Cannabis Nutrient Deficiencies: Top 5 and How to Correct Them
As a cannabis grower, watching your plants wither and die can be a disheartening experience. When your plants fail to grow as expected, the reason could be nutrient deficiencies. Nutrients are essential for the growth and development of cannabis plants, just as they are for humans. Identifying nutrient deficiencies can be a tricky task, especially for novice growers. However, with the right knowledge and expertise, you can easily point out the symptoms and take quick corrective measures. In this article, we’ll review the top 5 cannabis nutrient deficiencies, their symptoms, and provide step-by-step guidance to remedy them. So, if you’re perplexed about why your plants are not thriving, read on to find out more.
Why are Nutrients Important for Cannabis Plants?
Contents
In order for cannabis plants to grow and thrive, they require a variety of nutrients. These nutrients are essential for the plant’s overall health and well-being. Nutrients play a crucial role in the growth and development of cannabis plants by aiding in photosynthesis, facilitating nutrient uptake, and promoting cell division.
Nitrogen is particularly important for cannabis plants, as it is an essential component of chlorophyll, which is responsible for the plant’s green color. Without adequate nitrogen, cannabis plants will have slow growth, and their leaves may turn yellow.
Phosphorus is another important nutrient for cannabis plants as it is necessary for flowering and root development. It also aids in the plant’s energy conversion processes and assists in the uptake of other nutrients.
Potassium is essential for overall plant health as it contributes to water and nutrient transport within the plant. It also promotes strong stalks and stems, which are important for supporting the plant’s weight.
Calcium is a vital nutrient for cannabis plants as it is necessary for the formation of cell walls and proper root development. It also aids in the transportation of other nutrients throughout the plant.
Magnesium is essential for chlorophyll production and overall plant health. Without adequate magnesium, leaves may become yellow, and the plants may show stunted growth.
In addition to these macronutrients, cannabis plants also require a variety of micronutrients such as iron, zinc, and copper. These micronutrients are essential in small amounts and can be easily overlooked or neglected.
Proper and adequate nutrient intake is crucial for the overall health and growth of cannabis plants. A deficiency of any of these essential nutrients can lead to stunted growth, yellowing leaves, and poor flowering. It is essential to identify and correct any nutrient deficiencies promptly to ensure a healthy and productive harvest.
Identifying Nutrient Deficiencies
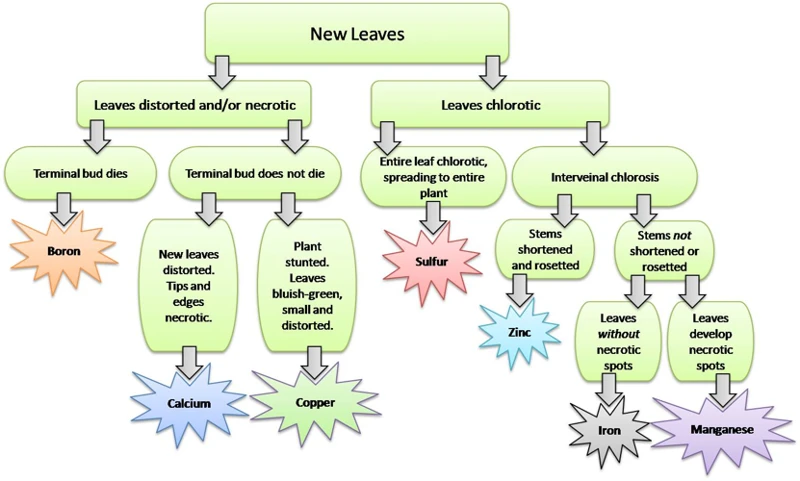
As a cannabis grower, it can be disheartening to watch your plants struggle without knowing why. Identifying nutrient deficiencies can be a challenging task, especially for beginners. However, it’s crucial to spot the signs early on to take the necessary corrective measures. Yellowing leaves, stunted growth, brown spots, brittle stems, and poor flowering are all symptoms that your plants may be lacking crucial nutrients. In this section, we’ll discuss each of these symptoms and their potential causes, so you can identify the nutrient deficiencies accurately.
Yellowing Leaves
Yellowing leaves can be a sign of various nutrient deficiencies, including nitrogen, iron, magnesium, or zinc. In order to properly diagnose which nutrient is lacking, look closely at the yellow leaves and examine their pattern. If the yellowing starts from the tips of the leaves and moves down towards the center or base, this may indicate a lack of nitrogen. On the other hand, if the yellowing appears between the veins of the leaves and progresses outwards, the plant may be lacking iron, magnesium or zinc.
If you determine that the cause of the yellowing leaves is nitrogen deficiency, you can correct it by incorporating a nitrogen-rich fertilizer into the soil or using a nitrogen supplement. However, be careful not to over-fertilize as this can cause other issues such as nutrient burn. Instead, follow the instructions on the fertilizer package and use the appropriate amount for your plant’s needs.
If you identify that the yellowing is caused by a lack of iron, magnesium, or zinc, you can add a chelated micronutrient supplement directly to the soil. Nutrient supplements can also be administered through foliar feeding or by using hydroponic nutrient solutions.
It is important to note that yellow leaves can also be a sign of overwatering, as excessive water can lead to root damage and poor nutrient absorption. To prevent this, make sure the plant is receiving adequate drainage and the soil is not staying too wet for too long. Additionally, pH imbalances can also interfere with nutrient absorption, so periodically check the soil pH levels.
By properly identifying and correcting nutrient deficiencies, you can prevent further damage to your cannabis plants and ultimately ensure their optimal growth and development.
Stunted Growth
One of the clearest indications of a nutrient deficiency in cannabis plants is stunted growth. When a plant is not receiving the nutrients it needs, it can have a difficult time growing properly. Stunted growth can manifest in various ways, including small, thin stems and branches, and an overall slow or stunted growth pattern.
To identify the specific nutrient that your cannabis plants are lacking, you should observe the other signs of nutrient deficiencies along with stunted growth. If you notice yellowing leaves, brown spots, or brittle stems, these visual cues can help you pinpoint the nutrient deficiency that is causing stunted growth in your plants.
One nutrient that is essential for healthy growth in cannabis plants is nitrogen. Nitrogen is necessary for the production of chlorophyll, which plants use to turn sunlight into food through the process of photosynthesis. If your cannabis plants are experiencing stunted growth, it may be a sign of a nitrogen deficiency.
Another nutrient that can cause stunted growth when lacking is phosphorus. Phosphorus is important for the development of roots and flowers, so a deficiency can cause the plant to struggle with growth and production.
Potassium is another essential nutrient for cannabis plants. It plays a crucial role in regulating water movement and helping plants withstand stress. A deficiency in potassium can lead to stunted growth and weak stems.
Calcium is also important for strong stems and healthy growth. A calcium deficiency can cause stunted growth and even lead to the death of the plant. To prevent calcium deficiency, it’s important to make sure your cannabis plants have access to an adequate amount of this nutrient.
Finally, magnesium is another nutrient that is important for healthy growth in cannabis plants. It functions as a building block for chlorophyll, and is necessary for the plant’s ability to produce energy through photosynthesis. A magnesium deficiency can cause stunted growth and yellowing leaves.
If you suspect that your cannabis plants are experiencing a nutrient deficiency that is causing stunted growth, it’s important to correct the problem as soon as possible. The best way to do this is by providing your plants with the nutrients they need. You can do this through careful fertilization, using nutrient-rich soils, and ensuring that your plants have access to clean, fresh water.
In the following table, we summarize the nutrients that can cause stunted growth and other symptoms in cannabis plants:
| Nutrient | Function | Symptoms of Deficiency |
|---|---|---|
| Nitrogen | Chlorophyll Production | Yellowing leaves, stunted growth |
| Phosphorus | Root and Flower Development | Stunted growth, weak stems |
| Potassium | Water Regulation | Stunted growth, weak stems |
| Calcium | Strong Stems | Stunted growth, brown spots on leaves |
| Magnesium | Chlorophyll Production | Yellowing leaves, stunted growth |
By addressing nutrient deficiencies quickly and effectively, you can help your cannabis plants grow strong, healthy, and bountiful.
Brown Spots
Another sign of nutrient deficiency is the appearance of brown spots on the leaves. This is usually caused by a lack of key minerals like calcium, magnesium, or copper. These brown spots can spread quickly, damaging the leaves and reducing the overall health of the plant.
To diagnose this problem, conduct a visual check for the brown spots on your plant’s leaves. The spots tend to be irregular in shape, and they may have a yellowish halo around them.
There are several things you can do to correct this nutrient deficiency. One option is to adjust the pH levels of your soil or growing medium to ensure that your plants can absorb the necessary nutrients more easily. You can also add specific mineral supplements to your growing environment to increase the levels of calcium, magnesium, or copper in the soil.
It’s important to ensure that your plants are getting enough sunlight, as this can affect the production of chlorophyll, a key component in the process of photosynthesis that helps your plants to generate energy. Make sure your plants are getting enough water and are not exposed to extreme temperatures or humidity levels.
Keep a close eye on your plants, remain vigilant for any signs of brown spots, and take early action to correct nutrient deficiencies. By following these steps, you can help promote healthy growth and a bountiful harvest.
Brittle Stems
One of the key indicators of a cannabis plant with nutrient deficiencies is brittle stems. When a cannabis plant has brittle stems, it means that it is lacking in one or more essential nutrients. In general, weak stems cause cannabis plants to be non-supportive and they can be damaged easily. If you notice your stems to be breaking too easily, then it could be a sign of a nutrient deficiency.
Below is a table that shows the potential nutrient deficiencies responsible for the brittleness of cannabis stems, in addition to the specific symptoms, and how to correct or prevent them.
| Nutrient Deficiency | Symptoms | Correction |
|---|---|---|
| Calcium Deficiency | Brittle stems, leaves, and newly growing tips. Deformed new growth. Yellowing and darkening of leaves. | To correct the deficiency, add a calcium-rich nutrient such as gypsum, eggshells, or limestone. Adjust the pH level of the soil to 6.2-7.0. |
| Magnesium Deficiency | Brittle stems, yellowing of older leaves, and may have purplish or red colorations. Leaf tips may initially go yellow and then brown. | The best way to correct magnesium deficiency is to add Epsom salt to the soil. Epsom salt is a great source of magnesium and can make up for the deficiency quickly. Add it to the water you use to irrigate the plant, and regularly check the pH level of the soil. |
It’s important to remember that brittle stems may not only be caused by nutrient deficiencies. High temperature and overwatering can also weaken stems, causing them to become brittle. Make sure to check the soil’s moisture levels and adjust watering accordingly to prevent overwatering. Additionally, maintaining the optimal temperature and humidity levels for your cannabis plant can promote healthy growth, strong stems, and prevent nutrient deficiencies from developing.
Poor Flowering
Poor flowering in cannabis plants can be caused by a variety of factors, one of which is nutrient deficiency. When the plant lacks certain essential nutrients, its reproductive system can be affected, leading to weak or stunted flowers. To address this issue, it is important to identify the nutrient deficiencies that are causing the problem and take appropriate actions to correct them.
The following table highlights the different nutrient deficiencies that can lead to poor flowering in cannabis plants, as well as the symptoms that accompany each deficiency:
| Nutrient Deficiency | Symptoms |
|---|---|
| Phosphorus | Small, weak flowers that may not fully develop or produce low yields. |
| Potassium | Leaves and stems may show signs of damage, flowers may be small or irregularly shaped, or the plant may not produce any flowers at all. |
| Magnesium | Yellowing leaves that may turn brown and curl at the edges. Flowers may be small, weak, or not develop at all. |
To correct these nutrient deficiencies, it is important to give the plant the nutrients it needs. In the case of phosphorus deficiency, adding a high-phosphorus fertilizer or bone meal to the soil can help. For potassium deficiency, adding a potassium-rich fertilizer or potassium sulfate can help the plant to absorb more of the nutrient. Magnesium deficiency can be corrected by applying Epsom salt or a magnesium-rich fertilizer.
It is also important to ensure that the plant is receiving adequate light and water. Without sufficient light, the plant will not be able to produce strong flowers, and without enough water, the plant may not be able to absorb the nutrients it needs. Additionally, it is important to ensure that the soil pH is within the appropriate range for cannabis plants, as nutrient uptake can be affected by an imbalanced pH.
Poor flowering in cannabis plants can be caused by nutrient deficiencies, but these can be corrected by addressing the specific nutrient imbalances and ensuring that the plant is receiving sufficient light, water, and appropriate pH levels. By taking steps to prevent nutrient deficiencies and monitoring the plant’s health, growers can help to ensure that their cannabis plants produce healthy, vibrant flowers.
Top 5 Nutrient Deficiencies and How to Correct Them
After identifying the nutrient deficiencies in your cannabis plants, it is important to take the necessary steps to correct them. There are several ways to do this, including adjusting the pH levels of your soil or growing medium, adding fertilizers that contain the lacking nutrients, or making changes to your watering schedule. In this section, we will explore the top 5 nutrient deficiencies that can occur in cannabis plants, and provide detailed guidance on how to correct them using natural and effective methods. By taking proactive steps to address these deficiencies, you can help your cannabis plants thrive and produce high-quality yields.
Nitrogen Deficiency
When a cannabis plant lacks nitrogen, it begins to show some distinct symptoms that are easy to spot. These symptoms include yellowing of leaves, starting from the oldest ones, and stunted growth. The leaves may also become pale or even white, with the veins remaining green or yellow. In extreme cases, the leaves may wilt and drop off the plant.
If you notice these symptoms in your cannabis plant, you must act quickly to correct the nitrogen deficiency. Here are some steps you can take to fix this issue:
1. Increase Nitrogen Intake: The plant needs more nitrogen to overcome the deficiency. You should add a high-nitrogen fertilizer to the soil or hydroponic system. You can also use organic fertilizers such as blood meal, fish meal or worm castings, which are an excellent source of nitrogen.
2. Adjust pH Levels: Nitrogen uptake is affected by the pH level of the soil or the nutrient solution. You should ensure that the pH level is between 6.0 and 7.0 for soil, and 5.5 and 6.5 for hydroponic systems. Adjust the pH as necessary.
3. Flush the System: Over-fertilization or salt buildup in the soil or hydroponic system can cause a deficiency of nitrogen. You can flush the system with plain water to remove the excess nitrogen and other nutrients.
4. Maintain Proper Lighting: Proper lighting is essential for the growth of cannabis. Ensure that the plant is getting adequate light, which is necessary for photosynthesis.
By taking these steps, you can correct a nitrogen deficiency in your cannabis plant and prevent it from recurring.
Phosphorus Deficiency
Phosphorus is an essential nutrient required for healthy cannabis growth as it helps in the development of strong roots and stems, enhances flower formation, and boosts plant metabolism. A deficiency in phosphorus can cause several problems in cannabis plants, such as poor yields, weak stems, slow growth, and reduced potency.
If your cannabis plants exhibit phosphorus deficiency, you can take the following corrective measures:
1. pH levels: Check the pH level of the soil or hydroponic solution. Phosphorus uptake depends on the pH range between 6.0 to 7.0, and if pH levels are too high or too low, phosphorus becomes less available to the cannabis roots.
2. Increase phosphorus intake: Fertilizers containing high levels of phosphorus can help correct the deficiency. Using a bloom fertilizer in the flowering stage can boost phosphorus levels and improve flower growth and development.
3. Bone meal: Bone meal is a natural fertilizer that contains a high amount of phosphorus. Adding bone meal to the soil can help correct the deficiency and promote healthy growth.
4. Bat guano: Bat guano is another natural fertilizer high in phosphorus that can help correct the deficiency. It also contains other beneficial nutrients that can improve cannabis growth.
5. Avoid overwatering: Overwatering can cause a deficiency in phosphorus as it leaches away from the soil. Only water cannabis plants when the top inch of soil feels dry.
By taking these corrective measures, you can ensure that your cannabis plants receive sufficient phosphorus for healthy growth and high yields.
Potassium Deficiency
Potassium deficiency in cannabis plants can lead to a variety of issues, such as poor flower growth and susceptibility to diseases. Here are the symptoms of potassium deficiency and how to correct it:
- Poor Flower Growth – Potassium is essential for the development of flowers in cannabis plants. If you notice weak or stunted flowers, it could be a sign of potassium deficiency.
- Yellow or Brown Leaf Edges – Plants lacking potassium may have yellow or brown edges around their leaves, while the rest of the leaf remains green.
- Weak Stems – A potassium deficiency can cause stems to become weak and brittle, making them more susceptible to breaking or bending.
To correct potassium deficiency:
- Use potassium-rich fertilizers – If you suspect a potassium deficiency, try adding a fertilizer rich in potassium to the soil. This will help provide the plant with the necessary potassium to grow and develop properly.
- Adjust the pH level – Potassium is less available to plants when the pH level of the soil is too low or too high. Adjusting the pH level to the appropriate range can help make potassium more readily available to the plant.
- Use compost or organic matter – Adding compost or other organic matter to the soil can help increase the amount of potassium available to the plant. This is because organic matter naturally contains potassium, and as it breaks down, it releases the nutrient into the soil.
By addressing potassium deficiency in your cannabis plants, you can help ensure healthy growth and higher yields.
Calcium Deficiency
Calcium is an essential nutrient for cannabis plants, and its deficiency can cause various problems in plant growth and development. Here are some signs that your cannabis plants may be experiencing a calcium deficiency:
- Tip Burn: One of the significant symptoms of calcium deficiency in cannabis plants is the presence of tip burn. Tip burn occurs when the tips of the leaves turn yellow or brown and start drying out. This is because calcium is not reaching the tips of the leaves, causing them to die.
- Leaf Deformation: Another symptom of calcium deficiency is the curling and deformation of the leaves. The leaves will start curling upwards, and the edges of the leaves will start turning brown.
- Leaf Drop: Calcium deficiency can also cause cannabis plants to drop their leaves prematurely. The leaves will become brittle and dry, and eventually drop from the plant.
To correct calcium deficiency in cannabis plants, you can take the following steps:
- Adjust the pH: Calcium deficiency can often be caused by an imbalanced pH level. Adjust the pH level of the soil or hydroponic system to ensure that it is between 6.0 and 7.0, which is the ideal range for cannabis plants.
- Add Calcium-Rich Nutrients: You can add calcium-rich nutrients to the soil or hydroponic system to help correct the deficiency. Some examples of calcium-rich nutrients include gypsum, dolomite lime, and bone meal.
- Use Calcium Supplements: You can also use calcium supplements to give your cannabis plants an extra boost of calcium. These supplements are available in different forms, such as calcium nitrate or calcium chloride.
Preventing calcium deficiency in cannabis plants can be done by ensuring that the soil or hydroponic system has adequate calcium levels. Adding calcium-rich nutrients and supplements can also help prevent deficiencies. Regularly monitoring the pH level and nutrient levels of your growing medium can also go a long way in preventing calcium deficiencies.
Magnesium Deficiency
A magnesium deficiency in cannabis plants can cause yellowing leaves and brown spots, much like a nitrogen deficiency. However, a magnesium deficiency will begin to affect the leaves’ veins, causing them to turn purple or red.
Magnesium is essential for the creation of chlorophyll, so a deficiency can lead to poor plant growth and less photosynthesis. To correct a magnesium deficiency, it is important to use a fertilizer with the proper amount of magnesium.
| Nutrient | Amount Needed |
|---|---|
| Magnesium | 0.10 – 0.20 grams per gallon of water |
In addition to using a proper fertilizer, it may also be helpful to adjust the pH levels in the soil to allow for optimal magnesium absorption. Adding dolomite lime or Epsom salts to the soil can also help to provide enough magnesium for the plants.
It is important to catch and correct a magnesium deficiency quickly, as it can quickly lead to stunted growth and poor yield. Regularly monitoring and adjusting nutrient levels is crucial for healthy cannabis plant growth.
Preventing Nutrient Deficiencies
Ensuring that cannabis plants receive the right amount of nutrients is crucial to their growth and development. To prevent nutrient deficiencies, it is important to maintain a proper feeding schedule and monitor the pH levels in the soil or growing medium.
Feeding Schedule: A balanced feeding schedule is essential for preventing nutrient deficiencies. It is important to follow the recommended dosage provided by the manufacturer of the nutrient solution. Overfeeding or underfeeding can cause problems, and it is important to ensure that the plant receives an adequate amount of nutrients without causing nutrient burn.
pH Level Monitoring: Maintaining the right pH level in the soil or growing medium is important for proper nutrient uptake. Cannabis plants prefer a slightly acidic soil pH between 6.0 and 6.5. If the pH level is too high or too low, the plant may not be able to absorb certain nutrients, leading to deficiencies.
Watering: Overwatering or underwatering can also cause nutrient deficiencies. Overwatering can cause root rot and limit the plant’s ability to absorb nutrients, while underwatering can limit the plant’s ability to absorb water and nutrients. It is important to maintain a proper watering schedule and ensure that the soil or growing medium is moist without being saturated.
Soil Quality: The quality of the soil or growing medium can also impact nutrient uptake. Poor quality soil or growing medium may lack essential nutrients, leading to deficiencies in the plant. It is important to use high-quality soil or growing medium and to add amendments and nutrients as needed.
Regular Inspections: Regularly inspecting the plants for signs of nutrient deficiencies can help prevent problems before they become severe. It is important to monitor the growth and development of the plants and to look for any signs of yellowing leaves, stunted growth, or poor flowering.
Preventing nutrient deficiencies requires a balanced feeding schedule, proper pH level monitoring, appropriate watering, and high-quality soil or growing medium. By regularly inspecting the plants and ensuring that they receive the right amount of nutrients, growers can prevent nutrient deficiencies and promote healthy plant growth.
Conclusion
As we have discussed throughout this article, nutrient deficiencies can have a significant impact on your cannabis plants. It is important to identify these deficiencies as early as possible so that corrective measures can be taken to ensure healthy and successful growth.
With the knowledge of the top 5 nutrient deficiencies and their respective corrective measures, you can now confidently tackle any deficiencies that may arise in your cannabis garden. However, prevention is always better than cure, and therefore it is recommended to maintain a proper nutrient regimen and observe your plants closely for any signs of deficiencies.
It is also important to note that nutrient deficiencies can be caused by a variety of factors, such as pH imbalances, over or underwatering, and inadequate lighting. Therefore, it is essential to maintain optimal growing conditions in addition to providing the correct nutrients.
In conclusion, by understanding the importance of nutrients for cannabis plants, identifying nutrient deficiencies, and taking appropriate corrective measures, you can ensure healthy and successful growth for your plants. Always monitor your plants closely, be proactive in your nutrient regimen, and address any issues promptly for the best results.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the best way to feed cannabis plants?
There are many different ways to feed cannabis plants, including soil, hydroponics, and aeroponics. Each method has its own advantages and disadvantages, so it is important to choose the one that works best for your needs.
How often should I water my cannabis plants?
The frequency of watering your cannabis plants will depend on a variety of factors, including the type of soil or growing medium you are using, the temperature and humidity levels in your grow room, and the size and stage of growth of your plants. Generally, it is best to water your plants only when the top inch of soil feels dry to the touch.
What are the signs of nutrient burn in cannabis plants?
Nutrient burn in cannabis plants can cause brown or yellow tips on leaves, as well as burned or curled edges. In severe cases, the entire leaf may turn brown and die.
What is pH and why is it important for cannabis plants?
pH is a measure of the acidity or alkalinity of a solution. For cannabis plants, it is important to maintain a pH level between 6.0 and 7.0 in order to keep the plants healthy and ensure proper nutrient uptake.
What are the benefits of using organic nutrients?
Organic nutrients are derived from natural sources and are often more easily absorbed by plants than synthetic nutrients. They also help to improve soil quality and promote healthy microbial activity in the soil.
What is the difference between macronutrients and micronutrients?
Macronutrients are nutrients that plants need in large quantities, such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. Micronutrients are nutrients that plants need in smaller quantities, such as iron, zinc, and manganese.
What are the best nutrients for growing cannabis?
There are many different nutrient formulations available for growing cannabis, including both organic and synthetic options. Some popular brands include Fox Farm, General Hydroponics, and Botanicare.
How do I know if my plant has too much nutrient?
If your plant has too much nutrient, you may notice burnt or dried out leaf tips, as well as slowed growth and reduced flowering. It is important to flush your plants with clean water and adjust your nutrient levels if necessary.
What is the best pH level for hydroponic cannabis plants?
The best pH level for hydroponic cannabis plants is between 5.5 and 6.5. This range helps to ensure proper nutrient uptake while also preventing nutrient lockout and other problems.
How can I test the nutrient levels in my soil?
There are many different soil testing kits available that can help you determine the nutrient levels in your soil. Alternatively, you can send a soil sample to a laboratory for analysis.