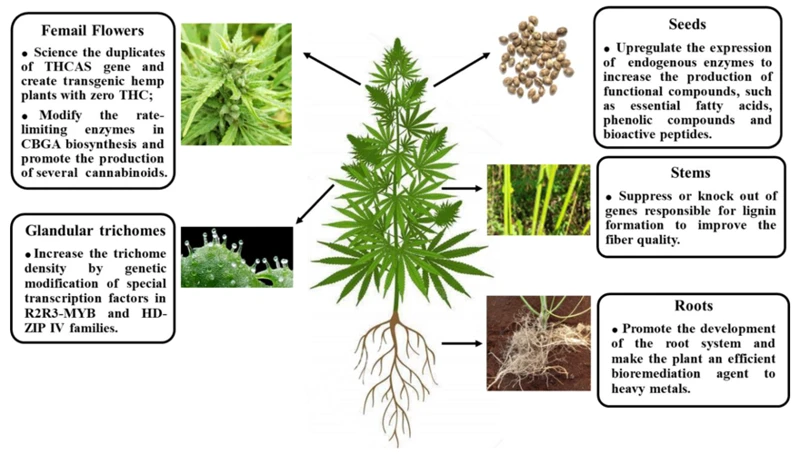
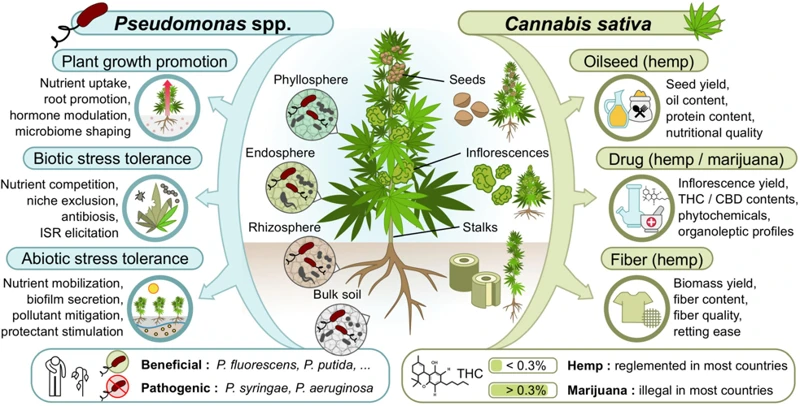
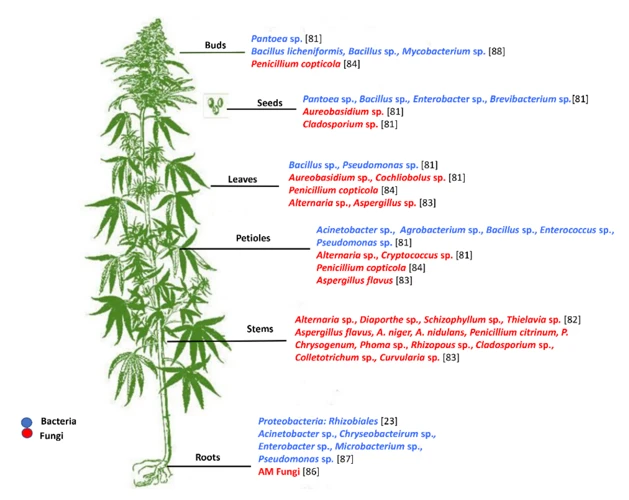
The Future of Disease-Resistant Cannabis Strains
The cannabis industry has been booming in recent years, thanks to the growing acceptance and legalization of the plant. However, the cultivation of cannabis comes with a significant challenge – the risk of disease. This has led to the development of disease-resistant cannabis strains that can combat and prevent disease, but the question remains: what does the future hold for these strains? In this article, we will explore the latest innovations and advancements in disease-resistant cannabis strains, as well as the future possibilities of these strains. Join us as we delve into the complex and rapidly evolving world of disease-resistant cannabis.
The Importance of Disease-Resistant Cannabis Strains
Contents
As the cannabis industry continues to grow, so does the need for disease-resistant strains. The cultivation of cannabis is not without its challenges, and one of the biggest hurdles that growers face is disease. It is imperative for growers to be able to combat these diseases in order to maintain their crop yield and quality. Disease-resistant cannabis strains are crucial to ensuring that growers can produce a successful crop without the threat of diseases wiping out their harvest. In this section of the article, we will explore what disease-resistant cannabis strains are, why they are important, and the economic impact of cannabis diseases.
What Are Disease-Resistant Cannabis Strains?
Disease-resistant cannabis strains are strains of cannabis that are genetically modified or selectively bred to be resistant to various diseases that can affect the plant during its growth. These strains have become increasingly important in the cannabis industry as growers seek to produce crops that are of high quality and have a high yield.
A disease is a harmful deviation from the normal functioning of a living organism’s biology. Fungi, bacteria, and viruses are common types of diseases that affect plants. In cannabis, some common diseases include Powdery Mildew, Botrytis, and Fusarium. These diseases can damage the plant, causing it to have a lower yield and poor quality.
To combat this, breeders and genetic engineers have developed strains that are resistant to specific diseases or have a higher tolerance to them. The process involves identifying the genes responsible for disease resistance and manipulating them to produce a desirable effect. These strains have become popular among growers as they reduce the risk of crop failure and increase the profitability of their operations.
In addition to genetic modification and selective breeding, other methods of disease prevention include the use of pesticides and fungicides, good hygiene practices, and sustainable growing practices. By implementing these methods, growers can reduce the chances of their plants succumbing to diseases, and ultimately, increase their yields and profits.
Disease-resistant cannabis strains are essential for the continued growth and success of the cannabis industry. With the help of advanced breeding techniques and the latest innovations in genetic engineering, researchers and growers can continue to develop new strains that are resistant to diseases, resulting in better crops and a sustainable future for the industry.
| Type of Disease | Effect on Cannabis Plant |
|---|---|
| Powdery Mildew | A white powdery substance found on leaves, stems, and buds. Can stunt plant growth and decrease yield. |
| Botrytis | A fungal disease that can cause gray mold on buds and leaves. Can decrease yield and cause buds to rot. |
| Fusarium | A fungal disease that can cause wilting, yellowing of leaves, and stem rot. Can decrease the plant’s overall health and yield. |
The Importance of Disease-Resistant Cannabis Strains
When it comes to cannabis cultivation, disease resistance is of utmost importance for ensuring a healthy, thriving crop. Disease-resistant cannabis strains refer to strains that have been specifically bred or developed to combat common diseases and pests that can devastate a cannabis crop. These strains have the ability to resist, tolerate, or recover from attacks by pathogens, viruses, fungi, and pests more easily than non-resistant strains.
The Importance of Disease-Resistant Cannabis Strains lies in the fact that they can provide a stable and consistent yield while minimizing the risk of crop loss. A strain’s disease resistance can make all the difference in the success and profitability of a grow operation. Disease resistance also helps to reduce the need for harsh chemicals and pesticides, which can negatively impact the environment and lead to health risks for growers and consumers.
Diseases and pests are significant threats to cannabis crops, and if not managed properly, can significantly reduce both the yield and quality of a harvest. This can lead to financial losses for growers as well as limit the availability of cannabis for medical and recreational use.
The Economic Impact of Cannabis Diseases is staggering. Diseases and pests can cost growers thousands of dollars in lost revenue and increased expenses for pesticides or treatments. Additionally, an outbreak of disease or pests in one grow facility can spread quickly to nearby facilities, potentially leading to a regional shortage of cannabis and higher prices for consumers.
The development and utilization of disease-resistant cannabis strains are critical to the sustainability and growth of the cannabis industry, both economically and environmentally. This is especially true as cannabis legalization continues to spread, leading to an increase in demand for high-quality, disease-resistant cannabis strains.
The Economic Impact of Cannabis Diseases
Cannabis diseases not only have a significant impact on the health and yield of plants, but also on the economy. The costs associated with the loss of crops due to diseases are substantial, ranging from decreased profit margins for growers to increased prices for consumers. Here is a table highlighting some of the economic impacts of cannabis diseases:
| Impact | Description |
|---|---|
| Decreased Yield | Cannabis plants affected by diseases may yield significantly less or die, resulting in lost profits for growers. |
| Increased Operational Costs | Growers may need to increase their operational costs to account for damage control, clean up, and disposal of infected crops. They may also need to invest in more expensive pesticides and fungicides. |
| Lost Investments | Growers may invest a significant amount of money into their crops, which can be lost if diseases destroy the plants. |
| Higher Prices for Consumers | As growers experience losses, they may need to increase the prices of their cannabis products to maintain their profit margins. This can result in higher prices for consumers. |
| Decreased Quality | Cannabis that is infected with diseases may have lower quality and potency, resulting in lower prices in the market and decreased demand. |
As the cannabis industry continues to grow, it’s important to address the issue of disease resistance to minimize the negative economic impacts associated with diseased crops. By investing in disease-resistant strains and implementing sustainable and responsible growing practices, growers can not only benefit financially, but also contribute to a healthier and more sustainable industry.
The Latest Innovations and Advancements in Disease-Resistant Cannabis Strains
In the ever-evolving cannabis industry, continuous efforts are being made to develop disease-resistant strains that can provide a secure and sustainable source of revenue for cultivators. With the constant threat of pests and diseases, the need for innovation in developing resilient cannabis strains has never been more urgent. Fortunately, there are several latest innovations and advancements that are changing the landscape of disease-resistant cannabis production. From genetic engineering and biotechnology to the use of natural pesticides and fungicides, these advancements are demonstrating promising results in pushing for a robust and sustainable future for the cannabis industry.
Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology
Genetic engineering and biotechnology are playing an important role in developing disease-resistant cannabis strains. With the advancements in biotechnology, scientists are now able to manipulate the genetic makeup of cannabis plants to create new strains with improved disease resistance. Here are some ways that genetic engineering and biotechnology are being used to develop disease-resistant cannabis strains:
- Gene Editing: Gene editing is a powerful tool that allows scientists to selectively modify specific genes within a plant’s DNA. By manipulating the genes that control disease-resistant traits, researchers can develop cannabis strains that are more resistant to diseases and pests.
- Marker-Assisted Selection: Marker-assisted selection is a technique that allows breeders to identify and select plants with desirable traits at an early stage of development. By using molecular markers to identify disease-resistant traits, breeders can develop cannabis strains with improved disease resistance.
- RNA Interference: RNA interference is a technique that involves silencing specific genes within a plant’s DNA. By selectively silencing genes that are responsible for disease susceptibility, scientists can develop cannabis strains that are more resistant to diseases.
- Genome Sequencing: Genome sequencing is a process that involves mapping out the entire genetic makeup of a plant. By sequencing the genomes of different cannabis strains, scientists can identify genetic markers that are associated with disease resistance. This information can then be used to develop new cannabis strains with improved disease resistance.
- Tissue Culture: Tissue culture is a technique that involves growing plant cells in a controlled environment. By manipulating the growth conditions of these cells, scientists can develop cannabis plants that are more resistant to diseases.
Genetic engineering and biotechnology are powerful tools that are being used to develop disease-resistant cannabis strains. By manipulating the genetic makeup of cannabis plants, scientists are able to create new strains with improved disease resistance, which can ultimately lead to more sustainable and profitable cannabis cultivation.
Natural Pesticides and Fungicides
One of the latest advancements in disease-resistant cannabis strains involves the use of natural pesticides and fungicides. Unlike traditional pesticides which can be harmful to the environment and human health, natural alternatives use plant-based or organic ingredients that are safe and effective.
Examples of natural pesticides include neem oil, garlic extract, and peppermint oil. Neem oil, for instance, is extracted from the seeds of the neem tree and has been proven to be effective against a wide range of pests and diseases. Garlic extract is known for its antifungal properties and can be used to control powdery mildew, a common disease in cannabis plants. Peppermint oil, on the other hand, is a natural insecticide that can be used to repel spider mites, aphids, and other pests.
Natural fungicides are also gaining popularity in disease control. These can be made from natural substances such as copper, which is effective against downy mildew and other fungal diseases. Other natural fungicides include baking soda, hydrogen peroxide, and vinegar. These substances are non-toxic and have no harmful side effects on the environment, humans or animals.
Incorporating natural pesticides and fungicides into cannabis cultivation has many benefits, including reducing the risk of pesticide resistance and preserving beneficial insects such as bees and ladybugs that play a crucial role in pollination and pest control. Additionally, natural pest control can often be more cost-effective than traditional chemical pesticides.
However, it is important to note that natural pesticides and fungicides do have some limitations. They may not be as potent as synthetic pesticides and may require more frequent applications. Additionally, they may not be suitable for all pest situations and may have a shorter shelf life.
The use of natural pesticides and fungicides is a promising solution for disease control in cannabis cultivation. By embracing sustainable and environmentally friendly practices, growers can produce high-quality, disease-resistant cannabis strains while minimizing harm to the planet and human health.
Crossbreeding and Hybridization
Crossbreeding and hybridization are traditional methods of developing new cannabis strains with better disease resistance. By selectively breeding plants with desirable traits, breeders can create offspring that are stronger and better suited for their environment. This process involves combining the genes of two different strains to produce a new hybrid strain that has the desired traits of both parent plants.
Advantages of Crossbreeding and Hybridization:
- Increases genetic diversity in the cannabis plant population, enhancing the potential for disease resistance.
- Allows growers to create strains that are specifically suited for their environment and growing conditions.
- Can produce hybrids that are more resilient to pests and diseases than their parent strains.
How Crossbreeding and Hybridization Works:
- Breeders select parent strains that have desirable traits, such as disease resistance or high yield.
- The chosen parent plants are pollinated with each other to create new offspring with a unique combination of genes.
- The seeds from the offspring are then planted and grown, and the resulting plants are evaluated for their desired traits.
- The best-performing plants are selected for further breeding, while the rest are discarded.
- The process is repeated until the desired traits are consistently present in the offspring, creating a stable new hybrid strain.
Crossbreeding and hybridization are tried and tested methods of developing new cannabis strains, and they have been used for decades by breeders to create stronger, more disease-resistant plants. However, they can also be time-consuming and unpredictable, as the traits of the offspring can vary significantly from those of their parent plants. As a result, some growers and breeders are turning to newer methods like genetic engineering to produce more reliable disease-resistant strains.
Cannabis Varieties with Natural Resistance
One potential approach to creating disease-resistant cannabis strains is the identification and cultivation of varieties with natural resistance. These strains have evolved over time to withstand certain diseases and pests, making them valuable resources for breeders and cultivators.
Examples of cannabis varieties with natural resistance include:
- Afghan Kush: A landrace strain originating from the mountainous regions of Afghanistan, Afghan Kush has natural resistance to pests and diseases common in those harsh environments. It is also known for its hardy nature and ability to withstand challenging growing conditions.
- Durban Poison: Originating from South Africa, Durban Poison is known for its resistance to mildew and mold, making it a valuable strain for those seeking natural resistance to these common cannabis ailments.
- ACDC: This high-CBD strain is believed to have natural resistance to pests and diseases due to its strong genetics, which include the landrace strain Cannatonic.
- Skunk #1: Developed in the 1970s by Dutch breeders, Skunk #1 is a classic strain known for its strong resistance to pests and diseases. It is also valued for its high yields and potent effects.
While these strains may not be completely immune to all cannabis diseases and pests, their natural resistance can be a valuable starting point for breeders and cultivators seeking to create new disease-resistant varieties. Through careful breeding and selection, it may be possible to further enhance the natural resistance of these strains and create new strains with even greater disease resistance.
Integrated Pest Management
Integrated Pest Management, or IPM, is a comprehensive approach to pest control that involves multiple strategies to prevent and manage pests while minimizing the use of harmful chemicals. In relation to cannabis cultivation, IPM is a crucial component of maintaining healthy and disease-resistant plants without compromising the quality of the final product.
Here are some strategies involved in IPM for cannabis cultivation:
- Prevention: The first line of defense against pests is prevention. This includes selecting disease-resistant strains, maintaining a clean environment, and using proper sanitation practices.
- Monitoring: Regular monitoring of plants is essential to identifying potential pest problems before they become too severe. This involves visually inspecting plants for signs of damage or pests, as well as using traps and other monitoring tools.
- Biological controls: Beneficial insects, such as ladybugs and praying mantises, can be introduced to the growing environment to naturally control pest populations.
- Cultural controls: Adjusting cultural practices can also help control pests. This can include adjusting temperature and humidity levels, as well as manipulating light cycles to discourage certain pests.
- Chemical controls: As a last resort, chemical controls can be used to manage pests. However, it is important to choose the least harmful option and use it sparingly to avoid damage to the plant and its ecosystem.
By incorporating these strategies into a comprehensive IPM plan, cannabis cultivators can prevent, manage and reduce pest infestations while protecting their crops and the environment.
Indoor Cannabis Cultivation
In addition to the various advancements in biotechnology, crossbreeding, and integrated pest management in the cannabis industry, one method that has gained significant popularity is indoor cultivation, which involves growing cannabis in a controlled environment. This method is particularly useful for growers who want to protect their crops from disease and other external factors that can negatively impact the plant’s growth.
Advantages of Indoor Cannabis Cultivation:
- Increased control over the growing environment.
- Optimal growing conditions can be maintained throughout the whole year.
- Protection from harsh weather conditions, pests, and disease.
- Reduced risk of contamination from external sources such as bugs, fungi, or pesticides.
- Improved plant quality and yields due to the precise control over light, temperature, humidity, and CO2 levels.
Techniques used in Indoor Cultivation:
- Hydroponics: a method of growing plants in a nutrient-rich solution without soil.
- Aeroponics: a method of growing plants in an air or mist environment, without the use of soil or hydroponic systems.
- Vertical Farming: a method of growing crops in vertically stacked layers, usually done in a controlled environment.
- Indoor Lighting: used to replicate natural sunlight, and carefully controlled to provide the ideal spectrum, intensity, and duration of light for each stage of growth.
- Closed-Loop Ventilation: allows growers to manage temperature, humidity, and air quality, while minimizing the need for external air exchange that could introduce contaminants.
While indoor cultivation does provide increased control over the growing environment, it also involves higher costs for setup, maintenance, and energy usage. It’s important to choose the appropriate cultivation method based on the needs and goals of the grower, as well as the constraints of their resources, such as location, budget, and access to technology.
The Future Possibilities of Disease-Resistant Cannabis Strains
As the cannabis industry continues to grow and evolve, there is great curiosity and intrigue surrounding the future possibilities of disease-resistant cannabis strains. With advancements in technology and research, the potential for creating super strains of cannabis that can resist a wide range of diseases seems within reach. The development of such strains could have a tremendous impact on the industry, leading to increased yields, improved product quality, and reduced costs. In this section, we will explore some of the most promising avenues for future innovation in disease-resistant cannabis strains.
Further Advancements in Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology
As technology continues to improve, the future of disease-resistant cannabis strains is likely to see further advancements in genetic engineering and biotechnology. Here are some potential developments to look out for:
- Gene Editing: With the advent of CRISPR-Cas9 technology, it may be possible to directly edit the DNA of cannabis plants to confer disease resistance. This could involve adding beneficial genes from other organisms or simply turning off undesirable genes in the plant’s own genome.
- Epigenetic Modification: Epigenetics involves altering gene expression without actually changing the DNA sequence. By tweaking factors like histone proteins or RNA molecules, researchers may be able to induce cannabis plants to activate genes that improve disease resistance.
- Bioengineering: Some scientists are exploring the possibility of designing new proteins and enzymes that can help cannabis plants fend off diseases more effectively. This could involve identifying specific proteins produced by the plant’s natural defenses and recreating them in a lab for more targeted protection.
- Microbial Solutions: Plants rely heavily on the bacteria and fungi that live in and around their roots for nutrients and protection. Researchers are investigating ways to manipulate these microbial communities to encourage the growth of beneficial organisms that naturally suppress cannabis diseases.
While these advancements in genetic engineering and biotechnology offer exciting possibilities for disease-resistant cannabis strains, it’s important to proceed with caution. Many people remain wary of genetically modified organisms (GMOs), and there are both ethical and safety concerns to address. As technology advances, it will be crucial to balance the benefits of disease resistance with the potential risks of genetic manipulation.
New Comprehensive Testing Methods for Disease Resistance
As the cannabis industry continues to grow, so does the need for comprehensive testing methods to ensure disease resistance. New technologies are emerging to tackle this issue and provide accurate screening of disease-resistant cannabis strains.
One of the most promising developments is the development of **genome sequencing techniques**. These allow researchers to study the DNA of cannabis plants in detail, providing valuable insights into the genetic basis of disease resistance. By analyzing the plant’s DNA, breeders can select and cross-breed strains that exhibit natural resistance to certain diseases.
Another innovative testing method is **proteomics**, which identifies the proteins within cannabis plants that contribute to disease resistance. This method allows for the analysis of cannabis plants at a molecular level, providing insights that were previously impossible to obtain.
Furthermore, **bioassays** allow growers to test the effectiveness of pesticides and fungicides on their plants without harming them or the environment. This method involves exposing the cannabis plant to a specific disease, and testing different treatments to see which are most effective.
Another approach is the use of **remote sensing technologies**, such as hyperspectral imaging, to identify and monitor disease in cannabis plants. This technology uses light-sensitive sensors to capture detailed images of the plants, highlighting areas that are affected by disease. This allows growers to detect disease at an early stage and take corrective action before it spreads.
Finally, **machine learning algorithms** are being developed to aid in the identification and diagnosis of disease through image recognition. This involves training computers to recognize patterns of disease in images of cannabis plants, allowing growers to quickly identify and treat potential issues.
There are a variety of testing methods being developed to ensure the disease resistance of cannabis strains. By utilizing these innovative techniques, growers can ensure a healthy, sustainable crop while minimizing environmental impact.
Increased Use of Natural Pesticides and Fungicides
Disease-resistant cannabis strains are in high demand due to the increasing prevalence of pests and diseases. The use of synthetic pesticides and fungicides has been widely criticized for being harmful to the environment and potentially hazardous to human health. As a result, growers are exploring new methods of protection that utilize natural substances.
Natural Pesticides and Fungicides are derived from organic compounds and are used to control pests and diseases. They are considered safer and more sustainable than synthetic chemicals. Some natural pesticides and fungicides that are commonly used in cannabis cultivation include neem oil, pyrethrum, garlic, and copper sulfate.
The use of natural pesticides and fungicides is on the rise, as cannabis growers try to minimize the risks associated with synthetic chemicals. One of the most popular natural pesticides is neem oil, which is extracted from the seeds of the neem tree. Neem oil is effective against a wide range of pests, including mites and aphids. It is also effective at controlling fungal diseases like powdery mildew and rust.
Another natural pesticide that is commonly used in cannabis cultivation is pyrethrum, which is derived from the chrysanthemum plant. Pyrethrum is effective against a wide range of pests, including spider mites, thrips, and whiteflies. It is also effective at preventing mold and mildew.
Copper sulfate is often used as a natural fungicide in cannabis cultivation. It is effective at controlling a wide range of fungal diseases, including powdery mildew and downy mildew. Copper sulfate is approved for use in organic farming and is considered safe for human consumption.
Garlic is another natural pesticide that is commonly used to control pests in cannabis cultivation. Garlic contains sulfur, which is toxic to many pests. It is effective against a wide range of insects, including aphids, spider mites, and whiteflies. Garlic can also be used to control fungal diseases like powdery mildew.
The use of natural pesticides and fungicides is a promising trend in the world of cannabis cultivation. While these substances may not be as potent as their synthetic counterparts, they offer a more sustainable and eco-friendly approach to pest and disease control. As the demand for organic and sustainable cannabis continues to grow, the use of natural pesticides and fungicides is likely to increase in popularity.
The Development of Super Strains of Disease-Resistant Cannabis
With the rapid advancements in cannabis research and development, the development of super strains of disease-resistant cannabis is becoming increasingly possible. These super strains would be genetically engineered or hybridized to possess a high level of resistance to a broad range of diseases and pests.
Some of the features that might be incorporated into these super strains include enhanced pest and disease resistance, higher yields, more potent cannabinoid profiles, and improved flavors and aromas. With these enhancements, super strains could help growers increase their yields while minimizing their reliance on pesticides and other chemicals.
To achieve such feats, researchers and breeders would have to continue exploring advanced genetic engineering techniques, developing new hybrid varieties, and experimenting with novel growing methods. They may also look to cannabis cultivars from other regions or countries with unique genetic traits that could be incorporated into the super strains.
However, concerns about genetically modified organisms and the impact on the environment and human health have been raised. The development of super strains must be done with caution and responsibility, ensuring that the benefits outweigh the potential risks.
The development of super strains of disease-resistant cannabis holds great potential for the cannabis industry. With the right approach, these super strains could provide a sustainable and responsible solution to the challenges of cannabis cultivation while also meeting the evolving demands of the market.
Increased Collaboration Between Researchers and Breeders
Collaboration plays a crucial role in the development of disease-resistant cannabis strains that can withstand various diseases and pests. By increasing collaboration between researchers and breeders, the cannabis industry can advance faster in disease resistance, resulting in more efficient and effective disease-resistant strains.
The following are some ways researchers and breeders can improve collaboration:
- Sharing Research Findings: Researchers can share their findings with breeders to help them understand how their work can be used in developing new and advanced strains. In turn, breeders can share their knowledge and experience in developing new strains with researchers, helping them identify areas that need more research.
- Collaborative Projects: Breeders and researchers can collaborate on projects that focus on developing specific disease-resistant strains. By pooling their resources and expertise, they can develop and improve new strains in a more efficient and effective manner.
- Networking: Both breeders and researchers can attend conferences, seminars, and other events in the industry to learn about new advancements in cannabis research and breeding. By networking, they can identify areas of common interest and develop collaborations.
- Sharing Genetic Data: Researchers can share genetic data and studies with breeders to help them develop new strains with desirable characteristics. This can help breeders to develop better strategies for creating disease-resistant strains.
- Investing in Collaboration: Companies and organizations can invest in new collaborations between breeders and researchers to encourage the development of disease-resistant strains. By supporting the development of collaborations, they can help to speed up the development of new strains and improve their quality.
By increasing collaboration between researchers and breeders, the cannabis industry can achieve more significant advancements in developing disease-resistant cannabis strains. Working together can help identify new strategies and technologies for creating more durable strains that can withstand various diseases and pests. The mutual sharing of resources, knowledge, and expertise can help speed up the development of new strains with improved resistance to diseases.
Adoption of Sustainable Growing Practices
One of the key ways to ensure that disease-resistant cannabis strains continue to thrive in the future is through the adoption of sustainable growing practices. This is an essential step towards creating a healthier, more environmentally friendly industry that prioritizes both quality and safety.
Here are some of the sustainable growing practices that can be adopted to ensure the continued success of disease-resistant cannabis strains:
- Organic Growing: Using organic growing methods is an effective way to ensure that plants remain healthy and free from disease. This means avoiding the use of synthetic pesticides, fertilizers, and additives, and instead relying on natural or organic products.
- Water Conservation: Conserving water is becoming increasingly important in regions where water supplies are limited. This can be achieved through methods such as drip irrigation, water catchment systems, and recycled water systems.
- Energy Efficiency: Growing cannabis indoors requires a substantial amount of energy to provide optimal growing conditions. Adopting energy-efficient lighting systems, using renewable energy sources like solar power, and minimizing overall energy usage can help reduce the environmental impact of indoor cultivation.
- Composting and Recycling: Recycling plant material and composting organic waste can help reduce waste and provide valuable nutrients for soil health.
- Integrated Pest Management: Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is an effective approach that involves using a combination of natural and synthetic pest control methods to keep plants healthy and disease-free. This approach minimizes the use of pesticides and fungicides while still ensuring optimal plant health.
- Crop Rotation: Rotating crops can help reduce the incidence of disease and pest infestations by providing a natural break in the life cycle of pathogens and pests.
- Regenerative Agriculture: Regenerative agriculture is an approach that focuses on building soil health and fostering biodiversity. By prioritizing soil health, this approach helps create more resilient plants that are better equipped to resist disease.
By adopting these sustainable growing practices, growers can help create a more environmentally friendly and sustainable cannabis industry that prioritizes both plant health and quality. This approach not only benefits the environment but can also lead to increased profitability and more robust, disease-resistant cannabis strains in the future.
How to Grow and Maintain Disease-Resistant Cannabis Strains
As we now know the importance of disease-resistant cannabis strains and the latest innovations and advancements in this area, it is crucial to understand how to grow and maintain these strains. By following certain steps and practices, you can ensure that your cannabis plants remain healthy and strong, even in the face of potential diseases. In this section, we will explore some tips and techniques for growing disease-resistant cannabis strains successfully. Let’s dive into the details and learn how to keep your plants healthy and disease-free.
Plan Ahead and Choose the Right Strain
Before you start planting cannabis, it is crucial to plan ahead and choose the right strain to ensure disease resistance and healthy growth. Proper planning and strain selection can make a significant impact on the overall success of your crop. Here are some things to consider when choosing a strain:
| Factors to Consider | Explanations |
|---|---|
| Climate | Take into account the climate of your grow area and choose a strain that is well-suited for those conditions. Some strains are better for warm and humid environments, while others can withstand colder and drier climates. |
| Growth Cycle | Consider the growth cycle of the strain you are interested in. Some strains have a short harvest cycle, while others take longer to mature. |
| Disease Resistance | Choose a strain that has a history of disease resistance, particularly to diseases that are common in your area. |
| Yield | Look for a strain that yields a high-quality and abundant crop. However, keep in mind that high yields may also mean higher susceptibility to disease. |
| Growing Method | Choose a strain that complements your preferred growing method. Some strains are better suited for indoor growing, while others are best grown outdoors. |
It is also important to do research on the genetics of the strain you are interested in. This can give valuable insight into its disease resistance, growth patterns, and other characteristics that can help you make an informed decision. By carefully selecting the right strain, you can set your cannabis crop up for success and ensure it is resistant to common diseases.
Maintain Ideal Growing Conditions
When it comes to maintaining disease-resistant cannabis strains, maintaining ideal growing conditions is crucial. This means providing the right amount of light, nutrients, and water for the plants. One effective way to ensure the ideal growing conditions is to use an indoor cultivation method, where environmental factors can be more easily controlled.
In order to maintain ideal growing conditions, it is important to monitor temperature and humidity levels regularly. These factors can greatly affect the growth and health of the plants. Temperature should be kept within a range of 65-80 °F (18-27 °C) during the day and no lower than 60 °F (15 °C) at night. Humidity levels should be kept between 40-60% during the vegetative stage, and around 40% during the flowering stage.
Additionally, providing the appropriate nutrients is necessary for maintaining ideal growing conditions. This can include a balance of macronutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium as well as micronutrients such as magnesium, calcium, and iron. It is important to follow the recommended nutrient regimen for the specific strain being grown.
Another important factor in maintaining ideal growing conditions is the pH level of the soil or growing medium. The pH level should be checked frequently using a pH meter or testing kit and adjusted if necessary. The ideal pH range for cannabis plants is between 6.0 and 7.0.
Lastly, it is important to ensure proper ventilation within the growing environment. This can help reduce the risk of mold and other fungi growth which can be detrimental to the plants’ health. This can be achieved through the use of fans and exhaust systems.
By maintaining ideal growing conditions, growers can help ensure the health and vitality of their disease-resistant cannabis strains. It is important to closely monitor and adjust environmental factors as needed throughout the growth cycle of the plants.
| Factor | Ideal Range |
|---|---|
| Temperature | 65-80 °F (18-27 °C) during the day, no lower than 60 °F (15 °C) at night |
| Humidity | 40-60% during vegetative stage, around 40% during flowering stage |
| Nutrients | Balance of macronutrients and micronutrients as recommended for specific strain |
| pH level | 6.0-7.0 |
| Ventilation | Proper airflow through use of fans and exhaust systems |
Use Appropriate Pesticides and Fungicides
When it comes to disease-resistant cannabis strains, the use of appropriate pesticides and fungicides cannot be understated. However, it’s important to note that not all pesticides and fungicides are suitable for use on cannabis plants. Using the wrong products or using them incorrectly can damage the plant and even harm the consumer. Here are some tips on how to use pesticides and fungicides appropriately:
- Research the product: Before applying any pesticide or fungicide, do your research on the specific product you plan to use. Look for reviews from other growers and check that it is approved for use on cannabis.
- Read the label: Always carefully read and follow the label instructions on the pesticide or fungicide. This will include details on the appropriate dosage, timing, and safety precautions.
- Use organic options: Consider using organic pesticides and fungicides instead of synthetic ones, as they are less harmful to the environment and the plant. Examples of organic options include neem oil, garlic oil, and potassium bicarbonate.
- Rotate products: To avoid pests and diseases building up resistance, rotate between different pesticide and fungicide products.
- Avoid spraying during flowering: Avoid spraying any pesticide or fungicide during flowering, as this can affect the taste and quality of the buds.
- Use protective gear: When applying any product, always wear protective gear such as gloves, goggles, and a mask to avoid inhaling or absorbing the chemicals.
By using appropriate pesticides and fungicides and following these tips, growers can protect their disease-resistant cannabis strains from harmful pests and diseases without compromising the quality of the plant or the safety of the consumer.
Practice Good Hygiene and Sanitation
Maintaining good hygiene and sanitation practices is crucial in cultivating disease-resistant cannabis strains. Cleanliness is key in preventing the spread of pathogens and diseases that can damage the crops. Here are some essential tips to ensure good hygiene and sanitation in your cannabis garden:
- Wash your hands: Always wash your hands before entering the garden, especially if you have been handling other plants, soil or contaminated materials.
- Clean and disinfect tools: Make sure to clean and disinfect your gardening tools before and after each use to prevent the spread of disease. Disinfectants, such as a diluted bleach solution, can be used to clean tools and surfaces in the garden.
- Wear clean clothes: Avoid bringing outside contaminants into your garden by wearing clean clothes each time you enter it.
- Use clean water: Ensure that the water you’re using to irrigate your plants is clean, and avoid using stagnant or contaminated water sources. You can install a filtration system or use distilled water to ensure that the water used for irrigation is clean and safe.
- Dispose of plant material properly: Any plant material that is damaged or dead should be removed immediately from the garden to prevent the spread of disease. Be sure to dispose of it properly to avoid contamination of other plants.
- Regularly sanitize your grow room or greenhouse: Keep your grow room or greenhouse clean and sanitized to prevent disease from spreading. Regularly sanitize all surfaces with a disinfectant solution and ensure proper air circulation to prevent the growth of mold and bacteria.
By practicing good hygiene and sanitation, you can reduce the risk of disease and pathogen contamination in your cannabis garden.
Regularly Inspect Plants for Signs of Disease
Regularly inspecting plants is a crucial aspect of successful disease management when growing cannabis. By regularly examining plants, growers can identify any signs of disease and take appropriate action to prevent further spread. Here are some steps to follow when inspecting your plants for disease:
- Check for discoloration: Look for any changes in plant color, including yellowing or browning. These can be signs of nutrient deficiencies or disease.
- Look for spots or lesions: Spots or lesions on leaves or stems can indicate a fungal or bacterial infection.
- Examine plant structure: Any abnormalities in the plant structure, such as stunted growth, can be signs of disease.
- Check for pests: Pests can lead to the spread of disease if not taken care of immediately. Look for any pests on the plants or in the surrounding soil.
- Inspect buds and flowers: Signs of mold, such as a white powdery substance or fuzzy growths, can be seen on buds and flowers.
Regular inspections should be done at least once a week, preferably twice a week during the vegetative and flowering stages. If any signs of disease are detected, it is important to take action immediately to prevent the spread of the disease. This may include removing infected plants, treating with appropriate pesticides or fungicides, or adjusting growing conditions to prevent further spread. By regularly inspecting plants, growers can ensure the health and success of their cannabis crop.
Proper Harvesting Techniques
Harvesting cannabis plants is a crucial aspect of the cultivation process that greatly impacts the final product’s quality and potency. Using proper harvesting techniques ensures maximum yields and optimal flavor and aroma. Here are some essential tips for harvesting disease-resistant cannabis strains:
| Technique | Description |
|---|---|
| Timing | Harvesting at the right time is crucial to achieving the best results. This varies depending on the strain and growing conditions. Observe the trichomes and pistils to determine when to harvest. |
| Trimming | Trimming the branches of the plant is necessary to remove large leaves and other debris. This process can be done before or after drying, depending on personal preference. |
| Curing | Curing is an important stage of the harvesting process that can improve the flavor and aroma of the final product. Hang the branches upside down in a cool, dry, and dark place for one to two weeks, and rotate the branches daily. |
| Storage | Proper storage of harvested cannabis is crucial for maintaining its quality and potency. Store it in an airtight container in a cool, dry, and dark place. |
Using these proper harvesting techniques can be the difference between producing a mediocre or high-quality product. Remember to be patient and attentive to your plants during the harvesting process, paying close attention to each stage to ensure optimal results.
Investing in Quality Genetics
When it comes to growing disease-resistant cannabis strains, one of the most crucial factors is investing in quality genetics. This refers to choosing and using high-quality seeds or clones from reputable sources that have a strong genetic resistance to various diseases and pests.
Why invest in quality genetics?
Investing in quality genetics can save growers a lot of time, money and hassle. When cannabis plants are grown from low-quality genetics that do not have the necessary resistance, they are more susceptible to diseases and pests, which can lead to lower yields and even loss of entire crops. On the other hand, starting with high-quality genetics can greatly reduce the risk of disease and pests, resulting in healthier and more productive plants.
What to look for in quality genetics?
When choosing quality genetics for disease-resistant cannabis strains, there are several factors to consider. These include:
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Genetic Diversity | A wide range of genetics can help increase disease resistance. |
| Lineage | Some strains have a genetic history of resistance to certain diseases. |
| Testing and Certification | Choose genetics that have been tested and certified to have high resistance to diseases and pests. |
| Reputable Sources | Choose seeds or clones from reputable breeders and suppliers who have a track record of producing quality genetics. |
How to invest in quality genetics?
Investing in quality genetics can be as simple as doing research on the various available options and selecting a reputable breeder or supplier. It is also recommended to ask other growers or experts for recommendations and to attend industry events where breeders and suppliers showcase their products.
Some breeders offer genetic testing services to help growers identify which strains are most resistant to certain diseases and pests. This can be a valuable tool in choosing the right genetics for disease-resistant cannabis strains.
Investing in quality genetics is a critical step in growing disease-resistant cannabis strains. It can save growers time, money, and resources, and ultimately result in healthier and more productive plants.
Conclusion
As we come to the end of our discussion on the future of disease-resistant cannabis strains, it’s clear that there is much to look forward to in the world of cannabis cultivation. The advancements in genetics, biotechnology, and sustainable practices promise to revolutionize the industry in the coming years. However, it’s important to note that responsible and sustainable growing practices must be prioritized for the long-term health of both the plant and the planet. Only by investing in quality genetics and maintaining ideal growing conditions can we truly harness the potential of disease-resistant cannabis strains. Let’s explore the key takeaways from this article in more detail.
Summary of the Current State of Disease-Resistant Cannabis Strains
When it comes to the current state of disease-resistant cannabis strains, it can be summarized as follows:
| Advancements | Limitations |
|---|---|
| Genetic engineering and biotechnology have led to the creation of new disease-resistant strains that were not previously available. | However, there is still some concern among consumers about genetically modified organisms (GMOs) and their safety. |
| Natural pesticides and fungicides have been identified and are being used more frequently by cultivators. | However, these natural solutions may not work as effectively as synthetic chemicals, and they may be more expensive. |
| Crossbreeding and hybridization have led to the development of disease-resistant strains that can thrive in different environments. | However, there is still a lack of standardization in the industry when it comes to defining what makes a strain “disease-resistant.” |
| Certain cannabis strains naturally have resistance to some diseases, making it easier for breeders to select and crossbreed new varieties with these traits. | However, these resistant strains may not be resistant to all diseases, and there is still a need for further research to identify and breed for resistance to other types of diseases. |
| Integrated pest management (IPM) approaches take a comprehensive and preventative approach to disease management in cannabis crops. | However, implementing effective IPM practices can be complex and time-consuming for cultivators, and may require significant investment in technology and training. |
| Indoor cultivation methods can help reduce the risk of disease transmission and infections from pests, as the growing environment is more easily controlled. | However, indoor growing requires significant investment in equipment and energy to maintain ideal growing conditions, which can drive up costs for cultivators. |
It is clear that while there are promising advancements and innovations in disease-resistant cannabis strains, there are also several limitations and challenges that need to be addressed. It is important for the industry to continue to invest in research and development of new varieties and growing practices to ensure a sustainable and resilient cannabis industry.
The Importance of Sustainable and Responsible Growing Practices
Growing disease-resistant cannabis strains is a critical step towards a sustainable and thriving cannabis industry. However, it’s also important to note that sustainable and responsible growing practices play an equally important role in maintaining the health and longevity of plants.
Here are some reasons why sustainable and responsible growing practices are so essential:
- Protecting the environment: When cannabis is grown using unsustainable and harmful techniques, it can have a significant impact on the surrounding ecosystem. For example, the use of chemical fertilizers and pesticides can pollute soil and water sources, while excessive water usage can lead to drought and other environmental impacts. By adopting sustainable growing practices, such as using organic methods and efficient watering systems, growers can help minimize harm to the environment.
- Ensuring quality crop: Responsible growing practices go hand in hand with producing high-quality cannabis crops. By using organic methods and avoiding harmful chemicals, growers can ensure their plants are healthy, robust, and free of chemical residues that could compromise their quality.
- Maintaining long-term profitability: Sustainable growing practices are not only good for the environment and crop quality, but they can also help ensure long-term profitability for growers. By adopting efficient and sustainable growing methods, growers can reduce their overhead costs, minimize waste and lost crops, and ultimately increase their profits.
- Meeting consumer demand: Finally, sustainable and responsible growing practices are becoming increasingly important to consumers who are looking for environmentally friendly and ethically produced cannabis products. By meeting this demand, growers can not only strengthen their customer base but also help pioneer a shift toward more sustainable and responsible practices in the industry as a whole.
In sum, sustainable and responsible growing practices are a critical part of ensuring the long-term health and success of disease-resistant cannabis strains, producers and the industry as a whole. By adopting these practices, growers can help protect the environment, produce high-quality crops, increase profitability, and meet the demands of the modern consumer. Ultimately, this benefits both the growers and the wider cannabis community.
The Future Possibilities of Disease-Resistant Cannabis Strains
The future possibilities of disease-resistant cannabis strains are promising, with ongoing research and development in the field of genetics and biotechnology, as well as a growing understanding of sustainable growing practices.
Further Advancements in Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology: With advancements in genetic engineering and biotechnology, researchers may be able to identify and manipulate specific genes responsible for disease resistance, creating even more resilient strains of cannabis.
New Comprehensive Testing Methods for Disease Resistance: As testing methods become more comprehensive and accurate, breeders will have a better understanding of a strain’s disease resistance, allowing for more targeted breeding and selection processes.
Increased Use of Natural Pesticides and Fungicides: As concerns over harmful chemicals in traditional pesticides and fungicides grow, there is a shift towards the increased use of natural alternatives. As research into these alternatives continues, we may see even more effective and environmentally friendly options become available.
The Development of Super Strains of Disease-Resistant Cannabis: Through crossbreeding and hybridization, breeders may be able to create “super strains” of cannabis that have natural resistance to a wide variety of diseases while still maintaining desirable qualities such as high potency and flavor.
Increased Collaboration Between Researchers and Breeders: As the demand for disease-resistant cannabis strains increases, there will likely be more collaboration between researchers and breeders to develop new varieties and solutions to combat diseases.
Adoption of Sustainable Growing Practices: As the cannabis industry becomes more mainstream, there is a growing emphasis on sustainable and responsible growing practices. From using renewable energy sources to reducing water consumption, there is a push towards sustainable practices that not only benefit the environment but also encourage disease resistance in plants.
Final Thoughts
The future of disease-resistant cannabis strains is looking bright, as innovative methods and technologies continue to be developed to combat the various diseases and pests that can threaten cannabis crops. However, it is important to also emphasize the need for sustainable and responsible growing practices, as well as collaboration between researchers and breeders.
Summary of the Current State of Disease-Resistant Cannabis Strains:
Currently, disease-resistant cannabis strains are being developed through various methods, including genetic engineering, crossbreeding, and the use of natural pesticides and fungicides. Indoor cultivation, integrated pest management, and varieties with natural resistance are also being explored. While there is still room for improvement, these advancements are providing promising solutions for the cannabis industry.
The Importance of Sustainable and Responsible Growing Practices:
As the cannabis industry continues to grow, it is important to prioritize sustainable and responsible growing practices. This includes minimizing the use of harmful chemicals, properly disposing of waste, and implementing energy-efficient cultivation methods. Adopting these practices not only benefits the environment, but also helps to ensure the long-term viability of the cannabis industry.
The Future Possibilities of Disease-Resistant Cannabis Strains:
Looking ahead, there are many exciting possibilities for the future of disease-resistant cannabis strains. These include the development of super strains with enhanced resistance, the increased use of natural pesticides and fungicides, and innovations in genetic engineering and biotechnology. With continued research and collaboration, the cannabis industry is poised to develop even more efficient and sustainable methods for cultivating disease-resistant strains.
| Advantages | Disadvantages | |
|---|---|---|
| Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology | – Can produce strains with enhanced resistance and desirable traits – Can target specific pests and diseases – Can potentially reduce the need for harmful chemicals |
– Can be controversial from an ethical standpoint – May not be cost-effective for smaller operations |
| Natural Pesticides and Fungicides | – Can be environmentally friendly – May have fewer health risks for humans and animals – Can be cost-effective for smaller operations |
– May not be as effective as synthetic chemicals – Can be labor-intensive to apply |
| Crossbreeding and Hybridization | – Can create genetic diversity and unique traits – Can be used to strengthen resistance in existing strains – Can potentially reduce the need for harmful chemicals |
– Can take time and resources to develop and test new strains – May not always result in desired traits or resistance |
| Cannabis Varieties with Natural Resistance | – Can be environmentally friendly – Can potentially reduce the need for harmful chemicals – May be more cost-effective for smaller operations |
– Limited availability of these varieties – May not have as strong of resistance as desired |
| Integrated Pest Management | – Can be a comprehensive approach to pest and disease management – Can reduce the need for harmful chemicals – Can involve multiple methods for increased effectiveness |
– Can require more planning and resources – May not be suitable for larger operations |
| Indoor Cannabis Cultivation | – Can provide a controlled environment with fewer risks for pests and diseases – Can be more sustainable and resource-efficient – Can potentially reduce the need for harmful chemicals |
– Can be more costly to set up and maintain – May not allow for as much genetic diversity |
The development of disease-resistant cannabis strains is crucial for the sustainability and growth of the cannabis industry. By utilizing a combination of innovative methods and sustainable practices, we can create a healthier and more resilient crop for the future. It is important for industry professionals to continue to collaborate and invest in these advancements to ensure a bright future for the cannabis industry.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are some common diseases that affect cannabis plants?
Common cannabis diseases include powdery mildew, gray mold, root rot, and bud rot.
What are the consequences of not using disease-resistant cannabis strains?
The consequences of not using disease-resistant cannabis strains include reduced crop yield, lower quality cannabis, and higher costs associated with pest and disease control.
Can natural pesticides and fungicides be used on cannabis plants?
Yes, natural pesticides and fungicides can be used on cannabis plants. Examples include neem oil, sulfur, and vinegar solutions.
What is integrated pest management?
Integrated pest management is a holistic approach to pest and disease control that combines multiple strategies, such as biological control, cultural practices, and chemical control.
How can genetics be used to create disease-resistant cannabis strains?
Genetic engineering and crossbreeding can be used to create cannabis strains with increased resistance to certain diseases.
What are some sustainable growing practices for disease-resistant cannabis?
Sustainable growing practices for disease-resistant cannabis include using organic fertilizers, composting, using natural pest control methods, and conserving water.
What should growers look for when choosing disease-resistant cannabis strains?
When choosing disease-resistant cannabis strains, growers should look for strains that are resistant to specific diseases, have high genetic stability, and have a track record of successful cultivation.
What is the significance of indoor cannabis cultivation in disease resistance?
Indoor cannabis cultivation allows for more control over environmental factors, which can help prevent disease outbreaks and improve overall plant health.
How can cannabis growers practice good hygiene and sanitation?
Cannabis growers can practice good hygiene and sanitation by regularly disinfecting growing equipment, using clean water and soil, and disposing of infected plant material properly.
Are disease-resistant cannabis strains more expensive than regular strains?
Not necessarily. The cost of disease-resistant cannabis strains can vary depending on the strain and availability, but they may ultimately save growers money by avoiding the costs associated with pest and disease control.