the pH as necessary to ensure that it remains between 6.0-7.0.
Benefits of Flushing
Flushing the cannabis plant before harvesting can lead to several benefits. It allows the plant to use up its remaining nutrients and produce a cleaner, smoother smoke. It can also improve the plant’s aroma and taste, as well as increase the potency of the buds. Lastly, flushing can help prevent nutrient buildup in the growing medium and ensure that the plant finishes flowering and matures properly.
Troubleshooting Nutrient Deficiencies and Excesses
When growing cannabis, it’s important to ensure the plant is receiving the correct balance of nutrients. However, even with proper care, nutrient deficiencies and excesses can still occur, which can negatively impact the plant’s growth and yield. It’s crucial to be able to troubleshoot these issues quickly to prevent further damage. This section will cover common nutrient deficiencies and excesses, as well as how to prevent them and how to flush the plant for better taste. Let’s dive in and learn how to identify and fix nutrient issues in cannabis plants.
Common Nutrient Deficiencies and How to Fix Them
One common issue that cannabis growers may face is nutrient deficiencies. These can happen due to a variety of reasons, such as poor soil quality, pH imbalances, or incorrect nutrient levels. It’s important to identify and address nutrient deficiencies as soon as possible to prevent the issue from worsening and impacting the plant’s growth and yield.
The table below outlines some common nutrient deficiencies, their symptoms, and how to fix them:
| Nutrient Deficiency | Symptoms | Fix |
|---|---|---|
| Nitrogen | Yellowing of lower leaves, stunted growth | Use a nitrogen-rich fertilizer or organic matter such as compost or fish emulsion. |
| Phosphorus | Purple or red stems, slow growth, reduced yield | Use a phosphorus-rich fertilizer or bone meal. |
| Potassium | Yellow or brown edges on leaves, weak stems | Use a potassium-rich fertilizer or wood ash. |
| Calcium | Brown spots on leaves, curled or distorted growth | Adjust pH levels to ensure calcium is available to the plant, use calcium-rich fertilizers or supplements such as gypsum or dolomite lime. |
| Magnesium | Yellowing between veins, leaves may curl upward | Use a magnesium-rich fertilizer or supplement such as Epsom salt. |
| Zinc | Yellowing between veins, smaller leaves | Use a zinc-rich fertilizer or supplement. |
While these are some common nutrient deficiencies, it’s important to note that there may be other issues impacting plant growth, such as pests or disease. If a nutrient deficiency is identified, it is important to address it in a timely manner and monitor the plant’s progress to ensure it is responding positively to the fix.
Preventing Nutrient Burn
Preventing Nutrient Burn is crucial for maintaining healthy cannabis plants. Nutrient Burn occurs when plants receive too many nutrients, causing the tips of the leaves to turn brown and die off. This can stunt the plant’s growth and reduce its overall yield.
To prevent Nutrient Burn, it’s important to keep a close eye on the nutrient levels in the growing medium. Using an EC (Electric Conductivity) meter or a PPM (Parts Per Million) meter can help you monitor the nutrient levels effectively. These tools measure the concentration of nutrients in the water or soil, allowing you to adjust the levels accordingly.
Maintain Proper pH Levels: Maintaining the proper pH levels is essential to prevent Nutrient Burn. If the pH level is too high or too low, the plant will not be able to absorb the nutrients properly. The optimal pH range for cannabis plants is between 6.0 and 7.0 for soil, and between 5.5 and 6.5 for hydroponics. By adjusting the pH level, you can ensure that the nutrients are available and accessible to the plant.
Gradual Nutrient Increase: It’s important to introduce nutrients gradually to the plant, especially during the vegetative stage. Starting with a low concentration of nutrients and gradually increasing it over time will allow the plant to adjust and prevent Nutrient Burn. A general guideline is to start with a quarter strength nutrient solution and then increase it gradually every week as the plant develops.
Flush Regularly: Flushing is the process of flushing out excess nutrients from the growing medium by watering the plants with plain water. This helps prevent the buildup of excess nutrients that can cause Nutrient Burn. Flushing should be done regularly, especially during the last two weeks of the flowering stage, to improve the plant’s overall taste and aroma.
Use Quality Nutrients: Using quality nutrients is essential to prevent Nutrient Burn. The best nutrients are those that are formulated specifically for cannabis plants, as they contain the right balance of macro and micronutrients that meet the plant’s needs. Always use high-quality nutrients and follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully to ensure that you’re giving your plants the best possible care.
By following these tips, you can prevent Nutrient Burn and ensure that your cannabis plants grow healthy and produce a bountiful harvest.
Flushing for a Better Taste
Flushing is a crucial step in the cultivation of cannabis that is often overlooked. When done correctly, it can greatly improve the taste and aroma of your buds. Flushing refers to the process of giving your plants plain water instead of nutrient-rich water in the last few weeks before harvest.
Why is flushing important?
During the flowering stage, cannabis plants will accumulate excess nutrients in their tissues if they are overfed. This can lead to a harsh, chemical taste in the final product. Flushing allows the plant to use up the excess nutrients and produce a cleaner, smoother taste in the buds.
How to flush your cannabis plants
To flush your plants, simply stop adding nutrients to the water and use plain, pH-balanced water for the last two weeks of the flowering stage. If you are growing in soil, it’s a good idea to water until you see runoff, then wait a few minutes and water again to ensure that all of the excess nutrients have been flushed out.
Measuring pH and EC levels during flushing
During flushing, it’s important to keep an eye on your pH and EC levels to make sure that your plants are getting the right amount of water. The pH level should be around 6.0, and the EC level should be around 0.4.
How to tell when your plants are ready to harvest
When your plants are ready to harvest, the leaves will start to turn yellow and die off. This is a sign that the plant is using up all of its stored nutrients, and is ready to be harvested. The buds will also start to swell and become sticky with resin.
Final thoughts
Flushing your cannabis plants is a simple step that can greatly improve the taste and aroma of your buds. By using plain, pH-balanced water for the last two weeks of the flowering stage, you can help your plants use up excess nutrients and produce a clean, smooth flavor in the final product. Keep an eye on your pH and EC levels during flushing, and harvest your plants when the leaves start to yellow and the buds become sticky. With these tips, you can enjoy a better-tasting, smoother smoke.
| Flushing Recommendations |
| Stop adding nutrients 2 weeks before harvest |
| Use plain, pH-balanced water |
| Water until you see runoff |
| Wait a few minutes and water again to ensure that all of the excess nutrients have been flushed out |
| Monitor pH and EC levels |
Conclusion
In conclusion, adjusting nutrient levels for different stages of cannabis growth is an essential aspect of successful cannabis cultivation. As we have discussed, understanding the nutrients that cannabis plants need, the role of N-P-K ratios and micronutrients, as well as the importance of adjusting nutrient levels based on the growing medium, will play a crucial role in achieving optimal growth and yield.
Furthermore, knowing how to use supplements effectively, monitoring and adjusting nutrient levels, and troubleshooting nutrient deficiencies and excesses will help prevent plant damage, promote better taste, and increase the quality and quantity of your harvest.
It is also essential to note that cannabis cultivation is a continuous learning process, and it may take some experimentation to find the nutrient levels that work best for your plants. However, with proper care, attention, and patience, you can grow healthy, high-yielding cannabis plants from start to finish.
Therefore, take the time to research and understand your plants’ nutrient requirements, use the appropriate supplements, and constantly monitor and adjust nutrient levels to achieve the best results. With these tips and tricks, you can become a successful cannabis cultivator and enjoy the fruits of your labor.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the ideal N-P-K ratio for cannabis plants?
The ideal N-P-K ratio for cannabis plants depends on the stage of growth. During the vegetative stage, a ratio of 2:1:2 is recommended. During the flowering stage, a ratio of 1:2:3 is recommended.
Can I use regular plant fertilizers on cannabis?
No, regular plant fertilizers may not provide adequate nutrients for cannabis plants. It is best to use fertilizers formulated specifically for cannabis.
What micronutrients do cannabis plants need?
Cannabis plants require micronutrients such as iron, zinc, manganese, and copper, among others. These micronutrients are essential for proper growth and development.
Can I adjust nutrient levels based on the strain of cannabis?
Yes, different strains of cannabis may have slightly different nutrient requirements. It is best to research the specific strain you are growing to determine its nutrient needs.
What is the difference between organic and synthetic fertilizers?
Organic fertilizers are made from natural materials such as compost and manure, while synthetic fertilizers are chemically formulated. Organic fertilizers tend to be slower-acting but provide longer-lasting benefits, while synthetic fertilizers are faster-acting but may require more frequent applications.
Why is it important to monitor pH levels?
pH levels can affect the availability of nutrients to the plant. If the pH is too high or too low, the plant may not be able to absorb certain nutrients, which can lead to deficiencies and stunted growth.
Should I adjust nutrient levels during flushing?
No, flushing is the process of flushing out excess nutrients before harvest. During this time, it is best to only give the plant plain water to allow it to use up any remaining nutrients. Adjusting nutrient levels during flushing can affect the taste and quality of the final product.
What is nutrient burn?
Nutrient burn occurs when the plant is over-fertilized, leading to a buildup of salts in the soil. This can cause the tips of the leaves to turn brown and dry out.
How do I fix nutrient deficiencies in my plants?
The solution depends on the specific nutrient deficiency, but in general, adding a fertilizer high in the deficient nutrient can help. It is important to research the symptoms of the deficiency and address it as soon as possible to prevent further damage to the plant.
Can I use compost tea as a fertilizer for cannabis?
Yes, compost tea can be an effective fertilizer for cannabis plants. It provides a rich source of nutrients as well as beneficial bacteria and fungi that can help promote healthy growth.