How Photoperiod Affects Cannabis Growth
As cannabis cultivation continues to gain popularity, it is essential to understand the factors that influence plant growth and development. One of the critical factors is photoperiod, the duration of light and dark periods that a plant receives. When it comes to cannabis growth, photoperiod can significantly impact the plant’s vegetative and flowering phases. Understanding photoperiod is crucial for achieving optimal cannabis growth and yield. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the types of photoperiod, how they affect cannabis growth, and how to control them during indoor and outdoor cultivation. We’ll also explore common mistakes to avoid, the best light schedules for cannabis growth, and factors that can affect photoperiod. By the end of this guide, you’ll have a clear understanding of photoperiod and its impact on cannabis cultivation.
What is Photoperiod?
Contents
Have you ever wondered why cannabis plants grow differently in different seasons? The answer lies in photoperiod, a crucial factor that plays a significant role in cannabis growth. Photoperiod refers to the duration of light and darkness in a day that affects the physiological and biochemical processes of the plant. Understanding the concept of photoperiod and its effects on cannabis growth is crucial in achieving optimal yields. In this section, we will delve deeper into what photoperiod is, its types, and how it affects cannabis growth.
Definition of Photoperiod
Photoperiod refers to the duration of light and darkness experienced by an organism in a 24 hour period. In the context of cannabis, photoperiod plays a critical role in determining when plants enter their flowering stage. A long-day plant requires a certain amount of light each day to initiate flowering, while a short-day plant will only start to flower once the days begin to shorten. Cannbis is considered a short-day plant, and typically requires at least 12 hours of uninterrupted darkness per day to trigger the flowering stage.
The duration of the photoperiod also affects the rate of growth during the vegetative stage. During this period, cannabis plants require a minimum of 18 hours of light each day to achieve optimal growth. Providing less light than this can result in slower growth and smaller plants. On the other hand, providing more than 18 hours of light can cause the plants to grow too quickly, resulting in weak stems and leaves.
In addition to affecting the timing and rate of growth, the photoperiod can also have an impact on the overall yield of cannabis plants. By optimizing the light cycle, growers can increase the number and size of buds produced during the flowering stage. However, mistakes made during this stage can also lead to reduced yields.
Photoperiod is an essential component of cannabis growth that helps to regulate the timing of plant development and ensure proper growth and yield. Understanding how photoperiod affects cannabis growth is an important part of successful cultivation.
Types of Photoperiod in Cannabis
Photoperiod plays a vital role in the growth and development of cannabis. There are two types of photoperiod in cannabis: short-day plants and long-day plants.
Short-day plants, also known as autoflowering plants require a certain period of darkness in order to flower. Typically, these plants require 12-14 hours of darkness per day to enter the flowering stage. Once initiated, flowering in these plants occurs rapidly, in as little as two to four weeks. As they do not rely on photoperiod to enter the flowering stage, short-day plants can be grown year-round.
Long-day plants, on the other hand, require a specific amount of light to enter the flowering stage. Typically, these plants require more than 12 hours of sunlight per day to remain in the vegetative stage, and less than 12 hours to enter the flowering stage. Cannabis belongs to this category of plants, and as such, growers need to pay attention to photoperiod schedules.
Long-day plants require a minimum of 12 hours of sunlight per day during the vegetative stage in order to thrive. Once the light cycle is reduced to 12 hours or less, the plant will enter the flowering stage, which can last up to two to three months. It is important to maintain a strict light schedule during the flowering stage to ensure that the plant receives the amount of light it needs to produce high-quality buds.
Understanding the photoperiod requirements of your cannabis plants is crucial for successful growth and yield. Table below provides a summary of the differences between short-day and long-day plants:
| Short-day Plants | Long-day Plants | |
|---|---|---|
| Light Requirements | 12-14 hours of darkness per day to flower | Minimum of 12 hours of sunlight per day during vegetative stage |
| Flowering Stage | Occur rapidly once initiated, in as little as two to four weeks | Last up to two to three months |
| Photoperiod Schedules | Can be grown year-round | Requires strict light schedule during flowering stage |
How Photoperiod Affects Cannabis Growth
Photoperiod is an essential factor that affects cannabis growth. It refers to the length of light and dark periods that a plant is exposed to in a 24-hour cycle. The photoperiod has a crucial role in regulating crucial plant functions, including growth, flowering, and overall development. Here are some ways in which photoperiod affects cannabis growth:
- Transition to Flowering Stage: Photoperiod triggers the transition from the vegetative growth phase to the flowering stage in cannabis plants. When the photoperiod shifts to 12 hours of darkness, the plant’s hormone production changes, and it initiates flowering.
- Plant Physiology: Photoperiod affects the plant’s physiology, including the size of the plant, leaf and stem growth, and the internodal spacing. Longer light periods during the vegetative growth phase contribute to more significant plant size whereas shorter periods initiate the shift to the flowering phase.
- Yield: The photoperiod determines the yield of the cannabis plants. If the grower wants the plant to produce buds abundantly, they should use specific light schedules that complement the plant’s needs throughout its life cycle.
- Potency: Photoperiod plays a significant role in determining the plant’s potency. More extended light periods during the vegetative phase can lead to a higher THC content.
Growers must carefully control the photoperiod when growing cannabis and closely monitor its progress to achieve the desired results. A well-planned photoperiod strategy can help maximize yields, enhance potency, and/or control when plants reach maturity.
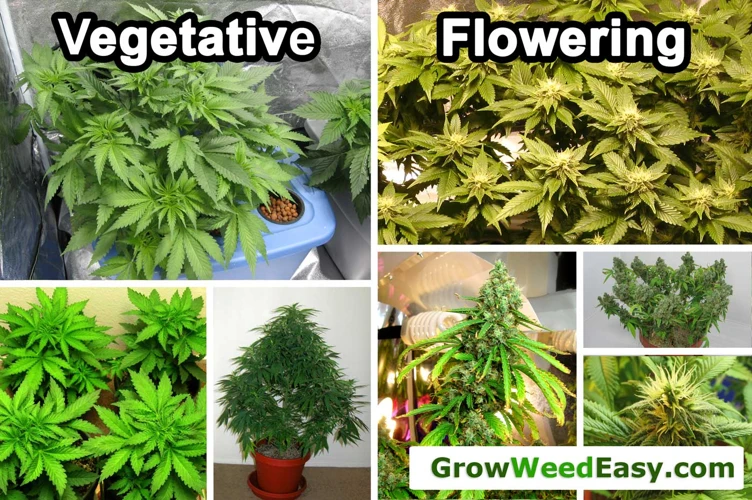
Understanding the Vegetative Stage
One of the most critical stages in the growth of cannabis plants is the vegetative stage, which is a preparatory period before the flowering stage. During this stage, the plants focus on building a solid foundation for strong growth, sturdy stems, and lush foliage that will ultimately support the plant’s flowers. Understanding the vegetative stage is crucial for developing a healthy and fruitful cannabis plant, and it requires proper management of photoperiod and environmental factors. Let’s delve deeper into this stage and explore the various ways that we can optimize growth within it.
What is the Vegetative Stage?
During the vegetative stage, cannabis plants focus on producing strong branches and healthy leaves. This stage of growth is crucial in determining the overall health and yield of your plants. Below is a table outlining the important characteristics of the vegetative stage:
| Duration: | The vegetative stage typically lasts anywhere from 4-8 weeks, depending on the strain and growing conditions. |
|---|---|
| Light Requirements: | Cannabis plants require between 18-24 hours of light per day during the vegetative stage. |
| Temperature: | The ideal temperature for the vegetative stage is between 68-77°F (20-25°C). |
| Humidity: | The ideal humidity level during the vegetative stage is between 50-70%. |
| Nutrient Requirements: | Cannabis plants require higher levels of nitrogen and potassium during the vegetative stage to support healthy growth. |
| Training Techniques: | The vegetative stage is the best time to train your plants using techniques such as topping, low stress training (LST), and high stress training (HST) to encourage lateral growth and improve yields. |
During the vegetative stage, it is important to provide your plants with the right amount of light, nutrients, and training techniques to ensure they are well-prepared for the flowering stage. Proper care and attention during the vegetative stage can result in larger yields and healthier plants overall.
Optimizing Growth During Vegetative Stage with Photoperiod Control
During the vegetative stage of cannabis growth, optimizing growth is crucial to ensure a healthy and robust plant. One way to achieve this is by controlling photoperiod, or the amount of light and darkness that the plant receives.
Cannabis plants typically require long periods of light during the vegetative stage in order to stimulate vigorous, healthy growth. This is because the plant uses the energy it receives from light to produce chlorophyll, which is essential for photosynthesis and overall plant growth.
Controlling the photoperiod during the vegetative stage involves providing the plant with a specific light schedule that mimics the natural light cycle of the plant’s native environment. This can be accomplished through the use of different lighting systems, such as high-intensity discharge (HID) lights, fluorescent lights, or light-emitting diodes (LEDs).
Table:
| Light Source | Recommended Light Cycle (On/Off) |
|---|---|
| HID Lights | 18/6 or 24/0 |
| Fluorescent Lights | 18/6 or 24/0 |
| LED Lights | 18/6 or 24/0 |
It is important to note that the specific light cycle recommended for the vegetative stage may vary depending on the strain of cannabis being grown and the specific growing environment. It is recommended to research the recommended light cycle for the specific strain being grown in order to achieve the best results.
Additionally, it is important to ensure that the cannabis plants receive proper nutrition during the vegetative stage in order to support healthy growth. This includes providing the plant with the appropriate balance of nutrients, including nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, as well as maintaining proper pH levels in the growing medium.
By controlling the photoperiod and providing the plant with the proper nutrition during the vegetative stage, growers can ensure that their cannabis plants are healthy, vigorous, and well-prepared for the flowering stage.
Understanding the Flowering Stage
The transition from vegetative growth to flowering is a crucial phase in the cannabis plant’s life cycle that requires careful observation and management. This is the stage where the plant begins to develop buds and ultimately reach its full maturity. Understanding the factors that influence the flowering stage, such as photoperiod and environmental conditions, is essential for maximizing yield and potency. In this section, we’ll dive deeper into the details of the flowering stage, the optimal conditions for growth, and common mistakes to avoid. Let’s explore this essential stage of cannabis growth together.
What is the Flowering Stage?
The flowering stage is a critical phase in the growth of a cannabis plant. At this point, the plant has reached its “adolescent” phase and begins producing flowers, which are the buds that we harvest and consume. This phase is characterized by significant changes in the plant’s physiology, including its growth rate, structure, and chemical profile. Here are some key aspects of the flowering stage to keep in mind:
| Duration: | The flowering stage typically lasts between 6-12 weeks, depending on the strain and growing conditions. |
| Light Schedule: | During the flowering stage, cannabis plants need a specific light schedule to produce the most potent and high-quality buds. The most common light schedule for flowering is a 12/12 cycle, where the plants receive 12 hours of light and 12 hours of darkness each day. This switch to a 12/12 cycle signals the plant that it’s time to start flowering. |
| Growth: | During the flowering stage, the plant’s growth rate slows down as it redirects its energy towards producing buds. The plant may also stretch or increase in height, and its branches may become heavier and start to droop under the weight of the buds. |
| Chemical Changes: | As the plant enters the flowering stage, it also undergoes significant chemical changes. The levels of THC and other cannabinoids increase, while the levels of chlorophyll and other green pigments decrease. This leads to a change in the color of the buds from green to shades of purple, blue, or reddish-brown. |
| Harvest: | Knowing when to harvest your cannabis plants is crucial to achieving the desired potency and flavor. Generally, you should harvest your plants when the trichomes (the tiny resin glands on the buds) turn a milky-white color and the pistils (the hair-like structures on the buds) start to curl and turn brown. Harvesting too early can result in lower potency and yield, while harvesting too late can lead to lower quality and harsher smoke. |
The flowering stage is a crucial aspect of cannabis growth and requires careful monitoring and management to ensure a successful harvest. By controlling the plant’s light schedule and providing optimal growing conditions, growers can produce high-quality buds that are both potent and flavorful.
Optimizing Yield During Flowering Stage with Photoperiod Control
During the flowering stage, photoperiod control will play a crucial role in maximizing the yield of your cannabis plants. Here are some tips for optimizing yield during the flowering stage with photoperiod control:
- Switch to a 12/12 light schedule: Once your plants have reached the desired height and have developed enough nodes, it’s time to initiate the flowering stage by switching to a 12/12 light schedule. This means 12 hours of light followed by 12 hours of complete darkness. This will trigger the plants to start producing flowers, which will eventually turn into buds.
- Maintain a consistent light schedule: During the flowering stage, it is important to maintain a consistent light schedule. Any disruption in the light cycle can cause stress to the plants, resulting in reduced yields. Use a timer to ensure that the lights come on and go off at the same time every day.
- Consider using supplemental lighting: While natural sunlight can be sufficient for outdoor growing, indoor growers may need to supplement their plants with artificial lighting. High-pressure sodium (HPS) and metal halide (MH) lights are popular options for indoor growers during the flowering stage as they provide the right spectrum and intensity of light needed for optimal bud development.
- Pay attention to temperature and humidity: The flowering stage requires specific temperature and humidity levels for optimal bud development. The temperature should be between 65-80°F during the day and slightly cooler at night. Humidity should be between 45-55%. Any significant changes in temperature or humidity can stress the plants and affect their yield.
- Use appropriate nutrients: During the flowering stage, cannabis plants require a different nutrient balance than during the vegetative stage. Using a fertilizer specifically designed for the flowering stage can help provide the necessary nutrients for optimal bud development.
By following these tips for optimizing yield during the flowering stage with photoperiod control, growers can ensure that they are getting the most out of their cannabis plants.
Common Mistakes to Avoid During Flowering Stage
During the flowering stage, it is important to avoid certain mistakes that can impact the yield and quality of your cannabis plants. Here are some common mistakes to avoid:
| Mistake | Impact on Plants |
|---|---|
| Interrupting the Dark Cycle | Can cause plants to become stressed and produce lower yields |
| Overfeeding | Can result in nutrient burn and damage to the plant |
| Underfeeding | Can stunt growth and result in lower yield and quality |
| Inadequate Airflow | Can lead to the growth of mold and mildew, which can damage or kill plants |
| Harvesting Too Early | Can result in lower yield and potency, as the buds have not fully matured |
| Harvesting Too Late | Can result in a decrease in potency and flavor, as well as the risk of mold and mildew |
It is important to monitor your plants closely during the flowering stage and take action to correct any issues that arise. This can include adjusting nutrient levels, improving airflow, and ensuring that your plants are receiving the correct amount of light and darkness. By avoiding these common mistakes, you can help ensure a successful harvest with high-quality cannabis buds.
Controlling Photoperiod in Indoor Vs. Outdoor Growing
When it comes to cultivating cannabis, understanding how to control photoperiod is essential for proper growth and development. However, the approach to managing photoperiod varies between indoor and outdoor growing. Indoor growers have full control over their lighting, while outdoor growers are at the mercy of natural light sources. Hybrid growers may find themselves navigating both worlds. So, how do you effectively control photoperiod in different environments? Let’s explore the nuances of indoor vs. outdoor growing for photoperiod control.
Indoor Growing
Indoor growing is a popular method for cultivating cannabis because it allows growers to have more control over the environment. To get the most out of indoor growing, it’s important to consider the impact of photoperiod on cannabis growth. Here are some factors to keep in mind for indoor growing:
- Light source: Indoor growers have the advantage of being able to use artificial lighting to provide consistent light to their plants. This means that they can easily adjust the light schedule to control photoperiod.
- Light leaks: It’s crucial to consider any potential light leaks in an indoor setup that could disrupt the photoperiod. Even small amounts of light during the dark period can throw off plant growth and result in lower yields.
- Control: Indoor growers have the ability to precisely control the light schedule and ensure that their plants are getting the right amount of light for each stage of growth. This allows for greater precision and optimization of plant growth.
- Flexibility: With indoor growing, growers have the flexibility to choose from a variety of light schedules and adjust them as needed throughout the plant’s growth cycle.
- Equipment: Setting up an indoor grow space requires some investment in equipment, such as grow lights, timers, and light-tight containers. However, with the right equipment, indoor growers can have a highly efficient and effective operation.
Indoor growing can be a highly effective method for controlling photoperiod and optimizing cannabis growth. However, it requires careful consideration of factors such as light leaks and equipment, and it may not be the right choice for every grower. By understanding the impact of photoperiod on plant growth and considering these factors, growers can make informed decisions about their growing environment.
Outdoor Growing
When it comes to outdoor growing, photoperiod control can be more challenging due to the natural fluctuations in daylight hours throughout the year. However, there are a few strategies that can be employed to regulate photoperiod and maximize cannabis growth.
One option is to select strains that are better suited for the local climate and have shorter flowering periods. This can help ensure the plants reach maturity before the days get too short in the fall.
Another strategy is to use light deprivation techniques, such as covering the plants with tarps or other light-blocking materials to simulate longer nights and trigger flowering earlier in the season. Additionally, shading the plants during the day can help increase the duration of the dark period and promote flowering.
It’s important to note that outdoor growers may also have to deal with environmental factors that can impact photoperiod, such as weather patterns and natural disasters. These can cause disruptions in the light cycle and affect the growth of the plants.
Despite the challenges, outdoor growing can have its advantages, such as natural sunlight and increased space for plants to grow. By taking measures to control photoperiod, outdoor growers can still achieve healthy and fruitful cannabis harvests.
Hybrid Growing
When it comes to cannabis cultivation, many growers opt for a hybrid approach that combines the benefits of both indoor and outdoor cultivation. This method, known as hybrid growing, involves starting plants indoors under controlled photoperiod conditions and then transitioning them outdoors once they’ve reached a certain stage of growth.
One of the main benefits of hybrid growing is that it allows for a greater degree of control over the growth process while still taking advantage of the natural outdoor environment. In the early stages, plants can be kept under 18/6 or 24-hour light schedules to encourage rapid vegetative growth. Once they’re big enough, they can be transplanted outside where they’ll have access to natural sunlight and the additional space needed for healthy root development.
However, transitioning from indoor to outdoor growing can also be a delicate process, as sudden changes in photoperiod can cause stress and potentially even harm the plants if not managed carefully. This is why it’s important to acclimate plants gradually by gradually reducing indoor light exposure and increasing outdoor exposure over the course of several days or even weeks.
Hybrid growing can be a great way to take advantage of both indoor and outdoor cultivation methods, but it requires careful planning and attention to detail in order to ensure the best possible results.
| Pros | Cons |
|——|——|
| Greater control over growth process | Requires careful acclimation process |
| Takes advantage of natural outdoor environment | Can be more time-consuming than a single indoor or outdoor approach |
| Allows for healthy root development | Inconsistent weather can affect outdoor growth |
| | Requires additional space for outdoor growth |
Choosing the Right Light Schedule for Your Cannabis Plants
When it comes to growing cannabis, one of the key factors to consider is the light schedule. Different light schedules can affect the growth and development of your plants in different ways, and choosing the right one for your particular strain and growing conditions can make a big difference in the final yield and quality of your harvest. In this section, we will explore some of the most popular light schedules used by cannabis growers, along with their advantages and potential drawbacks.
18/6 Light Schedule
An 18/6 light schedule is one of the most common light schedules used during the cannabis vegetative stage. This refers to a period of 18 hours of light, followed by 6 hours of darkness. This schedule allows for consistent and healthy growth during the vegetative stage.
During the vegetative stage, cannabis plants need a lot of light to grow and develop. An 18/6 light schedule ensures that the plants receive enough light each day to grow rapidly. The 6 hours of darkness helps the plants rest, which is important for photosynthesis and overall health.
Here is an example of how an 18/6 light schedule could be structured:
| Time | Light | Darkness |
|---|---|---|
| 6:00 AM | On | Off |
| 12:00 PM | On | Off |
| 6:00 PM | On | Off |
| 12:00 AM | Off | On |
It is important to note that this schedule can be adjusted slightly to suit the needs of the specific strains being grown. Some strains may require a little more or less light, so growers should pay attention to the plants and adjust the schedule as necessary. An 18/6 light schedule is a great choice for growers who want to encourage healthy, vigorous growth during the vegetative stage.
24-Hour Light Schedule
The 24-hour light schedule is an unconventional approach to photoperiod that involves providing continuous light to cannabis plants during both the vegetative and flowering stages. While this method may seem like it would provide maximum growth potential, it can actually be harmful to plants if not done correctly.
Pros:
- Plants can absorb more light, potentially leading to increased growth and yield.
- Eliminates the need for a separate flowering schedule, as plants will automatically start flowering once they reach maturity.
- Can be beneficial for certain strains that are adapted to high light environments.
Cons:
- 24-hour light schedules can be expensive due to the high energy consumption of continuous lighting.
- The constant light can cause heat stress on plants, requiring additional cooling measures.
- Plants that do not tolerate continuous light well may experience stunted growth and reduced yield.
- May not be as effective for strains that are adapted to more natural light cycles.
If you do choose to use a 24-hour light schedule, it is important to closely monitor your plants for any signs of stress or damage. Providing adequate cooling and ventilation can help prevent heat stress, while choosing a strain that is suited for high light environments can also improve your chances of success. As with any unconventional method, it is always a good idea to start slowly and experiment to find what works best for your specific plants and growing conditions.
12/12 Light Schedule
The 12/12 light schedule is a popular choice for growers during the flowering stage of cannabis growth. With this light schedule, the plants are given 12 hours of light and 12 hours of darkness each day, which mimics the natural light cycle of the autumn season.
Pros of Using a 12/12 Light Schedule:
- Encourages the plant to focus on flowering rather than vegetative growth.
- Potentially increases yields, as the plant dedicates more energy to producing buds rather than stems and leaves.
- Allows for easier management of light leaks, as any extra light during the dark period could disrupt the entire photoperiod cycle.
Cons of Using a 12/12 Light Schedule:
- Requires precise timing and consistency, as any alterations to the light schedule could potentially harm the plant and disrupt the flowering process.
- Shorter vegetative stage could result in smaller overall plant size if not managed properly.
- May require additional environmental control to ensure ideal conditions for flowering.
When using a 12/12 light schedule, it is important to note that the plants will typically take around 8-10 weeks to fully flower, depending on the strain. It is also important to avoid any light leaks during the dark period, as even a small amount of light exposure can disrupt the photoperiod cycle and delay or reduce the overall yield.
The 12/12 light schedule can be a great option for growers looking to optimize their yield and focus on producing high-quality buds. However, it requires careful monitoring and precise timing to ensure that the plants are receiving the correct amount of light and darkness throughout the entire flowering stage.
Other Light Schedules to Consider
When it comes to choosing light schedules for your cannabis plants, there are several options to consider. While the 18/6 and 12/12 schedules are the most common choices, other light schedules can also be effective depending on your specific goals and needs.
20/4 Light Schedule: This schedule provides your plants with four extra hours of light during the vegetative stage. This can promote faster growth and potentially lead to larger yields.
14/10 Light Schedule: This schedule is often used by growers who want to slowly transition their plants from the vegetative stage to the flowering stage. By gradually reducing light hours over time, you can help your plants adjust and avoid shock.
15/9 Light Schedule: This schedule is a compromise between the 18/6 and 12/12 schedules, providing slightly longer dark periods without significantly reducing vegetative growth.
11/13 Light Schedule: This schedule is often used by experienced growers to manipulate the sex of their plants. By exposing female plants to slightly longer dark periods, you can encourage them to produce more male flowers, while exposing male plants to slightly shorter dark periods can promote the development of female flowers.
It is important to note that experimenting with non-standard light schedules may require more experience and knowledge to achieve desired results, and may not be suitable for novice growers. Always research and experiment cautiously before making significant changes to your light schedule.
Factors That Can Affect Photoperiod
As much as photoperiod is important for cannabis growth, there are factors that can affect it negatively. These factors can disrupt the light cycle, affecting the plant’s ability to switch between vegetative and flowering stages. It is important to identify and address these factors to ensure optimal growth and maximum yield. In this section, we will discuss some of the factors that can affect photoperiod and offer some solutions to mitigate their impact.
Light Leaks
Light leaks can be a major issue for cannabis growers because they can disrupt the photoperiod, which can have negative effects on plant growth and yield. Light leaks refer to any unwanted light that enters the grow space. This can come from a variety of sources, such as cracks in walls, windows, or doors, or even from neighboring light sources.
To prevent light leaks, it is important to properly seal the grow space and eliminate any sources of external light. This can be done by covering windows with blackout curtains, using weather stripping to seal doors, and even using light-proof ducting to seal ventilation systems.
It is also important to regularly check for any signs of light leaks, especially during the dark cycle. Even the smallest amount of light can disrupt the photoperiod, so it is best to address any leaks immediately.
Ultimately, preventing light leaks is an essential part of controlling the photoperiod for optimal cannabis growth and yield. By taking the necessary steps to eliminate light leaks, growers can ensure that their plants receive the proper amount of light and darkness required for each stage of growth.
Artificial Light Sources
One of the factors that can affect photoperiod and subsequently impact cannabis growth are artificial light sources. Here are some examples of how artificial light sources can create disruptions and influence photoperiod:
- Streetlights: If cannabis plants are exposed to streetlights that are too bright during the night, their photoperiod can be disrupted, which can negatively impact their growth and development.
- Exterior lights: Growers can use exterior lights during the night to check on their cannabis plants or to protect them from animals or intruders. However, these lights can interfere with the natural day-night cycle of the plants.
- Interior lights: If grow lights used indoors are not installed properly or are too bright, they can emit light leaks that can disrupt the photoperiod of the cannabis plants.
- Timer malfunctions: Artificial lights are typically controlled using timers. If these timers malfunction, the light schedule can be disrupted and negatively affect the photoperiod of the cannabis plants.
It is important for growers to be aware of these potential disruptions and to take steps to prevent them. Some solutions include using opaque materials to block out ambient light, installing proper grow light fixtures, and regularly monitoring light schedules and timers. By taking these measures, growers can help ensure that their cannabis plants receive consistent and healthy light cycles throughout their growth cycle.
Natural Disruptions to Photoperiod
Natural disruptions to photoperiod can have a significant impact on cannabis growth. Some of the natural factors that can affect photoperiod include:
- Latitude: The closer a grower is to the equator, the less variation there is in photoperiod throughout the year. For example, a grower in Ecuador will have a photoperiod of roughly 12 hours of daylight throughout the year.
- Season: As seasons change, so too does photoperiod. For example, in the summer months, the days are longer, which means more sunlight for cannabis plants. In the winter months, the days are shorter, which can cause flowering to occur earlier than intended.
- Cloud Cover: Cloudy days can reduce the amount of sunlight that reaches cannabis plants, which can affect when flowering occurs.
It is important to be aware of these factors and adjust your growing techniques as needed. For example, if you are growing outdoors in a location with a lot of cloud cover, you may want to consider using supplemental grow lights to ensure your plants are getting enough light to reach their full potential. Similarly, if you are growing in a location with highly variable photoperiods, you may need to adjust your planting schedule accordingly to ensure your plants have enough time in the vegetative stage before flowering.
Conclusion
Overall, understanding the role of photoperiod in cannabis growth is essential for any successful grower. Proper management and control of light cycles can make a significant difference in the yield and quality of your cannabis plants.
Whether you are growing indoors or outdoors, there are several factors to consider when it comes to photoperiod control. Light leaks, artificial light sources, natural disruptions to photoperiod, and other environmental factors can all affect the growth of your plants in different ways. It is important to monitor and adjust your light schedule accordingly to ensure optimal growth and yield.
During the vegetative stage, longer light cycles can help promote vegetative growth and prepare your plants for flowering. While during the flowering stage, shorter light cycles can encourage the bud production and increase yield. Carefully monitoring and adjusting your light schedule during these stages can significantly enhance the growth and quality of your cannabis plants.
When choosing your light schedule, it is important to consider factors such as energy costs, strain type, and growing environment. There are several light schedules to choose from, including 18/6, 24-hour, and 12/12. Each has its own benefits and drawbacks, so it is essential to choose the one that is best suited for your specific grow.
In conclusion, understanding photoperiod and its relationship with cannabis growth is crucial for any aspiring cannabis grower. Paying attention to the light schedule during different growth stages, controlling the photoperiod for maximum yield, and monitoring environmental factors that can disrupt photoperiod are all necessary steps to take for optimal cannabis growth. With enough knowledge and experience, you can achieve great results in your cannabis cultivation endeavors.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is photoperiodism and how does it affect cannabis growth?
Photoperiodism is the response of plants to changes in daylight hours, which affects their growth and development. Cannabis is a photoperiodic plant, meaning its growth and reproductive cycle is closely tied to changes in light exposure.
What are the different types of photoperiods in cannabis?
The two main types of photoperiods in cannabis are the short-day or long-night plants (which typically flower in the fall) and the long-day or short-night plants (which typically flower in the summer).
What is the vegetative stage of cannabis growth?
The vegetative stage is the period of growth that occurs after the seedling stage and before the flowering stage. During this stage, the plant develops its stem, leaves, branches, and roots.
How can photoperiod control be used to optimize growth during the vegetative stage?
During the vegetative stage, cannabis plants typically require 18-24 hours of light and 6-0 hours of darkness to thrive. By controlling the photoperiod, growers can ensure that their plants receive the optimal amount of light for growth.
What is the flowering stage of cannabis growth?
The flowering stage is the period of growth when the cannabis plant produces flowers or buds. This stage is triggered by changes in the photoperiod, typically a shift from longer periods of light to longer periods of darkness.
How can photoperiod control be used to optimize yield during the flowering stage?
During the flowering stage, cannabis plants typically require 12 hours of light and 12 hours of darkness to initiate and maintain bud production. By controlling the photoperiod, growers can ensure that their plants receive the optimal amount of light for flowering and maximize their yield.
What are some common mistakes to avoid during the flowering stage?
Some common mistakes to avoid during the flowering stage include light leaks (which can disrupt the photoperiod and cause the plant to revert back to the vegetative stage), overfeeding, and under watering.
What are the differences between controlling photoperiod in indoor vs. outdoor growing?
Indoor growers have more control over the photoperiod and can easily manipulate the amount of light their plants receive. Outdoor growers, on the other hand, are more at the mercy of natural light cycles and may need to adjust their planting times to account for changes in daylight hours.
What is a hybrid growing technique?
A hybrid growing technique involves using a combination of indoor and outdoor growing methods to optimize plant growth and yield. For example, growers might start their plants indoors during the vegetative stage and then move them outside during the flowering stage.
What is the 18/6 light schedule and when is it typically used?
The 18/6 light schedule involves providing 18 hours of light and 6 hours of darkness to cannabis plants. This schedule is typically used during the vegetative stage, as it provides plants with the maximum amount of light for growth.
What other light schedules should growers consider?
Other light schedules to consider include the 24-hour light schedule (which provides non-stop light and can be used for certain strains during the vegetative stage), the 12/12 light schedule (which is used to trigger flowering), and the 13/11 light schedule (which can be used to speed up flower production).