How Hard Water Affects Cannabis Plants
Growing cannabis plants can be a rewarding experience, but it requires careful attention to detail. One aspect that often goes overlooked is the quality of the water used to nourish the plants. Many cannabis growers are perplexed when their plants are not thriving, despite their best efforts. In this article, we will explore the effects of hard water on cannabis plants, and how it can impact the growth and health of the plants. We’ll also discuss ways to test water hardness and provide preventative measures and best practices to help you achieve the best results possible. So, pull up a chair and let’s dive in!
What is Hard Water?
Contents
As cannabis cultivation requires close attention and a precise set of circumstances, any factor that can impede growth or development must be understood. One such factor is the presence of hard water, which can be detrimental to the plant’s growth. Hard water is water that contains high levels of dissolved minerals, mainly magnesium and calcium, which can interfere with the plant’s ability to absorb the necessary nutrients. Understanding the characteristics of hard water is crucial for growers looking to optimize their cannabis plants’ growth and yield. Let’s dive deeper into the topic of hard water and what it means for cannabis cultivation.
How is Hard Water Formed?
Hard water is formed due to the presence of certain minerals and ions in the water. These minerals are picked up by natural water sources such as underground aquifers and surface water bodies as they flow through rocks and soils. The table below outlines the common minerals and ions that contribute to hard water and their sources:
| Mineral/Ion | Source |
|---|---|
| Calcium (Ca2+) | Limestone, dolomite, gypsum |
| Magnesium (Mg2+) | Dolomite, magnesite, talc |
| Iron (Fe2+) | Iron-containing rocks and sediments |
| Manganese (Mn2+) | Manganese-containing rocks and sediments |
| Carbonate (CO32-) | Limestone, chalk, marble |
| Bicarbonate (HCO3-) | Carbon dioxide in the atmosphere or soil |
| Sulfate (SO42-) | Gypsum, anhydrite, pyrite |
| Chloride (Cl-) | Saltwater intrusion into freshwater sources |
As water picks up these minerals and ions, the concentration of dissolved solids increases, resulting in hard water. Water hardness is typically measured in parts per million (ppm) or grains per gallon (GPG). The higher the concentration of minerals and ions, the harder the water.
Understanding Hardness in Water
Understanding Hardness in Water
When we talk about “hard water,” we’re referring to a specific quality of water that can have a range of negative effects on cannabis plants. But what exactly makes water “hard,” and how does that hardness impact the growth and health of cannabis plants?
In essence, water hardness is a measure of the concentration of minerals present in the water. Specifically, it refers to the amount of calcium (Ca) and magnesium (Mg) ions present in the water. These ions can cause the water to become “hard,” which means that it has a higher level of dissolved minerals.
There are two main types of hardness that can be present in water: temporary hardness and permanent hardness. Temporary hardness is caused by the presence of carbonate minerals in the water, such as calcium carbonate (CaCO3) and magnesium carbonate (MgCO3). These minerals can dissolve in water, but they can also precipitate out of it when the water is heated or boiled. This can create scale buildup in pipes and other equipment.
Permanent hardness, on the other hand, is caused by the presence of sulfate and chloride minerals, such as calcium sulfate (CaSO4) and magnesium chloride (MgCl2). These minerals don’t precipitate out of the water when it’s heated or boiled, and they can cause more serious problems with mineral buildup in irrigation systems and plant tissue.
In general, water hardness is measured in terms of “parts per million” (ppm) of dissolved minerals. A water sample with a ppm measurement of less than 60 is considered “soft,” while a measurement between 60 and 180 is considered “moderately hard.” Water with a measurement of 180 ppm or higher is considered “hard.”
Understanding the hardness of your water is crucial when it comes to growing cannabis plants, as water with high levels of dissolved minerals can cause a variety of problems. From affecting the pH level of your soil to limiting nutrient uptake, hard water can interfere with the growth and health of your plants in a number of ways. That’s why it’s important to test your water hardness and take steps to address any issues that arise.
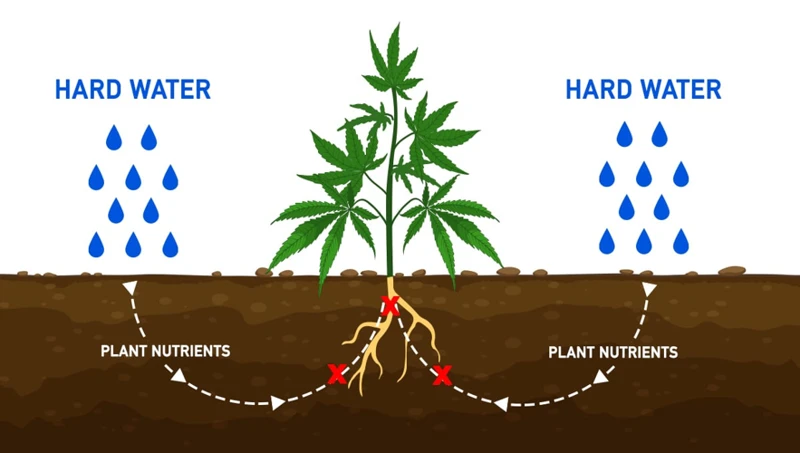
How Hard Water Affects Cannabis Plants
As cannabis plants require meticulous care and a well-regulated environment to achieve optimal growth, it is crucial to be familiar with how every component in their surroundings may potentially impact their progress. One of the most commonly overlooked factors when it comes to cultivating cannabis plants is the type of water used for watering them. Specifically, hard water can have significant implications on the health and development of cannabis plants. In this section, we will explore how hard water affects cannabis plants and its potential consequences.
1. pH level
The pH level of water is a crucial factor when it comes to growing healthy cannabis plants. Hard water usually has a high pH level, meaning it is alkaline. This alkalinity can have negative effects on cannabis plants. When the pH level is too high, it can lead to pH lockout, which occurs when the nutrients in the soil become insoluble and unavailable to the plant. This, in turn, can cause nutrient deficiencies and negatively impact the plant’s growth.
Effects on Cannabis Plants:
- High pH level causing pH lockout and nutrient deficiencies
- Slower growth and development
- Lower yields
- Altered taste and smell of buds
It’s crucial to monitor and adjust the pH level of the water to ensure that it falls within the optimal range for cannabis plants, which is between 6.0 and 7.0. This can be done with the help of pH tests and pH adjustment solutions. Adjusting the pH level will not only prevent pH lockout but also enable the plant to absorb nutrients efficiently.
Preventive Measures:
- Regularly test the pH level of water
- Adjust the pH level to the optimal range
- Monitor pH levels regularly throughout the growth cycle
Maintaining the correct pH level is crucial to ensure that the cannabis plants grow and develop normally. Neglecting this can lead to negative effects on the quality of buds and result in lower yields. It is essential to take measures to adjust the pH level of the water to the optimal range and maintain it consistently throughout the growth cycle.
2. Nutrient Uptake
One of the significant impacts of hard water on cannabis plants is its ability to affect nutrient uptake. Hard water contains elevated levels of dissolved minerals such as calcium and magnesium that form insoluble compounds with essential plant nutrients, making them unavailable for plant uptake. The presence of these minerals in the water can hinder the absorption of critical elements, leading to nutrient deficiencies and affecting plant growth.
The minerals that exist in hard water may even compete with nutrients essential for plant growth. As a result, the plant may appear to have adequate nutrient levels, but the presence of minerals hinders nutrient uptake, leading to stunted growth and an overall reduction in crop yield.
Nutrient deficiencies owing to hard water can also cause visible symptoms on cannabis plants, such as yellowing or browning of leaves, slowed growth, and even death. The accumulation of these minerals can lead to the deposition of salts on the roots, which can make it challenging for plants to absorb water and nutrients, causing roots to dry out and die.
To ensure that cannabis plants receive the required nutrients, it’s important to minimize the impact of hard water. Treating water or using alternative sources such as rainwater can reduce the amount of dissolved minerals in the water, making it more suitable for the plant’s nutrient uptake.
3. Mineral Buildup
Hard water is also known for causing mineral buildup, which can have a negative impact on cannabis plants. When hard water evaporates, it can leave behind minerals such as calcium and magnesium. This can result in a buildup of minerals in the soil, which can affect the plant’s ability to absorb nutrients.
Here are some of the ways mineral buildup can affect cannabis plants:
- Damaged roots: The buildup of minerals in the soil can damage the roots of the cannabis plant, making it harder for the plant to absorb water and nutrients.
- Increase in pH level: As the minerals accumulate in the soil, the pH level of the soil can also increase, making it harder for the plant to absorb certain nutrients it needs to grow.
- Burnt leaves: The excess minerals in the soil can cause the leaves of the cannabis plant to become burnt or discolored, which can stunt the plant’s growth and overall health.
To prevent mineral buildup in the soil, it’s important to regularly flush the soil with fresh, clean water. This can help to remove any excess minerals that may be present in the soil. It’s also important to choose the right type of soil for your cannabis plants. Some soils are designed to prevent mineral buildup, while others may exacerbate the problem.
In addition to regularly flushing the soil, it may also be necessary to adjust the pH level of the water you use to water your cannabis plants. This can help to prevent the buildup of minerals in the soil and ensure that the plants are getting the nutrients they need to grow and thrive.
Mineral buildup can have a negative impact on the growth and health of cannabis plants. It’s important to take steps to prevent this issue and ensure that your plants are getting the nutrients they need to flourish.
Testing Water Hardness
When it comes to growing cannabis plants, treating the water you use is just as important as choosing the proper soil and nutrients for your garden. Hard water, which is water with high mineral content, may hinder the growth and yield of your plants. It’s essential to test the hardness of your water to determine the appropriate measures you can take to ensure optimal plant growth. In this section, we’ll explore various ways to determine the hardness of your water, including DIY tests and professional methods.
1. DIY Tests
For those who want to test the hardness of their water at home, there are several DIY tests that can be easily conducted with simple household supplies. These tests may not be as accurate as professional testing options, but they can still give an idea of the water hardness level.
Table 1: DIY Hard Water Test Methods and Materials
| Test Method | Materials Needed |
|---|---|
| Soap Test | Dish soap, water, container |
| Water and Vinegar Test | White vinegar, water, container |
| Hardness Test Kit | Testing strips or drops, container |
The first DIY test is the Soap Test. To conduct this test, mix a small amount of dish soap with water in a container and stir it vigorously. If the soap forms suds easily, the water is likely to be soft. However, if the water does not form suds easily and the soap scum floats on top of the water, this indicates hard water.
Another DIY testing method is the Water and Vinegar Test. In this test, mix equal parts of white vinegar and water in a container. Soak a clean cloth or towel in the mixture and then rub it over a surface that has been in contact with water, such as a faucet or showerhead. If the surface has white or gray buildup, this indicates hard water.
The Hardness Test Kit is another effective way to test for hard water at home. Test strips or drops can be used to measure the hardness level of the water. Simply follow the instructions on the kit to get accurate results. These kits can be purchased at home improvement or hardware stores.
While DIY tests can be helpful, it’s important to note that they may not provide exact hardness measurements. It’s a good idea to also consider professional testing options for a more accurate understanding of water hardness levels.
2. Professional Tests
For those who prefer a more precise measurement of hard water levels, professional tests conducted by labs or water treatment companies can provide accurate results. These tests offer a more detailed analysis of the mineral content in water and can give insight into the specific minerals present in the water supply.
Benefits of Professional Tests:
- Accurate results: Unlike DIY tests, professional tests are conducted by experts with specialized equipment and can provide more precise measurements of mineral content in water.
- Detailed analysis: Professional tests can provide specific information on the types and levels of minerals present in the water supply, allowing for more targeted treatment methods.
- Peace of mind: Knowing the exact hard water level can give growers peace of mind and assurance that they are taking the necessary steps to ensure the health and vitality of their cannabis plants.
How Professional Tests Work:
Professional tests typically involve sending a water sample to a lab or water treatment company, where it is analyzed for mineral content. The lab will provide a detailed report outlining the levels of various minerals found in the water, such as calcium, magnesium, and iron.
When to Consider Professional Tests:
While DIY tests can provide a general idea of water hardness, professional tests may be necessary for growers who are experiencing issues with nutrient uptake or plant growth despite their best efforts to treat the water. Professional tests can help identify specific mineral imbalances and provide guidance on how to address them effectively.
Cost of Professional Tests:
Professional tests can be more expensive than DIY tests, and the cost can vary depending on the lab or water treatment company conducting the analysis. However, for growers who are struggling with water-related issues, the investment in a professional test may be worth it in terms of improving plant health and yield.
How to Treat Hard Water for Cannabis Plants
If you are struggling with hard water and its effects on your cannabis plants, it’s essential to take action. The high mineral content can cause significant damage, such as affecting the plant’s pH level and nutrient uptake. However, treating hard water doesn’t have to be a daunting task. By using water softeners, pH adjustment, and pre-filters and reverse osmosis, you can help your plants thrive. Here are some effective ways to treat hard water for your cannabis plants.
1. Water Softeners
One way to treat hard water for cannabis plants is through the use of water softeners.
Water softeners are devices that remove the minerals responsible for hard water and replace them with sodium ions. This process is called ion exchange.
The most common type of water softener is the ion exchange water softener, which typically consists of a tank filled with resin beads. These beads are negatively charged and attract positively charged minerals such as calcium and magnesium found in the hard water. Sodium ions from the softener are then exchanged with the minerals, effectively softening the water.
While water softeners can be effective in removing minerals that cause hardness in water, they can also add sodium and potentially increase the pH level of the water. It’s important to monitor the salt intake and pH level to ensure they remain within a safe range for cannabis plants.
Here is a table summarizing the advantages and disadvantages of using water softeners for treating hard water in cannabis plants:
| Advantages of Water Softeners | Disadvantages of Water Softeners |
|---|---|
| Effective in removing minerals causing hard water | Can increase the sodium and pH levels in water |
| Improves nutrient uptake and reduces mineral buildup in soil | May require more frequent maintenance and salt replenishment |
| Can extend the lifespan of irrigation equipment | May not be cost-effective for small-scale grows |
Water softeners can be a good option for treating hard water in cannabis plants, but growers should carefully monitor pH and sodium levels and consider the cost-effectiveness of the solution for their specific grow setup.
2. pH Adjustment
Maintaining the proper pH level is essential to the healthy growth of cannabis plants. Hard water, which has a high mineral content, typically has a high pH level, making it too alkaline for plant growth. This can lead to nutrient deficiencies, stunted growth, and other issues.
To adjust the pH level of hard water for cannabis plants, there are a few options:
1. Acidic Additives: Adding acidic compounds like citric acid, vinegar, or phosphoric acid to hard water can lower its pH level. However, this method can be tricky as adding too much acid can harm the plants.
2. Base Additives: Adding alkaline compounds like baking soda or potash to hard water can raise its pH level. As with acidic additives, care must be taken to avoid adding too much and causing harm to the plants.
3. pH-Adjusting Products: There are a variety of specialized products available on the market that can adjust the pH level of hard water. These products are specifically designed for use with plants and can be a reliable option.
When adjusting the pH level of hard water, it’s important to monitor the levels closely and make small adjustments over time to avoid any sudden changes that could harm the plants. pH test kits or meters can be used to determine the current pH level and ensure that adjustments are being made correctly.
Ultimately, adjusting the pH level of hard water for cannabis plants requires careful attention and a bit of experimentation to find the right solution for each individual setup. However, with the right approach, it’s possible to provide the ideal growing conditions for healthy cannabis plants.
3. Pre-filters and Reverse Osmosis
One effective way to treat hard water for cannabis plants is by using pre-filters and reverse osmosis (RO) systems. A pre-filter is a device that removes impurities and sediments from water before it enters the reverse osmosis system. Once the water is filtered, it goes into the RO system where it passes through a semipermeable membrane that removes minerals, salts, and other contaminants.
Here are the benefits of using pre-filters and reverse osmosis systems:
- Improved water quality: The pre-filter removes large particles and impurities that could clog or damage the reverse osmosis system. The RO system, in turn, removes minerals and other contaminants that could affect the pH level and nutrient uptake of cannabis plants.
- Adjustable TDS levels: Total dissolved solids (TDS) refer to the amount of minerals and salts in water. Pre-filters and RO systems allow growers to adjust the TDS levels of their water, ensuring that it is optimal for cannabis growth.
- Cost-effective: While pre-filters and RO systems can be costly, they are a worthwhile investment for cannabis growers who want to ensure the health and quality of their plants. With proper maintenance and care, these systems can last for years, making them a cost-effective solution for treating hard water.
Some pre-filters and reverse osmosis systems incorporate additional features such as pH adjustments and carbon filtration, which further enhance the quality of the water. However, it is important to keep in mind that reverse osmosis systems can also remove beneficial minerals from the water. As such, it is crucial to test the water and monitor pH and nutrient levels to ensure that plants receive the necessary minerals and nutrients for optimal growth.
Preventive Measures and Best Practices
As a cannabis cultivator, preventing issues before they occur is essential to maximizing your plant’s growth and yield. Fortunately, there are preventive measures and best practices you can implement to avoid the negative effects of hard water on your cannabis plants. By taking a proactive approach and utilizing the following tips and tricks, you can help your plants thrive and produce top-quality buds. Let’s dive into some of the most effective ways to prevent hard water issues in your cannabis grow.
1. Rainwater Collection
Collecting rainwater is a great way to prevent the negative effects of hard water on cannabis plants. Rainwater is naturally soft, making it an ideal alternative for watering cannabis plants. Here are some advantages of using rainwater:
| Advantages of using rainwater for cannabis plants: | |
|---|---|
| 1. | It does not contain minerals or salts that can cause mineral buildup in the soil or medium, which can suffocate the roots and impede nutrient uptake. |
| 2. | Rainwater is slightly acidic, which can help balance the pH level of the soil or medium, making it easier for the plant to take in the nutrients it needs to grow and thrive. |
| 3. | It is free and abundant, especially during the rainy season. Collecting it is an eco-friendly and cost-effective solution to watering cannabis plants. |
How to collect rainwater:
Collecting rainwater is easy and requires minimal resources. To start, all you need is a collection container and a rainwater diverter. Here are some steps to follow:
1. Choose a collection container: This can be a large drum, a bucket, a plastic storage bin, or any other large container that can hold water.
2. Install a rainwater diverter: A rainwater diverter is a device that is attached to your roof gutter downspout, allowing you to divert the rainwater into your collection container. You can purchase one at your local hardware store or online.
3. Position the collection container: Place the container near your cannabis plants or growing area for easy access.
4. Wait for rain: Once it starts raining, the water will flow into the collection container through the rainwater diverter.
5. Use the collected rainwater to water your cannabis plants: When the rain stops, you can use the collected rainwater to water your cannabis plants.
Additional tips:
– Make sure your collection container has a lid to prevent debris, insects, or animals from getting into the water.
– If you live in an area with heavy rainfall, consider installing multiple collection containers to store excess rainwater.
– Use rainwater within a week of collection to prevent bacterial growth.
– Do not collect rainwater from roofs made of asbestos, lead, or other hazardous materials.
– If you are using rainwater as your primary water source, test the pH level and nutrient content periodically to ensure your plants are getting the right balance of nutrients.
2. Clean Equipment
Keeping equipment clean is essential when cultivating cannabis, especially when using hard water. Any buildup of mineral deposits on equipment can lead to poor water circulation, resulting in further mineral accumulation on plants. Here are some steps to follow to ensure equipment is properly maintained:
- Regular cleaning: Equipment should be regularly cleaned to remove any mineral or algae buildup. This includes tubing, pumps, and reservoirs. For smaller items, such as air stones and net pots, they can be soaked in a vinegar solution to dissolve any mineral buildup.
- Replacement: If equipment is heavily damaged from mineral buildup or is no longer functioning properly, it may need to be replaced. This is particularly true for items such as air stones and net pots, which can quickly become clogged.
- DIY cleaning solutions: In addition to vinegar, there are other DIY cleaning solutions that can be used to remove mineral buildup. For example, a mixture of baking soda and water can be used to clean hydroponic systems, while a mixture of citric acid and water can be used to clean mineral buildup from pumps and tubing.
- Professional cleaning: For larger hydroponic systems, it may be necessary to bring in a professional cleaning service. They will have the necessary equipment to thoroughly clean the system and remove any mineral buildup. This can be particularly useful in commercial cannabis operations where hydroponic systems are large and require regular maintenance.
By following these steps to keep equipment clean, cannabis growers can avoid the negative effects of hard water and ensure that their plants are healthy and thriving.
3. Monitoring and Adjusting pH
Maintaining the correct pH level in the cannabis plant’s root zone is crucial for healthy growth and nutrient uptake. When hard water is used, the pH level can become too high or too low, causing nutrient deficiencies or toxicities. Monitoring and adjusting pH is an essential practice for any cannabis grower.
Monitoring pH: pH meters and testing kits are essential tools for monitoring pH levels. The ideal pH range for cannabis plants is slightly acidic, between 5.5 and 6.5. As hard water contains dissolved minerals that can affect pH levels, it’s essential to check pH regularly and adjust it accordingly.
Adjusting pH: There are several ways to adjust pH levels in hard water. One of the most effective methods is to use pH adjusters, such as pH up and pH down solutions. These solutions contain acidic or basic compounds that can adjust pH levels quickly.
Another way to adjust pH is to use buffers. Buffers are substances that can resist pH changes, keeping it within a certain range. Cannabis growers can add buffers to the water to stabilize pH levels.
Using pH Meters: pH meters are valuable tools for accurate pH testing. These handheld devices can provide precise pH measurements, allowing growers to adjust levels precisely. When using a pH meter, it’s important to calibrate it regularly and follow the manufacturer’s instructions.
Monitoring and adjusting pH levels is critical for cannabis growers who use hard water. By keeping pH levels in the optimal range, growers can ensure their plants receive the correct nutrients and thrive.
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Step 1 | Obtain a pH meter or testing kit |
| Step 2 | Test the pH of the water before adding nutrients or adjusting pH |
| Step 3 | If the pH is too high, add a pH down solution to lower the pH |
| Step 4 | If the pH is too low, add a pH up solution to raise the pH |
| Step 5 | Test the pH again after adding solutions and adjust if needed |
| Step 6 | Use a buffer solution to stabilize pH levels if necessary |
| Step 7 | Calibrate the pH meter regularly and follow the manufacturer’s instructions |
Conclusion
After evaluating the effects of hard water on cannabis plants, it’s evident that this issue needs to be addressed for optimal growth and yield. Hard water can impact the pH level of the soil, hinder nutrient uptake, and lead to mineral buildup, all of which can negatively impact the health of cannabis plants.
There are several methods for testing water hardness, ranging from DIY tests to professional testing services. Once you’ve determined the hardness of your water, several solutions are available to help treat it for cannabis plants. Water softeners, pH adjustment, and pre-filters with reverse osmosis are all viable options to consider.
To prevent issues caused by hard water, it’s recommended to collect rainwater, which is naturally soft and free of impurities. Additionally, keeping equipment clean and regularly monitoring and adjusting pH levels can help ensure the optimal growth of cannabis plants.
In conclusion, addressing the effects of hard water on cannabis plants is essential for maximizing growth and yield. By testing water hardness, implementing treatment methods, and taking preventative measures, you can ensure the health and vitality of your cannabis plants. With attention to detail and proper care, you can grow healthy, robust plants with impressive yields.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the optimal pH level for cannabis plants?
The optimal pH level for cannabis plants is between 6.0 and 7.0.
What are the signs that my cannabis plant is suffering from hard water?
Signs that your cannabis plant is suffering from hard water include stunted growth, yellow leaves, and an overall decline in plant health.
How can I test the hardness of my water at home?
You can test the hardness of your water at home using a soap test kit, a boiling water test, or a vinegar test.
Can hard water affect the potency of my cannabis plant?
Yes, hard water can affect the potency of your cannabis plant by hindering its nutrient uptake and causing mineral buildup in the soil.
What is reverse osmosis and how does it help treat hard water?
Reverse osmosis is a water treatment process that involves forcing water through a semipermeable membrane to remove impurities and minerals. It can help treat hard water by removing excessive minerals that can damage your cannabis plant.
Can boiling hard water make it soft?
No, boiling hard water does not make it soft. Boiling hard water only removes bacteria and viruses, but not the minerals that make the water hard.
What is the best way to adjust the pH level of my hard water?
The best way to adjust the pH level of your hard water is to use a pH adjustment kit or product designed specifically for cannabis plants.
How often should I monitor the pH level of my cannabis plant’s soil?
You should monitor the pH level of your cannabis plant’s soil at least once a week to ensure it stays within the optimal range.
Can I use rainwater to water my cannabis plants?
Yes, rainwater can be used to water your cannabis plants as it is free of minerals and chemicals found in tap water, but it is important to monitor the pH level of the rainwater as well.
What is the best way to prevent hard water from affecting my cannabis plants?
The best way to prevent hard water from affecting your cannabis plants is to use a water softener, pH adjustment products, and pre-filters or to collect rainwater. Additionally, keeping your equipment clean and monitoring your plant’s pH level regularly can help prevent damage caused by hard water.