Chemical Pesticides to Avoid When Cultivating Cannabis
As more and more states legalize the cultivation of cannabis, it is important for growers to be aware of the potential dangers of using chemical pesticides on their crops. While pesticides may seem like a quick and easy solution to pest problems, prolonged exposure to these chemicals can have negative effects on both human health and the environment. In this article, we will explore the common chemical pesticides to avoid when growing cannabis, as well as alternative methods for pest control that are safer and more sustainable.
Why Avoid Chemical Pesticides?
Contents
As cannabis cultivation continues to grow, so does the concern regarding the use of chemical pesticides in the process. While the use of these pesticides can seem like an easy solution to controlling pests and increasing yields, it comes with several drawbacks that can pose a risk to both the consumer and the environment. It is important to understand the reasons for avoiding chemical pesticides in cannabis cultivation.
Prolonged Chemical Exposure
Prolonged chemical exposure can have adverse effects on human health, especially if the exposure is frequent and prolonged. It can lead to various health issues such as respiratory problems, neurological complications, and cancer. The prolonged exposure to chemicals can happen to cultivators when handling pesticides without the required protective gear. Chemicals can accumulate in human organs and tissues, leading to potentially harmful levels of exposure.
Additionally, chemicals can be transferred from cannabis leaves and buds to those who consume the final product. This can be a significant health concern, especially for regular cannabis users. Even trace amounts of chemical residues can accumulate in the body and lead to harmful outcomes in the long run.
To minimize the risk of exposure, it is recommended to avoid the use of chemical pesticides whenever possible. Alternative methods discussed in this article can be utilized to safely and sustainably control pests without putting human health at risk.
Potency Diminishing
The use of chemical pesticides in cannabis cultivation can have a detrimental effect on the potency of the final product. Research has shown that exposure to certain pesticides can decrease the concentration of cannabinoids, including THC and CBD. Diminished potency as a result of pesticide use can have a variety of negative effects on the end product, including reduced medicinal effectiveness and decreased recreational value.
Examples of the potency diminishing effects of commonly used chemical pesticides:
| Chemical Pesticide | Potency Diminishing Effect |
|---|---|
| Neonicotinoids | Decreased levels of THC and CBD |
| Organophosphates | Reduction in overall cannabinoid content |
| Pyrethroids | Decreased levels of THC and other cannabinoids |
| Carbamates | Reduced potency of cannabinoids and terpenes |
In addition to diminished potency, the use of chemical pesticides can also result in the presence of harmful chemical residues, which can pose serious health risks to consumers. It’s essential for growers to avoid chemical pesticides and instead use alternative methods of pest control that are safer and more sustainable.
Environmental Impact
The use of chemical pesticides can have a detrimental impact not only on our health but also on the environment. These pesticides can easily leak into nearby bodies of water, contaminate the soil, and even drift into the air, ultimately affecting both wildlife and humans. Some of the ways in which pesticides can harm the environment are:
- Interrupting the natural ecosystem: Pesticides can kill not only the targeted pests, but also non-targeted organisms such as beneficial insects and microorganisms that play a critical role in maintaining the ecological balance of nature.
- Water pollution: When pesticides are sprayed on plants, they can easily be washed into nearby lakes, rivers or underground water sources through runoff, ultimately contaminating these sources and creating a hazardous environment for aquatic life.
- Soil degradation: Chemical pesticides can accumulate in the soil over time, altering the pH, degrading soil nutrients, and ultimately making it unsuitable for growing crops.
- Resistance: Pesticides can cause pests to develop a resistance, reducing their effectiveness and prompting farmers to apply even stronger pesticides, creating a vicious cycle of even stronger pesticides used to combat resistant pests.
- Contamination of nearby crops: Pesticides often drift through the air to neighboring farms, contaminating not only other crops but also the soil and water sources.
Relying on chemical pesticides in the long run proves to be harmful for both the environment we live in and our health. It is important for farmers to adopt alternative pest control methods that are both more effective and safer for the environment.
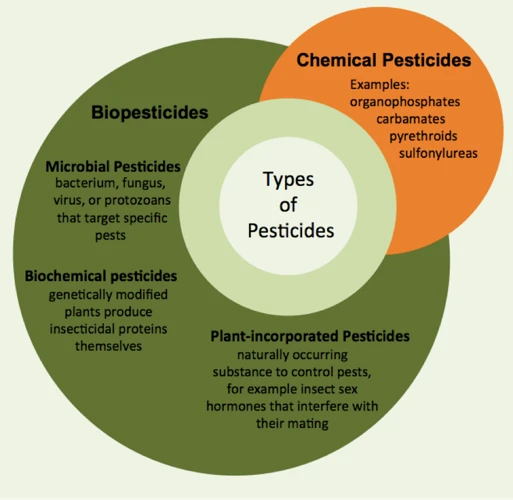
Common Chemical Pesticides to Avoid
As a cannabis grower, it is essential to keep in mind the harmful chemicals that are often present in pesticides. Many chemical pesticides are widely used, but they can have adverse effects on both the environment and the plants they are meant to protect. These harsh chemicals can quickly accumulate in the soil and plants, leading to serious health concerns. It’s crucial to recognize and avoid these pesticides, and instead, opt for safer alternatives. Let’s take a closer look at some common chemical pesticides to avoid when growing cannabis.
Neonicotinoids
One of the most widely-used pesticides, neonicotinoids, are a class of neuro-active synthetic insecticides chemically similar to nicotine. They attack the nervous system of pests and interfere with their ability to feed and reproduce. However, neonicotinoids have been linked to negative effects on honey bees and other pollinators, as well as aquatic invertebrates and birds, making them a threat to the wider ecosystem.
The most commonly used neonicotinoids are clothianidin, imidacloprid, thiamethoxam, dinotefuran, and acetamiprid. Many large-scale growers use these pesticides to protect their crops from pests like aphids, whiteflies, and spider mites. However, research has shown that these chemicals can persist in the environment for a long time, contaminating soil, water, and air.
Some of the impacts of neonicotinoid use include:
| Impact | Description |
|---|---|
| Loss of pollinators | Neonicotinoids have been shown to reduce bee and butterfly populations, which are essential for pollinating crops. |
| Toxicity to birds and aquatic invertebrates | Exposure to neonicotinoids has been linked to deaths and disabilities in birds and aquatic invertebrates, disrupting the food chain and ecosystem. |
| Resistance in pests | Some pests have developed resistance to neonicotinoids, making them less effective over time and requiring higher doses or different chemicals. |
Given these negative impacts, it is important for cannabis growers to avoid using neonicotinoids and find alternative methods for controlling pests.
Organophosphates
Organophosphates are another group of chemical pesticides commonly used in agriculture. These pesticides are highly toxic and can have harmful effects on both human and environmental health. It’s important to avoid using any products that contain organophosphates when growing cannabis.
Health Effects of Organophosphates
Organophosphates can have severe effects on human health. They are known to affect the nervous system and can cause symptoms such as headaches, fatigue, dizziness, and confusion. Long-term exposure to these pesticides has been linked to neurological disorders, such as Parkinson’s disease.
These pesticides can also be harmful to the environment. They can contaminate soil and water, and can be toxic to non-target organisms such as bees, birds, and fish. It’s essential to avoid using organophosphates when growing cannabis to ensure the safety of both the user and the environment.
Here is a table of some common products that contain organophosphates:
| Product | Active Ingredient |
|---|---|
| Malathion | Malathion |
| Diazinon | Diazinon |
| Chlorpyrifos | Chlorpyrifos |
| Disulfoton | Disulfoton |
It’s crucial to read labels carefully and avoid any products that contain organophosphates. Instead, consider using alternative methods to control pests, such as biological control, companion planting, or physical barriers. These methods are less harmful to the environment and can be just as effective at controlling pests.
Pyrethroids
Pyrethroids are synthetic insecticides that mimic the natural insecticide pyrethrin, which is derived from chrysanthemum flowers. Pyrethroids are commonly used in household insecticides and are also sprayed on crops. They are categorized as neurotoxins that target the nervous system of insects, leading to paralysis or death. However, they can also harm non-target organisms, such as fish, bees, and birds.
Pyrethroid insecticides and their potential hazards:
| Pyrethroid Insecticide | Potential Hazards |
|---|---|
| Bifenthrin |
|
| Permethrin |
|
| Cyfluthrin |
|
| lambda-Cyhalothrin |
|
In addition to their harmful effects on the environment and non-target organisms, pyrethroids can also have negative impacts on the quality of cannabis. These pesticides can accumulate in the trichomes of the plant, which contain the cannabinoids and terpenes that give cannabis its medicinal and psychoactive properties. Exposure to pyrethroids can diminish the potency and quality of the final product.
To avoid the negative impacts of pyrethroids, it is important to choose alternative methods of pest control when growing cannabis. Some effective alternatives include biological control methods, companion planting, physical barriers, and organic sprays. By avoiding the use of harmful pesticides like pyrethroids, growers can ensure that their cannabis is safe for consumption and environmentally responsible.
Carbamates
Carbamates are a class of chemical pesticides that are widely used in agriculture and horticulture to control pests. They work by inhibiting the activity of an enzyme called acetylcholinesterase. This results in the accumulation of a neurotransmitter called acetylcholine, which leads to overstimulation of the nervous system and eventual death of the pest. However, carbamates can also be harmful to humans and animals, as they have been linked to a range of health problems.
Common Carbamates used in Cannabis Cultivation
Below is a table showing examples of carbamates that are commonly used as pesticides in cannabis cultivation:
| Carbamate | Trade Name | Mode of Action | Health Effects |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbaryl | Sevin | Inhibits acetylcholinesterase | Linked to cancer, reproductive and developmental problems, and neurotoxicity |
| Propoxur | Baygon | Inhibits acetylcholinesterase | Linked to cancer, developmental and reproductive problems, and neurotoxicity |
| Aldicarb | Temik | Inhibits acetylcholinesterase | Highly toxic, linked to cancer, developmental and reproductive problems, and neurotoxicity |
Health Effects of Carbamates
Carbamates can have a range of health effects on humans, depending on the level and duration of exposure. Acute exposure to carbamates can cause symptoms such as headache, nausea, vomiting, dizziness, and seizures. Chronic exposure can lead to more serious health problems, such as cancer, reproductive and developmental problems, and neurotoxicity. It is important to avoid using carbamates in cannabis cultivation and opt for alternative methods of pest control that are safer for both the crop and the environment.
Alternatives to Carbamates
There are several alternative methods of pest control that can be used in cannabis cultivation, including biological control methods, companion planting, physical barriers, and organic sprays. These methods are safer and more sustainable than chemical pesticides, and can help to maintain the health of the crop and the environment. By avoiding the use of carbamates and other chemical pesticides, cannabis growers can ensure that their product is safe and of high quality for both medical and recreational purposes.
Alternative Ways to Control Pests
As we have seen, chemical pesticides are not the best choice when it comes to growing cannabis. However, pests can pose a serious threat to the health and yield of your plants. So, what are some alternative methods you can use to control pests without harming your plants or the environment? Let’s explore some of the eco-friendlier options available to you.
Biological control methods
When it comes to pest control in cannabis cultivation, biological control methods offer a natural and sustainable solution. Unlike chemical pesticides, biological control methods do not leave harmful residues on the plant or in the environment. Instead, they rely on natural predators to keep pest populations under control.
Here are some examples of biological control methods and the pests they target:
| Biological Control Method | Pests Targeted |
|---|---|
| Ladybugs | Aphids, spider mites, whiteflies |
| Praying mantis | Aphids, flies, grasshoppers, spider mites |
| Nematodes | Fungus gnats, root aphids, thrips |
| Predatory mites | Spider mites, thrips |
These predators can be purchased from specialized suppliers and released into the growing environment. However, it is important to note that biological control methods require a certain level of knowledge and experience to implement effectively.
In addition to predators, companion planting can also be used as a biological control method. Certain plants can repel pests, while others can attract beneficial insects. For example, planting herbs like basil or lavender can help repel aphids, while flowers like marigolds can attract ladybugs.
Biological control methods offer a natural and sustainable solution to pest control in cannabis cultivation. By relying on natural predators and companion planting, growers can avoid the harmful effects of chemical pesticides and promote a healthier growing environment.
Companion planting
Companion planting is the practice of growing different plants close to each other, which can help control pests naturally. This is because certain plants contain compounds that repel or deter insects, or attract beneficial insects that prey on pests.
Plant | Benefit
———— | ————-
Marigolds | Repel nematodes
Basil | Repel flies, mosquitoes, and thrips
Lavender | Repel moths and fleas
Mint | Repel ants and aphids
Chamomile | Attract beneficial insects, such as wasps and hoverflies, which prey on pests
Clover | Fix nitrogen in soil, which can benefit other plants
Dill | Attract beneficial insects, such as wasps and ladybugs, which prey on pests
Sage | Repel cabbage moths and carrot flies
In addition to repelling or attracting insects, companion planting can also improve soil health and boost crop yields. For example, planting clover between cannabis plants can help fix nitrogen in the soil, which can benefit the growth of the cannabis plants.
It’s important to note that companion planting is not a guarantee to control pests completely. It is always recommended to combine this approach with other methods of pest control, such as physical barriers or organic sprays, for best results.
Physical barriers
Physical barriers can be an effective way to keep pests away from cannabis plants without using chemical pesticides. By creating a physical obstacle between the plants and the pests, growers can prevent the insects from causing damage. Here are some common physical barriers and how they can be used:
| Barrier | Description | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Row covers | Lights weight fabric covers that allow light and water to pass through while keeping pests out | Easy to install and remove, reusable, effective against many types of insects and birds | May reduce pollination if not lifted occasionally, may need to be removed during hot weather, may trap beneficial insects |
| Netting | Heavy-duty mesh that provides a protective barrier against birds, larger insects, and animals | Durable, long-lasting, can be used year after year, does not trap heat | May not stop smaller insects, may require additional support to prevent sagging or tearing |
| Collars | Plastic or paper barriers that wrap around the base of the plant to prevent pests from crawling up the stem | Easy to install, inexpensive, reusable, effective against crawling insects such as cutworms and slugs | May need to be replaced if damaged or if new growth requires a larger diameter collar |
| Sticky traps | Yellow or blue adhesive traps that attract and catch flying insects | Easy to use, non-toxic, can help monitor pest populations | May not be effective against all types of insects, may attract beneficial insects or other small animals |
Physical barriers can be combined with other pest control methods, such as biological controls or organic sprays, for added effectiveness. It is important to periodically check physical barriers to ensure they are still functioning properly and to remove any debris that may accumulate. Physical barriers offer a safe and environmentally friendly way to protect cannabis plants from pests without using harmful chemicals.
Organic sprays
Organic sprays are a safe, natural alternative to chemical pesticides. These sprays are made with natural ingredients that are derived from plants, minerals, or beneficial bacteria.
Here are some common organic sprays that cannabis growers can use:
| Neem oil | Derived from the neem tree, neem oil is a natural insecticide and fungicide. It works by disrupting the insect’s hormonal balance and preventing them from eating or breeding. |
| Garlic spray | Made with garlic, water, and a mild soap, garlic spray is an effective pesticide that repels insects and kills their eggs. Garlic contains sulfur, which is toxic to many pests, including spider mites and aphids. |
| Chile pepper spray | Chile pepper spray is a natural insecticide that works by irritating the pests’ mouthparts and digestive systems, causing them to flee or starve. It is made by steeping dried chile peppers in water and adding a small amount of dish soap. |
| Diatomaceous earth | A fine powder made from the fossilized remains of diatoms, diatomaceous earth is an effective natural pest control that kills insects by dehydrating them. It is safe for humans and pets and can be applied directly to the plants or soil. |
Organic sprays are easy to make and use, and they are safe for both the grower and the environment. However, it is important to note that organic sprays may not be as effective as chemical pesticides and may need to be applied more frequently. Additionally, they may leave a residue on the plants that can affect the taste and smell of the final product, so it is important to use them sparingly and follow the recommended application guidelines.
How to Identify Pesticide Residues in Cannabis
As a cannabis grower, it is important to ensure that your plants are free from harmful pesticide residues. However, even when all precautions are taken, pesticide contamination is still possible. This is why it is critical to learn how to identify pesticide residues in cannabis. By doing so, you can take action to prevent contamination and ensure that you’re consuming a safe product. In this section of the article, we will discuss the basic extraction procedure and sample analysis using GC-MS. So, buckle up and prepare to learn the necessary steps to identify pesticide residues!
Basic Extraction Procedure
To identify pesticide residues in cannabis, a basic extraction procedure can be followed. This involves using solvents to extract the pesticides from the plant material. Here are the steps involved in the basic extraction procedure:
- Sample Preparation: First, the cannabis sample is ground into a powder to increase the surface area for extraction.
- Extraction: The powdered sample is then mixed with a solvent such as acetone, hexane or ethyl acetate. The mixture is then shaken vigorously to extract the pesticides from the plant material.
- Evaporation: Once the extraction is complete, the solvent is evaporated using a rotary evaporator or a stream of nitrogen gas. This leaves behind a concentrated residue that contains the pesticides.
- Reconstitution: The residue is then reconstituted in a solvent such as methanol or acetonitrile. This makes it easier to analyze the sample using chromatography techniques such as gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS).
It is important to note that this procedure requires careful handling and safety measures as solvents can be flammable and toxic. It is also important to follow proper safety protocols and to wear protective gear such as gloves, safety goggles and a lab coat.
The basic extraction procedure is an important step in identifying pesticide residues in cannabis. By following this procedure, it is possible to detect the presence of harmful chemicals and to ensure that the cannabis is safe for consumption.
Sample Analysis using GC-MS
After extracting the pesticide residues from the cannabis plant, the next step is to analyze the samples using GC-MS (Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry). This process separates the different components of the sample and identifies any chemicals present. Here is a step-by-step guide to sample analysis using GC-MS:
- Sample preparation: After extraction, the sample is prepared for GC-MS analysis by converting it into a gas-phase molecule using a technique called derivatization. This allows the sample to be introduced into the GC-MS instrument.
- Separation: The GC part of GC-MS refers to Gas Chromatography, which separates the different components of the sample based on their physical and chemical properties. The sample is injected into the instrument and vaporized, and then it passes through a column filled with a stationary phase. Different components of the sample interact with the stationary phase to different degrees, causing them to be separated as they move through the column.
- Identification: The MS part of GC-MS refers to Mass Spectrometry, which identifies the individual components of the separated sample. As each component exits the column, it passes through an ionization source that ionizes the molecules. These ions are then separated by their mass-to-charge ratio in the mass analyzer, and a spectrum of the ions is produced. This spectrum can be used to identify the individual components of the sample.
- Quantification: Once the individual components of the sample have been identified, they can be quantified to determine the amount of each present. This allows for the detection of even trace amounts of pesticides in the cannabis plant.
It is important to note that GC-MS analysis requires specialized equipment and expertise, and should only be conducted by trained professionals in a certified laboratory.
Conclusion
In conclusion, it is crucial for cannabis growers to pay attention to the pesticides they use to avoid any negative consequences. The use of chemical pesticides can have harmful effects on individuals, including prolonged exposure to dangerous chemicals, potency loss in cannabis, and potential environmental damage. Therefore, it’s important to steer clear of using common chemical pesticides like neonicotinoids, organophosphates, pyrethroids, and carbamates.
Instead, growers can opt for alternative methods of pest control, such as biological control methods, companion planting, physical barriers, and organic sprays that are less harmful to the environment and human health.
It’s important to know that the presence of harmful pesticide residues in cannabis can be detected through basic extraction procedures, and sample analysis using GC-MS. These methods can ensure the safety and purity of the cannabis products and provide assurance to consumers that the product they are buying has not been treated with harmful pesticides.
Ultimately, by avoiding chemical pesticides and opting for alternative, organic pest control methods, cannabis growers can take steps towards promoting sustainable and environmentally-friendly cultivation practices, while also ensuring the health and safety of their consumers.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Is it safe to consume cannabis that has been treated with chemical pesticides?
No, it is not safe to consume cannabis that has been treated with chemical pesticides as it can lead to adverse health effects.
2. Is there a way to completely remove pesticide residues from cannabis?
While it is difficult to completely remove pesticide residues from cannabis, there are steps that can be taken to reduce their presence, such as using organic growing methods and proper extraction techniques.
3. Are all chemical pesticides harmful to cannabis plants?
No, not all chemical pesticides are harmful to cannabis plants. However, it is important to choose the right pesticide that is approved for use on cannabis, and to follow the instructions carefully.
4. What are neonicotinoids?
Neonicotinoids are a class of insecticides that are commonly used in agriculture to control pests. However, they have been linked to negative effects on bees and other beneficial insects, and should be avoided when growing cannabis.
5. What are organophosphates?
Organophosphates are a class of insecticides that work by disrupting the nervous system of insects. They are highly toxic and should be avoided when growing cannabis, as they can have negative effects on human health and the environment.
6. What are pyrethroids?
Pyrethroids are a class of insecticides that are commonly used in household pesticides. While they are relatively safe for humans, they can have negative effects on beneficial insects and should be avoided when growing cannabis.
7. What are carbamates?
Carbamates are a class of insecticides that are commonly used in agriculture. They work by interfering with the nervous system of insects and can have negative effects on human health and the environment, making them unsuitable for use in cannabis cultivation.
8. What are some alternative ways to control pests when growing cannabis?
Alternative methods to control pests when growing cannabis include biological control methods such as introducing beneficial insects, companion planting, physical barriers, and using organic sprays.
9. How can I tell if my cannabis has been treated with chemical pesticides?
The best way to tell if cannabis has been treated with chemical pesticides is to have it tested in a lab using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) analysis.
10. Why is it important to avoid chemical pesticides when growing cannabis?
It is important to avoid chemical pesticides when growing cannabis as they can have negative effects on human health, the environment, and the potency of the cannabis. Additionally, the use of chemical pesticides is not legal on cannabis crops in all states and countries.