Adjusting Light Schedules for Different Cannabis Strains – A Comprehensive Guide
As cannabis cultivation gains popularity, growers face the challenge of adjusting their light schedules during flowering. While it may seem overwhelming at first, understanding the importance of light cycles and how to adjust them based on different strain genetics, grow space, and climate can lead to successful harvests with potent yields. This article aims to guide growers through the process of adjusting light schedules during flowering for various cannabis strains, as well as monitoring plant growth and harvesting techniques. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced grower, this comprehensive guide will help you optimize your cannabis cultivation.
Understanding the Importance of Light Schedules During Flowering
Contents
As a cannabis grower, you are likely aware that light plays a crucial role in the production of dense, potent buds during the flowering stage. However, the importance of properly adjusting your light schedule may not be immediately apparent. Without the right balance of light and darkness, your plants may experience negative effects such as stunted growth and reduced potency. To understand why light cycles are so essential to the flowering process, let’s explore the following topics: What is flowering? Why are light cycles important during flowering? And What happens if you don’t adjust light cycles during flowering?
What is Flowering?
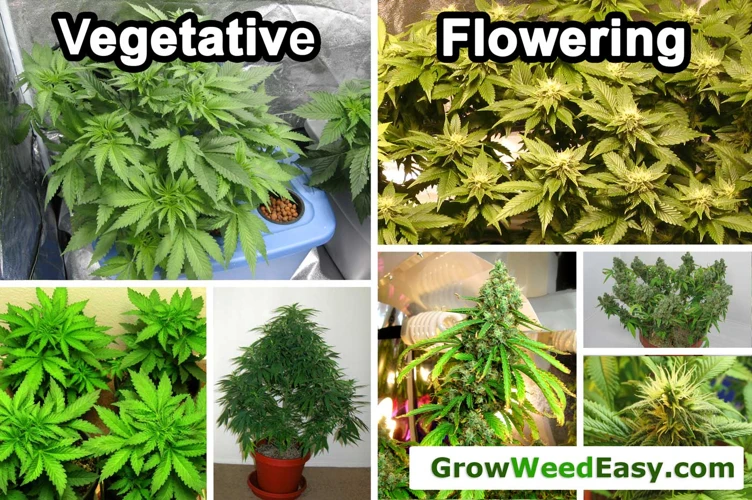
Flowering refers to the reproductive stage of a cannabis plant’s life cycle. During this stage, the plant begins to produce flowers or buds, which are the part of the plant that is harvested for consumption.
Flowering is triggered by changes in the amount of light the plant receives. Specifically, as the amount of daylight hours decreases and the amount of darkness hours increases, the plant naturally begins to shift from a vegetative state into a flowering state.
This transition from vegetative growth to flowering growth is an important process for cannabis growers, as it ultimately determines the quality and yield of their harvest. It is crucial to understand how light cycles affect flowering in each individual strain in order to maximize the potential for a successful harvest.
The duration of the flowering stage varies depending on the strain of cannabis being grown, as well as other factors such as the growing environment and the specific light schedule being used. Typically, flowering can last anywhere from 6-12 weeks, with some strains taking longer or shorter than others.
Understanding the fundamentals of flowering is key to successfully growing high quality cannabis. By adjusting light schedules and monitoring the plants carefully throughout the flowering stage, growers can ensure a bountiful harvest of healthy, potent cannabis buds.
| Key Points |
|---|
| Flowering is the reproductive stage of a cannabis plant’s life cycle where it produces buds. |
| Changes in the amount of light a plant receives trigger the flowering stage. |
| The duration of flowering varies based on strain, growing environment, and light schedule. |
| Successfully adjusting light schedules during flowering is crucial for maximizing quality and yield. |
Why Are Light Cycles Important During Flowering?
During flowering, light cycles play a crucial role in determining the yield, potency, and overall quality of your cannabis crop. Here are some of the reasons why maintaining the appropriate light cycle is vital during flowering:
| Potency | Light cycles can significantly affect the amount of THC and other cannabinoids produced by the plant. Switching to a 12/12 light cycle during flowering triggers the production of more psychoactive compounds, resulting in a more potent crop. |
| Yield | The amount of light your cannabis plants receive during flowering can significantly impact your yield. By adjusting your light schedule, you can control the size and number of buds your plants produce. |
| Timing | Adjusting your light cycle during flowering can help control the timing of your harvest. By manipulating the light schedule, you can shorten or lengthen the flowering period, allowing you to harvest your plants at the optimal time. |
| Stress | Stress caused by light cycles (or lack thereof) during flowering can negatively impact your plants’ overall health and productivity. A sudden change in light schedule can cause shock, leading to stunted growth or even plant death. |
| Sexual Differentiation | Light cycles during flowering can also impact the sexual differentiation of your plants. By adjusting the light schedule, you can control whether your plants develop male or female flowers, resulting in either seeds or bud production. |
Proper light schedule adjustment is essential for maximizing yield and potency while minimizing stress during flowering.
What Happens if You Don’t Adjust Light Cycles During Flowering?
When you fail to adjust light cycles during the flowering stage, a number of negative effects can occur that will ultimately impact the yield and potency of your plants. Here are some potential consequences of not adjusting light cycles:
- Stunted growth: Without a proper light schedule, plants may not receive the right amount of light and dark periods they need to flourish. This can lead to stunted growth and smaller yields.
- Hermaphroditism: If plants do not receive the appropriate light cycles during flowering, they may become stressed and develop both male and female reproductive organs, a trait called hermaphroditism. This can severely impact the quality of the crop and reduce yields.
- Delayed maturity: Inconsistent light cycles can lead to a delay in maturity of the plants, which can delay the harvesting process, and result in a lower quality crop.
- Poor quality buds: Lack of proper light cycles can lead to low-quality buds that are less potent and less flavorful.
It is essential to pay close attention to your plant’s needs and adjust your light schedule appropriately to ensure a healthy and high-quality yield.
How to Adjust Light Cycles for Different Strains
As a cannabis grower, it’s essential to understand that different strains have varying light cycle requirements during the flowering phase to achieve optimal results. The amount of light that your plants receive can affect everything from yield to potency, so it’s crucial to adjust your light schedules appropriately. However, with so many strains available, it can be perplexing to know how to adjust light cycles for each one. In this section, we’ll discuss some general guidelines for adjusting light cycles for indica, sativa, and hybrid strains to help you achieve the best results in your grow.
Indica Strains
When growing Indica strains, adjusting the light schedule for flowering is crucial to ensure the plant produces high-quality buds. Indicas generally have a shorter flowering time, ranging from 6-9 weeks, compared to Sativas, which can take up to 14 weeks to fully flower.
It’s recommended to start with a 12/12 light cycle during flowering for Indicas, which means 12 hours of light and 12 hours of darkness. This will help the plant begin the flowering process and trigger the growth of buds. Some growers may choose to switch to a 10/14 light cycle towards the end of flowering in order to encourage the development of trichomes and resin, which can increase the potency of the buds.
It’s important to closely monitor the plants for signs of stress during the light adjustment process. Indicas can be sensitive to changes in light schedules, so it’s best to make any adjustments gradually. A sudden shift in light cycles can cause the plant to become stressed and grow unevenly.
Here are some other factors to consider when adjusting the light schedule for Indica strains:
| Factor | Consideration |
|---|---|
| Strain Genetics | Research the specific strain’s flowering time and light preferences |
| Grow Space and Equipment | Ensure the grow space has proper ventilation and the right lighting equipment for the chosen light cycle |
| Climate and Environment | Control temperature and humidity levels to prevent stress on the plants |
By considering these factors and adjusting the light schedule appropriately, you can achieve a successful harvest of high-quality buds from your Indica strain cannabis plant.
Sativa Strains
When it comes to adjusting light schedules during flowering for sativa strains, there are a few key things to keep in mind. Sativa strains are known for their tall, lanky growth and longer flowering times compared to indica strains. Here are some tips for adjusting light schedules for sativa strains:
- Reduce the Vegetative Stage: Since sativa strains tend to grow taller, it’s important to keep the vegetative stage short to avoid stretching during flowering. A 4-6 week vegetative period is usually sufficient for most sativa strains.
- Increase the Flowering Stage: Sativa strains also typically require a longer flowering time compared to indica strains. It’s common for sativa strains to take anywhere from 10-16 weeks to fully mature. Adjust your light schedule accordingly to provide enough light for the extended flowering period.
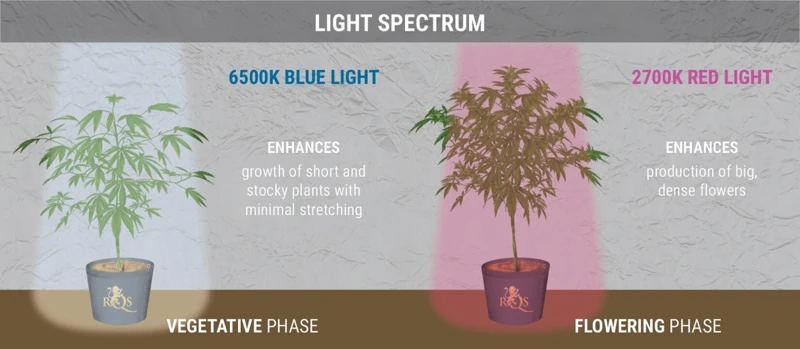
- Consider Using Blue Light: Sativa strains tend to respond well to blue spectrum light, which promotes compact, dense buds. Consider using a light that is labeled as “cool” or “blue” for the last few weeks of flowering to encourage bud development.
- Be Mindful of Height: As mentioned before, sativa strains can grow quite tall. Make sure to adjust your light schedule to avoid excessive stretching during the flowering stage, since the plants may become too tall to manage easily.
By following these tips for adjusting light schedules for sativa strains, you should be able to produce healthy, fully mature plants with the desired bud development.
Hybrid Strains
When it comes to adjusting light schedules during flowering for hybrid strains, things can get a bit more complicated. This is because hybrid strains are a mix of both Indica and Sativa genetics, and therefore, their light needs can vary greatly. Here are some factors to consider when adjusting light cycles for hybrid strains:
- Ratio: The ratio of Indica to Sativa genetics in the hybrid strain can greatly affect its light schedule needs. If the strain is more Indica-dominant, it may require a shorter light cycle during flowering than a Sativa-dominant hybrid.
- Phenotype: Different phenotypes within the same hybrid strain can also have varying light needs. It’s important to monitor each plant individually to determine its specific requirements.
- Grow Space: The size of the grow space and available equipment can also impact the light schedule for hybrid strains. If there is limited space, a shorter light cycle may be necessary to control plant height and manage yield.
- Climate: The climate and environment in which the hybrid strain is grown can also affect its light needs. If the temperature is too high or too low, it may require a shorter or longer light cycle to compensate.
It’s important to keep in mind that every hybrid strain is unique, and their light needs may vary based on a combination of these factors. As always, monitoring the plants closely and adjusting the light schedule based on their response is crucial for a successful harvest.
Factors to Consider When Adjusting Light Schedules
As you strive to maximize the yield and potency of your cannabis plants during the flowering stage, there are several factors to consider when adjusting light schedules. These factors include the strain genetics, grow space and equipment, and the climate and environment in which the plants are growing. By taking these factors into account, you can ensure that your plants receive the optimal light exposure to produce healthy growth and maximize yield while avoiding potential stress and issues that may arise from improper lighting. Let’s take a closer look at each of these factors and their role in adjusting light schedules during flowering.
Strain Genetics
When adjusting light schedules for flowering cannabis plants, it’s important to consider the genetics of your strain. Different strains have different requirements for light cycles during flowering.
To better understand the genetics of your strain, you can refer to the breeder’s recommendations or look up information on the strain’s general characteristics. Some strains are more tolerant of longer periods of darkness, while others require more light.
To make it easier to adjust the light schedule for your particular strain, we’ve created a table outlining the light cycle preferences for some common cannabis strains:
| Strain | Preferred Light Cycle |
|---|---|
| Indica | 12/12 |
| Sativa | 12/12 or 13/11 |
| Hybrid (Indica Dominant) | 12/12 |
| Hybrid (Sativa Dominant) | 12/12 or 13/11 |
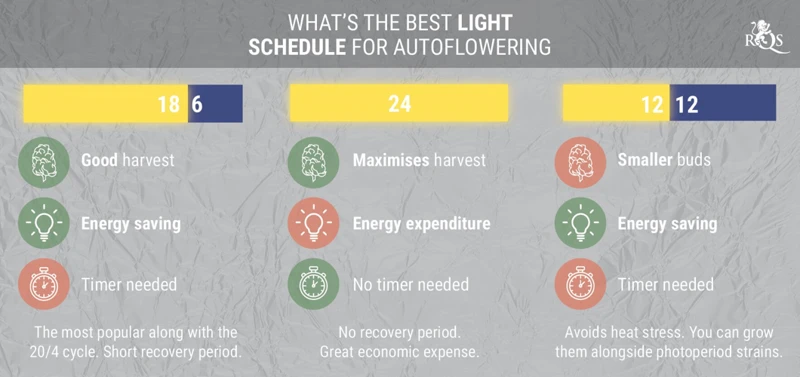
| Auto-flowering | 18/6 or 20/4 |
As you can see, indica strains generally prefer a 12/12 light cycle, while sativa strains may require a 13/11 light cycle. Hybrid strains can vary depending on whether they are indica or sativa dominant. Auto-flowering strains have their own unique requirements and generally prefer longer periods of light.
By understanding the preferred light cycle for your strain, you can ensure that your plants receive the optimal amount of light during the flowering process. This can lead to higher yields and better quality buds.
Grow Space and Equipment
Grow Space and Equipment:
When adjusting light schedules during flowering, the available grow space and equipment must also be taken into consideration. The size and layout of your grow space can significantly impact the type of lighting system and light cycle that you can use.
Grow Space: Your grow space should have ample room for your plants to grow and be properly supported. The lighting system you choose should cover the entire grow space, so consider the size and arrangement of your plants when selecting lights.
In addition to space, the environment in which you grow your plants must have proper ventilation, temperature control, and humidity balance. Poor environmental factors may cause stress to the plants and may impact their ability to properly utilize light cycles.
Equipment: The lighting system you choose will have a direct effect on your plants and their growth during flowering. Factors like the type of bulb, wattage, and hood reflector can influence the intensity and coverage of your lighting system.
In general, high-intensity discharge (HID) lights are commonly used during flowering and provide intense light coverage for maximum bud development. LED lights are a more energy-efficient option and can still provide ample bud growth with the right spectrum of light.
The table below highlights some considerations for grow space and lighting equipment:
| Factors | Considerations |
|---|---|
| Grow Space |
|
| Lighting Equipment |
|
All of these factors should be examined before initiating any changes to your light cycles. Keeping your grow space and equipment in mind can help you select the best light cycle and system for your particular strain to ensure maximum fragrant and potent buds.
Climate and Environment
When adjusting light schedules for different cannabis strains during flowering, it’s important to take into account the climate and environment in which the plants are being grown. Here are some factors to consider:
- Temperature:
- Cannabis plants thrive in temperatures between 68 and 77 degrees Fahrenheit during the day and slightly cooler temperatures at night.
- High temperatures can decrease yields and cause stress, while cooler temperatures can slow down growth.
- Humidity:
- Cannabis plants need humidity levels between 40% and 60% during vegetative growth and slightly lower levels during flowering.
- High humidity levels can increase the risk of mold and disease, while low humidity can cause leaves to dry out and reduce growth.
- Air circulation:
- Proper air circulation is necessary to prevent the buildup of stale air, excess heat, and humidity.
- Plants that are too close together or in an environment with poor air flow can increase the risk of pests and disease.
- Light intensity:
- Light intensity can affect plant growth and yield.
- Plants grown in high-intensity light environments may need less light and more frequent watering.
Taking all of these factors into account when adjusting your light schedules can help ensure healthy plant growth and optimal yields during the flowering stage. It’s important to monitor your plants regularly to make adjustments as needed.
Common Light Schedules for Flowering Cannabis Plants
Deciding on the right light schedule for your cannabis plants during the flowering phase can be perplexing. There are various light cycles to choose from, and each one affects the growth and development of your plants differently. Additionally, certain strains may respond better to specific light schedules, making the decision even more challenging. In this section, we’ll explore some of the most common light schedules for flowering cannabis plants, their benefits, and the factors to consider when choosing the best one for your specific setup.
12/12 Light Cycle
12/12 Light Cycle: The 12/12 light cycle is the most commonly used light cycle during flowering. It involves providing the plants with 12 hours of uninterrupted darkness followed by 12 hours of bright light. This light cycle signals to the plants that it’s time to start flowering and triggers the production of buds.
- This light cycle is particularly beneficial for Indica strains as they tend to have a shorter flowering period and can be induced to flower more quickly than Sativa strains.
- It is important to note that plants may take some time to adjust to the change in light cycle, and it’s not uncommon for them to show signs of stress during this period.
- It’s essential to keep the light intensity and temperature stable during the 12/12 cycle to ensure healthy growth and maximum yield.
- Some growers may choose to gradually reduce the light cycle from 18/6 or 16/8 to 12/12 over a period of several weeks to minimize stress on the plants.
- The 12/12 light cycle should be maintained for 8-12 weeks depending on the strain’s genetics and desired potency.
- It’s essential to monitor the plants closely during this time and adjust the light schedules if necessary based on their response.
13/11 Light Cycle
One light cycle that is sometimes used during the flowering stage is the 13/11 light cycle. This means that the plants receive 13 hours of light and 11 hours of darkness each day.
This light cycle is often used with strains that require a slightly longer flowering period than usual. By giving them slightly shorter periods of light each day, their flowering time is extended, which can result in higher yields and better potency.
However, the 13/11 light cycle can also be risky, as it can potentially lead to unstable plant growth and decreased yields if not properly monitored. It is important to carefully observe plant growth and adjust the light schedule as needed.
Here is a table summarizing the pros and cons of using the 13/11 light cycle during the flowering stage:
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Extended flowering period can result in higher yields and better potency | Can potentially lead to unstable plant growth if not properly monitored |
| May be beneficial for strains that require longer flowering times | Requires careful observation and adjustment of plant growth |
| May allow for more efficient use of energy and resources | May result in decreased yields if not properly managed |
The 13/11 light cycle can be a useful tool for growers who are trying to extend the flowering period of their cannabis plants. However, it is important to closely monitor the plants and adjust the light schedule as needed to ensure healthy and stable growth.
10/14 Light Cycle
One light cycle that is sometimes used during the flowering stage is the 10/14 light cycle. This means that the plants are given 10 hours of light followed by 14 hours of darkness each day. Some growers prefer this light cycle because they believe it can increase resin production and potency in the buds.
However, it is important to note that this light cycle may not be suitable for all strains, and growers should consider the specific genetics of their plants before implementing it. Certain strains may be more sensitive to light changes and may not respond well to a 10/14 light cycle.
Another factor to consider when using the 10/14 light cycle is the grow space and equipment. Since the plants will be receiving less light, it is important to ensure that they are not overcrowded and have enough room to grow. Additionally, growers may need to adjust their lighting equipment to ensure that the plants are still receiving enough light to grow and produce buds.
Climate and environment can also play a role in the success of a 10/14 light cycle. Growers should monitor the temperature and humidity levels in their grow space to ensure that they remain within optimal ranges for their plants.
When using the 10/14 light cycle, it is important to carefully monitor the plants for signs of stress or healthy growth. Growers should look for signs of drooping, yellowing or browning leaves which can indicate a problem with the light cycle or other growing conditions.
The 10/14 light cycle can be a useful tool for increasing resin production and potency in some strains, but it is important to consider the specific needs of the plants and to monitor them closely for signs of stress or healthy growth.
Other Light Schedule Variations
There are several other light schedule variations that growers may use during the flowering stage, depending on their preferences and the specific needs of their cannabis plants. These variations include:
- 11/13 Light Cycle: This light cycle is similar to the more commonly used 13/11 cycle, but involves slightly more darkness. Some growers believe that this can lead to increased resin production and potency.
- 9/15 Light Cycle: This light cycle involves shorter periods of light and longer periods of darkness than the 12/12 cycle, and can be used to encourage the plants to finish flowering more quickly.
- 14/10 Light Cycle: This light cycle involves slightly longer periods of light than the 12/12 cycle, and is sometimes used by growers who believe it can increase yields.
- 24/0 Light Cycle: This light cycle involves 24 hours of light per day and no darkness. While this schedule can be used during both the vegetative and flowering stages, some growers believe it can lead to increased yields.
It’s important to note that while these light schedule variations can be effective for some growers, they may not work as well for others. It’s always a good idea to experiment with different light schedules and monitor plant growth and health to determine what works best for specific strains and growing conditions.
Monitoring Your Plants During Flowering
As your cannabis plants progress through the flowering stage, it’s crucial to monitor them closely to ensure healthy growth and a bountiful harvest. By observing your plants on a regular basis, you can detect signs of both stress and healthy development. As you evaluate your plants, keep in mind that adjusting their light schedules may be necessary based on their response. In this section, we will delve into the specifics of monitoring your cannabis plants during flowering and the importance of paying attention to their visual cues.
Signs of Stress
During the flowering stage of cannabis plants, it’s important to monitor them for any signs of stress that might affect their growth and yield. Here are some common signs of stress to look out for:
| Sign of Stress | Description |
|---|---|
| Wilting leaves | Leaves that are drooping or curling downwards, indicating a lack of water or nutrients. |
| Browned or yellowed leaves | Leaves that are turning yellow or brown could be a sign of nutrient deficiencies or overwatering. |
| Burnt tips or edges | Leaves that have yellow or brown tips or edges are likely experiencing nutrient burn from over-fertilization or too-high temperatures. |
| Stunted growth | Plants that are not developing as quickly as they should could be experiencing a lack of nutrients or light. |
| Slow development | Plants that are taking longer than expected to flower or develop buds could be a result of too much or too little light, nutrients, or temperature changes. |
It’s important to address these issues as soon as possible to ensure that your plants have the best chance of producing a healthy yield. If you notice any signs of stress, adjust your light schedules or nutrient feeding accordingly to help your plants recover. By monitoring your plants closely, you can ensure that they have the conditions they need to produce high-quality buds.
Signs of Healthy Growth
During the flowering stage, it’s essential to monitor your cannabis plants for signs of healthy growth. Here are some key indicators of healthy growth to look out for:
| Lush Green Leaves | Cannabis plants with healthy growth will have vibrant, lush green leaves. If the leaves start turning yellow or brown, it may be a sign of a nutrient deficiency or other issue. |
| Buds Develop | As the plant progresses through the flowering stage, buds will begin to develop. Look for buds that are dense, sticky, and have a strong aroma. |
| Strong Stem | A healthy cannabis plant will have a strong stem that can support the weight of the developing buds. A weak stem may indicate a nutrient deficiency, overwatering, or other issues. |
| No Pests | Healthy plants will typically be pest-free. Keep an eye out for common cannabis pests like spider mites, thrips, and whiteflies. |
| Proper pH and Nutrient Levels | A healthy cannabis plant will have a pH level between 6.0 and 7.0, and proper nutrient levels. Check the pH and nutrient levels regularly to ensure they are in the correct range. |
If your cannabis plants are exhibiting these signs of healthy growth during the flowering stage, they are on track for a successful harvest. Keep monitoring your plants closely to catch any issues early and make adjustments as needed.
Adjusting Light Schedules Based on Plant Response
One of the most important factors to consider when adjusting light schedules during flowering is plant response. You need to closely monitor your plants to ensure they’re responding positively to the amount of light they’re receiving. Here are some key steps to help you adjust your light schedules based on your plants’ responses:
- Observe your plants regularly: Check on your plants at regular intervals each day, and look for any signs of stress or unhealthy growth.
- Adjust light schedules gradually: If you notice any negative plant response, adjust your light schedules gradually to avoid shocking your plants.
- Consider plant genetics: Different strains may respond differently to light schedules, so take this into account when monitoring your plants.
- Make notes: Keep a record of any adjustments you make to your light schedules, and take note of how your plants respond.
- Look for signs of healthy growth: If your plants are responding well to your light schedules, look for signs of healthy growth such as strong stems, dense foliage, and plenty of budding sites.
- Adjust as needed: If you notice any negative plant response, adjust your light schedules accordingly, and continue to monitor your plants closely.
Remember, your plants’ health and growth are directly impacted by the amount and timing of light they receive. By carefully monitoring your plants and adjusting your light schedules as needed, you can help ensure a healthy, successful harvest.
Harvesting Your Plants After Flowering
After all the hard work put into growing your cannabis plants and adjusting their light schedules during flowering, the time has finally come to harvest your plants. This is an exciting and nerve-wracking time for any grower, as the quality and potency of your final product will largely depend on how well you manage the harvesting process. From identifying the right time to harvest to properly handling the plants, there are several important factors to consider. In this section, we will discuss the key aspects of harvesting your cannabis plants after flowering, including how light schedules affect your harvest and potency, and proper harvesting techniques to ensure the best possible outcome.
Identifying When to Harvest
One of the most critical steps in the cannabis cultivation process is identifying the right time to harvest your plants. Harvesting too early or too late can significantly impact yield and potency. Here is a detailed guide on how to identify when to harvest your cannabis plants:
1. Observe the Trichomes: Trichomes are tiny mushroom-shaped structures that appear on the buds and leaves of cannabis plants. They contain the majority of the plant’s cannabinoids, including THC and CBD. Use a magnifying glass or microscope to observe the trichomes closely. When the trichomes start to change from clear to milky, it is usually an indication that the plants are ready to be harvested. When they begin to turn amber, it may be an indication that you have waited too long and may result in a lower potency.
2. Look for Changes in the Pistils: Another way to identify when to harvest is by observing the pistils. Pistils are the tiny hairs that grow on the plant’s buds. They usually start out white and turn to red, orange, or brown as the plant matures. When about 70-80% of the pistils have turned orange or brown, it may be an indication that the plant is ready for harvesting.
3. Measure the Plant’s Height: A general indication of when to harvest your cannabis plants is by measuring their height. A plant that has stopped growing and has reached its full height is typically ready to be harvested.
4. Use a pH Meter: Measuring the pH levels of your plants can help you determine when to harvest. When the pH levels are between 6.0 and 7.0, it is usually an indication that the plant is nearing the end of its life cycle.
5. Monitor the Plant’s Smell: One tell-tale sign that your cannabis plants are ready to be harvested is when they start producing a strong, pungent aroma. The smell can become quite overpowering once you’re in the flowering stage of the plant’s life cycle.
6. Check the Trunk’s Sturdiness: A final sign to look for when determining when to harvest your cannabis plants is the trunk’s sturdiness. When the trunk begins to feel rigid, it may indicate that the plant is ready to be harvested.
Using a combination of these methods, you can be sure to harvest your cannabis plants at the optimal time to achieve the best results in terms of yield and potency.
How Light Schedules Affect Harvest and Potency
One of the most important factors in determining the quality and potency of your cannabis harvest is the light schedule during the flowering stage. Here are some ways in which light schedules can affect your final product:
- Yield: Light schedules can have a significant impact on the size and weight of your buds. Different strains may respond differently to different light schedules, so it’s important to experiment and monitor your plants to find the optimal light schedule for your specific strain. In general, a 12/12 light cycle is considered the standard for maximum yields, but some growers have had success with longer or shorter cycles.
- Potency: A plant’s potency is determined by its cannabinoid and terpene content, which are influenced by a variety of factors including genetics, nutrients, and environmental conditions. However, light schedules are also an important factor. In general, longer dark periods during the flowering stage have been associated with increased potency, as this allows for more time for trichome production and maturation.
- Flavor and aroma: Terpenes, the aromatic compounds found in cannabis, are responsible for the plant’s distinctive flavors and aromas. The types and concentrations of terpenes present in a particular strain may be influenced by its light schedule. Some growers believe that low-intensity light during the flowering stage can help enhance terpene production, leading to more flavorful and aromatic buds.
- Uniformity: A consistent light schedule can help ensure that your plants grow evenly and consistently. An irregular or inconsistent light schedule can lead to uneven growth patterns, which can ultimately impact your yields and potency.
Finding the right light schedule for your cannabis plants can be a bit of a trial-and-error process. However, by monitoring your plants closely and making adjustments as needed, you can maximize your yields, potency, and overall quality of your cannabis harvest.
Proper Harvesting Techniques
Once you’ve identified that your plants are ready for harvest, it’s important to use proper techniques to ensure the best quality buds. Here are some essential harvesting techniques to keep in mind:
- Timing: Harvest your plants at the right time. Don’t wait too long or harvest too early. Keep an eye on your trichomes to determine when your plants are at their peak.
- Cutting: To avoid damaging the buds, use sharp, clean scissors or pruning shears to cut the stems one at a time. Cut the plant at the base, leaving the roots intact for easy disposal.
- Drying: Hang the buds upside down in a dark, cool, and dry space with good ventilation. Make sure to keep the temperature and humidity levels consistent to avoid mold or mildew. Drying usually takes about one to two weeks depending on the climate and environment.
- Curing: Proper curing is essential for maximum potency and flavor. Place the dried buds in airtight containers and store them in a cool, dry place for two to four weeks. Open the containers daily to let the buds breathe and release any excess moisture. This process allows the buds to develop their full flavor and aroma while maintaining their potency.
- Trimming: After the buds are dried and cured, it’s time to trim off any excess leaves or stems. Use sharp scissors or a trimmer to remove any unwanted material. This will improve the visual appeal of your buds and enhance the smoking experience.
Proper harvesting techniques can make a significant difference in the quality of your buds. Taking the time to harvest, dry, cure, and trim your plants carefully will yield the best possible results. Always remember to keep an eye on your plants and adjust your techniques accordingly based on their response.
Conclusion
In conclusion, adjusting light schedules during flowering is a critical aspect of growing healthy and potent cannabis plants. The process of flowering is a delicate stage in the plant’s lifecycle, and the duration and intensity of light exposure play a vital role in the plant’s growth and development.
It is essential to understand the unique light requirements of each cannabis strain to ensure that it receives the correct light cycle during flowering. Indica, Sativa, and Hybrid strains have different genetic backgrounds, which affects their preferred light schedules, making it essential to research and fine-tune your growing practices for optimal results.
Factors such as grow space and equipment, climate, and environmental conditions also play a role in adjusting light schedules, and growers must create a balance between these factors to produce healthy and bountiful harvests.
Monitoring plant growth during flowering is crucial to identifying signs of stress and healthy growth, and responding promptly by adjusting light schedules if necessary. Properly harvested cannabis plants should have their timing and light schedules optimized, resulting in the highest yield and potency.
In conclusion, by understanding the nuances of light schedules and adapting them to suit cannabis plants’ individual needs, growers can achieve the best results in both quality and quantity. As with any new growing practice, it may take some trial and error to get it right, but the rewards are well worth it. Happy growing!
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the ideal light schedule for flowering cannabis plants?
There is no one-size-fits-all answer to this question, as different strains may have different light requirements during flowering. However, most growers use a 12/12 light cycle during flowering.
Can I change the light schedule during flowering?
Yes, it is possible to change the light schedule during the flowering stage. However, sudden changes can stress the plants, so it’s important to make any adjustments slowly over a period of a few days.
What is the difference between indica and sativa strains when it comes to light schedules?
Indica strains tend to have a shorter flowering time and may require less light than sativa strains. Sativa strains may have a longer flowering time and may require more light to reach their full potential.
Will adjusting the light schedule affect the potency of my cannabis plants?
Yes, adjusting the light schedule can affect the potency of your cannabis plants. For example, longer light cycles can lead to higher THC levels, while shorter light cycles can increase CBD levels.
Do temperature and humidity levels affect the light schedule during flowering?
Yes, temperature and humidity levels can affect the light schedule during flowering. Higher temperatures and lower humidity levels may require shorter light cycles, while lower temperatures and higher humidity levels may require longer light cycles.
What are the signs that my cannabis plant is experiencing stress during flowering?
Signs of stress during flowering can include yellowing or drooping leaves, stunted growth, and bud rot. If you notice any of these symptoms, it may be a sign that you need to adjust your light schedule.
Can I use LED lights during flowering?
Yes, LED lights can be used during flowering, but it’s important to choose a high-quality LED grow light that provides sufficient intensity and spectrum for your plants’ needs.
How long does the flowering stage usually last?
The flowering stage can last anywhere from 6-12 weeks, depending on the strain and growing conditions.
What is the best way to harvest my cannabis plants after flowering?
The best way to harvest cannabis plants is to wait until the trichomes have turned cloudy or amber in color and then cut the plants down and hang them upside down to dry.
How can I tell if my cannabis plants are ready to harvest?
You can tell if your cannabis plants are ready to harvest by examining the color of the trichomes under a magnifying glass. When the trichomes are mostly cloudy or amber in color, it’s time to harvest.